RS Aggarwal Class 7 Solutions Chapter 17 Constructions Ex 17C
These Solutions are part of RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7. Here we have given RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 17 Constructions Ex 17C.
Other Exercises
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 17 Constructions Ex 17A
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 17 Constructions Ex 17B
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 17 Constructions Ex 17C
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 17 Constructions CCE Test Paper
Mark (✓) against the correct answer in each of the following:
Question 1.
Solution:
(c) Supplement of 45° is 135°
135°+ 45° = 180°
Question 2.
Solution:
(b) Complement of 80° is 10°
10° + 80° = 90°
Question 3.
Solution:
(b) The angle is its own complement.
The measure of the angles will be 45° (45° + 45° = 90°)
Question 4.
Solution:
(a) The angle is one-fifth of its supplement
Let angle be x, then
x + 5x = 180°
⇒ 6x = 180°
⇒ x = 30°
Angle is 30°
Question 5.
Solution:
(b) Let angle is x
Then its complement angle=x-24° But x + x- 24° = 90°
⇒ 2x = 90° + 24° = 114°
⇒ x = 57°
The required angle is 57°
Question 6.
Solution:
(b) Let required angle = x
Then its supplement angle = x + 32
But x + x + 32° = 180°
⇒ 2x = 180° – 32 = 148°
⇒ x = 74°
Required angle = 74°
Question 7.
Solution:
(c) Two supplementary angle are in the ratio = 3 : 2
Let first angle = 3x
Second angle = 2x
But 3x + 2x = 180°
⇒ 5x = 180°
⇒ x = 36°
Smaller angle = 2x = 2 x 36° = 72°
Question 8.
Solution:
(b) In the figure ∠BOC = 132°
But ∠AOC + ∠BOC =180° (Linear pair)
⇒ ∠AOC + 132° = 180°
⇒ ∠AOC = 180° – 132° = 48°
Question 9.
Solution:
(c) In the figure, ∠AOC = 68°
But ∠AOC + ∠BOC = 180° (Linear pair)
⇒ 68° + x = 180°
⇒ x = 180° – 68° = 112°
Question 10.
Solution:
(b) In the figure,
AOB is a straight line
∠AOC + ∠BOC = 180° (Linear pair)
⇒ 2x – 10° + 3x + 15° = 180°
⇒ 5x = 180° + 10° – 15° = 175°
⇒ x = 35°
x = 35
Question 11.
Solution:
(d) In the figure,
AOB is a straight line
∠AOC + ∠COD + ∠DOB = 180°
⇒ 55° + x + 45° = 180°
⇒ x + 100° = 180°
⇒ x = 180° – 100° = 80°
Question 12.
Solution:
(a) AOB is a straight line
x + y = 180°
But 4x = 5y
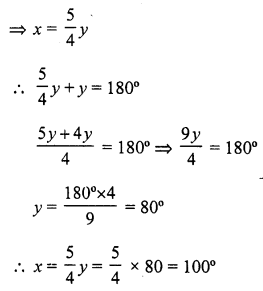
Question 13.
Solution:
(b) AB and CD intersect each other at O and ∠AOC = 50°
∠BOD = ∠AOC = 50° (Vertically opposite angles)
Question 14.
Solution:
(a) AOB is a straight line
∠AOC + ∠COD + ∠DOB = 180°
⇒ 3x – 8° + 50° + x + 10° = 180°
⇒ 4x = 180° + 8° – 50° – 10°
⇒ 4x = 128°
⇒ x = 32°
Question 15.
Solution:
(b) In ∆ABC, side BC is produced to D
∠ACD = 132° and ∠A = 54°
Ext. ∠ACD = ∠A + ∠B
⇒ 132° = 54° + ∠B
⇒ ∠B = 132° – 54° = 78°
Question 16.
Solution:
(c) In ∆ABC,
Side BC is produced to D
∠A = 45°, ∠B = 55°
Ext. ∠ACD = ∠A + ∠B = 45° + 55° = 100°
Question 17.
Solution:
(b) In ∆ABC, side BC is produced to D
∠ABC = 70° and ∠ACD = 120°
Ext. ∠ACD = ∠BAC + ∠ABC
⇒ 120° = ∠BAC + 70°
⇒ ∠BAC = 120° – 70° = 50°
Question 18.
Solution:
(c) In the figure,
∠AOB = 50°, ∠BOC = 90°
∠COD = 70°, ∠AOD = x.
But ∠AOB + ∠BOC + ∠COD + ∠DOA = 360° (Angles at a point)
⇒ 50° + 90° + 70° + x = 360°
⇒ 210 + x = 360°
⇒ x = 360° – 210°
⇒ x = 150°
Question 19.
Solution:
(c) In the figure,
Side BC of ∆ABC is produced to D
CE || BA is drawn
∠A = 50° and ∠ECD = 60°
AB || CE
∠ABC = ∠ECD (corresponding angle) = 60°
But in ∆ABC,
∠A + ∠B + ∠ACB = 180° (Angles of a triangles)
⇒ 50° + 60° + ∠ACB = 180°
⇒ ∠ACB = 180° – 50° – 60° = 70°
Question 20.
Solution:
(b) In ∆ABC,
∠A = 65°, ∠C = 85°
But ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180° (Angles of a triangle)
⇒ 65° +∠B+ 85° = 180°
⇒ 150° + ∠B = 180°
⇒ ∠B = 180° – 150° = 30°
Question 21.
Solution:
(d) Sum of angles of a triangle = 180°
Question 22.
Solution:
(c) Sum of angles of a quadrilateral = 360°
Question 23.
Solution:
(b) In the figure, AB || CD
∠OAB = 150°, ∠OCD = 120°
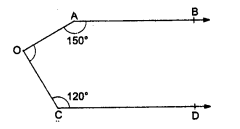
From O, draw OE || AB or CD
AB || DE
∠OAB + ∠AOE =180°
⇒ 150° + ∠AOE = 180°
⇒ ∠AOE = 180° – 150° = 30°
Similarly DE || CD
∠EOC + ∠OCD = 180°
⇒ ∠EOC + 120° = 180°
⇒ ∠EOC = 180° – 120° = 60°
Now ∠AOC = ∠AOE + ∠EOC = 30° + 60° = 90°
Question 24.
Solution:
(a) In the given figure,
PQ || RS,
∠PAB = 60° and ∠ACS = 100°
PQ || RS
∠ABC = ∠PAB (alternate angles) = 60°
But Ext. ∠ACS = ∠BAC + ∠ABC
⇒ 100° = ∠BAC + 60°
⇒ ∠BAC = 100° – 60° = 40°
Question 25.
Solution:
(c) In the figure, AB || CD || EF
∠ABG =110° and ∠GCD = 100°
∠BGC = x°
AB || EF
∠ABG + ∠BGE = 180°
⇒ 110° + ∠BGE = 180°
⇒ ∠BGE = 180° – 110° = 70°
Similarly CD || EF
∠GCD + ∠CGF = 180°
⇒ 100° + ∠CGF = 180°
⇒ ∠CGF = 180° – 100° = 80°
But ∠BGE + ∠BGC + ∠CGF = 180°
⇒ 70° + x + 80° = 180°
⇒ 150° + x = 180°
⇒ x = 180° – 150° = 30°
Question 26.
Solution:
(d) Sum of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the third side
Question 27.
Solution:
(d) The diagonals of a rhombus always bisect each other at right angles.
Question 28.
Solution:
(c) In ∆ABC, ∠B = 90°
AB = 5 cm and AC = 13 cm
But AC² = AB² + BC² (By Pythagoras Theorem)
⇒ (13)² = (5)² + BC²
⇒ 169 = 25 + BC2
⇒ BC² = 169 – 25 = 144 = (12)²
BC = 12 cm
Question 29.
Solution:
(c) In ∆ABC, ∠B = 37°, ∠G = 29°
But ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180° (angles of a triangle)
⇒ ∠A + 37° + 29° = 180°
⇒ ∠A + 66° = 180°
⇒ ∠A = 180° – 66° = 114°
Question 30.
Solution:
(c) The ratio of angles of a triangle is 2 : 3 : 7
But sum of angles of a triangle = 180°
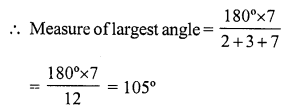
Question 31.
Solution:
In ∆ABC,
Let 2∠A = 3∠B = 6∠C = x
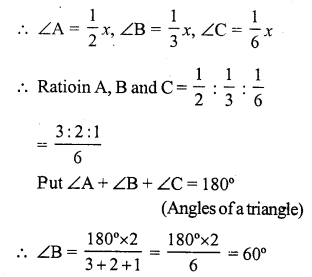
Question 32.
Solution:
(a) In ∆ABC,
∠A + ∠B = 65°, ∠B + ∠C = 140°
∠A = 65°
∠C = 140° – ∠B
But ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180° (Angles of a triangle)
⇒ 65° – ∠B + 140° – ∠B + ∠B = 180°
⇒ 205° – ∠B = 180°
⇒ ∠B = 205° – 180° = 25°
Question 33.
Solution:
(b) In ∆ABC, ∠A – ∠B = 33°
and ∠B – ∠C = 18°
∠A = 33° + ∠B and ∠C = ∠B – 18°
But ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
⇒ 33° + ∠B + ∠B + ∠B – 18° = 180°
⇒ 3∠B = 180° – 33° + 18° = 165°
⇒ ∠B = 55°
Question 34.
Solution:
(c) In ∆ABC
∠A + ∠B + ∠C= 180° (Sum of angles of a triangle)
But angles are (3x)°, (2x – 7)° and (4x – 11)°
3x + (2x – 7) + (4x – 11)° = 180°
⇒ 3x + 2x – 7 + 4x – 11° = 180°
⇒ 9x – 18° = 180°
⇒ 9x = 180° + 18° = 198°
⇒ x = 22°
Question 35.
Solution:
(c) ∆ABC is a right angled, ∠A = 90°
AB = 24 cm, AC = 7 cm
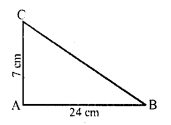
but BC² = AB² + AC²
⇒ BC² = (24)² + (7)² = 576 + 49 = 625 = (25)²
BC = 25 cm
Question 36.
Solution:
(b) Let AB is a ladder and A is the window
BC = 15 m, AC = 20 m
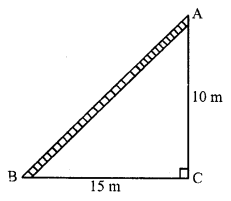
Now in right ∆ABC
AB² = BC² + AC² = (15)² + (20)² = 225 + 400 = 625 = (25)²
AB = 25 m
Length of ladder = 25 m
Question 37.
Solution:
(a) Let AB and CD are two poles such that
AB = 6 m, CD = 11 m
and distance between two poles BD = 12m
From A, draw AE || BD
AE = BD = 12m
CE = CD – ED = 11 – 6 = 5 m
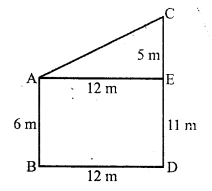
Now in right ∆AEC
AC² = AE² + CE² = (12)² + (5)² = 144 + 25 = 169 = (13)²
AC = 13 m
Distance between tops of poles = 13 m
Question 38.
Solution:
(d) ∆ABC is an isosceles triangle
∠C = 90°,
AC = 5 cm
BC = AC = 5 cm
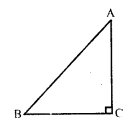
In right ∆ABC
AB² = AC² + BC² = (5)² + (5)² = 25 + 25 = 50 = 2 x 25
AB = √(2 x 25) = 5√2 cm
Hope given RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 17 Constructions Ex 17C are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.