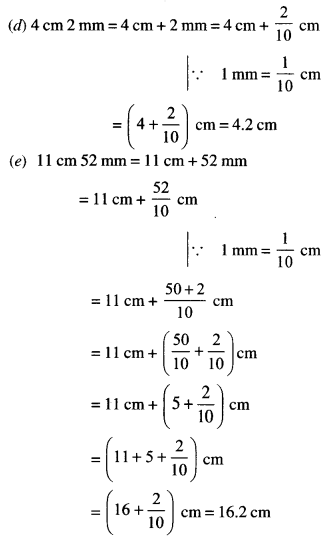
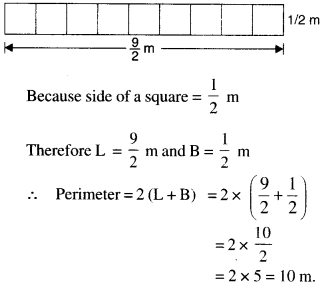
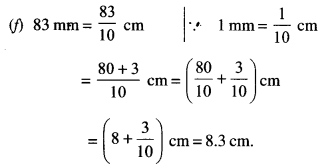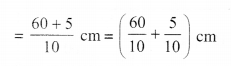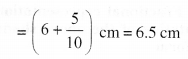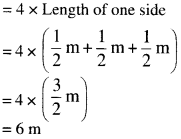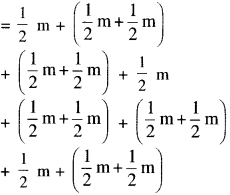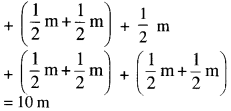NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Ex 2.2 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Ex 2.2.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 6 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 2 |
| Chapter Name | Whole Numbers |
| Exercise | Ex 2.2 |
| Number of Questions Solved | 7 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Ex 2.2
Question 1.
Find the sum by suitable rearrangement :
(a) 837 + 208 + 363
(b) 1962 + 453 + 1538 + 647.
Solution :
(a) 837 + 208 + 363
= 837 + 363 + 208 = (837 + 363) + 208 = 1200 + 208 = 1408
(b) 1962+ 453+ 1538 + 647
= 1962 + 1538 + 453 + 647 = (1962 + 1538) + (453 + 647)
= 3500+ 1100 = 4600.
Question 2.
Find the product by a suitable rearrangement :
(a) 2 × 1768 × 50
(b) 4 × 166 × 25
(c) 8 × 291 × 125
(d) 625 × 279 × 16
(e) 285 × 5 × 60
(f) 125 × 40 × 8 × 25.
Solution :
(a) 2 × 1768 × 50
= 2 × 50 × 1768 = (2 × 50) × 1768 = 100 × 1768= 1,76,800
(b) 4 × 166 × 25 = 4 × 25 × 166 = (4 × 25) × 166 = 100 × 166 = 16,600
(c) 8 × 291 × 125 = 8 × 125 × 291
= (8 × 125) × 291 = 1000 × 291 =2,91,000
(d) 625 × 279 × 16 = 625 × 16 × 279
= (625 × 16) × 279 = 10000 ×279 = 27,90,000
(e) 285 × 5 × 60 = 285 × (5 × 60) = 285 × 300
= 85,500
(f) 125 × 40 × 8 × 25 = (125 × 40) × (8 × 25) = 5000 × 200 = 10,00,000.
Question 3.
Find the value of the following :
(a) 297 × 17+297 × 3
(b) 54279 × 92 + 8 × 54279
(c) 81265 × 169 – 81265 × 69
(d) 3845 × 5 × 782 + 769 × 25 × 218.
Solution :
(a) 297 × 17 + 297 × 3 = 297 × (17+ 3)
= 297 × 20 = 5940
(b) 54279 × 92 + 8 × 54279
= 54279 × 92 + 54279 × 8 = 54279 × (92 + 8)
= 54279 × 100 = 54,27,900
(c) 81265 × 169-81265 × 69
= 81265 × (169-69)
= 81265 × 100 = 81,26,500
(d) 3845 × 5 × 782 + 769 × 25 × 218
= 3845 × 5 × 782 + 769 × 5 × 5 × 218 = 3845 × 5 × 782 + (769 × 5) × 5 × 218 = 3845 × 5 × 782 + 3845 × 5 × 218 = 3845 × 5 × (782 + 218)
= 3845 × 5 × 1000 = 19225 × 1000 = 1,92,25,000.
Question 4.
Find the product, using suitable properties :
(a) 738 × 103
(b) 854 × 102
(c) 258 × 1008
(d) 1005 × 168.
Solution :
(a) 738 × 103
= 738 × (100+ 3)
= 738 × 100 + 738 × 3 = 73,800 + 2,214 = 76,014
(b) 854 × 102
= 854 × (100 + 2)
= 854 × 100 + 854 × 2 = 85,400+ 1,708 = 87,108
(c) 258 × 1008
= 258 × (1000+ 8)
= 258 × 1000 + 258 × 8 = 2,58,000 + 2,064 = 2,60,064
(d) 1005 × 168
= 168 × 1005
= 168 × (1000+ 5)
= 168 × 1000+ 168 × 5
= 1,68,000 + 840 = 1,68,840.
Question 5.
A taxi driver filled his car petrol tank with 40 liters of petrol on Monday. The next day he filled the tank with 50 liters of petrol. If the petrol costs ₹ 44 per liter, how much did he spend all on petrol?
Solution :
Petrol filled on Monday = 40 litres
Petrol filled the next day = 50 litres
∴ Total petrol filled on the two days = 40 litres + 50 litres = 90 litres
∴ Cost of petrol per litre = ₹ 44
∴ Cost of 90 litres of 7 petrol = ₹ 44 × 90 = ? 3960.
Question 6.
A vendor’supplies 32 liters of milk to a hotel in the morning and 68 liters of milk in the evening. If the milk costs ₹ 15 per liter, how much money is due to the vendor per day?
Solution :
Milk supplied in the morning = 32 liters
Milk supplied in the evening = 68 liters
∴ Milk supplied per day = 32 litres + 68 litres = 100 litres
Cost of milk per liter = ₹ 15
Money due to the vendor per day = Cost of
100 litres of milk = ₹ 15 × 100 = ₹ 1500.
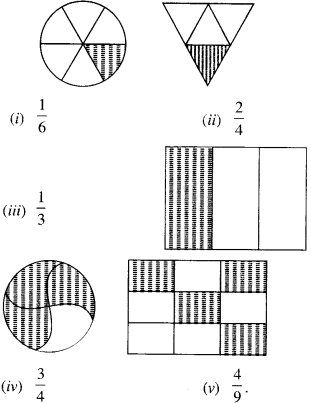
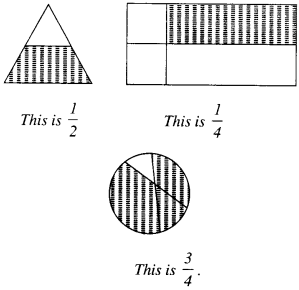
Question 7.
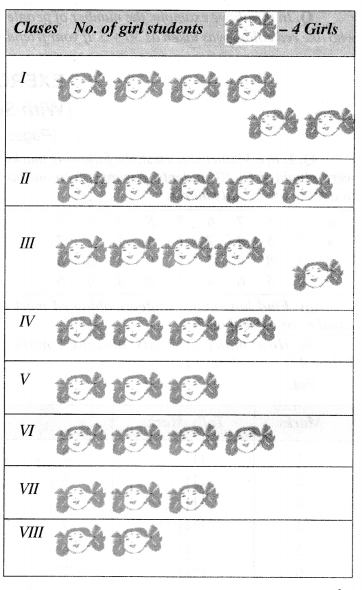
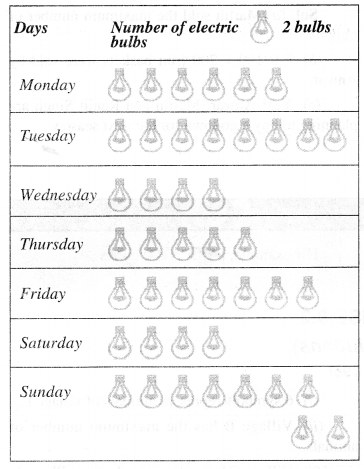
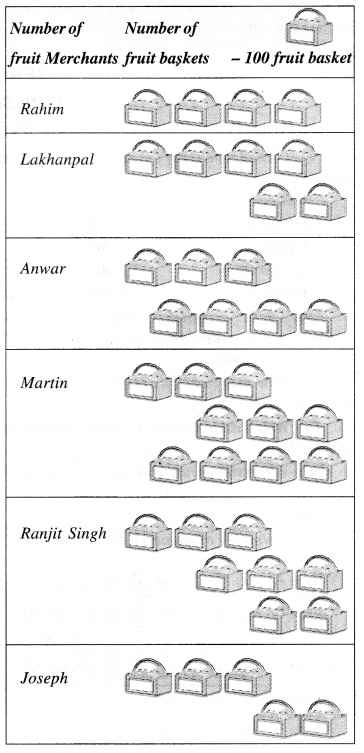
Match the following :

Solution :

We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Ex 2.2 help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Ex 2.2, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.