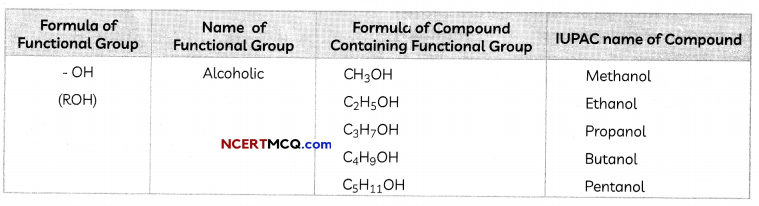
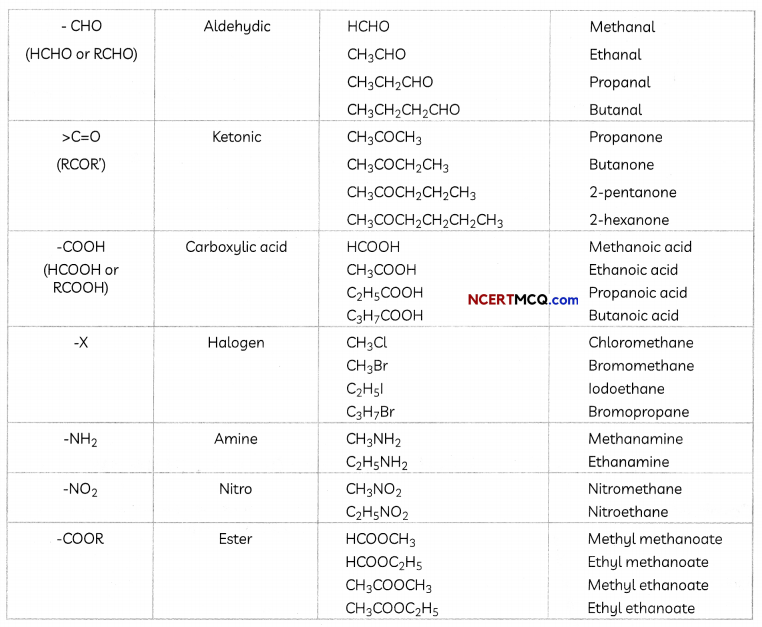
Functional Groups
A functional group in an organic compound is an atom or a group of atoms bonded together in a unique fashion, which is usually the site of chemical reactivity in an organic molecule.
If in a hydrocarbon chain, one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by atoms of other elements such as halogens, oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur etc, such that the valency of carbon remains satisfied, then the element replacing hydrogen is referred to as a heteroatom. These heteroatoms confer specific properties to the compound, regardless of the length and nature of the carbon chain, and hence are called functional groups.
![]()
Important Functional Groups
Some important functional groups are given in the table below.
Free valency or vaLencies of the group are shown by the single line. The functional group is attached to the carbon chain through this valency by replacing one hydrogen atom or atoms.
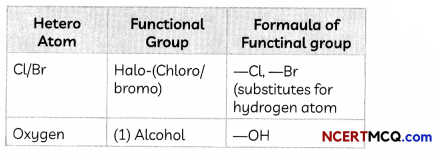
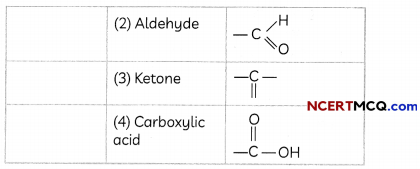
The electron dot structure of two compounds propanal, an aldehyde having molecular formula C2H5CHO and propanone, a ketone, having molecular formula CH3COCH3 are shown below:
![]()
Electron Dot Structure of Propanal
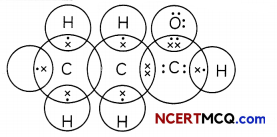
Electron Dot Structure of Propanone
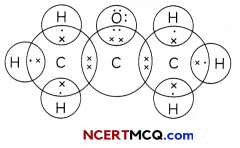
Some More Examples of Functional Groups