Check the below Online Education NCERT MCQ Questions for Winds, Storms and Cyclones Class 7 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 8 with Answers Pdf free download. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-7-science/
Online Education for Class 7 Science Chapter 8 Extra Questions and Answers Winds, Storms and Cyclones
Class 7 Science Chapter 8 Extra Questions Question 1.
What is wind?
Answer:
Moving air is called wind.
Winds, Storms And Cyclones Class 7 Extra Questions With Answers Question 2.
What is the direction of flow of air?
Answer:
Air moves from the region where the air pressure is high to the region where the pressure is low.
Ncert Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 8 Extra Questions Question 3.
Which air is lighter, hot or cool?
Answer:
Hot air is lighter.
Class 7 Science Ch 8 Extra Questions Question 4.
Which region gets maximum sunlight?
Answer:
Regions close to the equator get maximum sunlight.
![]()
Winds, Storms And Cyclones Class 7 Questions And Answers Question 5.
What does monsoon wind carry?
Answer:
Water (moisture).
Ncert Class 7 Science Chapter 8 Extra Questions Question 6.
Where do thunderstorms develop mostly?
Answer:
Thunderstorms develop in hot, humid tropical areas like India very frequently.
Winds Storms And Cyclones Class 7 Extra Questions With Answers Question 7.
What do you mean by the eye of a storm?
Answer:
The centre of a cyclone is a calm area. It is called the eye of the storm.
Wind Storm And Cyclone Class 7 Extra Questions Question 8.
Which factors contribute to the development of cyclone?
Answer:
Factors like wind speed, wind direction, temperature and humidity contribute to the development of cyclones.
Class 7 Chapter 8 Science Extra Questions Question 9.
When is cyclone alert issued?
Answer:
A cyclone alert or cyclone watch is issued 48 hours in advance of any expected storm.
Chapter 8 Science Class 7 Extra Questions Question 10.
When is cyclone warning issued?
Answer:
A cyclone warning is issued 24 hours in advance.
Extra Questions On Wind Storms And Cyclones Question 11.
How are clouds helpful?
Answer:
Clouds bring rain which is vital for survival of living beings. Farmers in our country depend mainly on rain for irrigation.
![]()
Wind Storms And Cyclones Class 7 Questions And Answers Question 12.
How does the eye of a cyclone harm us?
Answer:
The low pressure in the eye lifts water surface in the centre. The rising water may be as high as 3-12 metres. It appears like a water-wall moving towards the shore. As a result, the seawater enters the low-lying coastal areas, causing severe loss of life and property. It also reduces the fertility of the soil.
Winds Storms And Cyclones Class 7 Questions And Answers Question 13.
How do high-speed winds accompanying a cyclone harm us?
Answer:
High-speed winds accompanying a cyclone can damage houses, telephones and other communication systems, trees, etc., causing tremendous loss of life and property.
Extra Questions For Class 7 Science Chapter 8 Question 14.
Explain the structure of a tornado?
Answer:
A tornado is a dark funnel-shaped cloud that reaches ground from the sky. The diameter of a tornado can be as small as a meter and as large as a kilometre, or even wider. The funnel of a tornado sucks dust, debris and everything near it at the base (due to low pressure) and throws them out near the top.
Wind Storms And Cyclones Class 7 Extra Questions Question 15.
Suggest three effective safety measures for cyclone.
Answer:
- A cyclone forecast and warning service.
- Rapid communication of warnings to the Government agencies, the ports, fishermen, ships and to the general public.
- Construction of cyclone shelters in the cyclone-prone areas, and administrative arrangements for moving people fast to safer places.
Question 16.
Suggest some precautions in a cyclone hit area.
Answer:
- Do not drink water that could be contaminated. Always store drinking water for emergencies.
- Do not touch wet switches and fallen power lines.
- Do not go out just for the sake of fun.
- Do not pressurise the rescue force by making undue demands.
- Cooperate and help your neighbours and friends.
Question 17.
Describe the structure of a cyclone.
Answer:
The centre of a cyclone is a calm area. It is called the eye of the storm. A large cyclone is a violently rotating mass of air in the atmosphere, 10 to 15 km high. The diameter of the eye varies from 10 to 30 km. It is a region free of clouds and has light winds. Around this calm and clear eye, there is a cloud region of about 150 km in size. In this region, there are high-speed winds (150-250 km/h) and thick clouds with heavy rain. Away from this region the wind speed gradually decreases.
![]()
Question 18.
How does a thunderstorm become a cyclone?
Answer:
Before cloud formation, water takes up heat from the atmosphere to change into vapour. When water vapour changes back to liquid form as raindrops, this heat is released to the atmosphere. The heat released to the atmosphere warms the air around. The air tends to rise and causes a drop in pressure. More air rushes to the centre of the storm. This cycle is repeated. The chain of events ends with the formation of a very low-pressure system with very high-speed winds revolving around it. It is this weather condition that we call a cyclone.
Question 19.
Suggest precautions if storm is accompanied by lightning.
Answer:
If a storm is accompanied by lightning, we must take the following precautions :
- We should not take shelter under an isolated tree. If in a forest, take shelter under a small tree.
- We must not take shelter under an umbrella with a metallic end.
- We should not sit near a window. Open garages, storage sheds, metal sheds are not safe places to take shelter.
- A car or a bus with closed windows is a safe place to take shelter.
- If in water, we should get out and go inside a building.
- We should not lie on the ground.
Question 20.
Draw a diagram to show the formation of cyclone.
Answer:
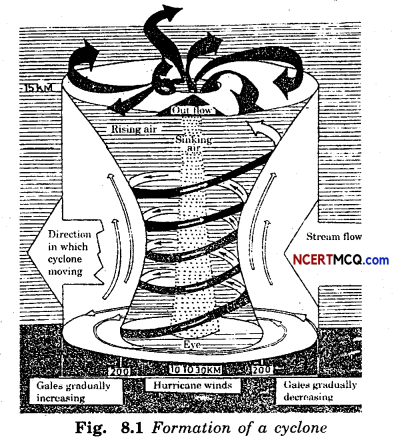
Question 21.
Show the phenomena that lead to the formation of clouds, falling of rain and creation of storms and cyclones with the help of a chart.
Answer:
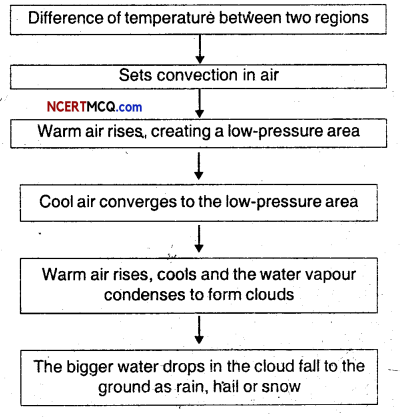
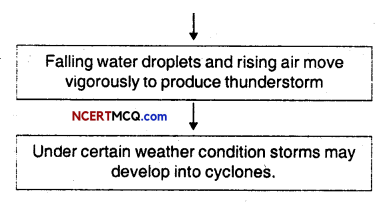
Question 22.
How will you help your neighbours in case cyclone approaches your village/town?
Answer:
I will help them in the following ways:
- By warning everyone about the coming danger.
- Searching for shelter.
- Keeping storage of water and food.
- By setting up first-aid facility.
Question 23.
What planning is required in advance to deal with the situation created by a cyclone?
Answer:
- Setting up of a cyclone forecast and warning service.
- Setting up of an arrangement for rapid communication of warnings to the government agencies, the ports, fishermen, ships and to the general public.
- Construction of cyclone shelters in the cyclone-prone areas, and administrative arrangements for moving people fast to safer places.
- Making stock of food and water.
- Keeping first aid facility along with.
Question 24.
Inactivity 8.3, when you blow between the balloons, they moved towards each other. How could this happen?
Answer:
This could happen if the pressure of air between the balloons were somehow reduced. The pressure outside the balloons would then push them towards each other.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions
1. When a can filled with hot water is cooled, the shape of the can gets distorted because :
(i) Some water vapour inside the can get condensed and atmospheric pressure distorts the can.
(ii) on heating the can becomes easy to be moulded and pouring water forces to distort the can.
(iii) on heating the can expands and loose intermolecular force of attraction results to distortion.
(iv) can gets distorted due to kinetic energy of water poured.
Answer:
(i) Some water vapour inside the can get condensed and atmospheric pressure distorts the can.
2. If you are in a boat, it is easier to row it if there is wind coming from behind because :
(i) the wind speed decreases boat speed.
(ii) the wind speed is added to boat speed.
(iii) it makes the boat streamlined.
(iv) none of these.
Answer:
(ii) the wind speed is added to boat speed.
3. Flags flutter when the wind blows because :
(i) of the design of the flag.
(ii) of the air pressure exerted by the wind.
(iii) of the potential energy within the flag.
(iv) none of these.
Answer:
(ii) of the air pressure exerted by the wind.
4. We fill air into the bicycle tube to keep it tight. What happens inside the tube?
(i) The air inside the tube exerts pressure on the wall of the tube.
(ii) The wall of the tube exerts pressure on the air inside.
(iii) Both exert pressure on each other.
(iv) The air within the tube does not exert any pressure.
Answer:
(iii) Both exert pressure on each other.
![]()
5. When a paper ball is placed in the mouth of a horizontally kept bottle and you are made to blow the ball why is it difficult to force the paper ball into the bottle?
(i) The air blown is reflected back from the bottom of bottle and the paper ball is made to remain at its initial point.
(ii) High-speed winds are accompanied by reduced air pressure, and the air pressuse inside the bottle is high, which pushes the ball out.
(iii) The paper ball is immovable by wind.
(iv) Paper wall is adhesive to bottle.
Answer:
(ii) High-speed winds are accompanied by reduced air pressure, and the air pressure inside the bottle is high, which pushes the ball out.
6. When two inflated balloons of equal size are hung 8-10 cm apart on a cycle spoke and you are made to blow in the space between the balloons. What happens?
(i) The balloons move away from each other.
(ii) The balloons move towards each other.
(iii) No change occurs in the position of the balloons.
(iv) Initially they move apart and then move towards each other.
Answer:
(ii) The balloons move towards each other.
7. The balloons move towards each other, when we blow between two hung balloons separated by a small distance, because :
(i) blowing resulted in increased air pressure between the balloons.
(ii) blowing resulted in reduced air pressure between the balloons.
(iii) two inflated balloons attract each other.
(iv) none of these.
Answer:
(ii) blowing resulted in reduced air pressure between the balloons.
8. When you blow over a small paper strip, which of the following happens?
(i) The strip will be lifted up.
(ii) The strip will bend down.
(iii) No movement in the strip occurs.
(iv) The strip will move to and fro horizontally.
Answer:
(i) The strip will be lifted up.
![]()
9. The paper strip rises upward because blowing over the paper :
(i) reduces the air pressure above the strip.
(ii) increases the air pressure above the strip.
(iii) reduces the air pressure below the strip.
(iv) increases the air pressure below the strip.
Answer:
(i) reduces the air pressure above the strip.
10. Which of the following is correct in context with air movement?
(i) Air moves from the region where the air pressure is high to the region where the pressure is low.
(ii) Air moves from the region when the air pressure is low to the region where the pressure is high.
(iii) Air pressure does not play any role in air movement, so the air movement can be arbitrary.
(iv) Air never moves, it is still.
Answer:
(i) Air moves from the region where the air pressure is high to the region where the pressure is low.
11. What happens to the air when it is heated?
(i) It expands, becomes light and moves downward.
(ii) It expands, becomes light and moves upward.
(iii) It expands, becomes heavy and moves downward.
(iv) It expands, becomes heavy and moves upward.
Answer:
(ii) It expands, becomes light and moves upward.
12. Let the balloon tied over neck of the boiling tube immersed in hot water be A and the balloon tied over the neck of the boiling tube immersed in cold water be B. What happens to A and B?
(i) A deflates and B inflates.
(ii) A inflates and B deflates.
(iii) Both A and B in flat.
(iv) Both A and B deflate.
Answer:
(ii) A inflates and B deflates.
![]()
13. Take two paper bags or empty paper cups of the same size. Hang the two bags in inverted position on the two ends of a wooden stick. When a candle is lighted below one of the cup, the balance is disturbed. The disturbance of the balance suggests that :
(i) warm air is lighter than the cold air.
(ii) warm air is heavier than the cold air.
(iii) the paper cup prevents itself from burning by moving up.
(iv) air expands on heating.
Answer:
(i) warm air is lighter than the cold air.
14. Why does smoke always rise up?
(i) Because it is hotter than the surrounding air and thus is heavier.
(ii) Because it is colder than the surrounding air and thus is heavier.
(iii) Because it is hotter than the surrounding air and thus is lighter.
(iv) Because it is colder than the surrounding air and thus is lighter.
Answer:
(iii) Because it is hotter than the surrounding air and thus is lighter.
Keyword:
→ Anemometer: The instrument that measures the wind speed is called an anemometer.
→ Cyclone: Sometimes there is a formation of very low-pressure system with very high-speed winds revolving around it. It is this weather condition that we call a cyclone.
→ Hurricane: Cyclone is called hurricane in American continent.
→ Lightning: The occurrence of bright flash (a natural electrical discharge) of very short duration and high voltage between a cloud and the ground or wìthin a cloud.
→ Low pressure: Reduced pressure.
![]()
→ Monsoon winds: In summer, near the equator, the land warms up faster and most of the time the temperature of the land is higher than that of water in the oceans. The air over the land gets heated and rises. This causes the winds along with moisture to flow from the oceans towards the land. These are monsoon winds.
→ Pressure: Force on unit area.
→ Thunderstorms: The swift movement of the falling water droplets along with the rising air create lightning and sound. It is this event that we call a thunderstorm.
→ Tornado: A tornado is a dark funnel-shaped cloud that reaches from the sky to the ground.
→ Typhoon: Cyclone is called typhoon in Japan and Phillippines.
→ Wind flow pattern: The pattern of flow of wind due to uneven heating on the earth.
