NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination and Integration
These Solutions are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination and Integration.
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
Which of the two adrenocortial layers, zona glomerulosa and zona reticularis lies outside enveloping the other?
Solution:
Zona glomerulosa envelops zona reticularis from the outside.
Question 2.
What is erythropoiesis? Which hormone stimulates it?
Solution:
The process of formation of RBC is Erythropoiesis. Erythropoietin, a Peptide hormone secreted from the juxtaglomerular cells of kidney stimulates erythropoiesis.
Question 3.
Name the only hormone secreted by pars intermedia of the pituitary gland.
Solution:
The only hormone secreted by Pars intermedia ^ of pituitary gland is Melanocyte Stimulating hormone (MSH). This hormone causes dispersal of pigment granules in the pigment cells, which darken the colour in certain animals like fishes and amphibians.
Question 4.
Name the endocrine gland that produces calcitonin and mention the role played by this ‘ hormone.
Solution:
Calcitonin/thyrocalcitonin linear polypeptide hormone comprising of 32 amino acids that is produced in humans primarily by the parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland. It checks excess Ca2+ and phosphate in plasma by • decreasing mobilization from bones.
Question 5.
Name the hormone that helps in cell-mediated immunity.
Solution:
The hormone thymosin plays a maj or role in the development and differentiation of T-lymphocytes, which provide cell-mediated immunity.
Question 6.
A patient complains of constant thirst, excessive 3. passing of urine and low blood pressure. When the doctor checked the patients’ blood glucose and blood insulin level, the level were normal or 4. slightly low. The doctor diagnosed the condition a diabetes insipid us. But he decided to measure one more hormone in patients blood. Which hormones does the doctor intend to measure?
Solution:
The doctor intends to measure the hyperglycaemia hormone, and its action is opposite to that of insulin Excess of glucose in blood suppresses the secretion of glucose, whereas fall in glucose level enhance glucose production.
Question 7.
Correct the following statements by replacing the term underlined.
(a) Insulin is a steroid hormone.
(b) TSH is secreted from the corpus leteum.
(c) Tetraiodothyronine is an emergency hormone.
(d) the pineal gland is located on the anterior part of the kidney.
Solution:
(a) Insulin is a peptide hormone
(b) TSH is secreted from the pars distalis region ofpitutary.
(c) Adrenaline is an emergency hormone.
(d) The adrenal gland is located on the anterior part of the kidney.
Question 8.
Match the following columns.
Column I Column II
A. Oxytocin 1. Amino acid derivative
B. Epinephrine 2. Steroid
C. Progesterone 3. Protein
D. Growth hormone 4. Peptide
Solution:
The correct matching is
Column I Column II
A. Oxytocin – Peptide
B. Epinephrine – Amino acid derivative
C. Progesterone – Steroid
D. Growth hormone – Protein
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
What is the role-played by luteinising hormones in males and females respectively.
Solution:
- LH and FSH stimulate activity of gonads and hence are called gonadotropins.
- Luteinising hormone (LH) in males stimulates the synthesis and secretion of hormones called androgens from testis. Androgens along with FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) regulate spermatogenesis.
- LH induces ovulation of fully mature follicles in females and maintains the corpus luteum, formed from the remnants of the graafian follicles after ovulation. This secretes progesterone.
Question 2.
George comes on a vacation to India from US. The long journey disturbs his biological system and he suffers from jet lag. What is the cause of his discomfort?
Solution:
- The melatonin hormone secreted by the pineal gland is also called as ‘sleep hormone’ as it promotes sleep-wake cycle.
- The disruption of the body clock as it is out of synchronisation because of the unfamiliar time zone of the destination causes Jet lag. The body experiences different patterns of light and dark conditions than it is normally used to, this disrupts the natural sleep-wake cycle.
- A hormone that plays a key role in body rhythms and causes jet lag is melatonin. Eyes perceive darkness after the sun sets and alert the hypothalamus to begin releasing melatonin, which promotes sleep. Conversely, when the eyes perceive sunlight, they induce the hypothalamus to with hold melatonin prodtiction.
- The hypothalamus however cannot readjust its schedule instantly and it may take several days, to overcome this problem.
Question 3.
Inflammatory responses can be controlled by a certain steroid. Name the steroid, its source and also its other important functions.
Solution:
- Glucocorticoids cortisol in particular, produce anti-inflammatory reactions and suppress the immune response.
- The middle zone, in adrenal cortex which is the widest of three zones called zona fasciculata is the source for glucocorticoids.
- The glucocorticoids as the name suggests affect carbohydrate metabolism and metabolism of proteins and fats.
- They stimulate gluconeogenesis, lipolysis and proteolysis. They also inhibit utilization of amino acid and cellular uptake. Cortisol is also called stress hormone as it copes with stress.
Question 4.
Old people have weak immune system. What could be the reasons?
Solution:
- A major role in the development of the immune system is played by thymus.
- The thymus gland is a lobular structure located on the dorsal side of the heart and the aorta. It is derived from the endoderm of the embryo. Thymus secretes a hormone named thymosin which stimulates the development of white blood cells (WBCs), involved in producing immunity.
- In old individuals, thymus is degenerated which results in decreased production of thymosin. The immune system as a result becomes weak, in old people.
LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
Calcium plays a very important role in the formation of bones. Write on the role of endocrine glands and hormones responsible for maintaining calcium homeostasis.
Solution:
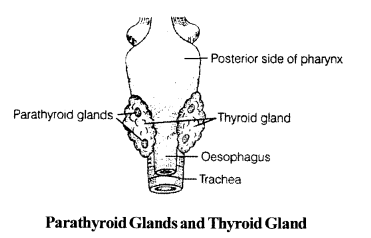
The hormones and endocrine glands that are responsible for maintaining calcium
homeostasis, are thyroid and parathyroid glands j and their associated hormones are calcitonin and Parathyroid Hormone (PTH).
(i) Parathyroid glands – These glands developed from the endoderm of the embryo. The cells of parathyroid glands are
of two types – chief cells and oxyphil cells. The chief cells of the parathyroid glands secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH).
This hormone (PTH) is involved in regulation of calcium and phosphate balance between the blood and other tissue. It mobilises the release of calcium into the blood from bones. PTH increases reabsorption of calcium by the body organs like intestine and kidneys.
(ii) Thyroid gland – It is the largest endocrine gland located anterior to the thyroid cartilage of the larynx in the neck.
This gland plays a major role in maintaining calcium homeostasis. It releases thyrocalcitonin hormone produced by the parafollicular cells, also called, ‘C’ cells. This hormone is secreted when the calcium level in blood gets high.
It is a 32 amino acid peptide hormone that lowers the calcium level by suppressing release of calcium ions from the bones. Calcitonin thus has an action opposite to that of the parathyroid hormone in calcium homeostasis.
Question 2.
Hypothalamus is a supper master endocrine gland. Elaborate.
Solution:
Hypothalamus is a minor but extremely important part of the diencephalon that is involved in the mediation of endocrine, autonomic and behavioural fiinction.
It consists of several groups of neuro secretory cells called nuclei which produce hormones. Hypothalamus provides anatomical connection between the nervous and endocrine system. It controls the release of major hormones by
hypophysis which include :
(i) Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone stimulates the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland to release growth hormone or somatostatin.
(ii) MSH Releasing Hormone stimulates the intermediate lobe of the pituitary gland to secrete Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (MSH)
The hormones released from hypothalamus are involved in the processes like temperature regulation, control of water balance in body, sexual behaviour and reproduction, control of daily cycles in physiological state, behaviour and mediation’ of emotional response hypothalamus is thus called as super master endocrine gland of body.
(iii) Prolactin Releasing Hormone (PRH) stimulates the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland to secret prolactin.
(iv) Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone stimulates the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland to release gonadotropic hormones (FSHandlH).
(v) Thyrotropm Releasing Hormone (TRH) stimulates the anterior lobe of pituitary gland to release Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH).
(vi) Adrenocorticotrophic releasing Hormone (ARH) stimulates the anterior lobe of pituitary gland to secrete Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH). ACTH stimulates the synthesis and secretion of steroid hormones called glucocorticoids by adrenal glands.
The hormones released from hypothalamus are involved in the processes like temperature regulation, control of water balance in body, sexual behaviour and reproduction, control of daily cycles in physiological state, behaviour and mediation of emotional responses. Hypothalamus is thus called as super master endocrine gland of body.
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology at Work Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination and Integration, help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology at Work Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination and Integration, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.