Physical Properties of Metals And Non-Metals:
On the basis of their properties, all the elements can be divided into two main groups: metals and non-metals, Apart from metals and non-metals, there are some elements that show characteristics of both metals and non-metals and known as metalloids, for example, Si, Ge, As, Sb and Te.
Metals are opaque, lustrous elements that are good conductors of heat and electricity. Examples: Copper, Iron, Silver, Aluminium, etc.
Non-metals are elements that have properties that are different from those of metals. Examples: Carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Sulphur etc.
Physical Properties of Metals:
- State: Metals are generally solids at room temperature except for mercury which is a liquid.
- Lustre: In pure state metals have a shining surface. Al and Mg are white whereas Au is yellow and Cu is reddish-brown in colour.
- Hardness: Metals are generally hard but hardness varies from metal to metal.
- Malleability: Some metals can be beaten into thin sheets and this property is called malleability. Gold and silver are the most malleable metals.
- Ductility: Some metals can be drawn into very thin wires and this property is called ductility. Gold is the most ductile metal.
- Thermal and electrical conductivity: Metals are generally good conductors of heat and electricity. Silver is the best conductor of heat followed by copper and aluminium. Silver and copper are the best conductors of electricity.
- Melting and Boiling points: Metals generally have high melting and boiling points. The boiling and melting points of aluminium are 933 K and 2792 K respectively.
- Sonorous: Metals that produce a sound on striking a hard surface are said to be sonorous.
![]()
Example 1.
Case-Based:
A student took an aluminium or copper wire and clamped this wire on a stand, as shown in Fig.
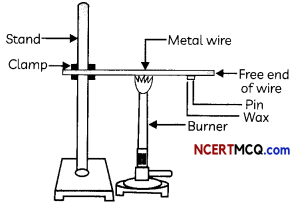
He then fixed a pin to the free end of the wire using wax and heated the wire with a spirit lamp, candle or a burner near the place where it is clamped.
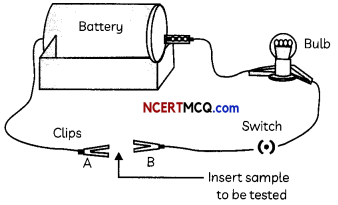
Another student set up an electric circuit as shown in the Figure below to test the electrical conductivity of metals. He placed the metal to be tested in the circuit between terminals A and B as shown.
(A) The activity performed by the first student (Figure) shows that:
(a) Metals are good conductors of heat and have low melting points.
(b) Metals are poor conductors of heat and have high melting points.
(c) Metals are good conductors of heat and have high melting points.
(d) Metals are poor conductors of heat and have low melting points.
Answer:
(c) Metals are good conductors of heat and have high melting points.
Explanation: Metals have a high melting point and are generally good conductors of heat. Most metals are also good conductors of electricity.
(B) The metals which are poor conductors of heat are:
(a) Lead and zinc
(b) Mercury and zinc
(c) Lead and tin
(d) Lead and mercury
Answer:
(d) Lead and mercury
Explanation: The metals lead and mercury are comparatively poor conductors of heat. Whereas the best conductors of heat are silver and copper.
(C) What conclusion can be drawn from the activity performed by the second student (Figure)?
Answer:
The conclusion that can be drawn from the activity performed by the second student (Figure) is that the bulb glows when a metal is inserted between A and B showing that most of the metals conduct electricity.
(D) Name the two best conductors of electricity.
Answer:
Silver and copper are the best conductors of electricity.
(E) Assertion (A): Metal such as aluminium is used for making cooking utensils.
Reason (R): Aluminium is a highly ductile metal.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the (A). Explanation: MetaL such as aluminium is used for making cooking utensils as it is a good conductor of heat and has high melting point. The property of metals used for making electrical wires is ductility and good electrical conductivity.
Physical Properties of Non-Metals:
- State: Non-metals are either solids or gases except bromine which is a liquid.
- Lustre: Non-metals do not have any lustre.
- Hardness: Non-Metals are generally soft. Exceptions: Diamond is an allotrope of carbon and is the hardest natural substance
- Malleability: Non-metals are not malleable. Actually, they are brittle.
- Ductility: Non-metals are not ductile also.
- Thermal and electrical Graphite, which is an allotrope of Carbon conducts electricity. Therefore, this is an exception. do not conduct heat and electricity.
- Melting and boiling points: Non-metals have low melting and boiling points.
![]()
Example 2.
You are given a hammer, a battery, a bulb, wires and a switch.
(A) How could you use them to distinguish between samples of metals and non-metals?
Answer:
Metals and non-metals have different physical properties. If we take the given samples and strike them with a hammer, metals will be converted into sheets, whereas non-metals will not. This is because metals are malleable.
Also, metals are sonorous and produce sound when hit with a hammer, whereas non-metals are not sonorous.
The battery, wires, bulb and switch can be arranged in the form of a circuit for testing the electrical conductivity of samples (refer to Figure).
When samples of metals are inserted between A and B, the bulb glows which shows that metals are good conductors of electricity, whereas the bulb does not glow when samples of non¬metals are inserted which shows that non-metals are poor conductors of electricity.
(B) Assess the usefulness of these tests in distinguishing between metals and non-metals.
Answer:
These tests are useful in distinguishing between metals and non-metals based on the differences in properties of metals and non-metals as metals are malleable, sonorous and good conductors of electricity whereas non-metaLs do not possess any of these properties.
Exceptions in Physical Properties:
|
Physical Property |
Exception |
| 1. Physical State | Mercury is a metal that is a liquid at room temperature. Bromine is a non-metal that is liquid at room temperature. |
| 2. Melting Point and Boiling point | Sodium, potassium, caesium and gallium are metals that have low melting points. Diamond is a non-metal which has a high melting point. |
| 3. Density | Alkali metals (lithium, sodium, potassium) are so soft that they can be cut with a knife. |
| 4.Electrical Conductivity | Mercury, a metal, offers very high resistance to the passage of current. |
| 5. Lustre | Iodine is a non-metal which is lustrous. |