Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 5 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Standard Term 2 Set 5 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has three sections and 13 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 6 questions of 2 marks each; Section-B has 6 questions of 3 marks each; and Section-C has a case-based question of 5 marks.
- There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
- Wherever necessary, neat and properly labeled diagrams should be drawn.
SECTION – A
(Section A has 6 Questions of 2 marks each.)
Question 1.
(A) The picture given below is of the bird named Dodo (Mauritius) that has become extinct. Write any two names of animals that have become recently extinct.

(B) Specify the main objective of establishment of IUCN. Also mention the year in which it was established. (2)
Answer:
(A) The animals that have become recently extinct are:
- Quagga (Africa)
- Thylacine (Australia)
- Steller’s Sea Cow (Russia) (Any two)
(B) The main aim of IUCN is to maintain a
complete record of every species that ever lived and it works in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. It was established in 1948.
Related Theory
IUCN stands for International Union for Conservation of Nature. The headquarter of IUCN is in Switzerland.
![]()
Question 2.
Given below is the picture of a hummingbird, which is known for its unique wings as it can fly backwards. Why polar region is not a suitable habitat for hummingbirds?

OR
What do you mean by phytophagous insects? Give an example. (2)
Answer:
The polar region is not a suitable habitat for hummingbirds because in small animals like hummingbirds, they have a larger surface area relative to their volume, therefore, they tend to lose body heat very fast when the outside temperature is cold. This means, they have to expend much energy to generate body heat through metabolism. This is why very small animals are rarely found in polar regions.
OR
Phytophagous insects are those insects that generally feed on plant sap and other parts of green plants. They include species that attack roots, stems, Leaves, flowers, and fruits, either as larvae or as adults or in both stages.
Example: Beetles, moths, grasshoppers
Related Theory
Some insects are leaf feeders, that are either external or they may mine the tissues. “Phytophagous” is often synonymous with “herbivorous,” although the herbivores are sometimes restricted to those species feeding on herbs. Phytophagous can be grouped as monophagous (using only one plant genus or species), oligophagous (use plants within a family), polyphagous (use plants in many plant families).
Question 3.
(A) What is the importance of distillation
process performed during the production of certain alcoholic drinks?
(B) Which organism is commercially exploited for the production of single cell protein? (2)
Answer:
(A) Distillation is the process of separating alcohol from water by the process of evaporation and condensation. It is performed to increase the alcoholic content of alcoholic drinks.
Related Theory
Wine and beer are filtered, pasteurized and bottled without distillation whereas whisky, brandy and rum are produced by distillation of the fermented broth. The alcoholic content of beer is 3-6% and in wines, it is around 9-12% whereas the alcoholic content of brandy is 35-60%, whisky is 40-50% and that of rum is 40%.
(B) The organism that is commercially used for the production of single cell protein is Spirulina.
![]()
Question 4.
(A) Every year we hear several incidences of Dengue fever in our country. Name the vector of this disease.
(B) Interferons play an important role during viral infection. Write their role. (2)
Answer:
(A) The vector for Dengue fever is Aedes aegypti mosquito.
Related Theory
The causative agent of the Dengue fever is Flavivirus. The symptoms of this disease include high fever, severe headache, joint pain, nausea and vomiting.
(B) Interferons are glycoprotein released by virus-infected cells. The non-infected cells are protected from further viral infection by these interferons.
Question 5.
(A) What will happen if oxygen availability is reduced to activated sludge floes?
(B) Who is responsible for the development of technology of biogas production in India? (2)
Answer:
(A) If oxygen availability is reduced it will cause center of the floes to become anoxic (oxygen deficient) that will result in the death of bacteria and fungi and eventually it leads to the breakage of floes.
(B) The efforts made by Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) and Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) led to the development of the technology of biogas production in India.
![]()
Question 6.
(A) Name any two genetically engineered
vaccines.
(B) Which antibody is produced in response to allergy in our body?
OR
Give one similarity and one difference between morphine and heroin. (2)
Answer:
(A) Two genetically engineered vaccines are:
- Hepatitis B vaccine
- Herpes vaccine
(B) The antibody that is produced in response to allergy in our body is IgE.
OR
Similarity: Both morphine and heroin are extracted from the latex of plant Papaver somniferum.
Difference: Morphine is an effective sedative and painkiller while heroin acts as depressant and slows down body functions.
Related Theory
Heroin is obtained from diacetylation of Morphine.
SECTION – B
(Section B has 6 Questions of 3 marks each.)
Question 7.
(A) Why the species diversity of animals
which is around 72%, is much more than the species diversity of plants which is only 22%?
(B) Certain regions have very high levels of species richness and high degree of endemism. What is the name given to such regions? (3)
Answer:
(A) Species diversity of plants less than that of animals because of the following reasons:
(i) The animals adapt themselves to ensure their survival in changing environments. For example: Most animals possess simple or complex nervous system to control and coordinate various activities. Since insects possess repeated body segments with external cuticles and paired appendages, they have developed a potential to survive in different habitats.
(ii) Plants being immobile as compared to animals that can move around, have less adaptations as they are not exposed to different habitats.
(B) The regions having high Levels of species richness and high degree of endemism are called as biodiversity hotspots.
Related Theory
Endemism refers to species confined to that region and not found anywhere else.
![]()
Question 8.
(A) Rahul while working in a company dealing with production of proteins in bioreactors, forgot to add antibiotic to the medium in a bioreactor in which the recombinant bacterium was growing. What would happen?
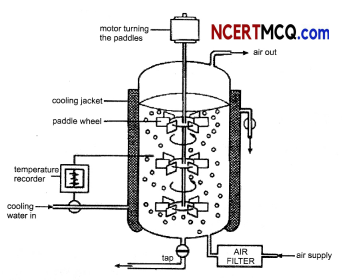
(B) Why ‘plasmid’ is regarded as an important tool in genetic engineering? (3)
Answer:
(A) In a bioreactor, where recombinant bacteria are growing, the presence of antibiotics in the medium makes sure that the bacteria retain the plasmid containing the antibiotic resistant gene as well as the gene of interest Therefore, in the absence of antibiotic, the recombinant bacterium does not need to produce a gene, which can make it resistant to antibiotic because the pressure will be eliminated and thus the bacteria will not maintain the copy number of the plasmid. Hence, the plasmid will be lost and also the gene of interest which will result in reduction of the quantity of the desired product.
(B) Plasmid is used to multiply or express particular genes and act as vector to transfer piece of foreign DNA attached to them.
Related Theory
Plasmid is defined as an autonomously replicating circular extra-chromosomal DNA present in some bacteria.
Question 9.
There has been an alarming situation globally about the gradually increasing average global temperatures in the recent years. If this situation continues, would you expect the distributional range of some species to be affected? If yes, how? Explain.
OR
Write any three features of animals that help them to survive in water scarce environment. (3)
Answer:
The geographical distribution of different species is largely dependent on their levels of thermal tolerance, water, light and soil In recent years the average global temperature is gradually increasing, which is a matter of great concern. If this continues, the distributional range of some species would be affected because increasing global temperature leads to excessive heat, drought, soil erosion, etc. Following points show how the plants and animals and abiotic factors are interdependent:
(i) On earth, life is not possible without water and life originated in water only. Also, the plants productivity and distribution are very much dependent on water. Plants require water and sunlight as a source of energy to prepare food through photosynthesis.
(ii) Many animals use diurnal and seasonal variations in light intensities and duration (photoperiod) as cues for timing their foraging, reproductive and migratory activities.
(iii) Water holding capacity of soils is determined by soil composition and grain size. Also, the type of vegetation which will grow in a particular type of soil depends on its pH, mineral composition and topography and indirectly it dictates the type of animals that can be supported there.
OR
Some features of animals which help them to survive in water scarce environment are:
- No sweating/uricotelic/deposition of fat in subepidermal layer/burrowing nature/thick skin/ body covered with scales.
- Use of metabolically produced water.
- Mucous layer on the surface to reduce water loss by perspiration.
- Various hormones in humans like ADH help
reduce water loss. (Any three)
![]()
Question 10.
In order to clean rivers, Government has initiated several plans such as Ganga Action Plan and Yamuna Action Plan. Which Ministry of Government had initiated these plans? What are the objectives of these plans? (3)
Answer:
The Ministry of Environment and Forests had initiated Ganga Action Plan and Yamuna Action Plan.
The major objectives of these plans are:
- To clean and save major rivers (Ganga and Yamuna) of the country from pollution.
- To improve the water quality by interception, diversion and treatment of domestic sewage and present toxic and industrial chemical wastes from identified grossly polluting units entering in to the river.
- To set up a greater number of sewage treatment plants.
Related Theory
Ganga action plan came into force in 1985 whereas Yamuna action plan was launched in 1993.
Question 11.
(A) Rishabh wants to separate DNA fragments according to their size. Which technique he should use?
(B) List the two core techniques of modern biotechnology. (3)
Answer:
(A) The technique which Rishabh should use to separate DNA fragments according to their size is gel electrophoresis.
(B) Modern biotechnology consists of two core techniques, which are:
(i) Genetic engineering: It refers to the field of biotechnology that involves the use of techniques to modify the chemical nature of genetic material (DNA and RNA). This includes the introduction
of the genetic material into another organism (host), in order to change the phenotype of the host organism.
(ii) Bioprocess engineering: These methods involve maintenance of sterile environment i.e., microbial contamination-free in chemical engineering processes to enable growth of only the desired microbe/ eukaryotic cell This results in production of microbes/cells in large quantities for the manufacture of biotechnological products like antibiotics, vaccines, enzymes, etc.
![]()
Question 12.
(A) All human beings do not suffer from cancer diseases although every individual have cellular oncogenes. Give reason.
(B) How cancerous cells are different from the normal cells? (3)
Answer:
(A) Every human being has cellular oncogenes or proto-oncogenes. These code for certain
growth factors. But under certain conditions, these proto-oncogenes get activated and Lead to oncogenic transformation of cells, thus, causing cancer. This activation is brought about by carcinogens which can be physical, chemical or biological.
Related Theory
The chemical carcinogens present in tobacco smoke have been identified as a major cause of lung cancer.
(B) In normal cells of human body, the cell growth and differentiation is a highly controlled and regulated process. But in cancerous cells, there is a breakdown of these regulatory mechanisms. Normal cells also shows the property of contact inhibition because of which contact with other cells inhibits their uncontrolled growth, whereas cancerous cells have Lost this property. As a result, the cancerous cells divide continuously to give rise to masses of cells called tumour or neoplasm.
SECTION – C
(Section C has a case-based question of 5 marks.)
Question 13.
Gene manipulation is a fast-emerging science that started with development of recombinant DNA molecule. It is also known as genetic engineering. This technology which basically involves cutting and Ligating of desired DNA fragments, is based on two important discoveries in bacteria. One of them is the plasmid in bacteria and the other is restriction endonucleases. The birth of recombinant DNA technology occurred when Cohen and Boyer (1973) successfully introduced a piece of gene containing foreign DNA into plasmid ofE coli.
Based on this answer the questions that follow:
(A) (i) A five-year-old boy was found to be deficient in his immune system since birth. His family was told that this was due to an enzyme deficiency which is very important for the
immune system to function properly. Name the enzyme whose deficiency is responsible for the disease. By which technique it can be cured?
(ii) Write any two advantages of genetically modified crops.
(B) Name two more methods that are used to treat the disease of the five-year-old boy.
OR
The teacher was comparing the conventional crops with transgenic crops and presented the picture shown below which depicts the advantages of a genetically modified corn over a conventionally grown corn.
Based on this answer the questions that follow:
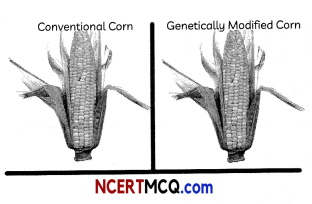
(A) In transgenics, which gene determines the expression of transgene in target tissue?
(B) Give one major concern regarding the production of genetically modified crops.
(C) Name any one genetically modified crop apart from corn and its genetically conferred trait.
(D) List any two advantages of producing genetically modified crops with respect to farmers. 5
Answer:
(A) (i) The enzyme whose deficiency is responsible for the disease is Adenosine deaminase. It can be cured by the technique of gene therapy.
(ii) Two advantages of genetically modified crops are:
- GM crops are tolerant to stresses such as heat, cold, drought.
- GM crops are pest resistant, thus reduce the use of pesticides.
Example: Bt cotton
(B) Two methods that are used to treat adenosine deaminase deficiency besides gene therapy are:
- Bone marrow transplantation
- Enzyme replacement therapy
OR
(A) A reporter gene is used to determine whether the recombinant DNA has been successfully introduced into a cell or not.
![]()
Related Theory
Reporters are used as indicators to study gene expression. A transgenic organism contains a
gene introduced by one or the other technique of transfection in its genome. This introduced gene with the help of transfection is called transgene.
(B)
- Development of resistant weeds and insects
- Difficulty of preserving the identity of non-GM crops
- Harm to other organisms (Any one)
Related Theory
Gene movement from crop to weed through pollen transfer has been seen for GM crops when the crop is grown near a closely related weed species. Similarly, insects developed a resistance to pesticides. Potential cross-pollination of GM seeds onto non- GM crops is also a concern to farmers
A study showed that a gene contained within Bt corn can be harmful to the larvae of a monarch butterfly.
(C)
| Genetically modified crop | Genetically conferred trait |
| Soyabean | Herbicide tolerance |
| Canola | Altered fatty acid composition |
| Plum | Virus resistance |
(D) The advantages are as follows:
- Increased crop yields
- Diminished use of pesticides and herbicides.
- Increased profits earned by farmers.
(Any two)