Homologous Series
A homologous series is a group of organic compounds having similar structures and similar chemical properties in which the successive compounds differ by CH2 group.
Characteristics of Homologous Series
- All the members of a homologous series can be represented by the same general formula.
- Any two adjacent homologues differ by -CH2 or 1 carbon atom and 2 hydrogen atoms in their molecular formula.
- The difference in the molecular masses of any two adjacent homologues is 14 u.
- All the compounds belonging to the same homologous series have similar chemicaL properties since these are determined solely by the functional group.
- The members of a homologous series show a gradual change in their physical properties with an increase in molecular mass. This is because the melting and boiling points increase with increasing molecular mass.
Nomenclature of Carbon Compounds
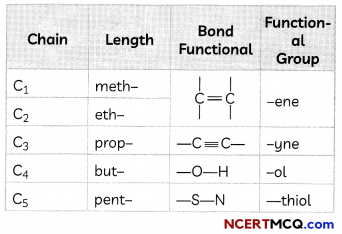
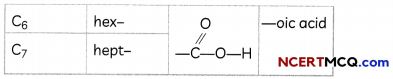
The names of compounds in a homologous series are based on the name of the basic carbon chain modified by a “prefix” “phrase before” or “suffix” “phrase after” indicating the nature of the functional group.
Naming a carbon compound can be done by the following method:
1. Identify the number of carbon atoms in the compound. A compound having three carbon atoms would have the name propane.
2. In case a functional group is present, it is indicated in the name of the compound with either a prefix or a suffix
3. If the name of the functional group is to be given as a suffix, the name of the carbon chain is modified by deleting the final ‘e’ and adding the appropriate suffix. For example, a three-carbon chain with a ketone group would be named in the following manner – Propane – ‘e’ = propane + ‘one’ = propanone.
4. If the carbon chain is unsaturated, then the final ‘ane’ in the name of the carbon chain is substituted by ‘ene’ or ‘yne’. For example, a three-carbon chain with a double bond would be called propene and if it has a triple bond, it would be called propyne.
![]()
Example 1.
How would you name the following compounds?
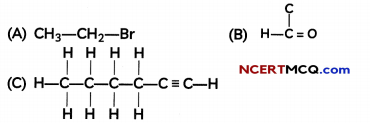
Answer:
(A) Bromoethane
(B) Methanal
(C) 1-hexyne (as the triple bond is between the first and second carbon atom when numbered from right)