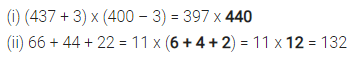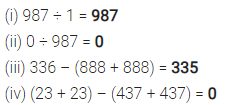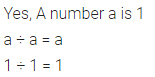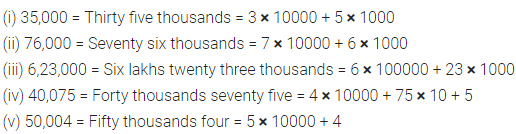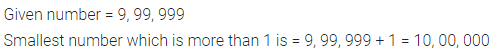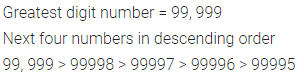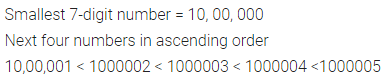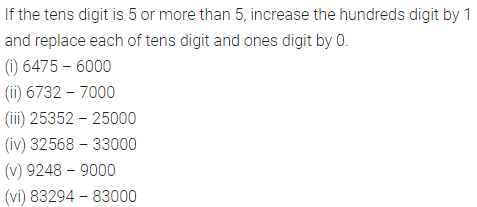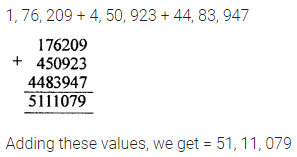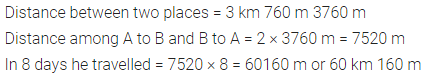Selina Publishers Concise Mathematics Class 7 ICSE Solutions Chapter 8 Percent and Percentage
Selina Publishers Concise Mathematics Class 7 ICSE Solutions Chapter 8 Percent and Percentage
Percent and Percentage Exercise 8A – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 7 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
Express each of the following as percent :
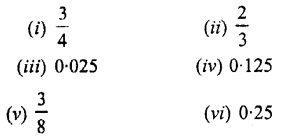
Solution :
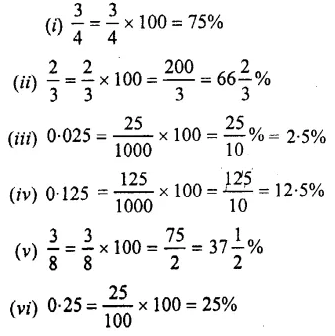
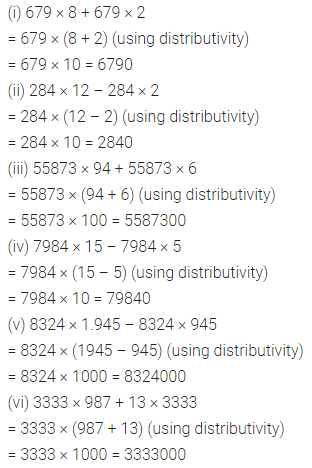
Question 2.
Express the following percentages as fractions and as decimal numbers :
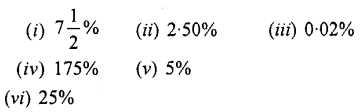
Solution :
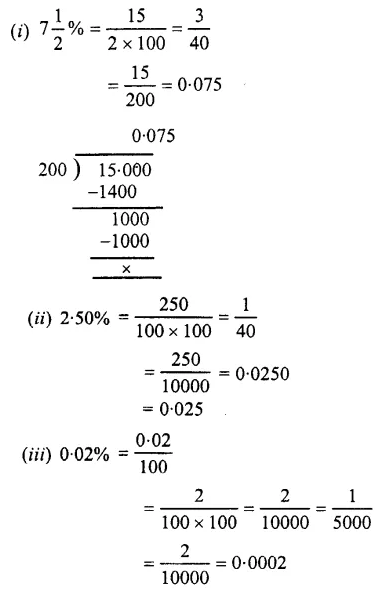
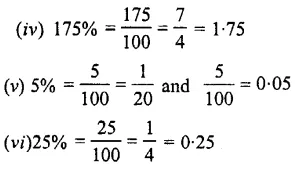
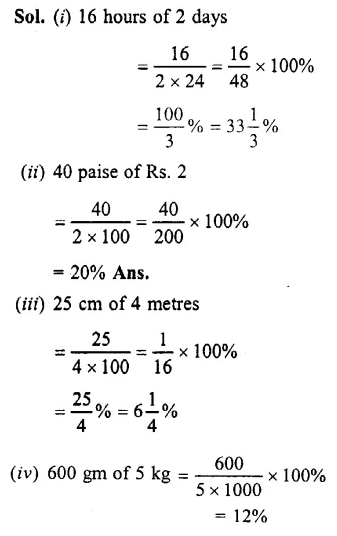
Question 3.
What percent is :
(i) 16 hours of 2 days ?
(ii) 40 paisa of Rs. 2 ?
(iii) 25 cm of 4 metres
(iv) 600 gm of 5 kg ?
Solution :
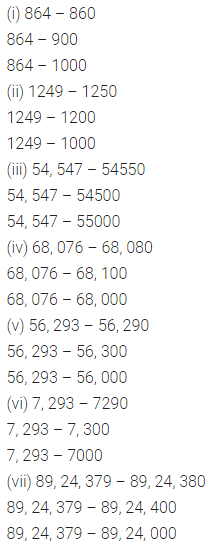
Question 4.
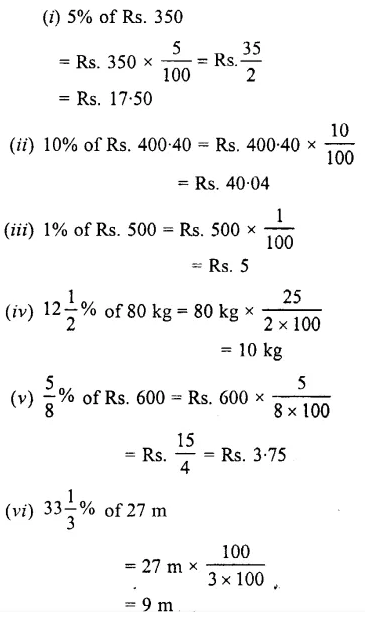
Find the value of:
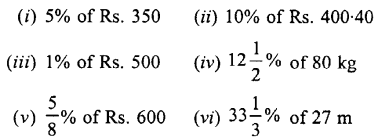
Solution :
Question 5.
In a class of 60 children, 30% are girls. How many boys are there ?
Solution :
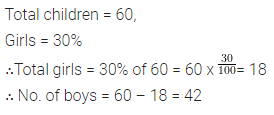
Question 6.
In an election, two candidates A and B contested. A got 60% of the votes. The total votes polled were 8000. How many votes did each get ?
Solution :

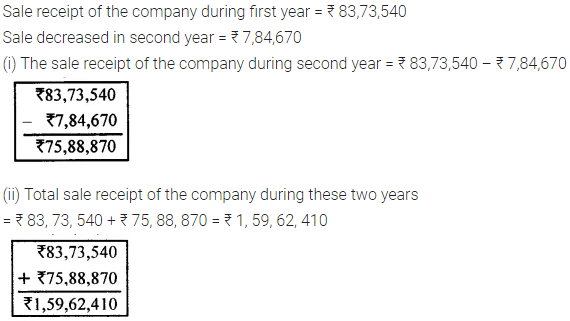
Question 7.
A person saves 12% of his salary every month. If his salary is ₹2,500, find his expenditure.
Solution :

Question 8.
Seeta got 75% marks out of a total of 800. How many marks did she lose ?
Solution :

Question 9.
A shop worth ₹25,000 was insured for 95% of its value. How much would the owner get in case of any mishappening ?
Solution :
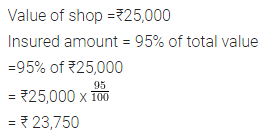
Question 10.
A class has 30 boys and 25 girls. What is the percentage of boys in the class ?
Solution :
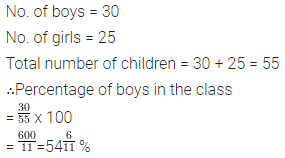
Question 11.
Express :
(i) 3 \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) as a percent
(ii) 0.0075 as percent
(iii) 3 : 20 as percent
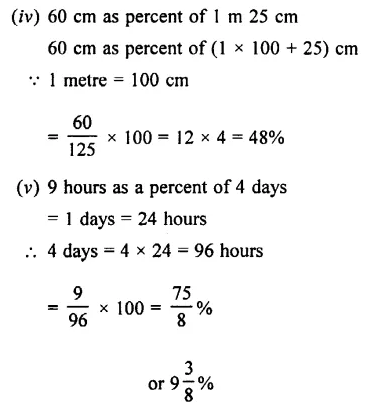
(iv) 60 cm as percent of 1 m 25 cm
(v) 9 hours as a percent of 4 days.
Solution :

Question 12.
(i) Find 2% of 2 hours 30 min.
(ii) What percent of 12 kg is 725 gm?
Solution :

Percent and Percentage Exercise 8B – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 7 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
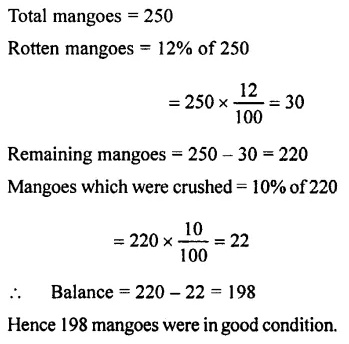
Deepak bought a basket of mangoes containing 250 mangoes 12% of these were found to be rotten. Of the remaining, 10% got crushed. How many mangoes were in good condition ?
Solution :
Question 2.
In a Maths Quiz of 60 questions, Chandra got 90% correct answers and Ram got 80% correct answers. How many correct answers did each give ?
What percent is Ram’s correct answers to Chandra’s correct answers ?
Solution :

Question 3.
In an examination, the maximum marks are 900. A student gets 33% of the maximum marks and fails by 45 marks. What is the passing mark ? Also, find the pass percentage.
Solution :

Question 4.
In a train, 15% people travel in first class, 35% travel in second class. The balance travel in the A.C. class ? Calculate the percentage of A.C. class travellers ?
Solution :
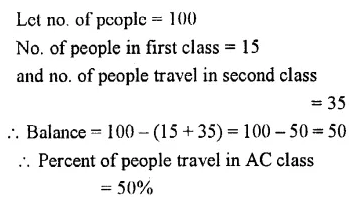
Question 5.
A boy eats 25% of the cake and gives away 35% of it to his friends. What percent of the cake is still left with him ?
Solution :
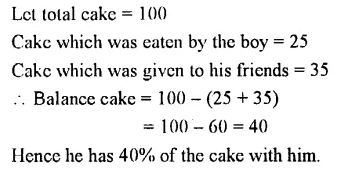
Question 6.
What is the percentage of vowels in the English alphabet ?
Solution :
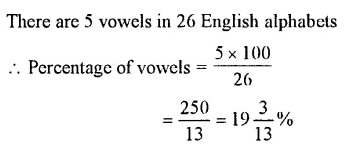
Question 7.

Solution :

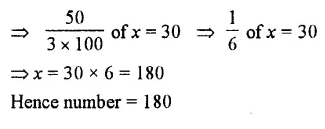
Question 8.
The money spent on the repairs of a house was 1% of its value. If the repair, costs Rs. 5,000, find the cost of the house.
Solution :
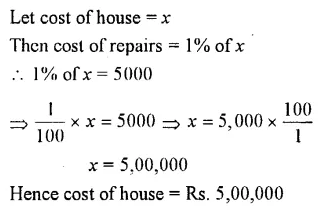
Question 9.
In a school out of300 students, 70% are girls and 30% are boys. If 30 girls leave and no new boy is admitted, what is the new percentage of girls in the school ?
Solution :
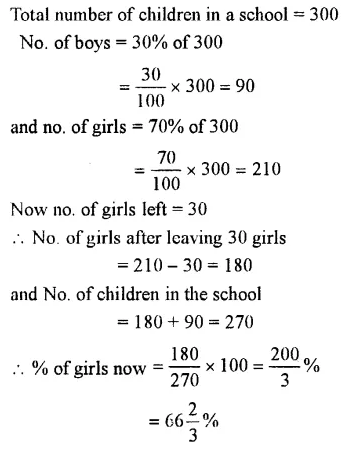
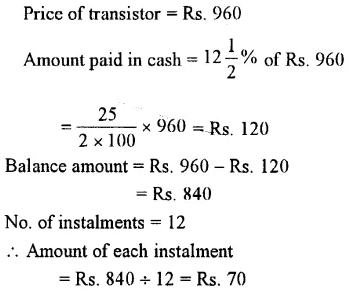
Question 10.
Kumar bought a transistor for Rs. 960. He paid 12 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) % cash money. The rest he agreed to pay in 12 equal monthly instalments. How much will he pay each month ?
Solution :
Question 11.
An ore contains 20% zinc. How many kg of ore will be required to get 45 kg of zinc ?
Solution :
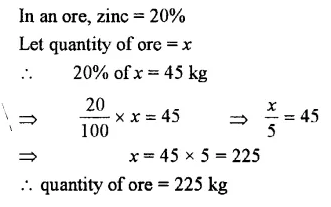
Percent and Percentage Exercise 8C – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 7 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
The salary of a man is increased from Rs. 600 per month to Rs. 850 per month. Express the increase in salary as percent.
Solution :
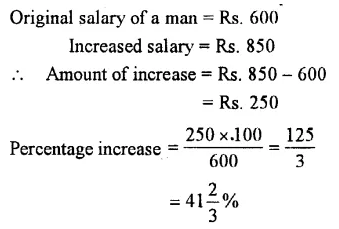
Question 2.
Increase :
(i) 60 by 5%
(ii) 20 by 15%
(iii) 48 by 121 %
(iv) 80 by 140%
(v) 1000 by 3.5%
Solution :

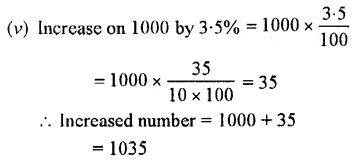
Question 3.
Decrease :
(i)80 by 20%
(ii) 300 by 10%
(iii) 50 by 12.5%
Solution :

Question 4.
What number :
(i) When increased by 10% becomes 88 ?
(ii) When increased by 15% becomes 230 ?
(iii) When decreased by 15% becomes 170 ?
(iv) When decreased by 40% becomes 480 ?
(v) When increased by 100% becomes 100 ?
(vi) When decreased by 50% becomes 50 ?
Solution :


Question 5.
The price of a car is lowered by 20% to Rs. 40,000. What was the original price ? Also, find the reduction in price.
Solution :

Question 6.
If the price of an article is increased by 25%, The increase is Rs. 10. Find the new price.
Solution :

Question 7.
If the price of an article is reduced by 10%, the reduction is Rs. 40. What is the old price ?
Solution :
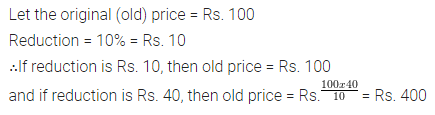
Question 8.
The price of a chair is reduced by 25%. What is the ratio of:
(i) Change in price to the old price.
(ii) Old price to the new price.
Solution :
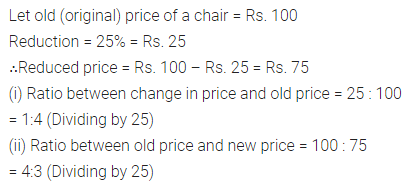
Question 9.
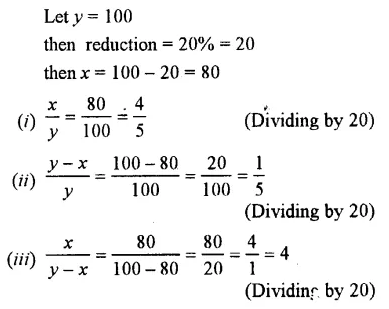
If x is 20% less than y, find :
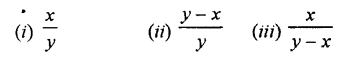
Solution :
Question 10.
If x is 30% more than y; find :
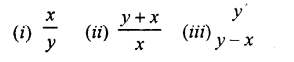
Solution :
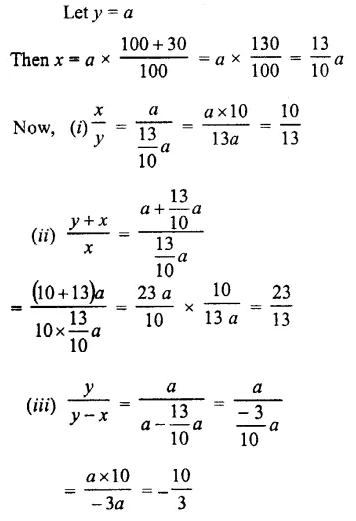
Question 11.
The weight of a machine is 40 kg. By mistake it was weighed as 40.8 kg. Find the error percent.
Solution :

Question 12.
From a cask, containing 450 litres of petrol, 8% of the petrol was lost by leakage and evaporation. How many litres of petrol was left in the cask ?
Solution :

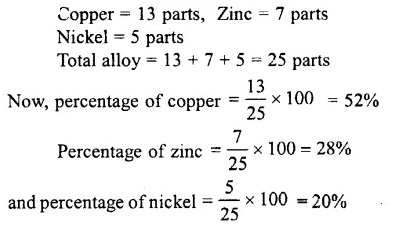
Question 13.
An alloy consists of 13 parts of copper, 7 parts of zinc and 5 parts of nickel. What is the percentage of each metal in the alloy?
Solution :
Question 14.
In an examination, first division marks are 60%. A student secures 538 marks and misses the first division by 2 marks. Find the total marks of the examination.
Solution :

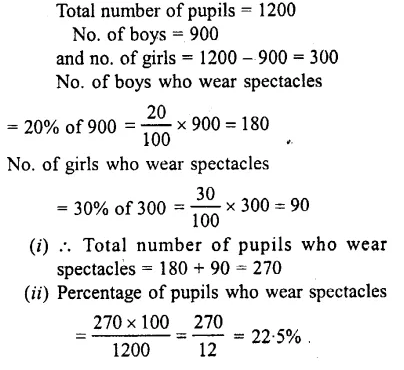
Question 15.
Out of 1200 pupils in a school, 900 are boys and the rest are girls. If 20% of the boys and 30% of the girls wear spectacles, find :
(i) how many pupils in all, wear spectacles ?
(ii) what percent of the total number of pupils wear spectacles ?
Solution :
Question 16.
Out of 25 identical bulbs, 17 are red, 3 are black and the remaining are yellow. Find the difference between the numbers of red and yellow bulbs and express this difference as percent.
Solution :

Question 17.
A number first increases by 20% and then decreases by 20%. Find the percentage increase or decrease on the whole.
Solution :

Question 18.
A number is first decreased by 40% and then again decreased by 60%. Find the percentage increase or decrease on the whole.
Solution :

Question 19.
If 150% of a number is 750, find 60% of this number.
Solution :