In this page, we are providing The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 5 pdf download. NCERT Extra Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life with Answers will help to score more marks in your CBSE Board Exams. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-9-science/
Class 9 Science Chapter 5 Extra Questions and Answers The Fundamental Unit of Life
Extra Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life with Answers Solutions
The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
The Fundamental Unit Of Life Class 9 Extra Questions And Answers Question 1.
What process is involved in the movement of O2 in and out of the cell?
Answer:
Diffusion.
Fundamental Unit Of Life Class 9 Extra Questions Question 2.
Which process is involved in the movement of water from outside into the cell?
Answer:
Osmosis.
Extra Questions For Class 9 Science Chapter 5 With Answers Question 3.
Mention the process by which CO2 and water move in and out of the cell.
Answer:
Movement of CO2 occurs by diffusion whereas that of water occurs by osmosis.
Class 9 Science Chapter 5 Extra Questions And Answers Question 4.
Who discovered cells in living organisms? Give an example of a unicellular organism.
Answer:
A.V. Leeuwenhoek observed the.cells in living organisms. Example of a unicellular organism is Amoeba, Paramoecium, etc.
Class 9 Fundamental Unit Of Life Extra Questions Question 5.
Give two examples of prokaryotic organisms.
Answer:
All the bacteria and cyanobacteria are prokaryotic. Example: Nostoc, Oscillatoria, etc.
Fundamental Unit Of Life Extra Questions Question 6.
Name the plastid which stores starch, oils and protein granules.
Answer:
Leucoplast
The Fundamental Unit Of Life Extra Questions Question 7.
List the constituents of plasma membrane.
Answer:
The plasma membrane is composed of lipids and proteins.
Class 9 Science Ch 5 Extra Questions Question 8.
Where do lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesised?
Answer:
The lipids are synthesised in smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) and the proteins are synthesised in the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER).
Chapter 5 Science Class 9 Extra Questions Question 9.
Name two unicellular organisms.
Answer:
Amoeba and Paramoecium are unicellular organisms.
Ch 5 Science Class 9 Extra Questions Question 10.
Name the process by which unicellular freshwater organisms and most plant cells tend to . gain water.
Answer:
Endosmosis.
The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Extra Questions Short Answer Type 1
The Fundamental Unit Of Life Class 9 Extra Questions And Answers Ncert Question 1.
Why is plasma membrane called selectively permeable membrane?
Answer:
Plasma membrane is called selectively permeable because it prevents the entry of some substances and allows the entry and exit of only some substances.
Class 9 Chapter 5 Science Extra Questions Question 2.
Define osmosis.
Answer:
The spontaneous movement of water molecules from a region of its high concentration to the region of its low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis.
Ncert Class 9 Science Chapter 5 Extra Questions Pdf Question 3.
What is membrane biogenesis?
Answer:
Some proteins and lipids made by smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) help in building the cell membrane of the cell and this process of making of plasma membrane is known as membrane biogenesis.
Ncert Class 9 Science Chapter 5 Extra Questions Question 4.
Why are mitochondria are referred to as strange organelles?
Answer:
Mitochondria are referred to as strange organelles as they have their own DNA and ribosomes so and can make some of their own proteins.
Class 9 Ch 5 Science Extra Questions Question 5.
What is the function of Golgi body?
Answer:
The functions of Golgi body are: storage, modification and packaging of products in vesicles and the formation of lysosomes.
Class 9 Science Chapter 5 Extra Questions Question 6.
(i) In what form do mitochondria release energy? Write its full form.
(ii) The inner membrane of mitochondria is deeply folded. What is the advantage of these folds?
Answer:
(i) The energy is released by mitochondria in form of ATP. Full form of ATP is adenosine triphosphate.
(ii) The folds present on the inner membrane of mitochondria help to provide a large surface area for the ATP generation reactions.
Class 9 The Fundamental Unit Of Life Extra Questions Question 7.
Give three differences between plasma membrane and the cell wall.
Answer:
Plasma Membrane:
- It is the outermost covering of the cell which separates the contents of the cell from its external environment.
- It is mainly composed of lipids and proteins.
- It is living, thin and elastic.
Cell Wall:
- It is a rigid outer covering which lies outside the plasma membrane.
- It is made of cellulose which provides structural strength to plants.
- It is non-living and rigid.
Extra Questions Of Fundamental Unit Of Life Question 8.
Differentiate between nucleus and nucleoid.
Answer:
Nucleus:
- It has a well defined nuclear membrane around it.
- It has chromatin network and contains more than one chromosome.
Nucleoid:
- It lacks a nuclear membrane.
- It has a single chromosome only.
Extra Questions For Class 9 Science Chapter 5 Question 9.
Write two statements to show that lysosomes are called as suicidal bags of the cell.
Answer:
Lysosomes are called as the suicidal bags of the cell as:
- They contain hydrolytic enzymes which can breakdown the organic material.
- If the cell gets damaged during disturbance in cellular metabolism, the lysosomes may burst and its enzymes digest their own cell.
Question 10.
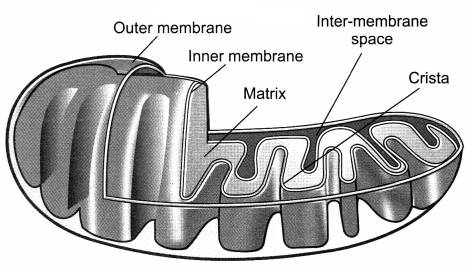
Describe the structure of mitochondria with special reference to its membrane covering.
Answer:
Mitochondrion is a double-membrane structure whose outer membrane is very porous while the inner membrane is deeply folded to form cristae. Cristae are folds which create a large surface area for ATP- generating chemical reactions.
The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Extra Questions Short Answer Type 2
Question 1.
Describe an activity to demonstrate endosmosis and exosmosis. Draw a diagram also.
Answer:
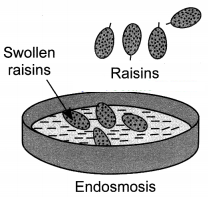
Put dried raisins or apricots in plain water and leave them for some time. Then place them into a concentrated solution of sugar or salt. You will observe the following:
(a) Each of the raisins or apricots gains water and swells when placed in water.
Reason: The raisins or apricots swell up as water moves inside them from outside because the water concentration is less inside the cell as compared to the solution outside. Hence, water moves inside the cell by endosmosis.
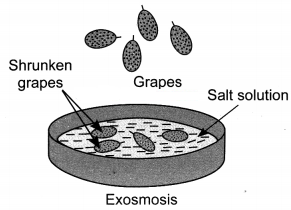
(b) However, when placed in the concentrated solution they lose water, and consequently shrink.
Reason: The raisins or apricots shrink as water moves outside from them because the water concentration is more inside the cell as compared to the solution outside. Hence, water moves out of the cell by exosmosis.
Question 2.
Differentiate between diffusion and osmosis. Write any two examples where a living organism uses osmosis to absorb water.
Answer:
Diffusion – The movement of a substance from a region of its high concentration to the region of its low concentration is called diffusion.
Osmosis – The spontaneous movement of water molecules from a region of its high concentration to the region of its low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis.
Examples where a living organism uses osmosis to absorb water are:
- Roots of plants absorb water by osmosis.
- Unicellular organisms like Amoeba absorb water by osmosis.
Question 3.
Differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell.
Answer:
Prokaryotic cell:
- Organisms whose cells lack a well defined nuclear membrane.
- They lack membrane bound cell organelles.
- Size is generally small (1-10 pm).
- Have a single chromosome.
Eukaryotic cell:
- Organisms with cells having a well defined nuclear membrane.
- They have membrane bound cell organelles.
- Size is generally large (5-100 pm).
- Have more than one chromosome.
Question 4.
Which organisms are called as the (i) powerhouse of the cell (ii) suicide bags of the cell (iii) kitchen of the cell?
Answer:
- Mitochondria
- Lysosomes
- Chloroplasts
Question 5.
(a) What would happen to the life of the cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?
(b) Which cell organelle detoxifies poisons and drugs in the liver of vertebrates?
Answer:
(a) If there was no golgi apparatus, then the following processes carried out by it would get affected:
- The storage, modification and packaging of products in vesicles.
- The packaging and dispatch of the material synthesised near the ER to various targets inside and outside the cell.
- The formation of lysosomes.
- The formation of cell plate during cell division.
So, in the absence of the Golgi apparatus, most of the functions of the cell would get disrupted.
(b) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum helps to detoxify poisons and drugs in the liver of vertebrates.
Question 6.
What are the functions of the Golgi apparatus?
Answer:
The Golgi apparatus is an important cell organelle as it performs several functions in the cell.
- Its functions include the storage, modification and packaging of products in vesicles.
- Golgi apparatus packages and dispatches the material synthesised near the ER to various targets inside and outside the cell.
- It is also involved in the formation of lysosomes.
Question 7.
What types of enzymes are present in the lysosomes? What is their function? Which cell organelle manufactures these enzymes?
Answer:
Lysosomes are membrane-bound sacs filled with hydrolytic and digestive enzymes. They help to keep the cell clean by digesting any foreign material as well as worn-out cell organelles. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) manufactures these enzymes.
Question 8.
What are chromoplasts and leucoplasts? Give an example of chromoplast which has green pigment.
Answer:
The coloured plastids which have pigments of different colours are called chromoplasts. The colourless plastids which help to store starch, oils or protein granules are called leucoplasts. The green coloured plastid is called chloroplast and it contains a green coloured pigment called chlorophyll.
Question 9.
Write the functions of:
(i) Inner membrane of mitochondria
(ii) Nucleus of the cell
(iii) Ribosomes present in active cells.
Answer:
The functions are:
(i) Inner membrane of mitochondria are the site for the formation of ATP.
(ii) Nucleus of the cell are the control centre of the cell as it controls all the activities of the cell, plays a central role in cellular reproduction and contains DNA which helps to transfer the genetic information from parents to their offsprings.
(iii) Ribosomes present in active cells are the sites for protein synthesis.
Question 10.
What are the different types of endoplasmic reticulum? Write the functions of each.
Answer:
There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum – Rough endoplasmic reticulum and smooth endoplasmic reticulum. The functions of these are:
Rough endoplasmic reticulum – It looks rough as it has particles called ribosomes attached to its surface. Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum:
- It helps in the manufacture of fat molecules, or lipids, important for cell function.
- Some proteins and lipids made by SER help in building the cell membrane and this process is known as membrane biogenesis.
- Helps in detoxifying many poisons and drugs in the liver cells of the group of vertebrates.
Question 11.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of a typical prokaryotic cell.
Answer:
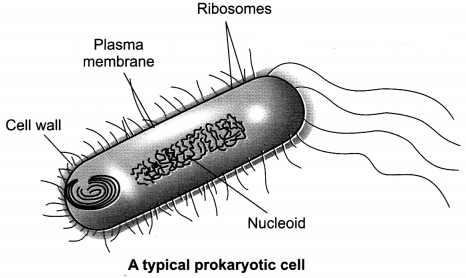
Question 12.
Why do plant cells possess large sized vacuole?
Answer:
Plant cells possess large sized vacuoles as the vacuoles help to store many important substances. They contain cell sap that gives turgidity and rigidity to the plant cell.
Question 13.
Describe the structural features of cell membrane and cell wall. Why is cell membrane called selectively permeable membrane?
Answer:
Cell wall:
- It is a rigid outer covering which lies outside the plasma membrane.
- It is made of cellulose which provides structural strength to plants.
- The shrinkage or contraction of the contents of the cell away from the cell wall when a living plant cell loses water through osmosis is known as plasmolysis.
Cell membrane:
- It is the outermost covering of the cell.
- It separates the contents of the cell from its external environment.
- It is mainly composed of lipids and proteins.
The cell membrane is called selectively permeable as it permits the entry and exit of only some materials in and out of the cell. It prevents the movement of the contents of the cell out of the cell.
Question 14.
Explain in detail what do you know about the structure of the nucleus.
Answer:
The nucleus was discovered by Robert Brown in 1831. The structure and the features of nucleus are:
- It is a dark coloured, spherical or oval, dot-like structure near the centre of each cell.
- It is the control centre of the cell as it controls all the activities of the cell.
- It has a double layered covering called nuclear membrane.
- The nuclear membrane has pores which allow the transfer of materials from inside the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
- The nucleus plays a central role in cellular reproduction (process by which a single cell divides and forms two new cells).
- Nucleus along with the environment directs the chemical activities of the cell to determine the way the cell will develop and the form it will exhibit at maturity.
- Nuclear region of the cell may be poorly defined due to the absence of a nuclear membrane in some organisms like bacteria. Such an undefined nuclear region containing only nucleic acids is called a nucleoid.
Question 15.
Differentiate between rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum. How is endoplasmic reticulum important for membrane biogenesis?
Answer:
The differences between smooth endoplasmic reticulum and the rough endoplasmic reticulum are:
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER):
- SER looks smooth as it does not have ribosomal particles on the surface.
- SER helps in the manufacture of lipids and fat molecules and also in detoxifying many poisons and drugs in the liver cells of the group of vertebrates.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER):
- RER appears rough as it has particles of ribosomes on the surface.
- Ribosomes present on RER are the sites of protein synthesis.
Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis in all active cells. Endoplasmic reticulum helps in transporting these proteins to various places. Some proteins and lipids made by SER help in building the cell membrane, this process is known as membrane biogenesis.
Question 16.
Describe the phenomenon of membrane biogenesis. Give one function of ER.
Answer:
Some proteins and lipids made by SER help in building the cell membrane and this process is known as membrane biogenesis.
ER serves as channels for the transport of materials (especially proteins) between various regions of the cytoplasm or between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. It also functions as a cytoplasmic framework providing a surface for some of the biochemical activities of the cell.
Question 17.
(i) Why are lysosomes known as ‘scavengers of the cell’?
(ii) Lysosomes are self-destructive. (True/False). Give reason.
Answer:
(i) The lysosomes are waste disposal system of the cell as they remove the debris and help to keep the cell clean by digesting any foreign material as well as worn-out cell organelles. Thus, they are known as the ‘scavengers of the cell’.
(ii) It is true that the lysosomes are self-destructive. They contain digestive enzymes. If the cell gets damaged during disturbance in cellular metabolism, the lysosomes may burst and its enzymes digest their own cell.
Question 18.
Name the organelle of the cell, which has membrane bound sac filled with powerful digestive enzymes. Write any four common functions it performs inside the cell.
Answer:
Lysosome is a membrane bound sac filled with powerful digestive enzymes.
The functions of lysosomes are:
- They are waste disposal system of the cell as they help to keep the cell clean by digesting any foreign material as well as worn-out cell organelles.
- They have digestive enzymes which are capable of breaking down all organic materials.
- If any disturbance occurs in the cellular metabolism or the cell gets damaged, the lysosomes burst open and its digestive enzymes digest all the contents of the cell. So, they are also called as the ‘suicide bags’ of the cell.
- During starvation they digest the food contents of the cell and provide energy to the cell.
Question 19.
State reasons for the following:
(i) Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell.
(ii) Plastids are able to make their own protein.
(iii) Plant cell shrinks when kept in hypertonic solution.
Answer:
(i) Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell as they are the site of storage of ATP which helps to provide energy for all the activities of the cell.
(ii) Plastids are able to make their own protein as they have their own DNA and ribosomes.
(iii) Hypertonic solution has a lower concentration of water than the cell. Due to this, the water moves out of the plant cell by exosmosis and results in shrinkage of the plant cell.
Question 20.
List the specific functions of the following:
(i) Endoplasmic reticulum
(ii) Golgi apparatus
(iii) Lysosomes
(iv) Plastids
(v) Mitochondria
(vi) Vacuoles.
Answer:
The specific functions are:
(i) Endoplasmic reticulum: Site of protein synthesis.
(ii) Golgi apparatus: Storage, modification and packaging of products in vesicles.
(iii) Lysosomes: Waste disposal system of the cell as they help to keep the cell clean by digesting any foreign material as well as worn-out cell organelles.
(iv) Plastids: Green coloured plastids are the site of photosynthesis.
(v) Mitochondria: They are called the powerhouse of the cell as they store energy required for the activities of the cell in the form of ATP.
(vi) Vacuoles: Provide turgidity and rigidity to the cell in plant cells. They also help in digestion of food and expulsion of excess water and waste from the cell in unicellular organisms like Amoeba.
Question 21.
Which types of plastids stores starch, oil and proteins?
Answer:
The leucoplasts help to store starch, oil and proteins in the amyloplasts, elaioplasts and aleuroplasts respectively.
Question 22.
How many membranes are present in mitochondria? Give the characteristic features of these membranes. What is the advantage of such features?
Answer:
Mitochondrion is a double-membrane structure whose outer membrane is very porous while the inner membrane is deeply folded to form cristae. The porous membrane helps in getting oxygen and food. Cristae present on the inner membrane are the folds which create a large surface area for ATP- generating chemical reactions.
Question 23.
Why are lysosomes known as ‘suicide-bags’ of a cell?
Answer:
Lysosomes are also known as the ‘suicide bags’ of a cell because if the cell gets damaged during disturbance in cellular metabolism, the lysosomes may burst and its enzymes digest their own cell.
Question 24.
Do you agree that “A cell is a building unit of an organism”. If yes, explain why?
Answer:
Yes, a cell is the building unit or the fundamental unit of an organism as the cells get organised to form tissues which in turn get organised into organs and further into organ system which organise to form an organism. It can be represented as:
Cell → tissue → organ → organ system organism
Question 25.
Why does the skin of your finger shrink when you wash clothes for a long time?
Answer:
The skin of our finger shrinks when we wash clothes for a long time because soap solution is a hypertonic solution i.e., very concentrated solution, so water moves out of our finger cells by the process of osmosis (called as exosmosis).
Question 26.
Why is endocytosis found in animals only?
Answer:
The plant cells have a rigid structure due to the presence of cell wall around their cell membrane whereas in the animals the cell membrane does not have a cell wall. So, endocytosis can occur only in the animal cells.
Question 27
A person takes concentrated solution of salt, after sometime, he starts vomiting. What is the phenomenon responsible for such situation? Explain.
Answer:
A concentrated solution of salt is hypertonic solution and causes dehydration. Water moves out of the cells and exosmosis in the parts of stomach and intestine make the person feel uncomfortable. Excessive dehydration results in anti-peristalsis due to which person starts vomiting.
Question 28.
Name any cell organelle which is non membranous.
Answer:
Ribosomes are non membranous organelles.
Question 29.
We eat food composed of all the nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals and water. After digestion, these are absorbed in the form of glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, glycerol, etc. What mechanisms are involved in absorption of digested food and water?
Answer:
Absorption of the nutrients takes place by diffusion and that of water occurs by the process of osmosis.
Question 30.
If you are provided with some vegetables to cook. You generally add salt into the vegetables during cooking process. After adding salt, vegetables release water. What mechanism is responsible for this?
Answer:
Adding salt into vegetables creates a hypertonic medium around them which results in exosmosis. Exosmosis causes release of water form vegetables.
Question 31.
If cells of onion peel and RBC are separately kept in hypotonic solution, what among the following will take place? Explain the reason for your answer.
(a) Both the cells will swell.
(b) RBC will burst easily while cells of onion peel will resist the bursting to some extent.
(c) a and b both are correct.
(d) RBC and onion peel cells will behave similarly.
Answer:
(b) RBC will burst easily while cells of onion peel will resist the bursting to some extent. This happens because the cells of onion peel have cell wall which prevents them from bursting. The RBC, being animal cells are devoid of cell wall and burst easily in hypotonic solution.
Question 32.
Bacteria do not have chloroplast but some bacteria are photo-autotrophic in nature and perform photosynthesis. Which part of bacterial cell performs this?
Answer:
The photo-autotrophic bacteria have small vesicles associated with plasma membrane which help in the process of photosynthesis.
Question 33.
Match the following A and B

Answer:
(a) (iv)
(b) (v)
(c) (iii)
(d) (i)
(e) (ii)
Question 34.
Write the name of different plant parts in which chromoplast, chloroplast and leucoplast are present. Chromoplasts are present in the flower and fruit.
Answer:
Chloroplasts are present in the leaves of the plant. Leucoplasts are present in the root of the plant.
Question 35.
Name the organelles which show the analogy written as under
(a) Transporting channels of the cell _______
(b) Powerhouse of the cell _______
(c) Packaging and dispatching unit of the cell _______
(d) Digestive bag of the cell _______
(e) Storage sacs of the cell _______
(f) Kitchen of the cell _______
(g) Control room of the cell _______
Answer:
(a) Transporting channels of the cell _______ Endoplasmic reticulum
(b) Powerhouse of the cell _______ Mitochondria
(c) Packaging and dispatching unit of the cell _______ Golgi body
(d) Digestive bag of the cell _______ Lysosome
(e) Storage sacs of the cell _______ Vacuole
(f) Kitchen of the cell _______ Chloroplast
(g) Control room of the cell _______ Nucleus
Question 36.
How is a bacterial cell different from an onion peel cell?
Answer:
Bacterial cell is a prokaryote so, they are smaller in size, their nucleus does not have a well defined nuclear membrane, possess a single chromosome and the cell is devoid of any cell organelles. Onion peel cell is an eukaryotic cell which is comparatively bigger in size, nucleus has a well defined nuclear membrane, possess more than one chromosome and have well defined cell organelles.
Question 37.
How do substances like carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) move in and out of the cell?
Answer:
The movement of carbon dioxide occurs by the process of diffusion in and out of the cell whereas the movement of water in and out of the cell occurs by the process of osmosis.
Question 38.
How does Amoeba obtain its food?
Answer:
Amoeba takes in food with the help of finger like extensions called pseudopodia by the process called endocytosis. Pseudopodia help to engulf the food which gets enclosed in a food vacuole. The complex particles of the food get broken down into simpler substances inside the food vacuole and diffuse into the cytoplasm of Amoeba. The undigested food particles are removed from the cell by exocytosis.
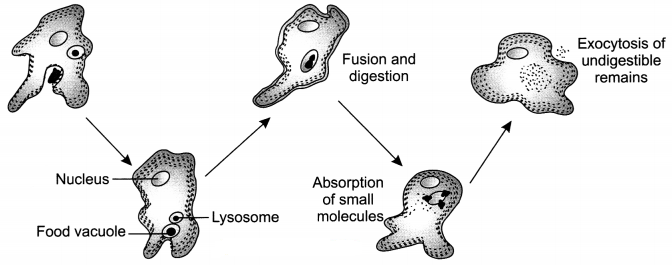
Question 39.
Name the two organelles in a plant cell that contain their own genetic material and ribosomes.
Answer:
Mitochondria and plastids (e.g. chloroplasts) contain their own genetic material and ribosomes.
Question 40.
Why are lysosomes also known as “scavengers of the cells”?
Answer:
The lysosomes are waste disposal system of the cell as they remove the debris and help to keep the cell clean by digesting any foreign material as well as worn-out cell organelles.
Question 41.
Which cell organelle controls most of the activities of the cell?
Answer:
Nucleus is the control centre of the cell and controls most of the activities of the cell.
Question 42.
Which kind of plastid is more common in
(a) roots of the plant
(b) leaves of the plant
(c) flowers and fruits
Answer:
The plastid that is more common in
(a) roots of the plant is leucoplast.
(b) leaves of the plant is chloroplast.
(c) flowers and fruits is chromoplast.
Question 43.
Why do plant cells possess large sized vacuole?
Answer:
The plant cells possess large sized vacuoles as the vacuoles help to store many important substances. They contain cell sap that gives turgidity and rigidity to the plant cell.
Question 44.
How are chromatin, chromatid and chromosomes related to each other?
Answer:
The chromatin material forms chromatids, i.e., chromatids are made up of chromatin. The chromosomes are made up of thread like structures called as chromatids.
Question 45.
What are the consequences of the following conditions?
(a) A cell containing higher water concentration than the surrounding medium
(b) A cell having low water concentration than the surrounding medium.
(c) A cell having equal water concentration to its surrounding medium.
Answer:
The consequences of the following conditions are:
(a) A cell containing higher water concentration than the surrounding medium will undergo exosmosis.
(b) A cell having low water concentration than the surrounding medium will undergo endosmosis.
(c) A cell having equal water concentration to its surrounding medium will not be affected as there won’t be any net movement of water into or outside the cell.
The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Distinguish between hypotonic solution, isotonic solution and hypertonic solution.
Answer:
The differences between the three kinds of solutions are:

Question 2.
Describe the roles played by lysosomes. Why are they termed as suicidal bags? How do they perform their function?
Answer:
Roles played by lysosomes are:
(i) They are waste disposal system of the cell as they help to keep the cell clean by digesting any foreign material as well as worn-out cell organelles.
(ii) Lysosomes have powerful digestive enzymes capable of breaking down all organic materials. Lysosomes are also known as the ‘suicide bags’ of a cell because if the cell gets damaged during disturbance in cellular metabolism, the lysosomes may burst and its enzymes digest their own cell. They perform this function as they are membrane-bound sacs filled with hydrolytic and digestive enzymes made by rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER).
Question 3.
(a) Name the organelle which provides turgidity and rigidity to the plant cell. Name any two substances which are present in it.
(b) How are they useful in unicellular organisms?
Answer:
(a) The organelle which provides turgidity and rigidity to the plant cell is the large central vacuole which is filled with cell sap. The substances present in it are amino acids, sugars, various organic acids and some proteins.
(b ) They are very useful for the unicellular organisms in the form of food vacuole and contractile vacuole which perform the following functions:
Food vacuole found in Amoeba contains the food items that the Amoeba has consumed.
Contractile vacuole found in some unicellular organisms help in expelling excess water and some wastes from the cell.
Question 4.
What will happen if:
(i) Ribosomes are removed from the cell?
(ii) Golgi apparatus is removed from the cell?
(iii) Plasma membrane ruptures?
Answer:
(i) If ribosomes are removed from the cell, protein synthesis will not take place, enzymes will not be formed and ultimately death of cell will occur.
(ii) If golgi apparatus is removed from the cell, storage, modification and the packaging of substances in vesicles will not occur and lysosomes will not be formed.
(iii) Plasma membrane is a selectively permeable membrane, so in its absence, the entry and exit of the substances will not be regulated, contents of the cell will leak out and the cell will die.
Question 5.
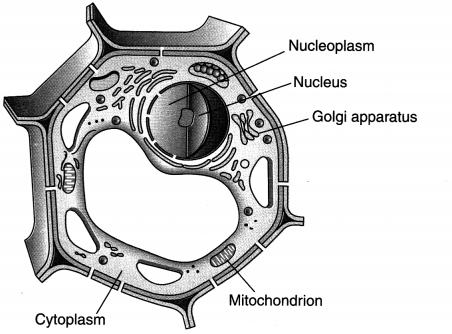
Draw a plant cell and label the parts which
(a) determines the function and development of the cell
(b) package materials coming, from the endoplasmic reticulum
(c) provides resistance to microbes to withstand hypotonic external media without bursting
(d) is site for many biochemical reactions necessary to sustain life
(e) is a fluid contained inside the nucleus
Answer:
(a) Nucleus
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) Cell wall
(d) Cytoplasm
(e) Nucleoplasm
Question 6.
Illustrate only a plant cell as seen under electron microscope. How is it different from an animal cell?
Answer:
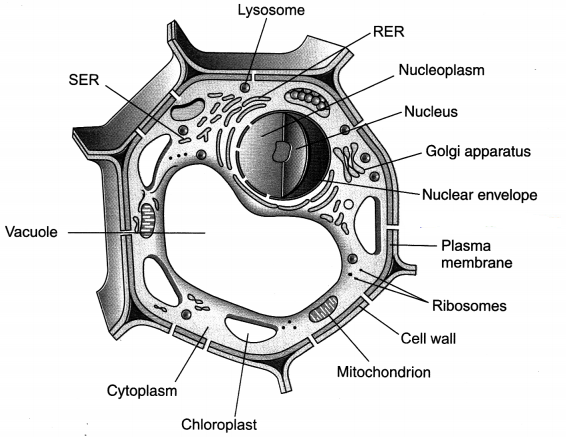
Plant Cell:
- Cell wall is present.
- Plastids are present.
- A large central vacuole is present.
- Centrioles are absent.
Animal Cell:
- Cell wall is absent.
- Plastids are absent.
- Vacuoles are either absent or very small.
- Centrioles are present.
Question 7.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of an animal cell.
Answer:
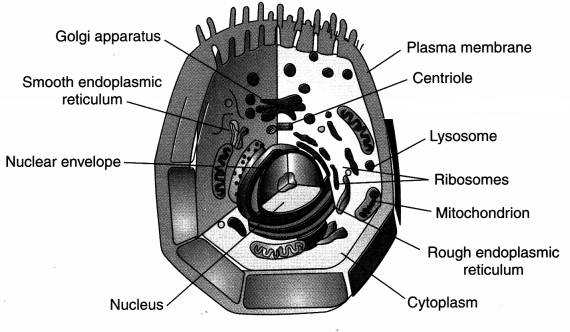
Question 8.
Draw a well labelled diagram of an eukaryotic nucleus. How is it different from a nucleoid?
Answer:
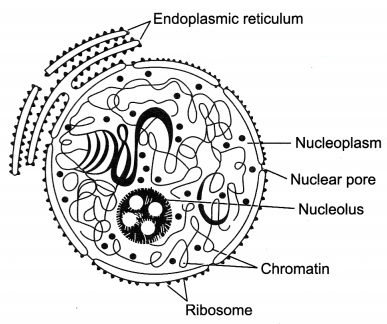
It is different from a nucleoid as it is a membrane bound organelle.
Question 9.
Differentiate between rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum. How is endoplasmic reticulum important for membrane biogenesis?
Answer:
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER):
- SER looks smooth as it does not have ribosomal particles on its surface.
- SER helps in the manufacture of lipids and fat molecules and also in detoxifying many poisons and drugs in the liver cells of the group of vertebrates.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER):
- RER appears rough as it has particles of ribosome on its surface.
- Ribosomes present on RER are the sites of protein synthesis.
Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis in all active cells. Endoplasmic reticulum helps in transporting these proteins to various places. Some proteins and lipids made by SER help in building the cell membrane, this process is known as membrane biogenesis.
Question 10.
In brief state what happens when
(a) dry apricots are left for sometime in pure water and later transferred to sugar solution?
(b) a red blood cell is kept in concentrated saline solution?
(c) the plasma-membrane of a cell breaks down?
(d) Rhoeo leaves are boiled in water first and then a drop of sugar syrup is put on it?
(e) golgi apparatus is removed from the cell?
Answer:
(a) If dry apricots are left for sometime in pure water they swell up due to endosmosis and later when they are transferred to sugar solution exosmosis occurs and they shrink.
(b) If a red blood cell is kept in concentrated saline solution it will lose water and shrink.
(c) If the plasma-membrane of a cell breaks down, the cell will die.
(d) If Rhoeo leaves are boiled in water first and then a drop of sugar syrup is put on it, no plasmolysis occurs as the cells get killed on boiling.
(e) If the golgi apparatus is removed from the cell, all sorts of vesicle formation in the cell get stopped.
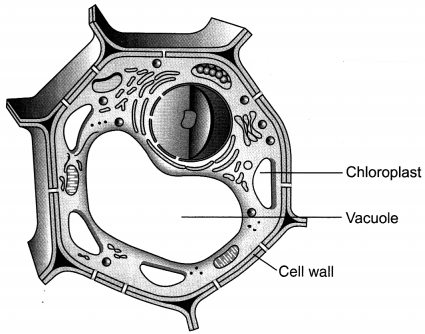
Question 11.
Draw a neat diagram of plant cell and label any three parts which differentiate it from animal cell.
Answer:
The plant cells have chloroplast, large central vacuole and the cell wall which are not present in animal cells.
The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Extra Questions HOTS
Question 1.
Unicellular organisms like Amoeba and Paramoecium survive as a single cell. How?
Answer:
In Amoeba and Paramoecium all the activities like digestion, absorption, assimilation, etc., which are necessary for life are carried out by a single cell. This enables them to survive even as a single cell.
Question 2.
Explain how cell walls permit the cells of fungi to withstand very dilute external media without bursting.
Answer:
The fungal cells swell up in very dilute external media as they take in water by the process of endosmosis. The plasma membrane of the cell exerts pressure on the cell wall and the cell wall also exerts an equal pressure on the membrane which helps to prevent the cell from bursting.
Question 3.
Give the roles of the following:
(i) Lipids and proteins of plasma membrane
(ii) Cellulose in the cell wall
(iii) Flexible nature of the cell membrane
(iv) Hydrolytic enzymes of lysosomes
(v) Ribosomes present on the RER
Answer:
The roles are:
(i) Lipids and proteins of plasma membrane: Provide flexibility to cell membrane and make it selectively permeable in nature.
(ii) Cellulose in the cell wall: Provides structural strength to the plants and prevents bursting of the cell when the cell swells in a hypotonic solution.
(iii) Flexible nature of the cell membrane: It helps organisms like Amoeba to engulf food by endocytosis.
(iv) Hydrolytic enzymes of lysosomes: Helps in the process of cell digestion and act as ‘scavengers of cell’.
(v) Ribosomes present on the RER: Are the site of protein synthesis.
Question 4.
Which cell organelle will play a major role when a cell is damaged due to disturbance in cellular metabolism? How?
Answer:
Lysosomes will play a major role when a cell is damaged due to disturbance in cellular metabolism. The lysosomes burst open and its hydrolytic digestive enzymes digest their own cell contents. Thus, lysosomes are also called as the ‘suicidal bags’.
Question 5.
What will be the effect on the cell when:
(a) The cell is placed in a medium having lower water concentration.
(b) The cell is placed in a medium having higher water concentration.
(c) The cell is placed in a medium having water concentration which is equal to that inside the cell.
Answer:
The consequences of the following conditions are:
(a) The cell having low water concentration than the surrounding medium will undergo endosmosis.
(b) The cell containing higher water concentration than the surrounding medium will undergo exosmosis.
(c) The cell having equal water concentration to its surrounding medium will not be affected as there won’t be any net movement of water into or outside the cell.
The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Extra Questions Value Based (VBQs)
Question 1.
Rajni was told by his teacher that cell is the structural and fundamental unit of life. She asked her teacher to give reasons to support her statement. She felt very happy when her teacher showed her the slide of onion peel with the help of a microscope. She was able to identify the various parts of the cells visible in the slide.
(i) Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of life?
(ii) With the help of a suitable diagram show the cells observed in onion peel and label them.
(iii) What values are shown by Rajni?
Answer:
(i) The body of all living organisms is composed of one or more cells, so cell is called the structural unit of life. Also, the various life processes like digestion, respiration, excretion, etc., are performed by the cells, so the cell is called the functional unit of life.
(ii) The cells of onion peel are shown in the diagram below.
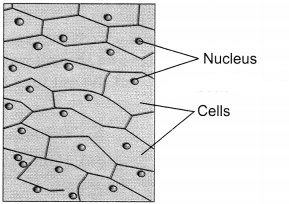
(iii) Values shown by Rajni are curiosity, scientific temper, knowledge and sincerity towards her work.
