Check the below Online Education NCERT MCQ Questions for Transportation in Animals and Plants Class 7 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 11 Pdf free download. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-7-science/
Online Education Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Extra Questions and Answers Transportation in Animals and Plants
Transportation In Plants And Animals Class 7 Extra Questions And Answers Question 1.
Name the transport medium in human beings.
Answer:
Blood.
Ncert Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Extra Questions Question 2.
What is pulse rate?
Answer:
The number of beats per minute is called the pulse rate.
Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Extra Questions Question 3.
What is the pulse rate of a resting person?
Answer:
A resting person, usually has a pulse rate between 72 and 80 beats per minute.
Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Extra Question Answer Question 4.
Where is heart located?
Answer:
The heart is located in the chest cavity with its lower tip slightly tilted towards the left.
Transportation In Animals And Plants Class 7 Extra Questions Question 5.
What are the two upper chamber of hearts called?
Answer:
Atria.
![]()
Transportation In Plants And Animals Class 7 Questions And Answers Question 6.
What are ventricles?
Answer:
The two lower chambers of heart are called ventricles.
Transportation In Plants And Animals Class 7 Questions And Answers Pdf Question 7.
What are the functions of arteries and veins?
Answer:
Arteries and veins are two types of blood vessels. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to all parts of the body. On the other hand, veins carry carbon dioxide-rich blood from all parts of the body back to the heart.
Transportation In Plants And Animals Class 7 Short Questions And Answers Question 8.
Why do arteries have thick elastic walls?
Answer:
Since the blood flow is rapid and at a high pressure, the arteries have thick elastic walls.
Transportation In Animals And Plants Extra Questions Question 9.
Pulmonary artery carries carbon dioxide-rich blood, yet is not called a vein. Why?
Answer:
Pulmonary artery carries blood from the heart to the lungs, so it is called an artery and not a vein.
Class 7 Science Ch 11 Extra Questions Question 10.
Write two functions of sweat.
Answer:
- Removal of waste products (excess salts).
- Cooling of body.
Ncert Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Extra Questions Question 11.
Write about circulation in sponges and hydra.
Answer:
Animals such as sponges and Hydra do not possess any circulatory system. The water in which they live brings food and oxygen as it enters their bodies. The water carries away waste materials and carbon dioxide as it moves out. Thus, these animals do not need a circulatory fluid like the blood.
![]()
Chapter 11 Science Class 7 Extra Questions Question 12.
What is the role of haemoglobin?
Answer:
Haemoglobin binds with oxygen and transports it to all the parts of the body and ultimately to the cells. It will be difficult to provide oxygen efficiently to all the cells of the body without haemoglobin. So, it is vital for life.
Class 7 Transportation In Plants And Animals Extra Questions Question 13.
Draw a schematic diagram of blood circulation.
Answer:
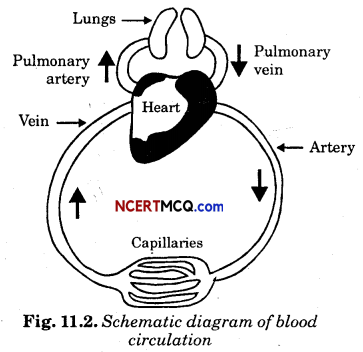
Extra Questions For Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Question 14.
Write about excretion in aquatic and land animals.
Answer:
The way in which waste chemicals are removed from the body of the animal depends on the availability of water. Aquatic animals like fishes, excrete cell waste in gaseous form (ammonia) which directly dissolves in water. Some land animals like birds, lizards, snakes excrete a semi-solid, white coloured compound (uric acid). The major excretory product in humans is urea.
Extra Questions On Transportation In Plants And Animals Question 15.
Describe the excretion in humans.
Answer:
Kidney is the most important organ of excretion in humans. The mechanism to filter the blood is done by the blood capillaries in the kidneys. When the blood reaches the two kidneys, it contains both useful and harmful substances. The useful substances are absorbed back into the blood. The wastes dissolved in water are removed as urine.
From the kidneys, the urine goes into the urinary bladder through tube-like ureters. It is stored in the bladder and is passed out through the urinary opening at the end of a muscular tube called urethra. The kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra form the excretory system.
![]()
Question 16.
How is water absorbed in plants?
Answer:
Plants absorb water and minerals by the roots. The root have root hairs. The root hairs increase the surface area of the root for the absorption of water and mineral nutrients dissolved in water. The root hairs are in contact with the water present between the soil particles.
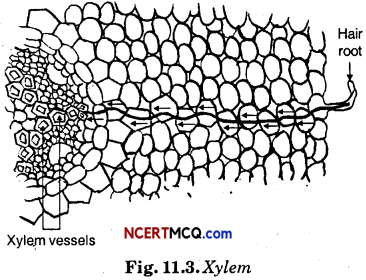
Question 17.
How is water transported in plants?
Answer:
Plants have pipe-like vessels to transport water and nutrients from the soil. The vessels are made of special cells, forming the vascular tissue. The vascular tissue for the transport of water and nutrients in the plant is called the xylem.
The xylem forms a continuous network of channels that connects roots to the leaves through the stem and branches and thus transports water to the entire plant. The process of osmosis and transpiration to helps in movement of water in plants.
Question 18.
What is blood? What is its function?
Answer:
Blood is a fluid which flows in blood vessels.
Functions :
- It transport substances like digested food from the small intestine to the other parts of the body.
- It carries oxygen from the lungs to the cells of the body and vice-versa in case for CO2.
- It also transports waste for removal from the body.
Question 19.
Why is transport of materials necessary in a plant or in an animal? Explain.
Answer:
Transport system is necessary in plants and in animals. In plants, water and minerals are transported from roots to leaves so that they may prepare food. The prepared food is transported from leaves to all parts of the plant. If there were no transport system in plants, the leaves would not be able to prepare food and all the parts of plants would not be able to survive without food and hence plants would die.
In case of animals, oxygen and food is transported to all parts of the body due to which oxidation of food takes place there and energy is released. Also, the waste products produced in the process of respiration are transported to their respective organs so that they may be excreted. In the absence of transport system, animals including humans would not be able to get energy and get rid of waste. So. their survival would not be possible. Thus, it is clear that transport system is necessary in plants and in animals.
Question 20.
When a person suffers from chest pain, the doctor immediately takes an ECG. Visit a doctor and get information about ECG. You may even lookup an encyclopaedia or the internet.
Answer:
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG abbreviated from the German Elektrokardio gram) is a graphic produced by an electrocardiograph, which records the electrical activity of the heart over time. Analysis of the various waves and normal vectors of depolarization and repolarization yields important diagnostic information. It guides therapy and risk stratification fo heart patients.
It helps detect electrolyte disturbances. It allows for the detection of conduction abnormalities.
It is used as a screening tool for ischemic heart disease during a cardiac stress test. It is occasionally helpful with non-cardiac In 1856 Koflicker and Mueller discovered the electrical activity of the heart when a frog sciatic nerve/gastrocnemius preparation fell onto an isolated frog heart and both muscles contracted synchronously.
Alexander Muirhead attached wires to a feverish patient’s wrist to obtain a record of the patient’s heart at while studying for his DSc (in electricity in 1872 at St Bartholomew’s Hospital This activity as directly recorded and visualized uiri Lippniann capillary electrometer by the British physiologist John Burdon Sanderson. The first to systematically approach the heart from an electrical point-of-view was Augustus Wailer, working in St Mary’s Hospital in Paddington, London. His electrocardiograph machine consisted of a Lippmann capillary electrometer fixed to a projector. The trace from the heartbeat was projected onto a photographic plate which was itself fixed to a toy train.
This allowed a heartbeat to be recorded in real-time. In 1911 he still saw little clinical application for his work. The breakthrough came when Willem Einthoven, working in Leiden, The Netherlands, used the string galvanometer invented by him in 1901, which was much more sensitive than the capillary electrometer that Wailer used.
Einthoven assigned the letters P, Q R, S and T to the various deflections, and described the electrocardiographic features of a number of cardiovascular disorders. In 1924, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine for his discovery.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Pulse felt on the inner side of your left wrist is due to blood flowing in the
(i) veins
(ii) arteries
(iii) capillaries
(iv) lymph vessel.
Answer:
(ii) arteries.
2. A resting person, usually has a pulse rate between :
(i) 72 – 80 beats per minute
(ii) 80 – 90 beats per minute
(iii) 90 – 100 beats per minute
(iv) 60 – 70 beats per minute.
Answer:
(i) 72 – 80 beats per minute.
3. Which of the following contains the haemoglobin?
(i) RBC
(ii) WBC
(iii) Platelets
(iv) Plasma.
Answer:
(i) RBC.
4. Clot is formed due to :
(i) RBC
(ii) WBC
(iii) Platelets
(iv) Plasma.
Answer:
(iii) Platelets.
5. The blood cells providing immunity to us are :
(i) RBC
(ii) WBC
(iii) Platelets
(iv) none of these.
Answer:
(ii) WBC.
![]()
6. Which of the following statements is correct?
(i) Sponges and hydra do not possess any circulatory system.
(ii) Sponges and hydra possess a circulatory system.
(iii) Sponges and hydra have blood but no circulatory system.
(iv) None of these.
Answer:
(i) Sponges and hydra do not possess any circulatory system.
7. The excreta of bird, fishes and human respectively are :
(i) uric acid, urea, ammonia
(ii) uric acid, ammonia, urea
(iii) ammonia, uric acid, urea
(iv) urea, uric acid, ammonia.
Answer:
(ii) uric acid, ammonia, urea.
8. The arrangement described is known as potato osmometer. What happens to the level of sugar solution :
(i) Decreases
(ii) Increases
(iii) Remains consistant
(iv) None of these.
Answer:
(ii) Increases.
Keywords:
→ Ammonia: A compound of nitrogen and hydrogen (NH<sub>3</sub.).
→ Artery: The blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to all parts of the body is called artery.
→ Blood: Blood is the vital fluid which flows in blood vessels.
→ Blood vessels: Vessels that carry blood in our body.
→ Capillary: These are thin tubes (blood vessels) which connect tissues with arteries.
→ Circulatory system: The organs involved in transportation of substances in our body constitute the circulatory system.
→ Dialysis: The process of filtering blood through an artificial kidney is called dialysis. This is helpful for the person, whose kidneys have stopped working due to infection or injury.
![]()
→ Excretion: The process of removal of wastes produced in the cells of the living organisms is called excretion.
→ Excretory system: The body parts involved in the excretion form the excretory system.
→ Haemoglobin: A red pigment found in blood. It helps in the transportation of oxygen.
→ Heartbeat: The walls of the chambers of the heart are made up of muscles. These muscles contract and relax rhythmically. The rhythmic contraction followed by relaxation of heart constitutes a heartbeat.
→ Kidney: The organ for filtering blood.
→ Xylem: The vascular tissue for the transport of water and nutrients in the plant is called the xylem.
→ Phloem: The vascular tissue involved in the movement of synthesized food from leaves to other parts of plant is known as phloem.
→ Plasma: The fluid part of the blood is called plasma.
→ Platelets: It is type of blood cells that is responsible for blood coagulation.
→ Pulse: The throbbing movement in blood vessels is called pulse.
→ Red blood cell: A type of cells in blood that contains haemoglobin.
![]()
→ Root hair: The hair-like projection from the root is called root hair. It increases the surface area of the root for the absorption of water and minerals dissolved in water.
→ Stethoscope: It is an instrument used to feel the heartbeat.
→ Sweat: A mixture of water and salt that is excreted by the skin.
→ Tissue: A group of cells that perform similar work.
→ Urea: A waste product produced in the body of most terrestrial animals.
→ Ureter: Carrier vessel of urine to urinary bladder.
→ Uric acid: Birds, insects and lizards excrete uric acid in semi-solid form.
→ Urinary bladder: The bladder meant for temporary storage of urine.
→ Veins: Veins are the vessels which carry carbon dioxide-rich blood from all parts of the body back to the heart.
→ White blood cell: A type of cells in blood which fight against germs that enter our body.
