Value Based Questions in Science for Class 10 Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
These Solutions are part of Value Based Questions in Science for Class 10. Here we have given Value Based Questions in Science for Class 10 Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Question 1.
A lady wanted to give a coating of white wash to her room. She purchased quick lime from the market and dissolved it in water and immediately applied the same on the wall. In this process, she spoiled her hands and even suffered minor burns. Her friend advised her not be in haste and keep the container overnight before applying a coating on the wall. She followed her advice and there was now no problem.
- What mistake was committed by the lady ?
- Why did she suffer from burns ?
- Why was so much heat evolved ?
- What values are exhibited by her friend in this episode ?
Answer:
- The lady should have waited for a few hours because when quick lime is dissolved in water, slaked lime is formed and this process is highly exothermic.
- The solution might have become very hot and that is why the lady suffered from burns.
- Quick lime is CaO and it reacts with water to form Ca(OH)2 which is known as slaked lime. The dissolution process is highly exothermic. That is why so much heat was evolved. By keeping container overnight, the chemical reaction subsided and now there was no problem to apply the coating of white wash on the wall. In this way, she rendered service to the lady.
- Her friend had the knowledge of chemistry.
More Resources
- Value Based Questions in Science for Class 10
- HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science
- Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science
Question 2.
Mohan was working in a factory. He purchased a new cycle but kept it in the open. After two months he found that the cycle chain and even the handles got rusted. His friend advised him to apply a coating of rust proof paint to the cycle and not to keep it in the open in future.
- Why was the cycle rusted ?
- What is the role of rust proof paint ?
- What values are associated with this gesture ?
Answer:
- Air contains both oxygen and moisture. In their presence iron slowly got rusted
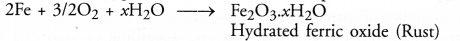
- The coating of rust proof paint checked further corrosion. Similarly, by keeping the cycle under a covered shed, rusting can be avoided.
- He played the role of a sincere friend and gave a very sincere advice to Mohan.
Question 3.
A student working in the laboratory prepared an aqueous solution of silver nitrate and kept it in a glass beaker overnight. Next morning, he found that the beaker has developed black turbidity.
- Why did the solution develop black turbidity ?
- In your opinion, what precaution he should have taken ?
Answer:
- The silver salts are sensitive to light. When kept exposed to light for a few hours silver nitrate decomposes and a black turbidity appears.
- The student should have covered the beaker from outside with the help of a brown paper to avoid direct action of sun light.
Question 4.
Sonia purchased a packet of potato chips from the shop. She opened the packet and ate some of the chips and left the packet as such in one comer of her study room. After a gap of about two weeks, she saw the packet and wanted to do so munching again. At that time, her elder sister Pallavi, a science student of class eleven was present in her room. She found that a foul smell was coming out from the packet. She immediately threw it in the dustbin and did not allow her sister to eat the chips.
- Why did potato chips develop foul smell ?
- What was the cause of the spoilage of the chips ?
- What is the nature of the chemical reaction involved in it ?
- Why do not sealed packets develop foul smell even if kept for months ?
- What values are displaced by Pallavi ?
Answer:
- Potato chips developed foul smell due to rancidity.
- Potato chips contain some oil as well as fat. These were slowly oxidised since they were exposed to air and therefore, developed foul smell.
- It is an oxidation reaction
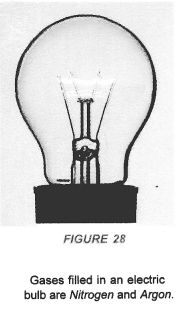
- The bags or packets containing chips or other such etables are filled with nitrogen and then sealed. This checks rancidity.
- The knowledge of science came to the help of Pallavi. She was aware of the consequences if one eats rancid food material. She therefore, did not allow her sister to eat the chips and thus, saved her from getting sick.
Hope given Value Based Questions in Science for Class 10 Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations are helpful to complete your science homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online science tutoring for you.