Electric Power
Electric power is defined as the rate at which electrical work is done or the rate at which electrical energy is consumed or dissipated. The power P is given by P= W/t = I2R
Watt
Watt is the unit of power and is defined as the power consumed when 1 A of current flows at a potential difference of 1 V. Thus, Electric Power in Watts = Volt ampere.
When electrical energy is consumed at the rate of 1 J per second, power consumed is said to be 1 Watt.
Kilowatt hour
A kilowatt-hour is the commercial unit of electric energy and is defined as the energy consumed when 1 KW is used for 1 hour.
1 kWh = 1 kW × 1 hour = 1000 watt × 3600 second = 3.6 × 106 joule
![]()
Electrical appliances are not connected in series
Different appliances need different values of current for their proper operation. Whereas, in a series circuit, the current is constant throughout the circuit. Also, when one component fails in a series circuit, the entire circuit is broken and none of the components work. On the other hand, a parallel circuit divides the current through the electrical gadgets.
Example 1.
An electric bulb is rated 220 V and 100 W. When it is operated on 110 V, the power consumed will be:
(a) 100 W
(b) 75 W
(c) 50 W
(d) 25 W
Answer:
(d) 25 W
Explanation: It is given that P = 100 W and V = 220 V. Therefore, we will first calcu¬late resistance of the bulb using the formula
R = \(\frac{V^{2}}{P}=\frac{220 \times 220}{100}\) = 484 Ohm.
When this bulb is operated on 110 V, power consumed will be
P = \(\frac{V^{2}}{R}=\frac{110 \times 110}{484}=\frac{12100}{484}\) = 25 W
![]()
Example 2.
Compare the power used in the 2 Ω resistor in each of the following circuits: (A) a 6 V battery in series with 1 Ω and 2 Ω resistors, and (B) a 4 V battery in parallel with 12 Ω and 2 Ω resistors.
Answer:
(A) The figure below shows a 6V battery in series with 1 Ω and 2 Ω resistors, in 2n
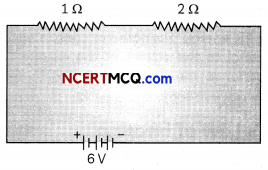
The total resistance in the series circuit = 1 Ω + 2 Ω = 30.
Current, I = V/R = 6/3 A = 2 A.
Power used in the 2 Ω resistor = I2R= 2 × 2 × 2 = 8W
(B) The figure below shows a 4 V battery in parallel with 12 Ω and 2 Ω resistors.
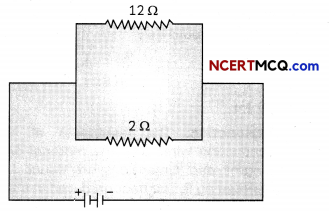
The current through the 2 Ω resistor = V/R = 4/2 = 2A (since the two resistors are connected in parallel, the potential difference across them is same). Power used = I2R = 2 × 2 × 2 = 8W.
Therefore, the power used in the 2 Ω resistors in both the circuits is the same.