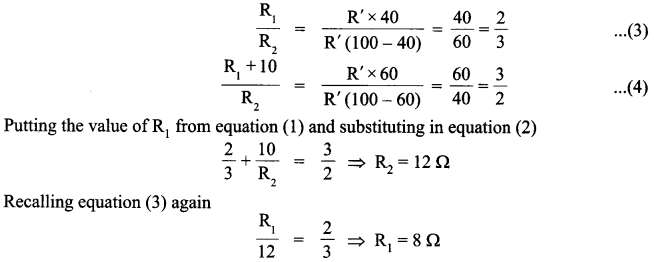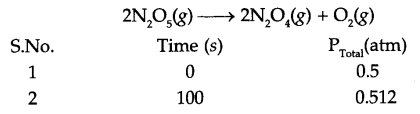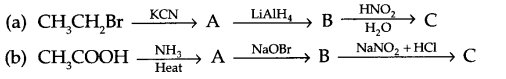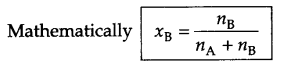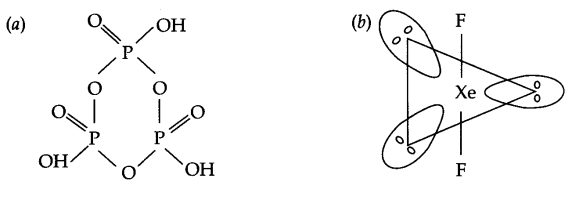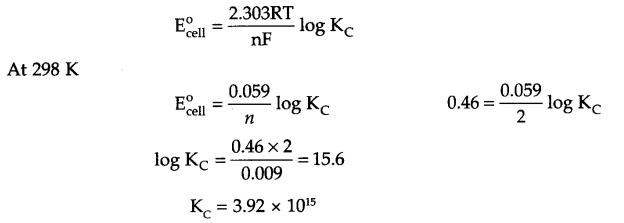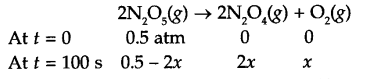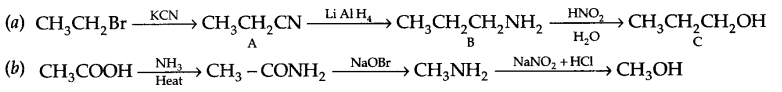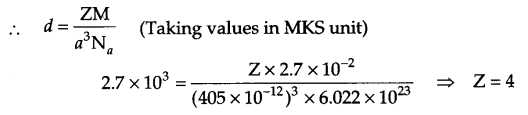CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 7 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 7.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 7
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | XII |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 7 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 12 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 7 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Chemistry is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time Allowed : 3 Hours
Max. Marks : 70
General Instructions
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question number 1 to 5 are very short answer questions and carry 1 mark each.
- Question number 6 to 10 are short answer questions and carry 2 marks each.
- Question number 11 to 22 are also short answer questions and carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 23 is a value based question and carry 4 marks.
- Question number 24 to 26 are long answer questions and carry 5 marks each.
- Use log table, if necessary. Use of calculators is not allowed.
Questions
Question 1.
Which of the 3d series element of the transition metals exhibits the largest number of oxidation state?
Question 2.
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
PhCH = CHCHO
Question 3.
In a reaction, 2A → Products, the concentration of reactant-‘A’ decreases from 0.5 mol L-1 to 0.4 mol L-1 in 10 minutes. Calculate the average rate during this time interval.
Question 4.
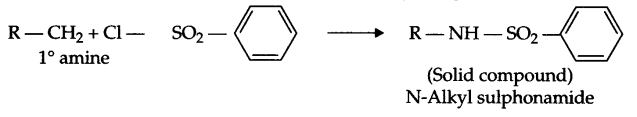
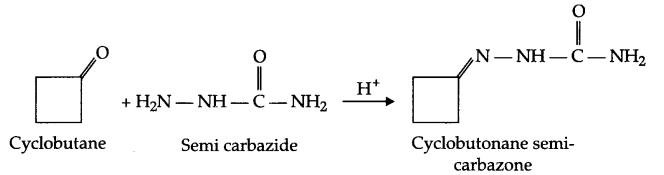
Write the structure and reaction for preparation of semicarbazone of cylcobutanone.
Question 5.
Write Freundlich’s relation for adsorpion in solution.
Question 6.
Complete the following reactions
- AgCl (s) + NH3 (aq) →
- XeF2 + H2O →
OR
- S + HNO3 (conc.) →
- P4 + NaOH →
Question 7.
Define the following terms:
- Isotonic solutions
- Azeotropic solutions
Question 8.
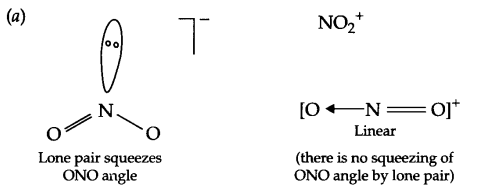
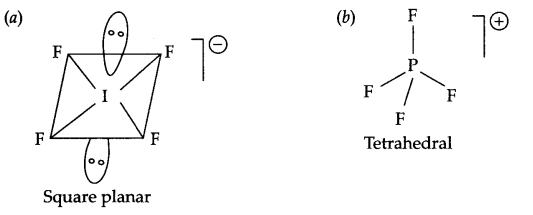
Draw the structures of the following:
(a) IF–4
(b) PF+4
Question 9.
For the following reaction,find the standard Gibbs energy.
![]()
Question 10.
Write the equation involved in the following reactions:
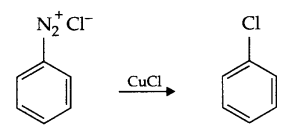
- Coupling reaction
- Ammonolysis
Question 11.
420 g of liquid A (molar mass 140 g mol-1) was dissolved in 900 g of liquid B (molar mass 180 g mol-1). The vapour pressure of pure liquid B was found to be 500 torr. Calculate the vapour pressure of pure liquid A and its vapour pressure in the solution, if the total vapour pressure of the solution is 487.5 torr.
Question 12.
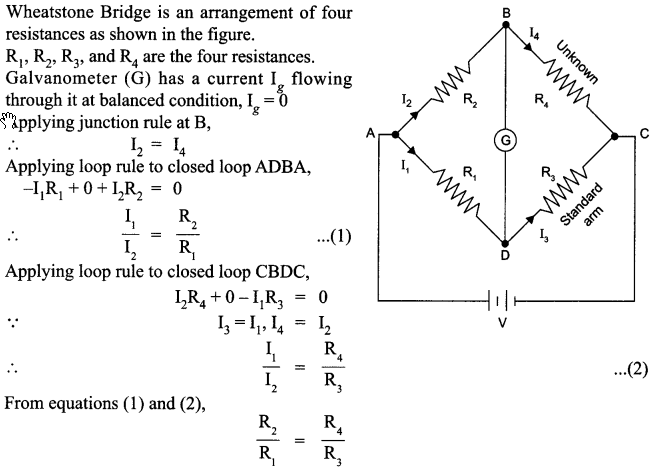
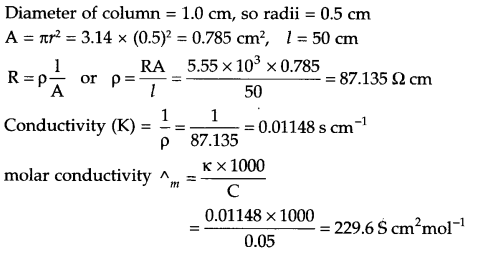
The electric resistance of a column of 0.05 mol L-1 NaOH solution of diameter 1 cm and length 50 cm is 5.55 × 103 ohm. Calculate its resistivity, conductivity and molar conductivity.
Question 13.
Explain [Fe(CN)6]4- and [Fe(H2O)6]2+ are of different colours in dilute solution.
Question 14.
Discuss the effect of temperature and pressure on the physisorption & chemisorption, in case of adsorption of gases on solid surface. Describe its applications in controlling humidity.
Question 15.
The initial concentration of N2O5 in the following first order reaction:
N2O5 (g) → 2NO2 (g) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) O2 (g) was 1.24 × 10-2 mol L-1 at 318 K
The concentration of N2O5 after 60 minutes was 0.20 × 10-2 mol L-1. Calculate the rate constant of the reaction at 318 K.
Question 16.
Arrange according to the given instruction in increasing order:
(a) CH3CH2CH2Br, CH3CH2 – CH2 – Cl, CH2 = CH – CH2F (for SN2 reaction)
(b) CH3 = CH CH(Br) CH3, CH3CH2CH (Br) CH3, CH2 = CH – Br (for SN1 reaction)
(c) C6H5Cl, p-C6H4Cl(NO2), C6H11Cl (cyclohexyl chloride) (for SE reaction)
Question 17.
Write the reaction involved in the following process:
(a) Leaching of bauxite ore to prepare pure Alumina
(b) Refining of zirconium by Van-Arkel method
(c) Recovery of gold from its leached ore with NaCN solution.
Question 18.
Give the structures of A,B and C in the following reactions
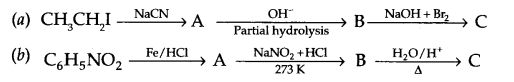
Question 19.
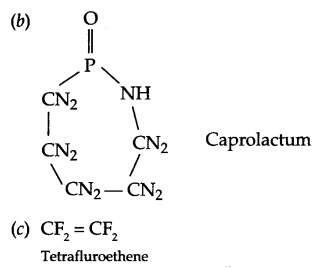
Write the structures of the monomers of the following polymers:
(a) Nylon 6, 6
(b) PHBV
(c) Nylon, 2, 6
Question 20.
Answer the following questions:
- Why do soap not work in hard water?
- What are analgesics?
- What are antacids?
Question 21.
Assign suitable reason for the following:
- N2 is less reactive at room temperature.
- H2S is less acidic than H2Te.
- Halogens are strong oxiding agents.
Question 22.
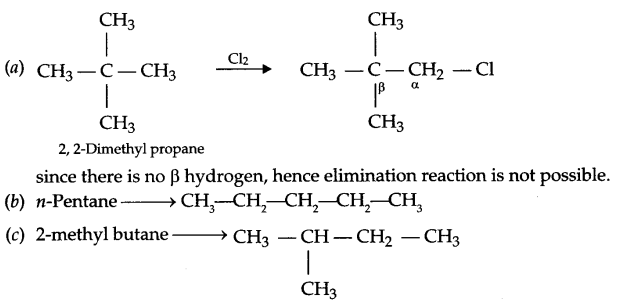
Carry out the following conversions in not more than 2 steps:
(a) Ethanol to 3-Hydroxybutanal
(b) Benzaldehyde to Benzophenone
(c) Benzaldehyde to 3-phenyl propar -1-ol
Question 23.
Seeing the growing cases of diabetes and depression among young children, Mr. Lugani, the principal of a reputed school organised a seminar in which he invited parents and principals. They all resolved this issue by strictly banning junk food in schools and introducing healthy snacks and drinks like soup, lassi, milk etc. in school canteens. They also decided to make compulsory half an hour of daily physical activities for the students in the morning assembly. After six months Mr. Lugani conducted the health survey in most of the schools and discovered a tremendous improvement in the health of the students. After reading the above passage, answer the following question:
- What are the values [at least two] displayed by Mr. Lugani?
- As the student how can you spread awareness about such issues?
- What are antidepressant drugs? Give one example.
- Name the sweetening agent used in the preparation of sweets for a diabetic patient.
Question 24.
Account for the following:
(a) La3+ (Z = 57) and Lu3+ (Z = 71) do not show any colour in the solution.
(b) There are irregularities in the electronic configuration of actinoids.
(c) There is great horizontal similarity in the properties of the transition elements than those of the main group elements.
(d) Write the reactions involved in preparation of KMnO4 from pyrolusite ore.
OR
- Compare the chemistry of actinoids with that of lanthanoids with reference to:
- atomic size
- oxidation state
- chemical reactivity
- Indicate the steps in the preparation of K2Cr2O7 from chromite ore.
Question 25.
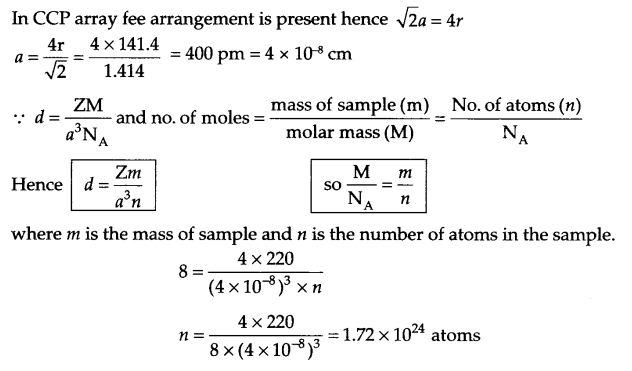
(a) Niobium (93 amu) crystallises in bcc structure. Its density is 8.55 g cm-3. Calculate the atomic radii of niobium.
(b) What are the two main non stoichiometric defects? Name these defects and explain with a suitable example.
OR
(a) What is meant by intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors?
(b) If KCl is doped with 5 × 10-2 mol % of TlCl3, what is the concentration of cation vacancies.
Question 26.
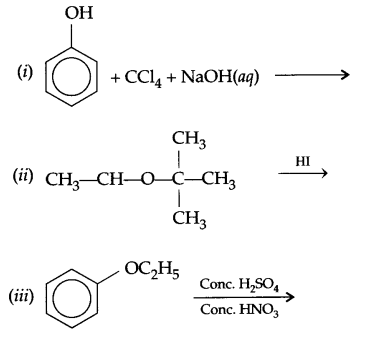
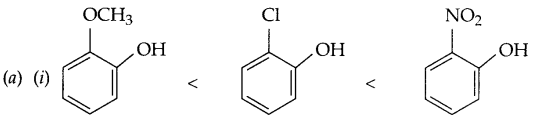
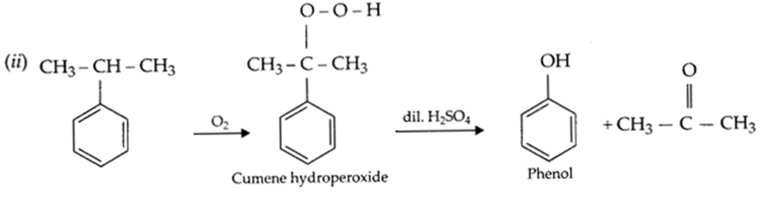
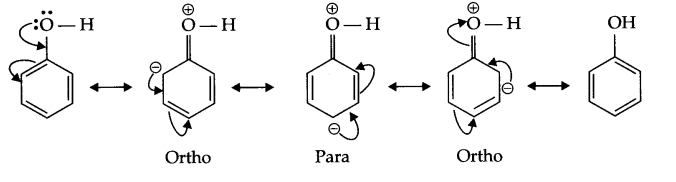
(b) Nitration of phenol gives only o and p-product. Give reason
OR
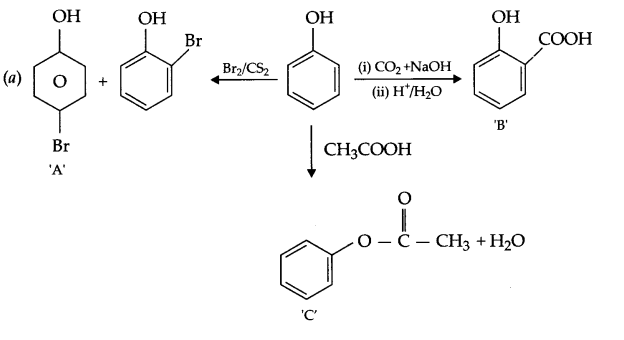
(a) Identify A,B & C:
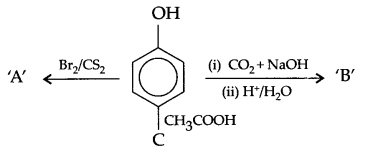
(b) (i) Anisole is treated with HI, what are the resultant products?
(ii) Write IUPAC name of salicylaldehyde.
Answers
Answer 1.
Mn (Manganese)
Answer 2.
3-Phenyl prop-2-enal
Answer 3.
Rate = \(\frac { 0.4-0.5 }{ 10 } =-\frac { 0.1 }{ 10 } \) = – 0.01 mol L-1 minute-1
Answer 4.
Answer 5.
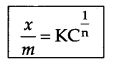
where \(\frac { x }{ m }\) = mass of adsorbate per unit mass of adsorbent m
n = number of layers of adsorption
C = concentration (mol L-1)
K = Constant for adsorption
Answer 6.
- AgCl (s) + NH3 (aq) → [Ag(NH3)2]Cl
- 2XeF2 + 2H2O → 2Xe(g) + 4HF + O2 (g)
OR
- S + HNO3 (conc.) → H2SO4 + NO2 + H2O
- P4 + NaOH → PH3 + NaH2PO2
Answer 7.
- Isotonic solutions : Two solutions having same osmotic pressure at a given temperature are called isotonic solutions.
- Azeotropic solutions : Some liquids on mixing form azeotropes which are the binary mixtures having the same composition in liquid and in the vapour phase and boils at a constant temperature. Such solutions are known as azeotropic solutions.
Answer 8.
Answer 9.
The reaction is
2Cr(s) + 3Cd2+ (aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 3Cd(s)
![]()
= -0.40 V – (- 0.74 V) = + 0.34 V
Change in number of electrons = +6
ΔG° = – nFE°
= -6 × 96500 × 0.34 = 196860 J/mole
Answer 10.
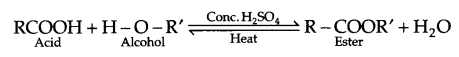
- Coupling reaction : When benzene diazonium chloride reacts with aniline or phenol, orange azo dye in formed. This reaction is known as coupling reaction.
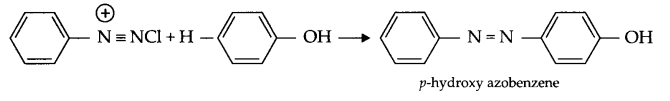
- Ammonolysis : When alkyl halide reacts with NH3, amines are formed. Such reactions are known to be ammonolysis.
C2H5Cl + NH3 → C2H5NH2 + HCl
Answer 11.

Answer 12.
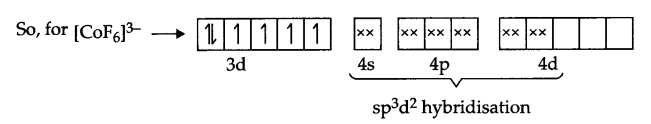
Answer 13.
Fe (28) = [Ar] 3d6 4s2
Fe2+ → [Ar] 3d6
Arrangement of electrons in [Fe(CN)6]4- and [Fe(H2O)6]2+ is as follows:
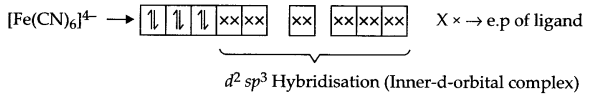
It does not have any unpaired electron so it is white in colour.
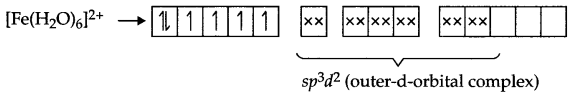
There are 4 unpaired electrons which makes this complex coloured.
Answer 14.
Effect of Temperature on physisorption and Chemisorption : On increasing the temperature, physisorption decreases due to increase in kinetic energy of adsorbate. On the other hand chemisorption increases initially with increase in temperature. The reason being it provides activation energy for the chemical adsorption and after that desorption takes place like physisorption.
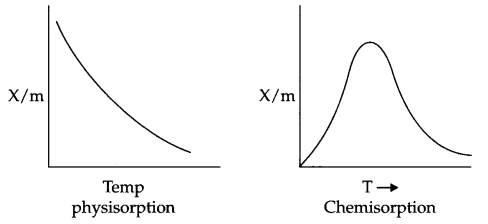
Effect of pressure : On increasing the pressure physisorption increases initially with a very fast rate and slowly it decreases.
But in case of chemisorption initial increase in pressure increases the extent of adsorption, but after that the extent of adsorption becomes constant.
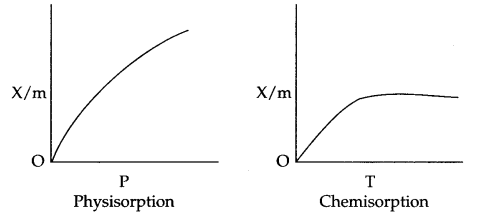
Applications of adsorption in controlling humidity : Silica gel adsorbs moisture from air which helps control humidity.
Answer 15.
From question: At 318 K,
At t = 0, [N2O5] = 1.24 × 10-2 mol L-1
At t = 60 minutes, [N2O5] = 0.20 × 10-2 mol L-1
Calculate K = ?
For a first order reaction
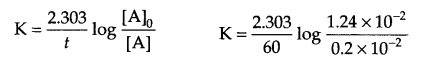
K = 0.03 min-1
Answer 16.
(a) CH3CH2CH2-Cl < CH3CH2CH2Br < CH2 = CH-CH2F
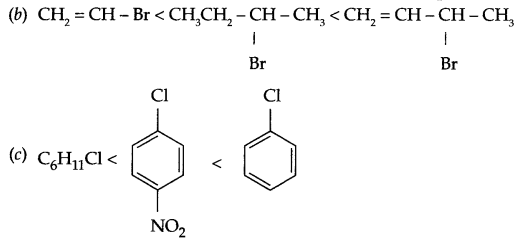
Answer 17.
(a) Al2O3 + NaOH(aq) → Na[Al(OH)4] (aq)
Na[Al(OH)4 ] \(\xrightarrow [ { CO }_{ 2 } ]{ dilution }\) Al2O3 . xH2O (s) + NaHCO3
Al2O3 . xH2O(s) \(\underrightarrow { 1470K } \) Al2O3 (s) + xH2O
(b) Van Arkel process :
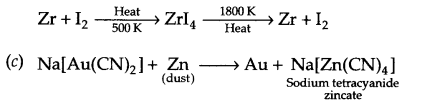
Answer 18.
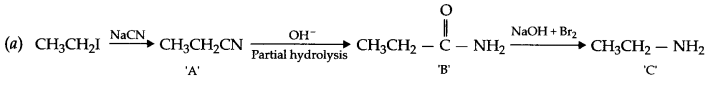
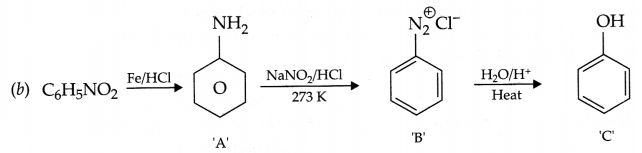
Answer 19.
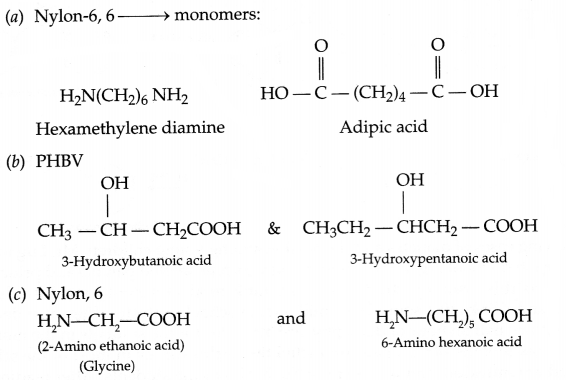
Answer 20.
- Soap forms scum with hard water:
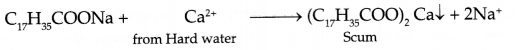
- Analgesics : Class of drugs used to reduce pain without causing impairment of consciousness, mental confusion etc.
- The drug which curtails excess acid formation in stomach, which causes irritation and pain are known as antacids.
Answer 21.
- Due to strong triple bond (pπ-pπ multiple bonding) between two nitrogen atoms, it is less reactive at room temperature.
- E-H bond length increases down the group, hence H2Te is more acidic than H2S.
- Due to high electron gain enthalpy and lower bond dissociation enthalpy of halogens, these acts as strong oxidising agents.
Answer 22.
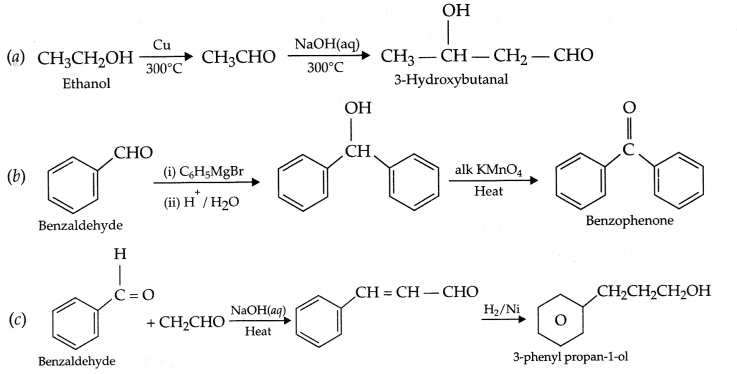
Answer 23.
- Concern for health and well being of students, creating awareness, social responsibility, sense of belongingness etc.
- As a student one can talk to friends, share it on social media, placing posters etc. on classroom and school notice board.
- Tranquilizers are the antidepressant drugs. A few examples are → Iproniazid, phenelzine etc.
- Sucralose
Answer 24.
(a)
- Electronic configuration. La3+ → [Xe] 4f0 and Lu3+ → [Xe] 4f14
Since in both of these ions there is no unpaired electron, so they do not show any colour in the solution. - Due to comparable energy of 5f, 6d and 7s orbitals, there is more irregularity in electronic configuration of actinoids.
- In transition elements, electrons are filled in the same atomic orbital which has the poor shielding effect and hence there is not much difference in properies in a series. On the other hand, there is all together different properties of main group elements due to lack of d-orbitals, multiple bond formation, different bond enthalpy etc.
(b) Reactions involved in the preparation of KMnO4 :
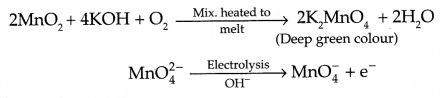
OR
(a) Comparison of Lanthanoids and Actinoids:
- Atomic size : Atomic size of both the series decreases from left to right but decrease is more in case of actinoids from element to element due to poorer shielding effect of 5if electrons.
- Oxidation state : Lanthanoids show +3 as general oxidation state except +2(Eu, Yb) and +4 (Ce etc.) for some elements. But actinoids show variable oxidation state from +3 to +7, (Although +3 and +4 are most common).
- Chemical reactivity : Actinoids are more reactive than lanthanoids due to bigger atomic size and lower ionisation energy as well as comparable energy of 5f, 6d and 7s orbitals, variable oxidation is also responsible for their more reactivity.
(b) Preparation of K2Cr2O7 :
Step I: Chromite ore is mixed with Na2CO3 and heated to melt as O2 gas is passed to give sodium chromate

Step II : Acidification of sodium chromate
![]()
Step III : Treatment with KCl
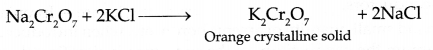
Answer 25.
(a) For bcc arrangement, Z = 2 and √3a = 4r.
density (d) – 8.55 g cm-3, atomic mass = 93 g mol-1 atomic radii = ?
d = \(\frac { ZM }{ { a }^{ 3 }{ N }_{ A } } \)

(b) Non stoichiometric defects are of two types, depending upon whether positive or negative ions are in excess. These defects are known as:
- metal excess defect;
- metal deficiency defect
1. Metal excess defect : When negative ion is missing from its lattice site and creates a hole which is occupied by the electron to maintain the electrical neutrality, e.g. NaCl crystals , turns yellow if excess of Na is present.
2. Metal deficiency defect : In many solids due to variable oxidation state it is difficult to prepare them in pure state and as a result there is a metal deficiency, e.g. due to Fe+2 and Fe3+ state of iron, there are always chances of formation of compounds like Fe0.95O, Fe0.98O etc.
OR
(a) Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors : Pure substances like silicon and germanium shows an increase in electrical conductivity with increase in temperature and they are called intrinsic semiconductors.
On the other hand small quantity of arsenic boron, etc. when introduced in substances like silicon, germanium the conductivity of the substance is significantly increased and such substances are known as extrinsic semiconductors. These are the two types: n-type and p-type semiconductors.
(b) In TlCl3, Tl3+ ions are there, to accomodate such ions in KCl lattice three K+ ions needs to be replaced for electrical neutrality. It means there will be two vacancies for each Tl3+ ion. Hence for
5 × 10-2 mol % TlCl3 doping → 2 × 5 × 10-2 cation vacancies will be generated.
Concentration of cation Vacancies = 2 × \(\frac { { 5\times 10 }^{ -2 } }{ 100 } \) × 6.002 × 1023 = 6.022 × 1020
Answer 26.
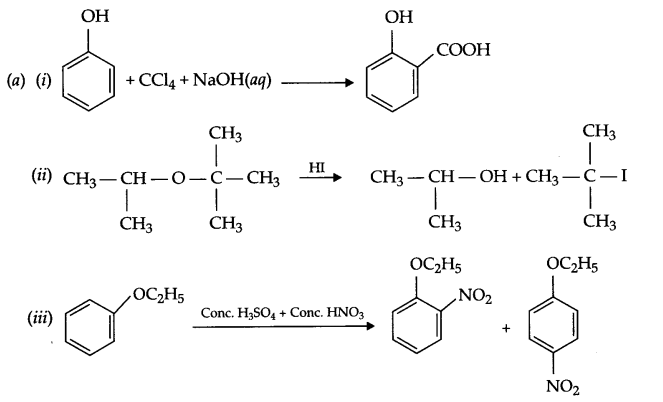
(b) In resonance structures of phenol, negative charge appears on ortho and para position, hence electrophilic substitution reaction is possible only on these two positions.
OR
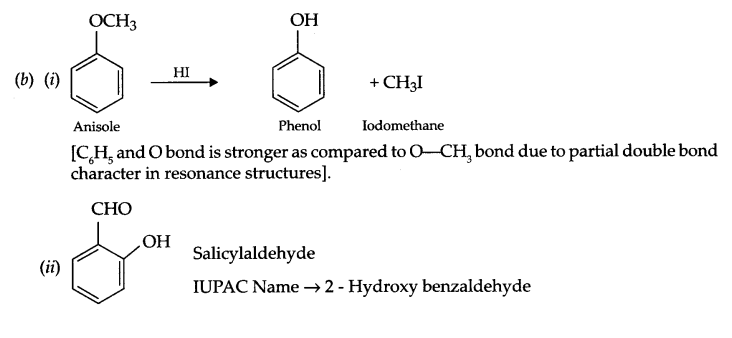
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 7 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 7, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.