NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants
These Solutions are part of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants.
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
Roots obtain oxygen from air in the soil for respiration. In the absence or deficiency of 02, root growth is restricted or completely stopped. How do, the plants growing in marsh lands or swamps obtain their 02 required for root respiration?
Solution:
The roots of the plants as Rhizophora that grow in marsh/swamp areas become negatively geotropic. They grow vertically upwards in air, above the soil level and respire. They are thus called respiratory roots or pneumatophores.
Question 2.
In Opuntia, the stem is modified into a flattened green structure to perform the function of leaves, (i.e., photosynthesis). Cite some other examples of modifications of plant parts for the purpose of photosytnthesis.
Solution:
In Opuntia a xerophytic plant leaves are modified into spine to reduce the rate of transpiration and they do not perform the photosynthesis at all.
The function of photosynthesis in Opuntia plant is performed by stem which is thick fleshy and flattened structure containing chlorophyll and stores food and known as phylloclade.
In some plants similarly roots become assimilatory e.g., case of Trapa and Tinospom. These roots grow outside the soil, develop chlorophyll in them and perform photosynthesis.
Question 3.
In swampy areas like the sunderbans in West Bengal, plants bear special kind of roots called……
Solution:
Pneumatophores Roots are meant for the absorption of water and minerals from the soil. Cells of roots require 02 to respire. In swampy areas, soil does not have air, so no 07 is available to them.
In such cases, roots come out of the soil showing negative geotropism and breathe after coming in contact with air, e.g., Rhizophora. Such roots are called pneumatophores or respiratory roots.
Question 4.
In aquatic plants like Pistia and Eichhornia, leaves and roots are found near…..
Solution:
In Pistia and Eichhonia, the stem is like a runner where it branches to form leaves at the
v apex and roots below. Both the plants are hydrophytes and thus the roots are found near the surface of water.
Question 5.
Which parts in ginger and onion are edible?
Solution:
The edible part of ginger is rhizome the modified stem which stores food material whreas the edible part in onion is fleshy leaves, where the internode becomes shortened, leaves get condensed to form a tunic and store food material.
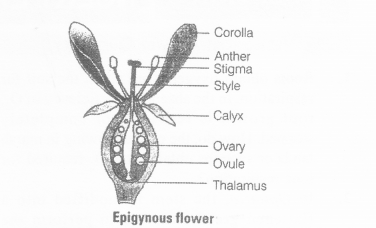
Question 6.
In epigynous flower, ovary is situated below the……….. .
Solution:
Ovary is situated below the thalamus (inferior) in epigynous flower while the other whorls of flower like sepals, petals and androecium grows above the ovary (superior), e.g., carrot, guava, Cucurbit a, sunflower, etc.
Question 7.
Add the missing floral organs of the given floral formula of Fabaceae.
![]()
Solution:
The floral formula of fabaceae family is
![]()
The flower of fabaceae is bisexual, zygomorphic, pentameros, gamosepalous, corolla-petals 5, androecium is ten diadelphous, gynoecium- superior, ovary monocarpellay.
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
Give two examples of roots that develop from different parts of the angiospermic plant other than the radicle.
Solution:
Prop roots are meant for support. Prop roots develop from the lower nodes of stem of banyan tree. They grow downwards and touch the soil.
Stilt roots arise from the lower nodes of stem in sugarcane and enter the soil to provide strength to the plant. These protect the plant against winds.
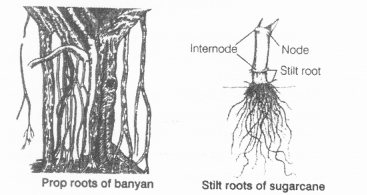
Question 2.
The essential functions of roots are anchorage and absorption of water and minerals in the terrestrial plant. What functions are associated with the roots of aquatic plants. How are roots of aquatic plants and terrestrial plants different?
Solution:
Usually the terrestrial roots show a branched network that helps in anchorage and absorption of water and minerals from soil to the plant. While in aquatic plants, roots show modification and deviation from their normal function.
Ex – in plants like Trapu, Tinospora the roots are green and highly branched to increase the photosynthetic area, whereas in plants like Jussiaecci they get inflated due to air project out of water so a to help the plant in floating and exchange of gases.
Difference between roots of aquatic plants and terrestrial plants are as:
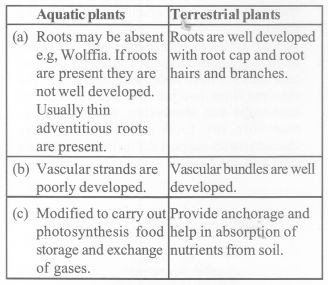
Question 3.
Draw diagrams of a typical monocot and dicot leaves to show their venation pattern.
Solution:
The pattern of distribution of veins and veinlets in the lamina of leaf is called Venation. It’s pattern is different in monocot and dicot leaf.
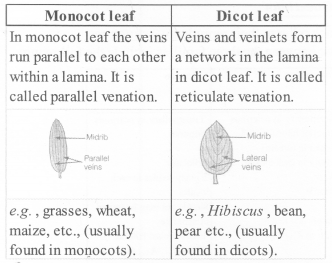
Question 4.
A typical angiosperm flower consists of four floral parts. Give the names of the floral parts and their arrangements sequentially.
Solution:
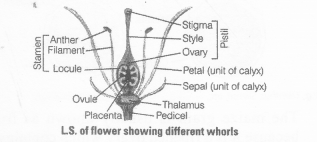
Following are the four floral parts of typical angiospermic flower.
- Calyx is the outermost whorl of the flower and comprised of sepals. These are usually green and (in bud stage) are protective in function.
- Corolla is composed of petals, usually bright coloured to attract insects for pollination.
- Androecium is composed of stamens, the male reproductive organ. Each stamen consists of stalk or filament and anther (containing pollen sac and pollen grains).
- Gynoecium is the female reproductive part and comprised of one or more carpels. Each
Question 5.
Reticulate venation is found in dicot leaves while in monocot leaves venation is of parallel type. Biology being a ‘Science of exceptions’, find out any exception to this generalisation.
Solution:
Reticulate venation is a characteristic of dicots and parallel venation is of monocots. But few exceptions are also seen in this generalisation, parallel venation is also found in dicot plants, e.g, Calophyllum, Corymbium, etc and reticulate venation is also found in monocot plants such as Alocasia, smilax, etc.
Question 6.
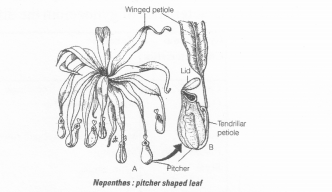
You have heard about several insectivorous plants that fee on insects. Nepenthes or the pitcher plant is one such example, which usually grows in shallow water or in march lands. What part of the plant is modified into a pitcher? How does this modification help the plant for food even though it can photosynthesise like any other green plant?
Solution:
- In insectivorous plant like Nepenthes, the leaf lamin is modified to form a pitcher and anterior part of petiole coils like tendril which keeps the pitcher in a vertical direction.
- Posterior part of the petiole remains flattened like a leaf. The apex of lamina forms a lid.
- Pitcher contains digestive enzyme for digesting trapped insects.
- All these modifications and adaptations are developed to make up for the nitrogen deficiency in the plant because these plants are found in N2 deficient soil, (marshy/swamp soils).
Question 7.
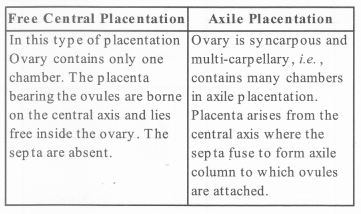
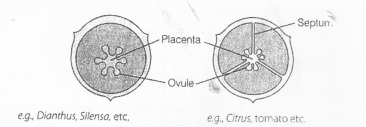
How can you differentiate between free central and axile placentation?
Solution:
The arrangement of ovules on the walls of ovary with the help of special kind of tissue called placenta is placentation. Plants show different types of placentation.
Difference between free central placentation and axile placentation include:
Question 8.
Why is maize grain usually called as a fruit and not a seed?
Solution:
The maize grain is usually known as fruit because it is a ripened ovary which contains a ripened ovule, e.g., a single seed. This fruit is known as caryopsis in which the pericarp is fused with the seed coat. The maize grain occurs attached to a thick cob or peduncle.
Question 9.
Tendrils of grapevins are homologous to the tendril of pumpkins, but are analogous to that of pea. Justify the above statement.
Solution:
Homologous organs are organs that have similar origin but they differ functionally. Axillary bud of stem gives rise to tendril of both grapevine and pumpkins so they have same origin, i.e., homologous, whereas analogous organs are organs having different origin, but perform same function. The tendril of pea arises from the leaf and helps the plant to climb.
Question 10.
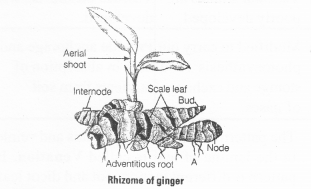
Rhizome of ginger is like the roots of other plants that grows underground. Despite this fact ginger is a stem and not a root. Justify.
Solution:
Rhizome of Ginger is a type of modified underground stem which grows horizontally underground and bears nodes, intemodes and scaly leaves and buds, which gives rise to aerial shoots.
The adventitious root arises from the lower surface of nodes. It is not a true root because root does not have nodes and intemodes. The rhizome does not perform the function of anchorage and absorption, rather serve as reservoir for food storage. All these characteristics support the fact that ginger is a stem and not a root.
LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Question 1.
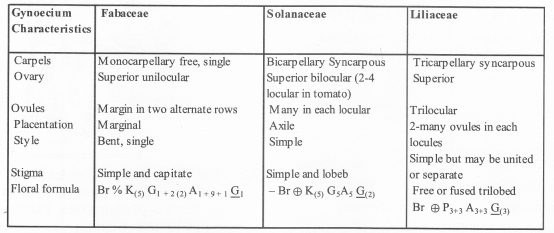
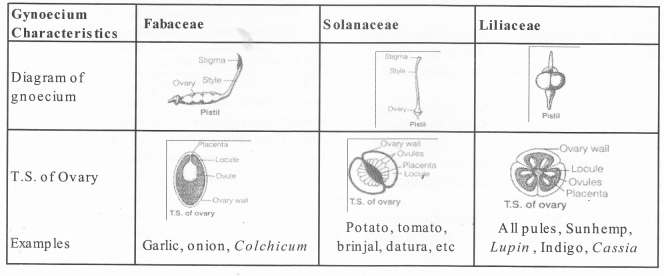
Distinguish between families – Fabaceae, solanaceae, Liliaceae on the basis of gynoecium characteristics (with figures). Also write economic importance of any one of the above family.
Solution:
The families in plant kingdom mainly differ from each other in their reproductive structures.
Based on characteristics of gynoecium the difference between the three families include the following:
Question 2.
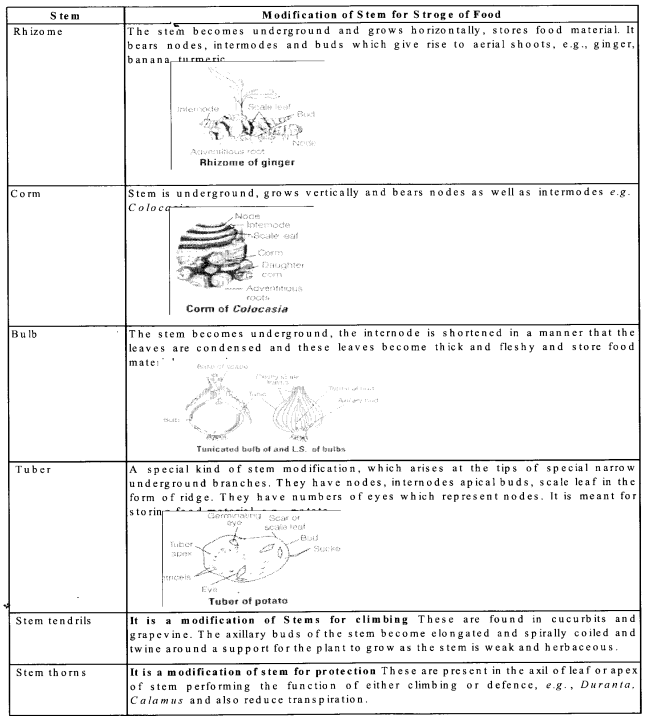
Describe various stem modifications associated with food storage climbing and protection.
Solution:
The aerial part of plant bearing nodes, intemodes, buds, flowers, fruits and seeds is stem. Besides these functions and forms, it gets modified and perform under spfccial conditions.
The various stem modifications include:
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology at Work Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants, help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology at Work Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.