NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 2 On the Trial of the Earliest People are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 2 On the Trial of the Earliest People.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 6 |
| Subject | Social Science History |
| Chapter | Chapter 2 |
| Chapter Name | On the Trial of the Earliest People |
| Number of Questions Solved | 8 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 2 On the Trial of the Earliest People
NCERT TEXTBOOK EXERCISES (Pages 20-21)
LET’S RECALL
Question 1.
Complete the sentences:
- Hunter-gatherers chose to live in caves and rock shelters because ……….
- Grasslands developed around ………… years ago.
- Early people painted on the ……….. of caves.
- In Hunsgi, tools were made of …………
Answer:
- they provided shelter from the rain, heat, and wind.
- 12,000
- walls
- limestone.
Question 2.
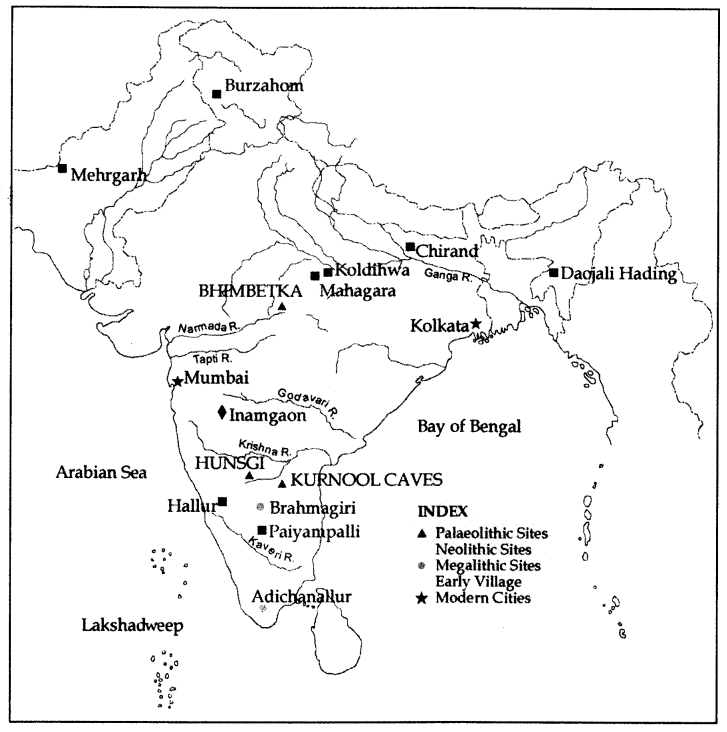
Look at the present-day political map of the subcontinent on page 136. Find out the states where Bhimbetka, Hunsgi, and Kurnool are located. Would Tushar’s train have passed near any of these sites?
Answer:
Self-study. For the map please see below.
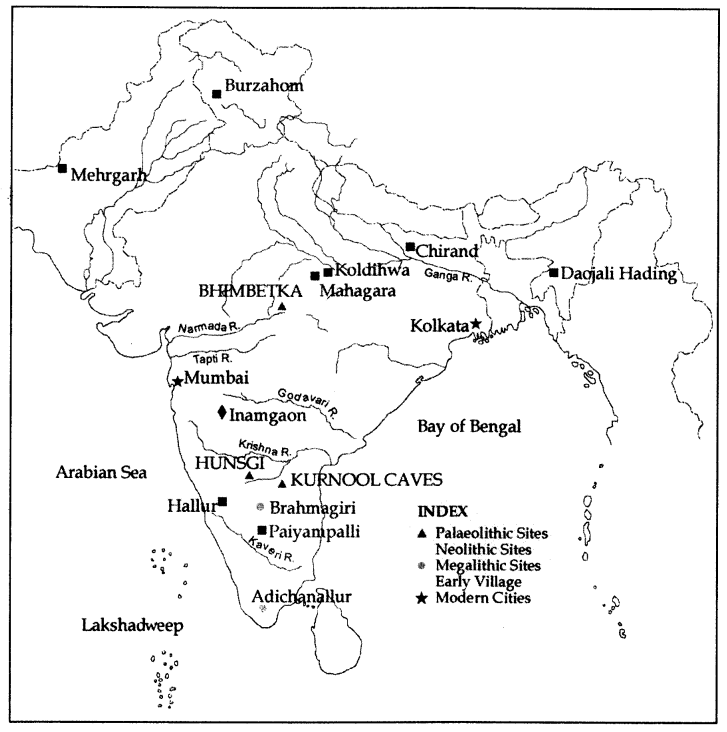
Hints/Brief Answers:
1. Bhimbetka = (M.P = Madhya Pradesh).
2. Hunsgi = (Karnataka).
3. Kurnool = (Andhra Pradesh).
Tushar’s train will have to pass by Hunsgi and Kurnool.
LET’S DISCUSS
Question 3.
Why did the hunter-gatherers travel from place to place? In what ways are these similar to/different from the reasons for which we travel today?
Answer:
(a) There were at least four to five reasons why hunter-gatherers moved from place to place.
- Hunter-gatherers moved from place to place to save plant and animal resources at those places.
- Animals moved from place to place-either in search of smaller prey or in the case of deer and wild cattle, in search of grass and leaves. That is why, those who hunted them had to follow their (i.e., animals’) movements.
- Plants and trees bear fruit in different seasons. So, people might have moved from season to season in search of different types of fruits.
- People, plants and animals need water to survive. Water is found in lakes, streams and rivers. Many rivers and lakes are perennial (with water throughout the year while others are seasonal. People living on seasonal river’s banks had had to go in search of water during the dry seasons (winter and summer).
- People might have travelled to meet their friends and relatives. They (hunter-gatherers) travelled on foot or on sledges (carts without wheels).
(b) In the following ways people may travel for similar reasons:
- In search of employment (or food) people have to move from one place to another.
- Due to shortage of land, raw-material, means of transportation, sources of energy (or power), capital etc. the people have to move from one place to another.
- People of some areas or regions have to move with their animals in search of grass or for their own protection due to adverse season or natural calamities (flood, drought or earthquake etc.).
(c) In the following ways the people move or travel differently from the regions nowa-days.
- The people now-a-days travel from one place to another by bus, train, aeroplane or car.
- Generally they do not like to give up their place due to shortage of water or change of seasons. Rather they arrange water through regular supply of water and they use electronic means (air-conditioners/fans/heaters etc.) according to seasons.
- People move from one place to another for better facilities of education, health, employment, business, tourism etc.
Question 4.
What tools would you use today for cutting fruit? What would they be made of?
Answer:
To cut fruits we use knives, made of steel or we use electric knives.
Question 5.
List three ways in which hunter-gatherers used fire (See page 16). Would you use fire for any of these purposes today?
Answer:
Hunter-gatherers may have used fire for cooking food, give light to the interior of the caves and gave security because animals were – afraid of fire. Yes, we use fire for cooking food today.
LET’S DO
Question 6.
Make two columns in your notebook. In the left-hand column, list the foods hunter-gatherers ate (see page 11). In the right-hand column, list some of the foods you eat. Do you notice any similarities/differences?
Answer:
For self-study.
Hints:
Food-hunter-gatherers used to eat meat or flesh of animals, fish, and birds. They used to eat uncooked food because they did not know how to cook food and they were not aware of the use of fire. They also ate gathered fruits, roots, nuts, seeds, leaves, stalks, and eggs. Nowadays we eat chapati of wheat, rice, pulses, vegetables, fruits, meat, chicken, eggs, etc.
Question 7.
If you had a natural pebble-like the ones shown on page 13, what would you use it for?
Answer:
The natural pebbles can be used to play games like (girls play the game gifts). The boys also play games (e.g. a group of boys keeps dropping pebbles at different places and another group of boys tries to find them. This is especially played in SCOUT games). The natural pebbles can be used to decorate the flower pots and flower beds.
Question 8.
List two tasks that are performed by both men and women at present, List another two that are performed only by women, and two that are performed only by men. Compare your list with that of any two of your classmates. Do you notice any similarities/differences in your lists?
Answer:
Two tasks that are performed by both men and women:
(a) Teaching (b) office jobs
Two tasks that are performed by only men:
(a) Mining (b) Working in a shipyard
Two tasks that are performed by only women:
(a) Nursing (b) Looking after home and hearth
Compare your lists yourself.
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 2 On the Trial of the Earliest People, help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 2 On the Trial of the Earliest People, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.