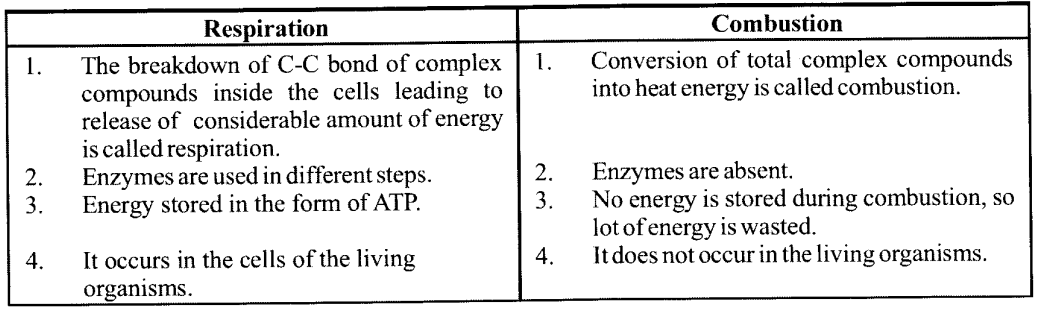
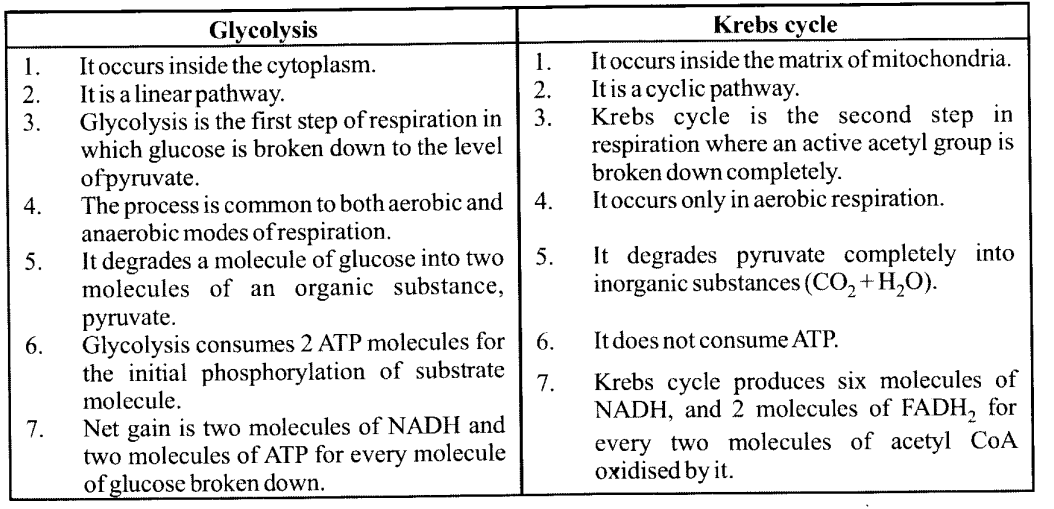
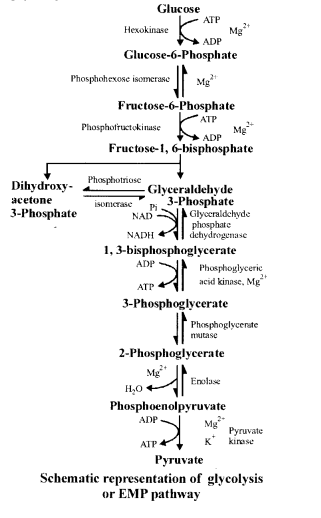
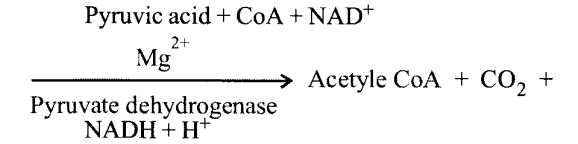
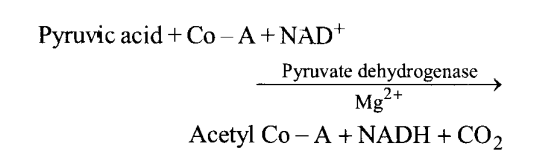NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 Structural Organization in Animals
These Solutions are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 Structural Organization in Animals.
Question 1.
Answer in one word or one line.
(i) Give the common name of Periplaneta americana.
(ii) How many spermathecae are found in earthworms?
(iii) What is the position of ovaries in cockroach?
(iv) How many segments are present in the abdomen of the cockroach?
(v) Where do you find malpighian tubules?
Solution:
(i) Cockroach
(ii) Four pairs of spermathecae are found in the 6“ to 9th segments (one pair in each segment).
(iii) Cockroach includes a pair of ovaries, that lies laterally in the 2nd to 6th abdominal segments of the abdomen.
(iv) Ten
(v) At the junction of midgut and hindgut. 100-150 yellow coloured thin filamentous ring is present in earthworm, which is called malpighian tubules.
Question 2.
Answer the following :
(i) What is the function of nephridia?
(ii) How many types of nephridia are found in earthworms based on their location?
Solution:
(i) Nephridia is the excretory organ of the earthworm or pheretima.
(ii) There are three types of nephridia –
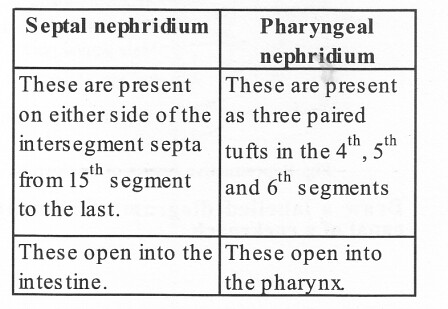
(i) Septal nephridia – Present on both the sides of intersegmental septa of segment 15 to the last that open into the intestine.
(ii) Integumentary nephridia – Attached to the lining of the body wall of segment 3 to the last that opens on the body surface.
(iii) Pharyngeal nephridia – Present as three paired tufts in the 4th, 5th, and 6th segments.
These three different types of nephridia are almost similar in structure.
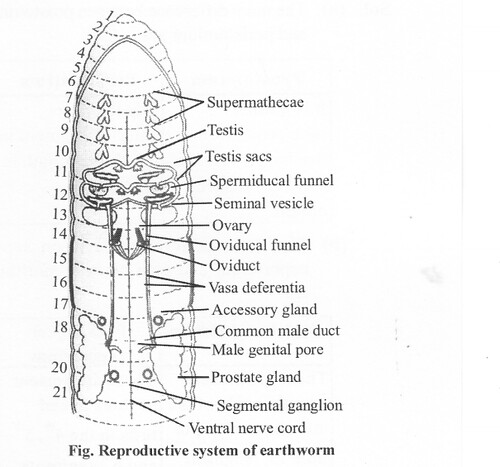
Question 3.
Draw a labelled diagram of the reproductive organs of an earthworm.
Solution:
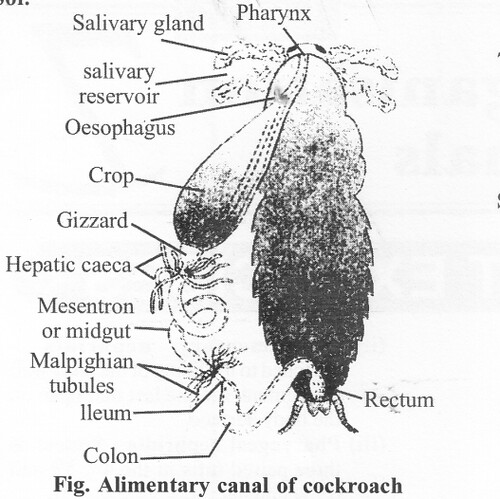
Question 4.
Draw a labelled diagram of the alimentary canal of a cockroach
Solution:
Question 5.
Distinguish between the followings :
(a) Prostomium and peristomium
(b) Septal nephridium and pharyngeal nephridium
Solution:
(a) The main difference between prostomium and peristomium are :

(b) The main difference between septal nephridium and pharyngeal nephridium are:
Question 6.
What are the cellular components of blood?
Solution:
Red blood cells and white blood cells are the cellular components of blood.
Question 7.
What are the following and where do you find them in an animal body.
1. Chondrocytes
2. Axons
3. Ciliated epithelium
Solution:
1. Chondriocytes: The intercellular material of cartilage is solid and pliable and resists compression. Cells of this tissue (Chondriocytes) are enclosed in small cavities within the matrix secreted by them. Most of the cartilages in vertebrate embryos are replaced by bones in adults. Cartilage is present in the tip of the nose, outer ear joints, between adjacent bones of the. vertebral column, limbs, and hands in adults.
2. Axons: It is found in the nervous system neuron. It is a long fiber, the distal end of which is branched. The main function of axons is the transmission of impulses by means of neurotransmitters.
3. Ciliated epithelium: If the columnar or cuboidal cells bear cilia on their free surface they are called the ciliated epithelium. They are found in the lining of the stomach and intestine and help in secretion and absorption, their function is to move particles or mucus in a specific direction over the epithelium. They are mainly present in the inner surface of hollow organs like bronchioles and fallopian tubes.
Question 8.
Describe various types of epithelial tissues with the help of labelled diagrams.
Solution:
Epithelial tissues
Epithelial tissues provide covering to the inner and outer lining of various organs. The cells of epithelial tissues are compactly packed with a little intercellular matrix.
There are two types of epithelial tissues:
(i) Simple epithelium
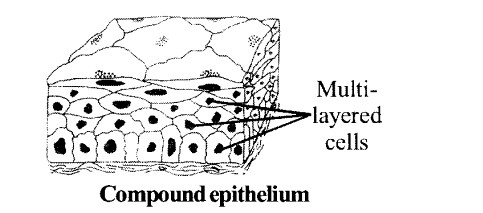
(ii) Compound epithelium
(i) Simple epithelium :
Composed of a single layer of cells and functions as a lining for body cavities ducts and tubes. It is further divided into three types on the basis of structure modifications-
(a) Squamous epithelium – It is made of a single layer of flattened cells with irregular boundaries.
It is found as a lining for body cavities, ducts, and tubes such as in the walls of blood vessels and air sacs of lungs.
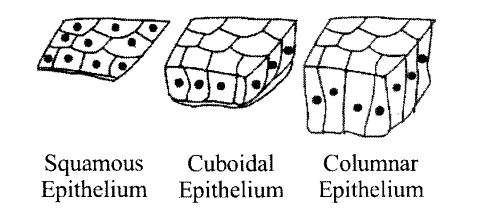
Functions – It helps in forming a diffusion boundary.
(b) Cuboidal epithelium – It is made of a single, layer of cube-like cells. It is commonly found in the ducts of glands and tubular parts of nephrons in kidneys. Specialized cuboidal cells are capable of producing gametes found in gonads called the germinal epithelium.
Functions- It helps in secretion and absorption and also in moving particles or mucus in a specific direction over the epithelium.
(c) Columnar epithelium – It is composed of a single layer of tall and slender cells. Nuclei are located at the base.
Its free surface may have microvilli.
It is found inlining of the stomach and intestine.
Functions – It helps in secretion and absorption.
Question 9.
Distinguish between
(a) Simple epithelium and compound epithelium
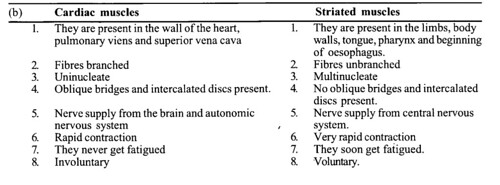
(b) Cardiac muscle and striated muscle
(c) Dense regular and dense irregular connective tissues
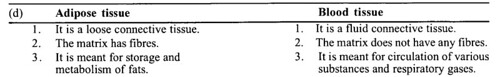
(d) Adipose and blood tissue
(e) Simple gland and compound gland
Solution:
(a) The main difference between simple epithelium and compound epithelium are as following.

The main difference between Cardiac muscles and striated muscle are as following.
The main difference between dense regular connective tissues and dense irregular connective tissues are as following.

The main difference between adipose tissue and blood tissue are as following.
The main difference between simple gland and compound gland are as following

Question 10.
Mark the odd one in each series:
(a) Areolar tissue; blood; neuron; tendon
(b) RBC; WBC; platelets; cartilage
(c) Exocrine: endocrine; salivary gland;ligament
(d) Maxilla; mandible; labrum; antennae
(e) Protonema; mesothorax; metathorax; coxa
Solution:
(a) Neuron
(b) Cartilage
(c) Ligament
(d) Antennae
(e) Protonema
Question 11.
Match the terms in column I with those in column II:
Column I Column II
(a) Compound epithelium – (i) Alimentary canal
(b) Compound eye – (ii) Cockroach
(c) Septal nephridia – ( iii) Skin
(d) Open circulatorysystem – (iv) Mosaic vision
(e) Typhlosole – (v) Earthworm
(f) Osteocytes – (vi) Phallomere
(g) Genitalia – (vii) Bone
Solution:
(a) Compound epithelium ( iii) Skin
(b) Compound eye – (iv) Mosaic vision
(c) Septal nephridia – (v) Earthworm
(d) Open circulatory system – (ii) Cockroach
(e) Typhlosole – (i) Alimentarycanal
(f) Osteocytes – (vii) Bone
(g) Genitalia – (vi) Phallomere
Question 12.
Mention briefly the circulatory system of earthworms.
Solution:
Pheretima exhibits a closed type of blood vascular system, consisting of blood vessels capillaries, and heart. Due to the closed circulatory system, blood is confined to the heart and blood vessels. Contractions keep blood circulating in one direction. Smaller blood vessels supply the gut, nerve cord, and body wall. Blood glands are present on the 4th, 5th, and 6th segments. They produce blood cells and hemoglobin which is dissolved in blood plasma. Blood cells are phagocytic in nature. Earthworms lack specialized breathing devices. Respiratory exchange occurs through moist body surfaces into their bloodstream.
Question 13.
Draw a neat diagram of the digestive system of the frog.
Solution:
The digestive system of frog:
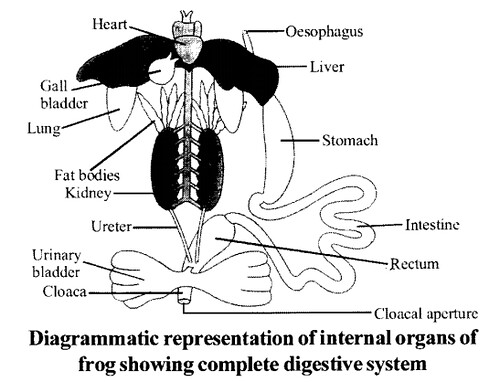
Question 14.
Mention the function of the following:
(a) Ureters in frog
(b) Malpighian tubules
(c) Body wall in earthworm
Solution:
Functions:
(1) Ureters in frog:
- They carry the urine from the kidneys to the cloaca.
- In males, it also conducts the sperm as it is the urinogenital duct.
- In females, the ureters and oviduct open- separately in the cloaca.
(2) Malpighian tubules:
- They are the excretory organs of a cockroach.
- They collect the nitrogenous wastes from the haeomolymph and send them into the intestine.
- Each tubule is lined by glandular and ciliated cells. They absorb nitrogenous waste products and convert them into uric acid which is excreted out through the hindgut.
(3) Body wall of earthworm:
The body wall of the earthworm is covered externally by a thin non-cellular cuticle
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
Name the protein found in white fibres.
Solution:
Collagen.
Question 2.
State the function of setae.
Solution:
It helps in locomotion by gripping the earth.
Question 3.
What is the functional unit of the cockroach eye?
Solution:
Ommatidium.
Question 4.
Name the unit of neural or nervous system.
Solution:
Neurons.
Question 5.
What is worm casting ?
Solution:
It is the insoluble and undigested food that is given out along with soil through anus.
Question 6.
Which cell covers the exposed surfaces of the body (skin) and internal passage ways (digestive tract and glands) ?
Solution:
Squamous epithelium
Question 7.
Name the type of epithelium that lines the inner surface of stomach.
Solution:
Columnar epithelium
Question 8.
Name the type of epithelium that lines the buccal cavity.
Solution:
Stratified squamous epithelium.
Question 9.
N ame of type of tissue that is the most abundant in animal body.
Solution:
Connective tissue.
Question 10.
What is the other name given to the gizzard of cockroach?
Solution:
Proventriculus.
Question 11.
Name the larva of a frog.
Solution:
Tadpole.
Question 12.
What is the scientific name of Indian (bull) frog?
Solution:
Rana tigrina.
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
What are the neuroglia cells?
Solution:
Cells which holds the neuron together are known as neuroglia cells.
Question 2.
What is vermicompositing?
Solution:
The process of increasing soil fertility by earthworms is known as vermicomposting.
Question 3.
What are exocrine glands? Name any two secretions of them.
Solution:
Exocrine glands : Those glands which have ducts to pour their secretion(s) into the respective site of action, are called exocrine.
(i) Salivary glands secrete saliva into the buccal cavity.
(ii) Liver secretes bile into the duodenum.
Question 4.
Write four functions of bones.
Solution:
Functions of bones:
(i) They provide place for attachment of muscles and help in movement and locomotion.
(ii) Bone marrow is the site of manufacture of blood cells.
(iii) Bones provide protection to the internal organs.
(iv) The long bones of the limbs serve the weight-bearing function.
(v) They act as the depot of calcium and phosphorus.
Question 5.
Describe the three types of cell junctions present in the epithelium and other tissues.
Solution:
Cell junctions
(i) Tight junctions – They check leaking of substances across a tissue.
(ii) Adhering junctions – They help in cementing the neighbouring cells together.
(iii) Gap junctions – They facilitate the cells to communicate with each other by cytoplasmic connections, for rapid transfer of ions, small molecules, etc.
Question 6.
How is the gizzard in the alimentary canal of a cockroach suitable for grinding the food?
Solution:
Gizzard of cockroach has following characteristics:
(i) The gizzard has an outer layer of thick circular muscles.
(ii) The inner thick layer of cuticle forms six plate like teeth.
(iii) The movement with the help of muscles and the teeth-like structures help in grinding the food.
Question 7.
What is a typhlosole in an earthworm? Where is it found? What is its function?
Solution:
Typhlosole: It is an internal median fold of the dorsal wall of the intestine. It is found in the intestine between 26th and 35th segments of the body.
It increases the effective area of absorption.
LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
Describe the female reproductive organs of frog.
Solution:
The female reproductive organs include a pair of ovaries. The ovaries are situated near kidneys and there is no functional connection with kidneys. A pair of oviduct arising from the ovaries opens into the cloaca separately. A mature female can lay 2500 to 3000 ova at a time.
Fertilisation is external and takes place in water. Development involves a larval stage called tadpole. Tadpole undergoes metamorphosis to form the adult.
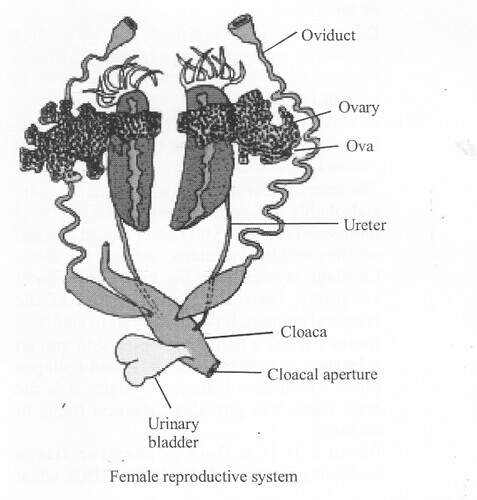
Question 2.
Describe with examples, various types of connective tissues.
Solution:
Connective tissues are most abundant and widely distributed in the body of complex animals. They are named connective tissues because of their special function of linking and supporting other tissues/C ••gans of the body. Connective tissues are classified into three types:
(i) Loose connective tissue,
(ii) Dense connective tissue and
(iii) Specialised connective tissue.
(i) Loose connective tissue:
- It has cells and fibres loosely arranged in a semi-fluid ground substance, for example, areolar tissue present beneath the skin.
- Often it serves as a support framework for epithelium. It contains fibroblasts (cells that produce and secrete fibres), macrophages and mast cells.
- Adipose tissue is another type of loose connective tissue located mainly beneath the skin. The cells of this tissue are specialised to store fats.
(ii) Dense connective tissue :
- Fibres and fibroblasts are compactly packed in the dense connective tissues.
- Orientation of fibres show a regular or irregular pattern and are called dense regular and dense irregular tissues.
- In the dense regular connective tissues, the collagen fibres are present in rows between many parallel bundles of fibres.
- Tendons, which attach skeletal muscles to bones and ligaments which attach one bone to another are examples of this tissue.
- Dense irregular connective tissue has fibroblasts and many fibres (mostly collagen) that are oriented differently. This tissue is present in the skin.
(iii) Specialised connective tissue :
- Cartilage, bones and blood are various types of specialised connective tissues.
- The intercellular material of cartilage is solid and pliable and resists compression.
- Cells of this tissue (chondrocytes) are enclosed in small cavities within the matrix secreted by them.
- Cartilage is present in the tip of nose, outer ear joints, between adjacent bones of the vertebral column, limbs and hands in adults.
Bones : It has a hard and non-pliable ground substance rich in calcium salts and collagen fibres which give bone its strength. It is the main tissue that provides structural frame to the body.
Blood : It is a fluid connective tissue containing plasma, red blood cells (RBC), white bloo4 cells (WBC) and platelets. It is the main circulating fluid that helps in the transport of various substances.
Question 3.
Describe the alimentary canal of earthworm.
Solution:
The alimentary canal is a straight tube and mns between first to last segment of the boay. It has following parts.
Mouth : A terminal mouth opens into the buccal cavity (1-3 segments) which leads into muscular pharynx.
oesophagus: A small narrow tube, oesophagus (5-7 segments), continues into a muscular gizzard (8-9 segments). It helps in grinding the soil particles and decaying leaves, etc.
Stomach : The stomach extends from 9-14 segments. The food of the earthworm is decaying leaves and organic matter mixed with soil. Calciferous glands, present in the stomach, neutralise the humic acid present in humus.
• Intestine starts from the 15th segment onwards and continues till the last segment. A pair of short and conical intestinal caecae project from the intestine on the 26th segment.
Typhosole : The characteristic feature of the intestine between 26-35 segments is the presence of internal median fold of dorsal wall called typhlosole. This increases the effective area of absorption in the intestine.
Anus : The alimentary canal opens to the exterior by a small rounded aperture called anus. The ingested organic rich soil passes through the digestive tract where digestive enzymes breakdown complex food into smaller absorbable units. These simpler molecules are absorbed through intestinal membranes and are utilised.
Question 4.
Draw a labelled diagram of external features of cockroach.
Solution:
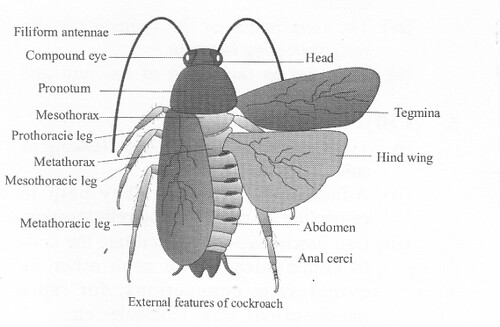
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology at Work Chapter 7 Structural Organization in Animals, help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology at Work Chapter 7 Structural Organization in Animals, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.