Here we are providing Online Education Soil Class 7 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 9 was designed by subject expert teachers. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-7-science/
Online Education for Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Extra Questions and Answers Soil
Soil Class 7 Extra Questions With Answers Question 1.
What is soil?
Answer:
The uppermost layer of land area of earth, which is a mixture of rock particles and humus is called soil.
Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Extra Questions Question 2.
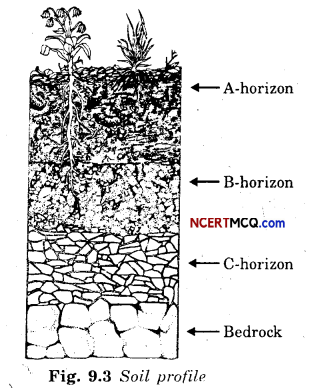
What is soil profile ?
Answer:
A vertical section through different layers of the soil is called the soil profile.
Class 7 Soil Extra Questions Question 3.
Write the formula for percolation rate.
Answer:
Percolation rate (ml/min)
amount of water (ml)
percolation time (min).
Ncert Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Soil Extra Questions Question 4.
Name the climatic factors affecting soil properties.
Answer:
Soil is affected by wind, rainfall, temperature, light and humidity.
![]()
Soil Extra Questions Class 7 Question 5.
What is the ideal soil for paddy?
Answer:
For paddy, soils rich in clay and organic matter, having a good capacity to retain water, are ideal.
Class 7 Science Ch 9 Extra Questions Question 6.
Which soil is suited for lentils?
Answer:
For lentils (masoor) and other pulses, loamy soils, which drain water easily, are required.
Soil Chapter Class 7 Extra Questions Question 7.
Which soil is suitable for cotton?
Answer:
For cotton, sandy-loam or loam, which drain water easily and can hold plenty of air, are more suitable.
Soil Class 7 Worksheet With Answers Question 8.
What is soil erosion?
Answer:
The removal of fertile topsoil by water, wind or ice is known as soil erosion.
Questions On Soil Class 7 Question 9.
Why is there a demand to ban polythene bags?
Answer:
Polythene bags and plastics pollute the soil. They also kill the organisms living in the soil. That is why there is a demand to ban polythene bags and plastics.
Class 7 Science Soil Extra Questions Question 10.
Name the layers of soil formed when soil is dissolved in water and left undisturbed.
Answer:
Humus, water, clay, sand and gravel.
![]()
Soil Class 7 Questions With Answers Question 11.
What is soil horizon?
Answer:
Each layer of soil differs in feel (texture), colour, depth and chemical composition. These layers are referred to as horizons.
Ncert Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Extra Questions Question 12.
What is B-horizon?
Answer:
The second layer of soil has a lesser amount of humus but more of minerals. This layer is generally harder and more compact and is called the B-horizon or the middle layer.
Class 7 Science Chapter Soil Extra Questions Question 13.
Write about C-horizon.
Answer:
The third layer of soil is the C-horizon, which is made up of small lumps of rocks with cracks and crevices. Below this layer is the bedrock, which is hard and difficult to dig with a spade.
Ncert Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Extra Questions Question 14.
Draw the different horizons of soil.
Answer:
Extra Questions Of Soil Class 7 Question 15.
Write briefly about the topsoil.
Answer:
The uppermost horizon is generally dark in colour as it is rich in humus and minerals. The humus makes the soil fertile and provides nutrients to growing plants. This layer is generally soft, porous and can retain more water. It is called the topsoil or the A-horizon.
This provides shelter for many living organisms such as worms, rodents, moles and beetles. The roots of small plants are embedded entirely in the topsoil.
![]()
Soil Questions And Answers For Class 7 Question 16.
Write briefly about loamy soil.
Answer:
The best topsoil for growing plants is loam. Loamy soil is a mixture of sand, clay and another type of soil particle known as silt. Silt occurs as a deposit in river beds. The loamy soil also has humus in it. It has the right water holding capacity for the growth of plants.
Soil Class 7 Questions And Answers Question 17.
Write about soil erosion.
Answer:
The removal of fertile topsoil by water, wind or ice is known as erosion. Plant roots firmly bind the soil. In the absence of plants, soil becomes loose. So it can be moved by wind and flowing water. So, cutting of trees and deforestation should be prevented and efforts should be made to increase the green areas.
Chapter 9 Science Class 7 Extra Questions Question 18.
Discuss the dependence of crop on soil type.
Answer:
The climatic factors, as well as the components of soil, determine the various types of vegetation and crops that might grow in any region. Clayey and loamy soils are both suitable for growing cereals like wheat and gram. Such soils are good at retaining water. For paddy, soils rich in clay and organic matter and having a good capacity to retain water, are ideal.
For lentils (masoor) and other pulses, loamy soils, which drain water easily, are required. For cotton, sandy-loam or loam, which drain water easily and can hold plenty of air, are more suitable. Crops such as wheat are grown in the fine clayey soils because they are rich in humus and are very fertile.
![]()
Ch 9 Science Class 7 Extra Questions Question 19.
What is the difference between rate of percolation and the amount of water retained?
Answer:
Rate of percolation is the amount of water percolated per unit time through soil. Whereas the amount of water retained is the amount of water absorbed by soil. Thus, rates of percolation and water retention are opposite attributes.
Class 7 Chapter 9 Science Extra Questions Question 20.
Can you suggest any method to let more rainwater percolate and reach the water underground?
Answer:
Plants roots increases the extent of percolation of water to groundwater. So by planting more and more trees, we can make more rainwater to percolate and reach the water underground.
Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Extra Question Answer Question 21.
Explain how soil is formed.
Answer:
Soil is fonned by the breaking down of rocks by the action of wind, water and climate. This process is called weathering and further addition õf humus formed by the decomposition of organic matter on the earth’s surface make it fertile.
Experiments:
Aim: To observe the layers of soil. Requirements: Glass tumbler, water, soil lump and stirrer.
Procedure:
- The lump of soil is powdered.
- The tumbler is filled 2/3rd with water.
- The soil powder is poured into water and stirred.
- The mixture is left aside for a while. ’
Observations: Different layers of soil have been formed in the glass.
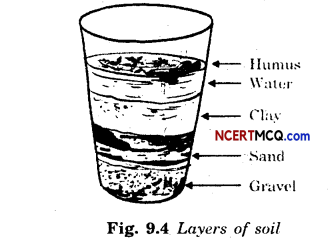
Conclusion: Soil consists of many layers like gravel, sand, clay, water and humus.
(2)
Aim: To measure rate of percolation of soil.
Requirements: Watch, cold drinks can (empty), soil and water (bottle 200 ml.
Procedure :
- The bottom of the can is cut off.
- The can is kept on a suitable place.
- The bottom of the can is filled with soil.
- 200 mL bottle is filled with water.
- The water is poured into the can and the time is noted.
- When the total water is percolated, time is noted again.
Observations :
Amount of water = 200 mL Initial time = 11:30 am Final time = 11:50 am Calculation :
Time required = Final time-initial time = 20 min
Percolation rate = 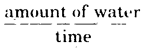
Conclusion: Rate of percolation of the sample of soil is 10 ml/min.
(3)
Aim: To study the water-retaining capacity of different soils.
Requirements: Strainers, beakers and samples to soils.
Procedure :
- Put the samples of sandy, loamy and clayey soils on the strainers in such a way that a layer is formed.
- Put the strainers on the mouth of the beakers.
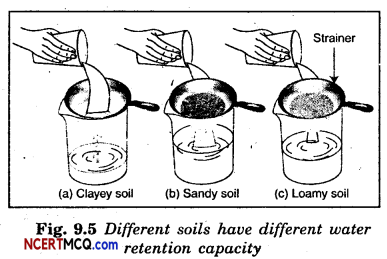
- Pour equal amount of water in each strainer. After some time observing the water collected in the beakers.
Observations: The beaker with sandy soil collected the most amount of water. Beaker with clayey soil collected the least amount of water and the beaker with loamy soil collected less amount of water than sandy but more than that of clayey soil.
Conclusion: Different soils have different water retaining capacities. Sandy soil has the least while clayey soil has the maximum water-retaining capacity.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Soil contains :
(i) only plants
(ii) only animals
(iii) only plants and animals
(iv) many other substances along with plant and animals.
Answer:
(iv) many other substances along with plant and animals.
2. Polythene bags and plastics found in the soil are :
(i) useful products
(ii) pollutants
(iii) required for growth of the plants in soil
(iv) required for growth of the animals in soil.
Answer:
(ii) pollutants.
3. When soil is crushed and dissolved in water and made to settle down, layers of particles of different sizes in the glass tumbler is seen. The profile thus obtained is layered according to :
(i) density
(ii) requirement
(iii) soil texture
(iv) soil formation.
Answer:
(i) density.
4. The process of forming soil by the breaking down of rocks by the action of wind, water and climate is known as :
(i) weathering
(ii) climating
(iii) soil profiling
(iv) humification.
Answer:
(i) weathering.
![]()
5. A vertical cross-section through different layers of the soil is called the :
(i) horizons
(ii) soil profile
(iii) topsoil
(iv) vertical soil alignment.
Answer:
(ii) soil profile.
6. Which type of soil would be best for making pots, toys and statues?
(i) Loamy
(ii) Clayey
(iii) Sandy
(iv) None of these.
Answer:
(ii) Clayey.
7. Which is the best topsoil for growing plants?
(i) Loamy
(ii) Clayey
(iii) Sandy
(iv) None of these.
Answer:
(i) Loamy.
8. Which of the following statement is true?
(i) Percolation rate of different soils is different.
(ii) Percolation rate of different soils is same.
(iii) Percolation rate of different soils is universally fixed and is independent of soil and amount of water.
(iv) None of these.
Answer:
(i) Percolation rate of different soils is different.
9. Which of the following soil types has the highest percolation rate?
(i) Sandy
(ii) Loamy
(iii) Clayey
(iv) Sub-loamy.
Answer:
(i) Sandy.
10. On hot summer day, the air above the land seems to shimmer because :
(i) of refraction due to forming of layering in air.
(ii) the vapour coming out of the soil reflects the sunlight.
(iii) the vapour coming out of the soil, refracts the sunlight.
(iv) none of these.
Answer:
(ii) the vapour coming out of the soil reflects the sunlight.
![]()
11. Which of the following- soil types has the highest moisture content?
(i) Sandy
(ii) Loamy
(iii) Clayey
(iv) Silt.
Answer:
(iii) Clayey.
12. Which of the following soil types has the lowest moisture content?
(i) Sandy
(ii) Loamy
(iii) Clayey
(iv) Silt.
Answer:
(i) Sandy.
13. Which soil would have the lowest percolation rate?
(i) Sandy
(ii) Clayey
(iii) Loamy
(iv) Silt.
Answer:
(ii) Clayey.
14. Which type of soil will allow water to reach a well faster and in greater amount?
(i) Sandy
(ii) Clayey
(iii) Loamy
(iv) Silt
Answer:
(i) Sandy.
Keywords:
→ Clayey soil: If the proportion of fine particles in soil is relatively higher, then the soil is called clayey soil.
→ Humus: The rotting dead organic matter in the soil is called humus.
→ Loamy: If the soil is a mixture of sand, clay and another type of soil particle such as silt, it is called loamy soil.
![]()
→ Percolation: Seeping down of water through soil.
→ Moisture: Water vapour content in air.
→ Sandy soil: When the soil contains greater proportion of big particles, i.e., sand. It is called
sandy soil.
→ Water retention: Capacity of soil to absorb water.
