NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 21 Neural control and co-ordination
These Solutions are part of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 21 Neural control and co-ordination.
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
Rearrange the following in the correct order of involvement in electrical impulse movement.
Solution:
The correct order of involvement in electrical impulse movement is as follows:
(i) Dendrites
(ii) Cell body
(iii) Axon
(iv) Axon terminal (vi) Synaptic knob
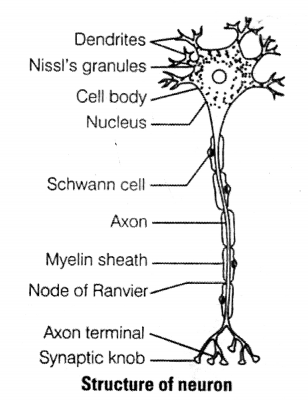
Question 2.
Which cells of the retina enable us to see coloured objects around us?
Solution:
Cone cells present in unable us to see the colours. There are three types of cones which possess their own characteristic photopigments that respond to red, green and blue light.
Question 3.
Arrange the following in the order of reception and transmission of sound wave from the ear drum. Cochlear nerve, external auditory canal, ear drum, stapes, incus, malleus, cochlea.
Solution:
The reception and transmission of sound waves occurs in following order – External Auditory canal —» Eardrum —» Malleus —> Incus —> Stapes —>• Cochlea —> Cochlear nerve
Question 4.
During resting potential, the axonal membrane is polarized, indicate the movement of H-ve and -ve ions leading to polarisation diagrammatically.
Solution:
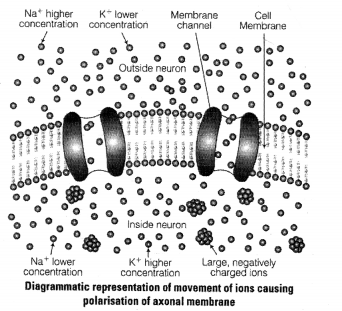
Question 5.
Our reaction like aggressive behaviour, use of abusive words, restlessness etc. are regulated by brain, name the parts involved.
Solution:
Functions as aggressive behaviour, use or abusive words, restlessness, etc. The inner part of cerebral hemispheres and a group of associated deep structures called limbic lobe or limbic system along with hypothalamus are involved.
Question 6.
What do grey and white matter in the brain represent?
Solution:
A major component of CNS is Grey matter consisting of neutronal cell bodies, dendrite, unmyelinated axons, glial cells and capillaries. White matter is also a component of CNS and consists mostly of gilal cell and myelinated axons.
Question 7.
Where is the hunger centre located in human brain?
Solution:
Hypothalamus in human brain contains many centres which control urge for eating and drinking.
Question 8.
Complete the statement by choosing appropriate match among the following.

Solution:
A. -> (3), B. -> (4), C. -> (2), D. -> (1)

SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
The major parts of the human neural system is depicted below. Fill in the empty boxes with appropriate
words.
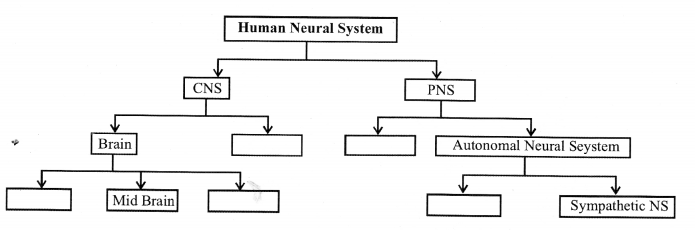
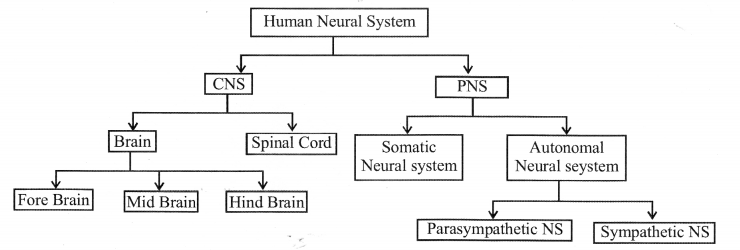
Solution:
The major parts of the human neural system is filled in the boxes with appropriate words
Question 2.
Neuron system and computers share certain common features. Comment in five lines.
Solution:
In various organs the sensory neurons is present to sense the environment and extend the message to the brain. So, it is equivalent to input device of computers.
Brain acts as the CPU, or Central Processing Unit. The information gathered by sensory neurons is processed by brain and it gives command to the concerned organ to act accordingly. This message is taken or conveyed by motor neurons which act as output devices.
Question 3.
What is the function described to Eustachian tube?
Solution:
The eustachian tube forms connection between the middle ear cavity with the pharynx. It helps in equalising the pressure on either sides of the ear drum. At the pharyngeal opening of the eustachian tube there is a valve which normally remains closed.
The valve opens during yawning, swallowing and during an abrupt change in altitude, when air enters or leaves the tympanic cavity to v equalise the pressure of air on the two sides of the tympanic membrane.
LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
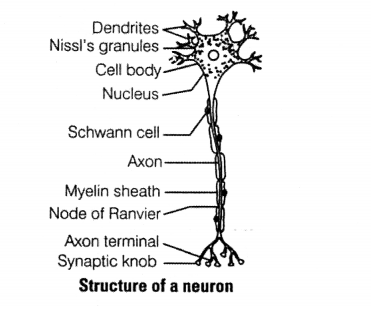
Explain the process of the transport and release of neurotransmitter with the help of a labelled diagram showing a complete neuron, axon terminal and synapse.
Solution:
The three main parts of a neuron include the
(i) Cell body
(ii) Axon
(iii) Dendrites
Stimulus or nerve impulse of any kind passes from one neuron to another via axon. This nerve impulse is wave of bioelectric/electrochemical disturbance that passes along the neuron during conduction of an excitation.
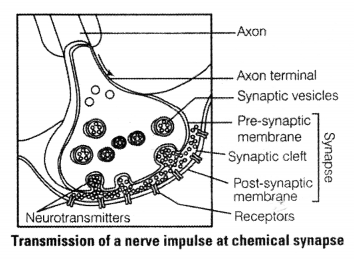
- Within a synapse transport and release of a neuro transmiter occurs.
- At a chemical synapse, the membranes of the pre- and post-synaptic neurons are separated by a fluid-filled space called synaptic cleft. Chemicals called neurotransmitters are involved in the transmission of impulses at these synapses.
- The axon terminals contain vesicles filled with these neurotransmitters.
- Upon arrival of an impulse (action potential) at the axon terminal, it stimulates the movement of the synaptic vesciles towards the membrane, where they fuse with the plasma membrane and release their neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft.
- The released neurotransmitters bind to their specific receptors, present on the post-synaptic membrane. This binding opens ion channels allowing the entry of ions, that can generate a new action potential in the
Question 2.
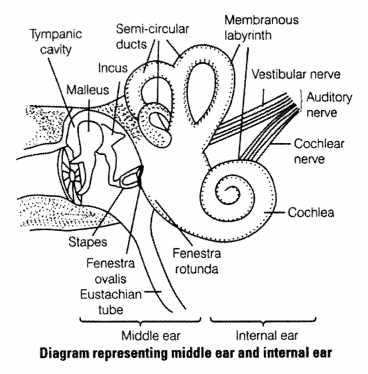
Explain the structure of middle and internal ear with the help of diagram.
Solution:
Ears are a part of statoacoustic organ meant for balancing and hearing the external ear in most mammals is a heap of tissue also called pinna. It is a part of auditory system.
The human ear consists of three main parts external ear, middle, ear and internal ear.
Structure of Middle Ear
- The middle ear consists of three bones or ossicles-the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil and stapes (stir-up).
- These bones are attached to one another in a chain-like manner.
- The malleus is attached to the tympanic membrane and the stapes is attached to the oval window (a membrane beneath the stapes) of cochlea.
- These three ossicles increase the efficiency of transmission of sound waves to the inner ear.
- The middle ear also opens into the eustachian tube, which connects with the pharynx and maintains the pressure between the middle ear and the outside atmosphere.
Structure of Internal Ear
- Thd inner ear consists of a labyrinth of chambers filled with fluid within temporal bone of the skull. The labyrinth consists of two parts the bony and membranous labyrinth. The bony labyrinth is a series of channels.
- Membranous labyrinth lies inside these channels which is surrounded by a fluid called perilymph. The membranous labyrinth is filled with a fluid called endolymph. The coiled portion of the labyrinth is called cochlea.
- The cochlea has two large canal separated by a small cochlear duct (scala media). An upper vestibular canal (scala vestibuli) and a lower tympanic canal (scala tympani). The vestibular and tympanic canals contain perilymph and the cochlear duct is filled with endolymph.
- The wall of membranous labyrinth comes in contact with the fenestra ovalis at the base of scale vestibuli while the fenestra rotunda.
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology at Work Chapter 21 Neural control and co-ordination, help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology at Work Chapter 21 Neural control and co-ordination, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.