Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Types of Cells and its Importance
On the basis of the cellular organization and the nuclear characteristics, the cell can be classified into:-
- Prokaryotes
- Mesokaryotes and
- Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes
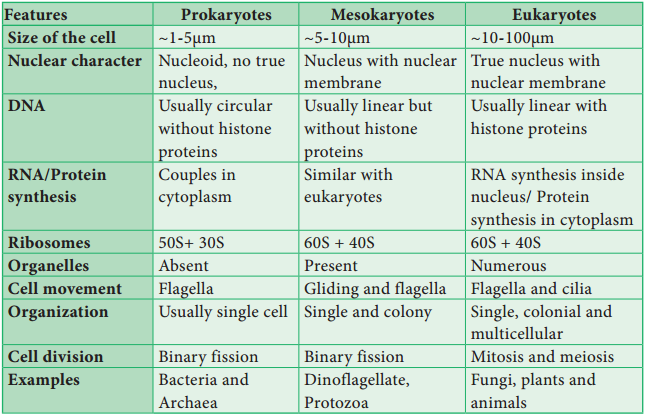
Those organisms with primitive nucleus are called as prokaryotes (pro – primitive; karyon – nucleus). The DNA lies in the ‘nucleoid’ which is not bound by the nuclear membrane and therefore it is not a true nucleus and is also a primitive type of nuclear material. The DNA is without histone proteins. Example: Bacteria, blue green algae, Mycoplasma, Rickettsiae and Spirochaetae.
Mesokaryotes
In the year 1966, scientist Dodge and his coworkers proposed another kind of organisms called mesokaryotes. These organisms which shares some of the characters of both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In other words these are organisms intermediate between pro and eukaryotes.
These contains well organized nucleus with nuclear membrane and the DNA is organized into chromosomes but without histone protein components divides through amitosis similar with prokaryotes. Certain Protozoa like Noctiluca, some phytoplanktons like Gymnodinium, Peridinium and Dinoflagellates are representatives of mesokaryotes.
Eukaryotes
Those organisms which have true nucleus are called Eukaryotes (Eu – True; karyon – nucleus). The DNA is associated with histones forming the chromosomes. Membrane bound organelles are present. Few organelles may have risen by endosymbiosis which is a cell living inside another cell. The Organelles like mitochondria and chloroplast well support this theory.
Origin of Eukaryotic cell:
Endosymbiont Theory:
Two eukaryotic organelles believed to be the descendants of the endosymbiotic prokaryotes. The ancestors of the eukaryotic cell engulfed a bacterium and the bacteria continued to function inside the host cell.
Comparison Between Types of Cellular Organisation