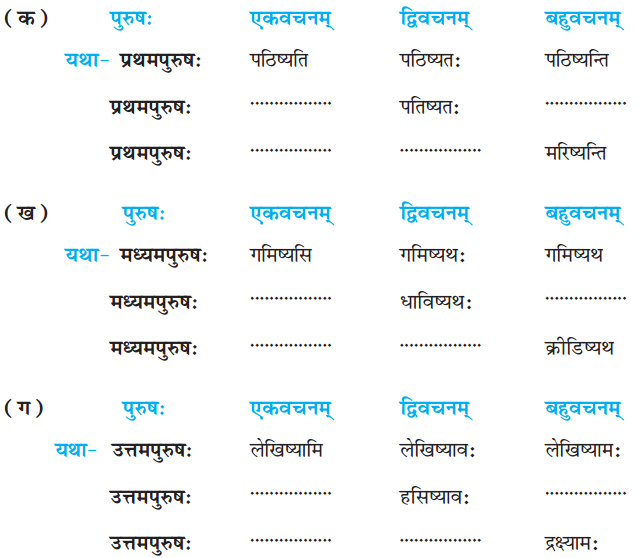
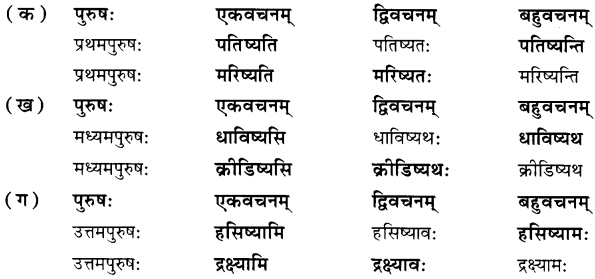
Here we are providing Online Education for Heat Acids, Bases and Salts Class 7 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 5 was designed by subject expert teachers. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-7-science/
Online Education for Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Extra Questions and Answers Acids, Bases and Salts
Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Extra Questions And Answers Question 1.
What is common in the sour-tasting substances?
Answer:
They contain acids.
Acids Bases And Salts Class 7 Extra Questions And Answers Question 2.
Name two naturally occurring indicators.
Answer:
Turmeric, litmus.
Acid Bases And Salts Class 7 Extra Questions Question 3.
Name some common acids and bases and their sources.
| Name of acid | Found in |
| Acetic acid | Vinegar |
| Formic acid | Ant’s sting |
| Citric acid, | Citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, etc. |
| Lactic acid | Curd |
| Oxalic acid | Spinach |
| Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) | Amla, Citrus fruits |
| Tartaric acid | Tamarind, grapes, unripe mangoes, etc. |
| All the acids mentioned above occur in nature. | |
| Name of base | Found in |
| Calcium hydroxide | Lime water |
| Ammonium hydroxide | Window cleaner |
| Sodium hydroxide / Potassium hydroxide | Soap |
| Magnesium hydroxide | Milk of magnesia |
Acids, Bases And Salts Class 7 Extra Questions And Answers Question 4.
What are the various colours of litmus paper?
Answer:
Red and blue.
![]()
Ncert Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Extra Questions Question 5.
What is the colour of litmus in distilled water?
Answer:
Mauve (purple).
Class 7 Acids Bases And Salts Extra Questions Question 6.
Why acids and bases should be handled with care.?
Answer:
Great care should be taken while handling laboratory acids and bases because these are corrosive in nature, irritating and harmful to skin.
Class 7 Science Ch 5 Extra Questions Question 7.
How is the soil treated when it becomes too acidic?
Answer:
When the soil becomes too acidic, it is treated with bases like quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide).
Acid Base And Salts Class 7 Extra Questions Question 8.
What is done if soil becomes too basic?
Answer:
If the soil becomes too basic, organic matter is added to it. Organic matter releases acids which neutralises the basic nature of the soil.
Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Extra Questions Question 9.
Name one antacid.
Answer:
Milk of magnesia, which contains magnesium hydroxide.
Extra Questions On Acids, Bases And Salts Class 7 Question 10.
What does calamine solution contain?
Answer:
Zinc Carbonate.
Extra Questions Of Acids Bases And Salts Class 7 Question 11.
How is lime water prepared?
Answer:
To prepare limewater, some lime (chuna) is dissolved in water. The solution is stirred and is left for some time. Later a little clear solution from the top is decanted. This is lime water.
![]()
Acids, Bases And Salts Class 7 Questions And Answers Pdf Question 12.
How does rain become acidic?
Answer:
The rain becomes acidic because carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide (which are released into the air as pollutants) dissolve in raindrops to form carbonic acid, sulphuric acid and nitric acid respectively, making rainwater acidic.
Questions On Acids, Bases And Salts Class 7 Question 13.
How is an ant’s sting relieved?
Answer:
When an ant bites, it injects an acidic liquid into the skin. The effect of the sting can be neutralised by rubbing moist baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate) or calamine solution which contain zinc carbonate as both of these are bases.
Extra Questions For Class 7 Science Acids Bases And Salts Question 14.
What should be done to neutralise acidic factory wastes and why?
Answer:
The wastes of many factories contain acids. If they are allowed to flow into the water bodies, the acids will kill fish and other organisms. The factory wastes are, therefore, neutralised by adding basic substances.
Class 7 Science Acids Bases And Salts Extra Questions Question 15.
Write a brief note on litmus?
Answer:
The most commonly used natural indicator is litmus. It is extracted from lichens. It has a mauve (purple) colour in distilled water. When added to an acidic solution, it turns red and when added to a basic solution, it turns blue. It is available in the form of a solution, or in the form of strips of paper, known as litmus paper. Generally, it is available as red and blue litmus paper.
Class 7 Chapter 5 Science Extra Questions Question 16.
I am not getting the same result when using baking soda or dry litmus paper. Why?
Answer:
Substances show their acidic or basic characteristics in solution or molten state. Therefore, instead of using dry baking soda, one should use its solution for testing their chemical nature.
![]()
Questions On Acids Bases And Salts Class 7 Question 17.
Explain why:
(a) An antacid tablet is taken when you suffer from acidity.
(b) Calamine solution is applied on the skin when an ant bites.
(c) Factory waste is neutralised before disposing it into the water bodies.
Answer:
(a) Antacids are nothing but bases. When there is excess of acid in stomach, antacids are taken. Antacid neutralises acids and relieves us.
(b) Ant injects an acid during bite which causes the burning sensation. Calamine solution is basic in nature. It neutralises the acid and relieves us from the pain.
(c) Factory wastes contain both acidic and basic substances. These are harmful for the organisms living in water (fishes etc). So, these are neutralised.
Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Acids Bases And Salts Extra Questions Question 18.
Three liquids are given to you. One is hydrochloric acid, another is sodium hydroxide and third is a sugar solution. How will you identify them? You have only turmeric indicator.
Answer:
Turmeric solution turns red on coming in contact with bases. It is not affected by acids and neutral substances. At first we will identify the base. Samples of the given three liquids are tested by adding a small quantity of turmeric to them.
The liquid in which the colour of turmeric changes from yellow to red, is a base, i.e., sodium hydroxide solution. Then, one of the remaining two unidentified solutions is added to it gradually. If the solution turns yellow again, the added liquid is hydrochloric acid (because it neutralises the base). Otherwise, the added liquid is sugar solution.
Extra Questions On Acids Bases And Salts Class 7 Question 19.
Dorji has a few bottles of soft drinks in his restaurant. But, unfortunately, these are not labelled. He has to serve the drinks on the demand of customers. One customer wants acidic drink, another wants basic and third one wants neutral drink. How will Dorji decide which drink is to be served to whom?
Answer:
He can decide by the use of indicators. If the sample of drink turns red litmus blue, it is basic. If it turns blue litmus red, it is acidic. If it does not affect litmus, it is neutral.
![]()
Chapter 5 Science Class 7 Extra Questions Question 20.
Describe the process of neutralisation with the help of an example.
Answer:
The reaction between an acid and a base is known as neutralisation. Salt and water are produced in this process with the evolution of heat.
Acid + Base → Salt + Water (Heat is also evolved in this process)
The following reaction is an example:
Hydrochloric acid (HCI) + Sodium hydroxide
(NaOH) →Sodium chloride (NaCI) + Water (H2O)
Experiments
(i)
Aim: To test substances to check whether they are acids, bases or neutrals. .
Requirements: Red and blue litmus papers, sample, test tubes, water. ‘
Procedures :
- Samples are taken in test tubes and some water is added.
- One strip each of red and blue litmus is dipped into each test tubes.
Observation and Conclusion :
Observation Conclusion
- Red litmus turns blue basic
- Blue litmus turns red acid
- No Change neutral.
(2)
Aim: To observe neutralisation reaction.
Requirements: Lime water, vinegar, litmus solution, beaker, dropper.
Procedure :
- Vinegar is taken in a beaker.
- Some litmus is poured into it.
- Now lime water is added drop by drop.
Observation :
The solution turns red as soon as litmus solution is poured.
As we go on adding drops of limewater, the redness decreases.
At a certain stage, the solution turns purple. Further addition, makes the solution blue.
Conclusion: The lime water neutralised vinegar.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions
1. If a drop of lemon juice, mixed with some water is dropped on a strip of blue litmus paper:
(i) the paper will turn red.
(ii) the paper will turn black.
(iii) the paper will turn white.
(iv) there will be no change on the litmus paper.
Answer:
(i) the paper will turn red.
2. Tap water is neutral while vinegar is acidic in nature. If in a beaker same quantity of tap water and vinegar are mixed together and red and blue litmus papers are dipped into it one by one then :
(i) there will be no effect on any of these two litmus papers.
(ii) the red litmus paper turns blue.
(iii) the blue litmus paper turns red.
(iv) there will be no effect on blue litmus paper.
Answer:
(iii) the blue litmus paper turns red.
3. Which of the following is acidic in nature?
(i) Sugar solution
(ii) Salt solution
(iii) Shampoo
(iv) Aerated drink.
Answer:
(iv) Aerated drink.
4. Which of the following is basic in nature?
(i) Amla
(ii) Vinegar
(iii) Limewater
(iv) Curd.
Answer:
(iii) Limewater.
![]()
5. Which of the following is neutral in nature?
(i) Detergent solution
(ii) Milk of magnesia
(iii) Tap water
(iv) Lemon juice
Answer:
(iii) Tap water.
6. When a few drops of soap solution are mixed in a yellow coloured solution, the solution turned brownish red. The yellow coloured solution may be :
(i) a solution of a yellow dye
(ii) a solution of besan
(iii) turmeric solution
(iv) mustard oil.
Answer:
(iii) turmeric solution.
7. A student performed the following steps to prepare an indicator of China rose:
A. Collected some fresh China rose petals in a beaker.
B. Added some cold water in it.
C. Kept the mixture for some time till water became coloured.
D. Extracted the coloured water in a separate beaker. This will work as an indicator.
Answer:
B. Added some cold water in it.
8. Which of the steps mentioned above is wrong?
(i) A
(ii) B
(iii) C
(iv) D.
Answer:
(ii) B.
9. China rose indicator turns acidic solutions to :
(i) red
(ii) magenta
(iii) green
(iv) blue.
Answer:
(iii) green.
![]()
10. China rose indicator turns basic solutions to :
(i) magenta
(ii) yellow
(iii) green
(iv) blue.
Answer:
(iv) blue.
11. Few drops of sugar solution are added into the indicator of China rose taken in a test tube. The colour of the solution will :
(i) become red
(ii) become green
(iii) become magenta
(iv) remains the same.
Answer:
(iii) become magenta.
12. A small quantity of China rose indicator is taken into a test tube and a few drops of ammonium hydroxide are mixed into it. The colour of the solution will turn :
(i) magenta
(ii)blue
(iii) green
(iv) yellow.
Answer:
(i) magenta.
13. A blue litmus paper is dipped into the solution of nitric acid. The paper :
(i) turns red
(ii) turns white
(iii) turns green
(iv) remains the same.
Answer:
(i) turns red.
![]()
14. Adrop of lime water is put on a strip of turmeric paper. It will:
(i) turn red
(ii) turn blue
(iii) turn green
(iv) remain the same.
Answer:
(ii) turn blue
15. A student added dilute sulphuric acid to lime water. The reaction mixture :
(i) will become cold
(ii) will become hot
(iii) will either become hot or cold
(iv) will remain the same.
Answer:
(ii) will become hot.
16. Which of the following statements is true regarding neutralisation reaction?
(i) It produces cooling effect.
(ii) Salt is produced.
(iii) The reaction mixture is always acidic.
(iv) The reaction mixture is always basic.
Answer:
(ii) Salt is produced.
Keyword:
→ Acid: An acid is a substance that tastes sour and turns the blue litmus paper red.
→ Acidic: The chemical nature of acids is called acidic.
→ Base: Substances which are bitter in taste and feel soapy on touching are known as bases.
→ Basic: The nature of base is said to be basic.
→ Indicator: Special type of substances are used to test whether a substance is acidic or basic. These substances are known as indicators.
→ Neutral solution: The solutions which do not change the colour of either red or blue litmus are known as neutral.
![]()
→ Neutralisation: The reaction between an acid and a base is known as neutralisation. Salt and water are produced in this process with the evolution of heat.
→ Salt: In neutralisation reaction, a new substance is formed. This is called salt.