Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules Class 9 Science Important Questions with Answers PDF will help you in scoring more marks in your exams.
Atoms and Molecules Class 9 Important Questions and Answers Science Chapter 3
Question 1.
What is cation ? Give one example.
Answer:
A cation is an atom or group of atoms carrying positive charge on it.
More Resources
- Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science
- Value Based Questions in Science for Class 9
- HOTS Questions for Class 9 Science
Question 2.
Mention two postulates of Daltons atomic theory that explain :
(a) Law of conservation of mass.
(b) Law of constant proportions.
Answer:
(a) Law of conservation of mass: The total mass of the products in a physical change or a chemical reaction is equal to the total mass of the reactants that have combined.
(b) Law of constant proportions: A pure chemical compound always consists of the same elements that are combined together in a fixed (or definite) proportion by mass.
Question 3.
Name the compound Al2(SO4), and mention the ions present in it.
Answer:
The compound is called aluminium sulphate; cation : Al3+ ; anion : (SO4)2-
Question 4.
Write the formulae and the names of the ions formed by the combination of
(i) Fe3+ and SO42-
(ii) NH4+ and CO32- . (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
(i) Fe2(SO4), : Ferric sulphate or Fe (III) sulphate.
(ii) (NH4)2CO3 : Ammonium carbonate or Ammonium(I)carbonate.
Question 5.
(a) Define ‘atomic mass unit’. How is it linked with relative atomic mass ?
(b) How do you know the presence of atoms if they do not exist independently for most of the elements ?
(CBSE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Atomic mass unit (u) is 1/12 of the mass of one atom of C-12. Relative atomic mass of the atom of an element is the average mass of the atom as compared to 1/12th of the mass of C-12 atom .
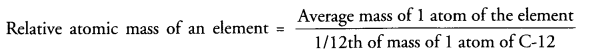
(b) Atoms of most of the elements do not exist independently. However, they combine in specific numbers to form molecules or ions which we can feel and know about their presence.
For example,
* A molecules of H2SO4 consists of 2 atoms of H + 1 atom of S + 4 atoms of O
* A molecules of C12H22O11 consists of 12 atoms of C + 22 atoms of H + 11 atoms of O
* Ammonium ion (NH4+) consists of 1 atom of N + 4 atoms of H
Question 6.
With the help of a labelled diagram describe an activity to demonstrate the law of conservation of mass.
(CBSE 2011)
Answer:
In order to illustrate the law of conservation of mass, let us carry the same chemical reaction in the laboratory. The procedure is quite simple. In a graduated cylinder, prepare about 10% solution of one of the reactants say barium chloride in water. For that, weigh accurately 10 gram of the sample and dissolve in water with stirring in the graduated cylinder. Add more of water so as to touch 100 mL mark. This is 10 percent solution of the reactant. Transfer a portion of this solution in a conical flask as shown in figure 3.1.
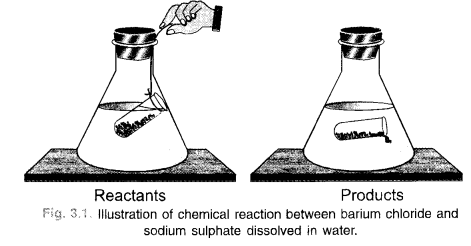
In a similar manner, prepare 10% solution of sodium sulphate also. Take a portion of this solution in a small glass tube. Place the tube carefully in the flask without disturbing it. Even a thread can be used for the purpose. Cork the flask and weigh it on a balance. Shake the flask for sometime by hand so that the two reactants mix together and react to form the products. Barium sulphate is in the form of a white precipitate. The other product sodium chloride is water soluble. Weigh the flask again and notice if there is any change in weight. No change will be noticed. This means that the mass of reactants is the same as the mass of the products and this verifies the law of conservation of mass.
Question 7.
(a) Define Avogadro’s number. Why is it also known as Avogadro’s constant ?
(b) Calculate the molar mass of Na2O.
(c) Find the mass of 10 moles of carbon dioxide. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Avogadro’s number is the number of particles (atoms, ions, molecules etc.) present in one mole of any substance. It is denoted either as NA or as NQ. The number is also called Avogadro’s constant because its value is fixed (6.022 x 1023) irrespective of the nature of the particles.
(b) Molar mass of Na2O = 2 x Atomic mass of Na + Atomic mass of O
= 2 x 23 u + 16 u = 62 u
(c) Mass of 10 moles of CO2= 10 x 44 u = 440 u.
Question 8.
(a) How many gram molecules of H2SO4 are present in 4.9 g of the acid ?
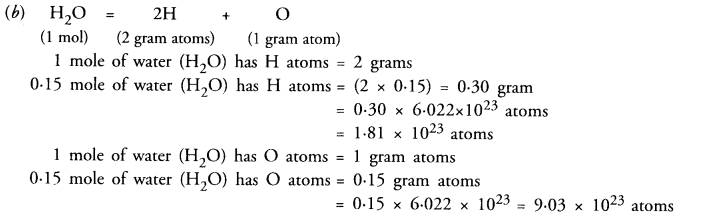
(b) How many atoms of hydrogen and oxygen are present in 0-15 mole of water (H2O) ? (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Gram molecular mass of H2SO4 = 2 x 1 + 32 + 4 x 16 = 98 g
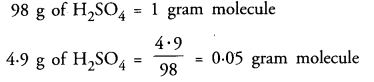
Question 9.
(a) Calculate the formula unit mass of Na2SO4
(b) What is the mass of one mole of sulphur atoms ?
(c) Convert 12 g of oxygen into mole. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Na2SO4 is an ionic compound. Therefore its formula unit mass is the same as its molecular mass
= 2 x 23 + 32 + 4 x 16 = 142 u
(b) The mass of one mole of sulphur atoms = 32 u.
(c) 32 g of sulphur = 1 mol
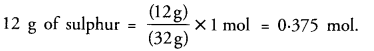
Question 10.
(a) Define atomic mass unit.
(b) Distinguish between molecular mass and molar mass.
Answer:
(a) Atomic mass unit (u) is 1/12 of the mass of one atom of C-12. Relative atomic mass of the atom of an element is the average mass of the atom as compared to 1/12th of the mass of C-12 atom.
(b) Molecular mass of a substance expressed in grams is known as its moles mass. This means that molecular mass is expressed in units ‘u’ while molar mass is expressed in units ‘grams’.
Question 11.
What is meant by the term chemical formula ? Write the chemical formula of calcium oxide. Calculate its formula unit mass. (Atomic mass of Ca = 40 u, O = 16 u).
Answer:
Molecule represents a group of two or more atoms (same or different) chemically bonded to each other and held tightly by strong attractive forces. Molecules are represented in terms of symbols of constituting atoms and it is known as chemical formula.
Chemical formula of calcium oxide = CaO.
Formula unit mass = Atomic mass of Ca + Atomic mass of O = (40 + 16) = 56 u.
Question 12.
Name a non-metal which is tetratomic. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
The non-metal is phosphorus. It exists as molecule and is tetratomic.
Question 13.
Name the cation and anion which constitute the molecule of magnesium oxide. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
The formula of magnesium oxide is MgO. The cation and anions which constitute the molecule are Mg2+ and O2- ions.
The percentage of three elements calcium , carbon and oxygen in a sample of calcium carbonate is given as : Calcium = 40% ; Carbon = 12.0% ; Oxygen = 48%
Question 14.
If the law of constant proportion is true, what weights of these elements will be present in 1.5 g of another sample of calcium. Carbonate ?
(Atomic mass of Ca = 40 u, C = 12 u, O = 16 u). (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
We have learnt that according to the law of constant proportions, the percentages of the elements present in different samples of a pure substance always remain the same. This means that in the second sample of calcium carbonate, the ratio of the different elements present will remain the same or will remain unchanged. Thus,

Question 15.
An element has valency 3. Write the formula of its oxide. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
The valency of oxygen is 2 while that of element E is 3. The formula of the oxide of the element is : E2O3.
Question 16.
Calculate formula unit mass of Al2(SO4)3. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
Formula unit mass of Al2(SO4)3 (Aluminium sulphate)
= (2 x Atomic mass of Al) + (3 x Atomic mass of S) + (12 x Atomic mass of O)
= (2 x 27) + (3 x 32) + (12 x 16)
= (54 + 96 + 192) = 342 u.
Question 17.
(a) State six postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory.
(b) A 0.24 g sample of compound of carbon and oxygen on analysis was found to contain 0.096 g of carbon and 0.144 g of oxygen. Find the percentage composition of the compound by weight. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
(a) The important features of the Dalton’s Atomic Theory are listed :
- Every matter is made up of very small particles known as atoms.
- Atoms are the ultimate particles of matter and cannot be further sub-divided into smaller particles.
- Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed during a physical change or a chemical reaction.
- All atoms of a particular element are identical in all respects. This means that they have same mass, size and also same chemical properties.
- Atoms of different elements have different masses, sizes and also chemical properties.
- Atoms are the smallest particles of matter which can take part in chemical combination.
- Atoms of the same or different elements combine in small whole number ratios to form molecules of a compound.
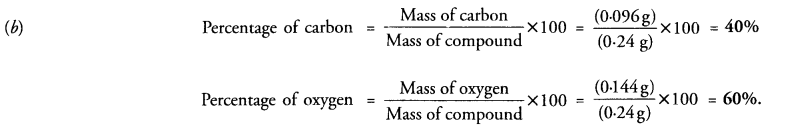
Question 18.
(a) Find the mass of 10 moles of sodium sulphite (Na2SO4).
(b) Calculate the number of molecules in 8 g of oxygen gas.
(c) Convert 22 g of CO2 into moles.
Answer:
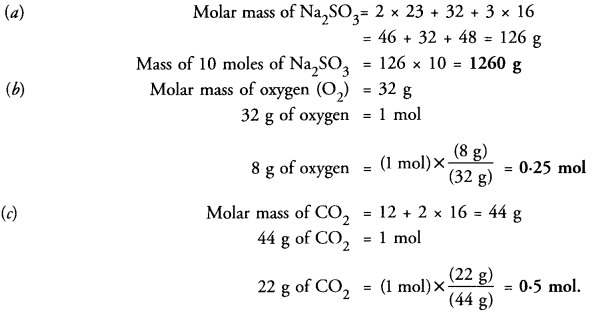
Question 19.
How many grams of sodium will have the same number of atoms as 6 grams of magnesium ?
(Given Na = 23 u, Mg = 24 u) ? (CBSE 2012, 2016)
Answer:
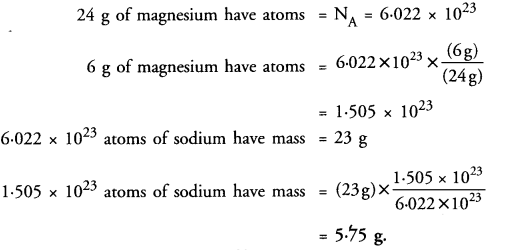
Question 20.
Calculate the mass of 1.2044 x 1023 molecules of O2 (Atomic mass of O = 16 u).
Answer:
6.022 x 1023 (NA) molecules of O2 have mass = 32 u
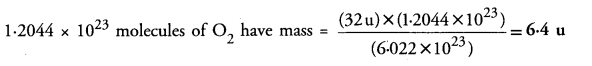
Question 21.
With the help of an activity, show that there is no change in mass when a chemical change (chemical reaction) takes place. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
The mass can neither he created nor destroyed in a physical change or a chemical reaction.
In other words, the mass remains unchanged or conserved in a chemical reaction. The law is also known as the Law of Indestructibility of Matter.
Explanation : Let us try to analyse as to what happens in a chemical reaction. To understand the same, let us consider a chemical reaction between barium chloride and sodium sulphate. When the solutions of these reactants prepared separately in water are mixed, the following chemical reaction takes place :
Barium chloride + Sodium sulphate ———– > Barium sulphate + Sodium chloride (white precipitate)
Question 22.
How are given mass, molar mass and number of moles related to each other ? (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
No. of moles = Mass/Molar mass.
Question 23.
(a) Define polyatomic ions. Write an example.
(b) Calculate the formula unit mass of CaCO3(Atomic mass of C = 12 u, Ca = 40 u, O = 16 u)
(c) Calculate the molecular mass of the following :
(i) HNO3
(ii) CH3COOH
Atomic mass of H = 14, N = 14 u, O = 16 u, C = 12 u) (CBSE 2013, 2015)
Answer:
(a) Polyatomic ions are the ions representing a group of atoms which carry either positive or negative charge. For example, SO4-2 ion.
(b) Formula unit mass of CaCO3 = (1 x Atomic mass of Ca) + (1 x Atomic mass of C) + (3 x Atomic mass of O)
= 4 (1 x 40 u) + (1 x 12 u) + (3 x 16 u) = 100 u .
(c) Molar mass of HNO3 = (1 x Atomic mass of H) + (1 x Atomic mass of N) + ( 3 x Atomic mass of O)
= (1 x 1 u) + (1 x 14 u) + (3 x 16 u) = 63 u.
Molecular mass of CH3COOH = (2 x Atomic mass of C) + (4 x Atomic mass of H) + (2 x Atomic mass of O) .
= (2 x 12 u) + (4 x 1 u) + (2 x 16 u) = 60u
Question 24.
What do you understand by 1 amu ? (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
1 amu (or lu) is l/12th of the mass of one atom of carbon taken as 12.
Question 25.
Write the molecular formulae of all the compounds that can be formed by the combination of the following ions : Cu2+, Na+, Fe3+, Cl–, SO4-2 (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
In this case, the compounds can be formed by the combination of cations and anion. Therefore, the molecular formulae of different compounds are :
CuCl2, CuSO4, NaCl, Na2SO4, FeCl3, Fe2(SO4)3.
Question 26.
What are chemical reactions according to the Law of conservation of mass ? (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
According to law of conservation of mass, chemical reactions involve only the exchange of partners in the reactants to form products. That is why, there is no change in mass.
Question 27.
Write any five features of Dalton’s atomic theory. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
The important features of the Dalton’s Atomic Theory are listed :
- Every matter is made up of very small particles known as atoms.
- Atoms are the ultimate particles of matter and cannot be further sub-divided into smaller particles.
- Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed during a physical change or a chemical reaction.
- All atoms of a particular element are identical in all respects. This means that they have same mass, size and also same chemical properties.
- Atoms of different elements have different masses, sizes and also chemical properties.
Question 28.
What is atomicity of an element ? Give two examples. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
The atomicity of an element is the number of atoms present in one molecule of the element. For example,
Atomicity of oxygen in O2 = 2
Atomicity of oxygen in O3 = 3.
Question 29.
Write the chemical formulae of the following :
(a) Magnesium sulphate
(b) Calcium oxide
(c) Sodium sulphide
(d) Aluminium phosphate
(e) Potassium chloride
(f) Calcium carbonate. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
(a) MgSO4
(b) CaO
(c) Na2S
(d) Al2(PO4)3
(e) KCl
(f) CaCO3.
Question 30.
A compound XH is formed by the combination of an element X with hydrogen. Find the valency of the element. State the formula of the compound formed by the combination of
(a) X with nitrogen
(b) X with oxygen. (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
In the compound XH, the valency of element X is 1.
(a) The valency of nitrogen is 3.
The valency of element X is 1.
The formula of the compound = NX3
(b) The valency of oxygen is 2.
The valency of element X is 1.
The formula of the compound = OX2
Question 31.
Calculate the number of molecules of SO2 present in 44 g of it.
Answer:
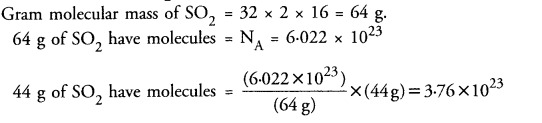
Question 32.
Write the Latin names of sodium and iron.
Answer:
Latin name of sodium (Na) = Natrium
Latin name of iron (Fe) = Ferrum.
Question 33.
Write the formula and names of the compounds formed by the following ions.
(a) Potassium ion and iodide ion.
(b) Sodium ion and sulphide ion.
(c) Aluminium ion and phosphate ion.
Answer:
The compounds are :
(a) KI (Potassium iodide)
(b) Na2S (Sodium sulphide)
(c) AlPO4 (Aluminium phosphate)
Question 34.
Calculate formula unit mass of Na2CO3.10H2O.
Answer:
Formula unit mass of Na2CO3.10H2O
= 2 x Atomic mass of Na + Atomic mass of C + 3 x Atomic mass of O + 10 x Molecular mass of H2O
= 2 x 23 + 12 +3 x 16 + 10 x 18 = 286 u.
Question 35.
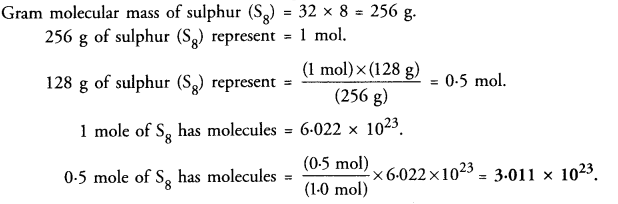
Calculate the number of molecules of sulphur (S8) present in 128 g of sulphur.
Answer:
Question 36.
Calculate the number of oxygen atoms present in 120 g of nitric acid.
Answer:
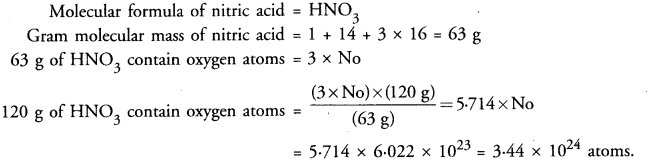
Question 37.
What do you understand by the word ‘mole’ ? (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
A mole denotes Avogadro’s number of particles i.e., 6.022 x 1023. These may be electrons, protons, neutrons, atoms, ions etc.
Question 38.
In a chemical reaction, 10.6 g of sodium carbonate reacted with 12 g of ethanoic acid. The products obtained were 4.4 g of carbon dioxide, 16.4 g of sodium ethanoate and 1.8 g of water.
(a) Write a word equation, clearly showing the reactants and products as given above.
(b) Also show that this data is in agreement with the law of conservation of mass. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
(a) The word equation for the chemical reaction is :

(b) Mass of reactants = (10.6 + 12) = 22.6 g
Mass of products = (16.4 + 4.4 +1.8) = 22.6 g
Since the mass of reactant species is equal to the mass of the product species, the data illustrates the law of conservation of mass.
Question 39.
What is the name given to the number of 6.022 x 1023 particles ? (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
It is called Avogadro’s number and is denoted by the sign NA or NQ.
Question 40.
Write the chemical names of the following compounds :
(a) K2SO4
(b) Mg3(PO4)2
(c) NH4Cl
(d) ZnS
(e) Na3N
(f) AgBr (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Potassium sulphate
(b) Magnesium phosphate
(c) Ammonium chloride
(d) Zinc sulphide
(e) Sodium nitride
(f) Silver bromide.
Question 41.
How did Berzelius assign symbols to the elements ? (CBSE 2016)
Answer:
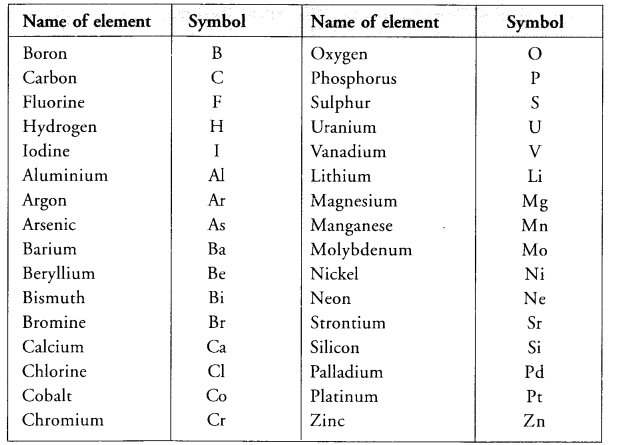
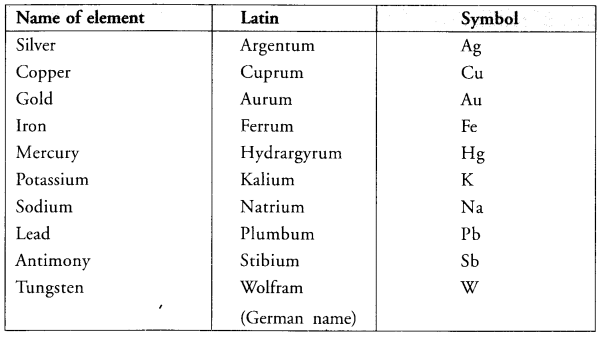
Hope given Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules are helpful to complete your science homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online science tutoring for you.