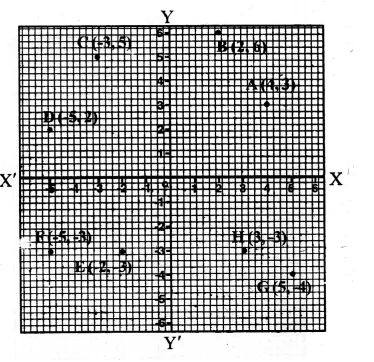
RS Aggarwal Class 8 Solutions Chapter 25 Graphs Ex 25C
These Solutions are part of RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 8. Here we have given RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 8 Chapter 25 Graphs Ex 25C.
Other Exercises
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 8 Chapter 25 Graphs Ex 25A
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 8 Chapter 25 Graphs Ex 25B
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 8 Chapter 25 Graphs Ex 25C
OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Tick the correct answer in each of the following:
Question 1.
Solution:
Answer = (a)
∵ In point (3, 6), both x and y are positive.
Question 2.
Solution:
Answer = (c)
∵ In point ( – 7, – 1) both x and y are negative.
Question 3.
Solution:
Answer = (d)
∵ In point (2, – 3), x is positive and y is negative.
Question 4.
Solution:
Answer = (b)
∵ In point ( – 4, 1), x is negative and y is positive.
Question 5.
Solution:
Answer = (c)
∵ Abscissa is distance of a point from y- axis
Question 6.
Solution:
Answer = (d)
y = a is a line parallel to x-axis at a distance of ‘a’ units.
Question 7.
Solution:
Answer = (a)
The equation of the line y-axis, is x = 0
Hope given RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 8 Chapter 25 Graphs Ex 25C are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.