Here we are providing Class 12 Biology Important Extra Questions and Answers Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare. Important Questions for Class 12 Biology are the best resource for students which helps in Class 12 board exams.
Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Important Extra Questions Microbes in Human Welfare
Microbes in Human Welfare Important Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Which bacterium Is responsible for the formation of curd from milk?
Answer:
Lactobacillus but Agaricus (Lactic acid bacteria).
Question 2.
What is brewing?
Answer:
Brewing is a complex fermentation process, which involves the production of malt beverages such as beer, ale, porter, and stout with the help of strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Question 3.
Name the type of association that genus Glomus exhibits with the higher plant. (CBSE2014)
Answer:
Mycorrhiza- Symbiotic association.
Question 4.
Which one of the following is the baker’s yeast used in fermentation-Saccharum Barberi, Saccharomyces cerevisiae or Sonalika? (CBSE2009)
Answer:
Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Question 5.
Milk starts to coagulate when Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) is added to milk as a starter. Mention two benefits that LAB provides. (CBSE 2009)
Answer:
- LAB checks the growth of disease-causing microbes.
- LAB converts milk into curd and also increases nutritional quality by increasing vitamin B12.
Question 6.
Give the scientific name of the source organism from which the first antibiotic was produced. (CBSE Sample paper 2018-19)
Answer:
Penicillium Notatum
Question 7.
Name the different vitamins which are produced by micro-organisms.
Answer:
- Riboflavin or Vitamin B2 is produced by yeast and bacteria.
- Vitamin B12 or cobalamine is produced by bacteria and actinomycetes.
Question 8.
Name the original wild strain of the mold by which vitamin B2 is produced.
Answer:
Ashbya Gossypii.
Question 9.
What is a single-cell protein (SCP)?
Answer:
Single-cell protein (SCP) refers to any microbial biomass produced by uni and multi-cellular organisms and can be used as food or feed additives.
Question 10.
Name a microbe used for statin production. How do statins lower blood cholesterol levels?
Answer:
Microbe:
Monascus Purpureus Mechanism: Statins are competitive inhibitors of enzymes required for cholesterol synthesis. Therefore, play role in decreasing cholesterol level in the body.
Question 11.
‘Swiss cheese’ is characterized by the presence of large holes. Name the bacterium responsible for it. (CBSE Delhi Outside 2019)
Answer:
Propionibacterium sharmanii
Question 12.
What for Nudeopolyhedra viruses (NVP) are being used nowadays? (CBSE, Delhi 2014, 2019C)
Answer:
Nudeopolyhedro viruses are being used to kill insects and other arthropods pests of crops. The viruses have no effect on plants and non-target animals. Thus used in biological control of pests.
Question 13.
How has the discovery of antibiotics helped mankind in the field of medicine?
Answer:
Antibiotics have helped mankind in treating most of the deadly bacterial and fungal diseases of humans.
Question 14.
Why is distillation required for producing certain alcoholic drinks?
Answer:
For increasing the alcohol strength or concentration of the drinks.
Question 15.
What is the primary sludge?
Answer:
All the solids that settle from the sewage on primary treatment constitute primary sludge.
Question 16.
What is the relationship between BOD and organic matter in sewage?
Answer:
The greater the BOD of wastewater more is the amount of organic matter in sewage.
Question 17.
Name two gases produced during secondary treatment by sewage.
Answer:
- Carbon dioxide and
- Hydrogen sulfide.
Question 18.
What are bioreactors?
Answer:
In the pilot plant, the glass vessels are replaced by stainless steel vessels. They are called bioreactors.
Question 19.
Name the bacteria which can be used for yogurt formation.
Answer:
- Lactobacillus bulsaricus.
- Streptococcus Thermophilus.
Question 20.
What is Bacitracin?
Answer:
It is an antibiotic obtained from Bacillus Licheniformis.
Question 21.
Name the group of organisms and the substrate they act on to produce biogas. (CBSE 2009)
Answer:
Methanogens such as Methanol bacterium act on activated sludge to produce biogas.
Question 22.
WrIte the scientific name of the microbe used for fermenting malted cereals and fruit juices. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Question 23.
Write an alternate source of protein for animal and human nutrition. (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
Single-cell proteins.
Question 24.
How are the members of the genus Glomus useful to organic farmers? (CBSE Delhi Outside 2019)
Answer:
Many members of the genus Glomus form mycorrhizae- symbiotic associations with roots of higher plants. The fungal component of these associations helps in the absorption of phosphorus from soil. It also makes the plant drought-resistant.
Microbes in Human Welfare Important Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Expand the ‘LAB’. How are LABs beneficial to humans? (Write any two benefits) (CBSE 2019 C)
Answer:
LAB-Lactic Acid Bacteria Benefits:
- Found in curd. They improve the nutritional quality of food.
- Yogurt is prepared from milk by Lactobacillus Bulgaricus.
Question 2.
What is cyclosporin A? What is its importance?
Answer:
Cyclosporin A. It is an eleven-membered cyclic oligopeptide obtained through the fermentative activity of fungus Trichoderma Polysporum.
Importance. It has antifungal, anti-inflammatory, and immunosuppressive properties. It inhibits the activation of T-cells and therefore, prevents rejection reactions in organ transplantation.
Question 3.
How do antibiotics act?
Answer:
Antibiotics do not have identical effects on all harmful microbes. All of them inhibit growth or destroy bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Actually, antibiotic molecules should disrupt a vital link in the microbe’s metabolism and this link is their target or point of impact.
Question 4.
Write the various steps of fermentation.
Answer:
The major steps of fermentation are:
- Sterilization of the fermenter and medium in steam. It is carried out under pressure and high temperature.
- Inoculation of a selected strain of the yeast.
- Recovery of the product.
Question 5.
What are the two ways by which micro-organisms can be grown in bioreactors?
Answer:
Micro-organisms can be grown in the bioreactors in two ways:
- As a layer or film on the surface of the nutrient medium. It is known as a support growth system.
- By suspending cells or mycelia in a liquid medium contained in the growth vessel. It is known as a suspended growth system.
Question 6.
What is sewage? In which way can this be harmful?
Answer:
Sewage is used and wastewater consisting of human excreta, wash waters, industrial and agricultural wastes that enter the sewage system. In general, sewage contains 95.5% water and 0.1 to 0.5% organic and inorganic matter. They are very harmful to us due to the presence of a variety of micro¬organisms in them, most of which are highly pathogenic. Sewage has a high BOD value, which develops anaerobic conditions in water resulting in the death of water animals and emitting foul smell due to incomplete oxidation of organic materials in the sewage.
Question 7.
What is the key difference between primary and secondary sewage treatment?
Answer:
Primary treatment of wastes is the screening and removal of insoluble particulate materials, by addition of alum and other coagulants. It is the physical removal of 20-30% of organic materials present in sewage in particulate form. Secondary treatment of waste is the biological removal of dissolved organic matter through trickling filters, activated sludge, lagoons, extended aeration systems, and anaerobic digestors.
Question 8.
Draw a simple diagram to show an anaerobic sludge digester.
Answer:
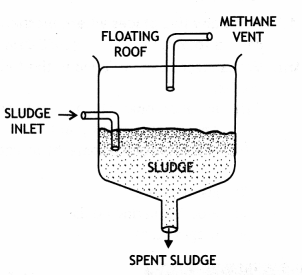
Anaerobic sludge digester.
Question 9.
GIve the full form of Bt. Name the insects killed by It.
Answer:
The full form of Bt is Bacillus Ttiuringiensis. It kills a wide range of Insects Like moths, beetles, mosquitoes, aphids, and termites.
Question 10.
Why are biofertilizers or biopesticides preferred to chemical fertilizers or pesticides? (CBSE Delhi 2011)
Answer:
Biofertilizers or biopesticides are preferred to chemical fertilizers or pesticides because
- They are safe to use and are biological in origin.
- They do not spoil the quality of the soil and are target-specific.
- They do not pollute the atmosphere and are non-poisonous.
- They are less expensive and are biodegradable.
Question 11.
Name the blank spaces a, b, c, and d from the table given below: (CBSE 2008)
| Type of microbe | Scientific name | Product | Medical application |
| (i) Fungus | a | Cyclosporin | B |
| (ii) c | Mascus Purpureus | Statin | d |
Answer:
(a) Trichoderma polypore
(b) Organ transplantation (Immunosuppressant)
(c) Yeast
(d) Blood cholesterol-lowering agent
Question 12.
How does the addition of a small amount of curd to fresh milk help the formation of curd? Mention a nutritional quality that gets added to the curd. (CBSE Delhi 2010 and Outside Delhi 2019)
Answer:
- Curd is prepared from milk.
- Microorganisms such as Lactobacillus and others commonly called lactic acid bacteria (LAB) grow in milk and convert it to curd.
- During growth, the LAB produces acids that coagulate and partially digest the milk proteins.
- A small amount of curd added into the fresh milk as inoculum or starter contains millions of LAB which at suitable temperatures multiply, thus converting milk to curd, which also improves its nutritional quality by increasing vitamin B12.
- In our stomach too, the LAB plays a very beneficial role in checking disease-causing microbes.
Question 13.
Name a free-living and symbiotic bacterium that serves as a biofertilizer. Why are they called so? (CBSE Outside Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria Azotobacter and Bacillus Polymyxa Symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Rhizobium.
These micro-organisms enrich the soil by fixing nitrogen. They enhance the availability of nutrients to crops, thus called biofertilizers.
Question 14.
(i) Why are fruit juices bought from the market clearer as compared to those made at home?
Answer:
Bottled juices are clarified by the use of pectinases and proteases.
(ii) Name the bioactive molecules produced by Trichoderma Polysporum and Monascus Purpureus. (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(a) Bioactive molecules produced by Trichoderma polypore are cyclosporin A. It is used as an immunosuppressive agent in organ- transplant patients.
(b) Bioactive molecules produced by Monascus Purpureus are statins. It is a blood cholesterol-lowering agent.
Question 15.
Your advice is sought to improve the nitrogen content of the soil to be used for the cultivation of a non-leguminous terrestrial crop.
(i) Recommend two microbes that can enrich the soil with nitrogen.
Answer:
Azospirillum, Azotobacter, Anabaena, Oscillatoria (Any two)
(ii) Why do leguminous crops not require such enrichment of the soil? (CBSE 2018)
Answer:
Leguminous crops do not require such enrichment of the soil because they have a symbiotic association with Rhizobium bacteria which traps nitrogen directly from the atmosphere and provides it to the plant and in turn gets food and shelter.
Question 16.
What are ‘floes’, formed during secondary treatment of sewage? (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Floes are masses of bacteria, associated with fungal filaments to form mesh-like structures.
Question 17.
Write any two places where methanogens can be found. (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Methanogens can be found in the following places:
- In anaerobic sludge (digester) of a sewage treatment plant
- In rumen (gut/stomach) of cattle or ruminants
- Marshy areas
- Flooded paddy fields
- Biogas plant Methane, H2S, and C02 are produced during microbial digestion of organic compounds in case of secondary treatment of sewage.
- The dung of the cattle produces methane gas in the biogas plants.
Microbes in Human Welfare Important Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Give examples to prove that microbes release gases during metabolism.
Answer:
- Large holes in ‘Swiss Cheese’ are due to the production of a large amount of C02 by a bacterium named Propionibacterium shamanic.
- The puffed-up appearance of dough is due to the production of C02 gas by yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
- Methane, H2S, and CO2 are produced during microbial digestion of organic compounds in the case of secondary treatment of sewage.
- The dung of the cattle produces methane gas in the biogas pLants.
Question 2.
Make a table showing industrial products obtained from activities of bacteria.
Answer:
industrial products obtained from use activities of Bacteria:
|
Products |
Bacteria |
| Acetone, butanol | Clostridium Aceto bretylium |
| Acetic acid, Vinegar | Acetobacter acetic |
| Curing of tobacco | Bacillus megatherium micrococcus |
| Curing of tea leaves | Micrococcus conditions |
| Lactic acid | Lactobacillus Delbreuckii |
| Lysine | Micrococcus glutamic |
| Retting of fibers | Clostridium but lyricism |
| Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) | Clostridium but lyricism |
| Cobalamin (Vit. B17) | Bacillus megatherium |
Question 3.
What are Baculo viruses? Write their significance.
Answer:
Baculoviruses are those viruses, which attack insects and other arthropods, e.g. Nuclepolyhedrovirus.
Significance:
- Baculoviruses are species-specific and narrow-spectrum insecticides.
- They have no negative impacts on plants, birds, mammals, or even other non-target insects.
- The desirable aspect In conservation of beneficial insects in overall integrated pest management (IPM) program as in an ecologically sensitive area.
Question 4.
Which nitrogen fixers are available on a commercial basis In the market? Also, name the beneficial crop.
Answer:
|
Products |
Microbe used |
Beneficial crop |
| 1. Nitragin TM | Rhizobium | Soybean |
| 2. Rhizocote | Rhizobium | Legumes |
| 3. Nodosit | Rhizobium | Legumes |
Question 5.
Distinguish between the roles of floes and anaerobic sludge digester in sewage treatment. (CBSE Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Floes are masses of bacteria associated with fungal filaments to form mesh-like structures. These microbes digest a lot of organic matter, converting it into microbial biomass and releasing a lot of minerals. Anaerobic sludge digester is a large tank in which anaerobic microbes digest the anaerobic mass as well as aerobic microbes of sludge. Biogas is produced by methanogens. It is inflammable and a source of energy.
Question 6.
Tabulate the list of common antibiotics, organisms producing them, and organisms sensitive to these antibiotics.
Answer:
|
Name of Antibiotic |
Name of Producing Organism |
Sensitive Organisms |
| (i) Penicillin | Penicillium | Most of the Gram+ve bacteria, Clostridium actinomycetes, Spirochaetae, and Corynebacterium. |
| (ii) Streptomycin | Streptomyces griseus | Gram + ve and Gram – ve bacteria; Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
| (iii) Bacitracin | Bacillus licheniformis | Treponema, Histoplasma, Clostridium. |
| (iv) Tetracycline and Chlorotetracycline | Streptomyces aureofaciens | Rickettsiae, Klebsiella pneumonia, Streptococcus. |
| (v) Synthromycin | Streptomyces erythematous | Gram+ve; Gram-ve bacteria and many viruses. |
| (vi) Chloromycetin | Streptomyces Venezuelae | Gram+ve; Gram-ve bacteria; Entamoeba, Borrelia. |
Question 7.
Give a flow chart of sewage treatment.
Answer:
Flow chart of sewage treatment:
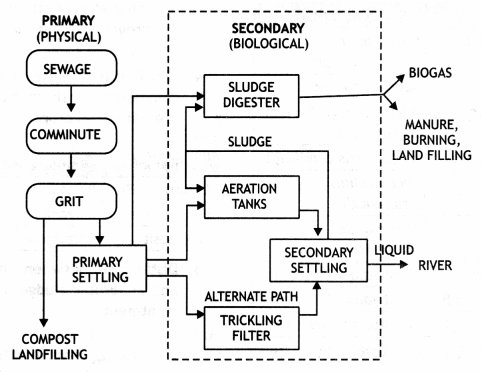
Flow chart of sewage treatment
Question 8.
List the events that lead to the production of biogas from wastewater whose BOD has been reduced significantly. (CBSE Dethi 2016)
Answer:
- During secondary treatment of wastewater, sewage fungus forms focus.
- BOD decreases. As it decreases to 10-15% of originaL sewage, the wastewater Is taken to a Large settling tank where the focus of sewage fungus settles down.
- The supernatant can be passed into water bodies or treated further.
- The organic sediment is passed into an anaerobic sludge digester where anaerobic microbes methanogens decompose organic matter.
- It is accompanied by the production of blogs and the formation of manure or compost.
Question 9.
Explain the basis of biological control of weeds.
Answer:
Basis of biological control of weeds:
- Biological control of weeds involves breeding of insects that would feed selectively a weed or use of certain micro-organisms which will produce diseases in the weeds and eliminate them.
- Certain crop plants do not allow the growth of weeds nearby. They are called smoother plants such as Barley, Rye, Sorghum, Millet, etc. They eliminate weeds through chemicals.
- In some cases, specially tailored plants called transgenic plants have been introduced which have tolerance against weeds.
- In India and Australia, the overgrowth of cacti was checked by the introduction of the cochineal insect (Cactoblastis cactorum).
- The latest technique is to use fungal spores to control weeds. These are suitable because they can be kept for a long time and also resist adverse conditions.
Question 10.
What are biofertilizers? What are the main sources of biological nitrogen fixation? Name two organisms that fix nitrogen symbiotically and two organisms that fix symbiotically.
Answer:
Biofertilizers are organisms that can bring about soil nutrient enrichment by their biological activity.
- Sources of biofertilizers: Bacteria, cyanobacteria, and fungi.
- Biological nitrogen fixation: The conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogenous compounds through the agency of living organisms is called biological nitrogen fixation.
Symbiotically nitrogen-fixing organisms:
- Rhizobium leguminosarum, Frankia Bacillus radicicola.
- Free-living/Asymbiotic nitrogen-fixing organisms-Cyanobacteria, Azotobacter.
Question 11.
(a) What is biogas? What are its components? What is the calorific value of biogas? (CBSE Outside Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Biogas is a methane-rich fuel gas produced by anaerobic breakdown or digestion of biomass with the help of methanogenic bacteria.
Components of biogas: Methane, Carbon dioxide, Hydrogen sulfide, hydrogen, and nitrogen.
Calorific value 23-28 MJ/m3.
(b) Why is a slurry of cattle dung (gobar) added to bio-wastes in the tank of a gobar gas plant for the generation of biogas? (CBSE Delhi 2019 C)
Answer:
Slurry consisting of excreta dung of cattle commonly called gobar is rich in methanogen bacteria. It is used for the generation of biogas. These bacteria called methane bacterium grow anaerobically and break down the cellulose of dung to liberate gases such as methane, C02, and H2.
Question 12.
(?) Name the toxin produced by B. Thuringiensis.
Answer:
∝-exotoxin, β-exotoxin, γ-exotoxin, and louse factor
(ii) Nitrogen fixers are available on a commercial basis in the market? Also, name the beneficial crop and microbes used in the following table.
|
Product |
Microbe used |
Beneficial crop |
| 1. NitraginTM | (A) | Soybean |
| 2. Rhizocote | Rhizobium | (B) |
| 3. Nodosit | Rhizobium | (C) |
Answer:
A. Rhizobium B. Legume C. Legume
(iii) Expand BOD and COD
Answer:
BOD- Biological Oxygen Demand COD- Chemical Oxygen Demand
Question 13.
By a flow chart showing the stages in anaerobic digestion during the production of biogas.
Answer:
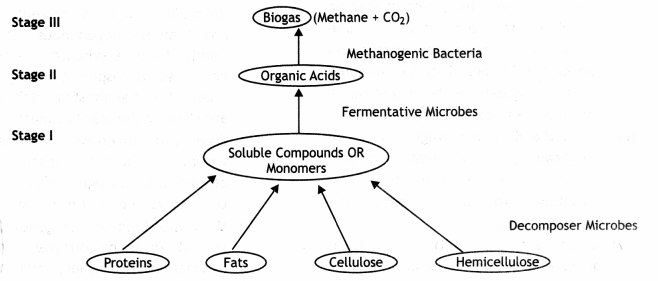
Stages in Anaerobic Digestion during biogas formation
Question 14.
Given below is a list of six microorganisms. State their usefulness to humans.
(i) Nucleopolyhedrovirus
(ii) Saccharomyces cerevisiae
(iii) Monascus Purpureus
(iv) Trichoderma polypore
(v) Penicillium Notatum
(vi) Propionibacterium shamanic. (CBSE Delhi 2016)
Answer:
|
Name of Micro-organisms |
Uses |
| (i) Nucleopolyhedrovirus | Used in biocontrol of insects |
| (ii) Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Bread making, Ethanol making |
| (iii) Monascus Purpureus | Produces Statin used as blood cholesterol-lowering agent |
| (iv) Trichoderma polypore | Preparation of cyclosporin having antifungal, anti-inflammatory, immuno-suppressive properties |
| (v) Penicillium Notatum | Production of antibiotic, Penicillin |
| (vi) Propionibacterium shamanic | Preparation of large-holed swiss cheese. |
Question 15.
Explain the different steps involved in the secondary treatment of sewage. (CBSE Sample paper 2018—19)
Or
Secondary treatment of sewage is also called biological treatment. Justify this statement and explain the process. (CBSE 2018)
Answer:
- Secondary treatment of sewage is a biological process that employs the heterotrophic bacteria naturally present in the sewage.
- The effluent from the primary treatment is passed into large aeration tanks, where it is constantly agitated and the air is pumped into it.
- This allows the rapid growth of aerobic microbes into ‘floes’ which consume the organic matter of the sewage and reduce the biological oxygen demand (BOD). The greater is the BOD of wastewater, the more is its polluting potential.
- When the BOD of sewage is reduced significantly, the effluent is passed into a settling tank, where the ‘floes’ are allowed to sediment forming the activated sludge.
- A small part of the activated sludge is pumped back into the aeration tanks.
- The remaining major part of the sludge is pumped into anaerobic sludge digesters, where the anaerobic bacteria digest the bacteria and fungi in the sludge-producing methane, hydrogen sulfide, and carbon dioxide,
i. e. biogas. This is why secondary treatment of sewage is also called biological treatment. - The effluent after secondary treatment is released into water-bodies like streams or rivers.
Question 16.
Microbes can be used to decrease the use of chemical fertilizers. Explain how this can be accomplished. (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
- Rhizobium bacteria present in the root nodules of leguminous plants (pea family) forms a symbiotic association and fixes atmospheric nitrogen into organic forms as nitrates/nitrites which are used by the plant as nutrient.
- Free-living bacteria in the soil Azospirillum and Azotobacter can fix atmospheric nitrogen thus enriching the nitrogen content of the soil.
- Many members of the genus Glomus (Fungi) form mycorrhizal symbiotic associations with higher plants. In these, the fungal symbiont absorbs phosphorus from soil and passes it to the plant.
Question 17.
(?) Organic farmers prefer biological control of diseases and pests to the use of chemicals for the same purpose. Justify.
Answer:
Chemical methods often kill both useful and harmful living beings indiscriminately. The organic farmer holds the view that the eradication of the creatures that are often described as pests is not only possible but also undesirable, for without them the beneficial predatory and parasitic insects which depend upon them as food or hosts would not be able to survive. Thus, the use of biocontrol measures will greatly reduce our dependence on toxic chemicals and pesticides.
(ii) Give an example of a bacterium, a fungus, and an insect that are used as biocontrol agents. (CBSE 2018)
Answer:
Insects = Ladybird and Dragonflies. Bacteria = Bacillus thuringiensis. Fungus = Trichoderma
Question 18.
The three microbes are listed below. Name the product produced by each one of them and mention their use.
(i) Aspergillus niger
(ii) Trichoderma polypore
(iii) Monascus Purpureus (CBSE Delhi 2018C)
Or
(i) A patient had suffered myocardial infarction and clots were found in his blood vessels. Name a ‘clot buster’ that can be used to dissolve clots and the microorganism from which it is obtained.
(ii) A woman had just undergone a kidney transplant. A bioactive molecular drug is administered to oppose kidney rejection by the body. What is the bioactive molecule? Name the microbe from which this is extracted.
(iii) What do doctors prescribe to lower the blood cholesterol level in patients with high blood cholesterol? Name the source organism from which this drug can be obtained. (CBSE Outside Delhi 2019)
Answer:
(i) Aspergillus niger produces citric acid. Citric acid is used as a flavoring agent and as a food preservative.
(ii) Trichoderma Polysporum produces a bioactive molecule cyclosporin A. It is used as an immunosuppressive agent in organ transplant patients.
(iii) Monascus Purpureus produces statins. Statins are capable of competitive inhibition of enzymes required for cholesterol synthesis. Hence, it is used as blood cholesterol-lowering agents.
Or
(i) Streptokinase-‘Clot buster’ can be used to dissolve clots. It is obtained from the bacteria Streptococcus.
(ii) The bioactive molecule is Cyclosporin A which is used as an immunosuppressive agent in organ transplantation. It is produced by the fungus Trichoderma Polysporum.
(iii) Doctors prescribe Statins to lower blood cholesterol. It is obtained from the fungus Monascus Purpureus.
Question 19.
Baculoviruses are good examples of biocontrol agents. Justify giving reasons. (CBSE Delhi 2018C)
Answer:
Baculoviruses kill insects and other arthropods, hence they are used as biocontrol agents especially Nucleopolyhedrovirus.
Reasons for their use:
- These viruses are species-specific and have narrow spectrum insecticidal applications.
- They do not harm non-target organisms like other harmless insects, birds, animals, etc.
- It is very useful in integrated pest management programs or treatment of ecologically sensitive areas.
Question 20.
Describe the primary and secondary treatment of domestic sewage before it is released for reuse. (CBSE, 2014)
Answer:
Treatment of domestic sewage. The municipal wastewaters are treated in Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) prior to disposal in water bodies.
It consists of 3 steps: primary, secondary, and tertiary.
1. Primary treatment. It includes physical processes, such as sedimentation, floatation, shredding (fragmenting and filtering). These processes remove most of the large debris.
2. Secondary treatment. It is a biological method. Activated sludge method. Sewage, after primary treatment, is pumped into aeration tanks or oxidation ponds. Here, it is mixed with air and sludge containing algae and bacteria. Bacteria consume organic matter. The process results in the release of C02 and the formation of sludge or biosolid. Algae produce oxygen for the bacteria. The water, which is now almost clear of organic matter, is chlorinated to kill microorganisms.
3. Tertiary treatment. It involves. removal of nitrates and phosphates. The water, after the above treatment, is then released. It can be reused.
Question 21.
Explain biological control of pests and plant pathogens with examples.
Answer:
The very familiar beetle with red and black markings the Ladybird, and Dragonflies are useful to get rid of aphids and mosquitoes, respectively.
Role of Bacillus Thuringinesis:
Bt Coming to microbial biocontrol agents that can be introduced in order to control butterfly caterpillars is the bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis (often written as Bt). These are available in sachets of dried spores which are mixed with water and sprayed onto vulnerable plants such as Brassica and fruit trees, where these are eaten by the insect larvae. In the gut of the larvae, the toxin is released and the larvae get killed.
The bacterial disease will kill the caterpillars, but leave other insects unharmed. Because of the development of the methods of genetic engineering in the last decade or so, scientists have introduced B. thuringiensis toxin genes into plants. Such plants are resistant to attack by insect pests. Bt-cotton is one such example which is being cultivated in some states of our country.
Biological control of plant pathogens: A biological control developed for use in the treatment of plant disease is the fungus Trichoderma. Trichoderma sp. are free-living fungi that are very common in soil and root ecosystems. They are effective biocontrol agents of several plant pathogens.
Baculoviruses are pathogens that attack insects and other arthropods. The majority of baculoviruses used as biological control agents are in the genus Nucleopolyhedrovirus. These viruses are excellent candidates for species-specific, narrow spectrum insecticidal applications.
They have been shown to have no negative impacts on plants, mammals, birds, fish, or even on non-target insects. This is especially desirable when beneficial insects are being conserved to aid in an overall IPM (integrated pest management) program, or when an ecologically sensitive area is being treated.
Question 22.
How do biofertilizers enrich the soil?
Answer:
Biofertilizers play a vital role to solve the problems of soil fertility and soil productivity.
- Anabaena azollae, a cyanobacterium, lives in symbiotic association with the free-floating water fern, Azolla. The symbiotic system Azolla-Anabaena complex is known to contribute 40-60 mg N ha-1 per rice crop. In addition to this, cyanobacteria add organic matter, secretes growth-promoting substances like auxins and vitamins, mobilizes insoluble phosphate, and thus improves the physical and chemical nature of the soil.
- Rhizobium Leguminoserum and Azospirillum fix atmospheric nitrogen as nitrates and nitrites.
- Mycorrhizae formed by an association of bacteria and roots of higher plants increase soil fertility.
Question 23.
Discuss the role of Microbes as Biofertilizers. (CBSE Delhi 2011, 2015, 2019)
Answer:
Role of microbes as biofertilizers:
Bacteria, cyanobacteria, and fungi (mycorrhiza) are the three groups of organisms used as biofertilizers.
1. Bacteria:
(a) Symbiotic bacteria Rhizobium.
(b) Free-living bacteria Azospirillum and Azotobacter.
(c) They fix the atmospheric nitrogen and enrich soil nutrients.
2. Cyanobacteria, e.g. Anabaena, Nostoc, Aulosira, Oscillatoria, etc.
(a) They function as biofertilizers by fixing atmospheric nitrogen and
(b) Increasing the organic matter of the soil through their photosynthetic activity.
3. Fungi/mycorrhizae:
(a) Fungi form a symbiotic association with roots of higher plants (mycorrhizae), e.g. Glomus.
(b) The fungus absorbs phosphorus and passes it on to the plant.
(c) Other benefits of mycorrhizae are :
- resistance to root-borne pathogens.
- tolerance to salinity.
- tolerance to drought.
- the overall increase in the plant growth and development
Question 24.
You have been deputed by your school principal to train local villagers in the use of biogas plants. With the help of a labeled sketch explain the various parts of the biogas plant. (CBSE Outside Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Biogas plant:
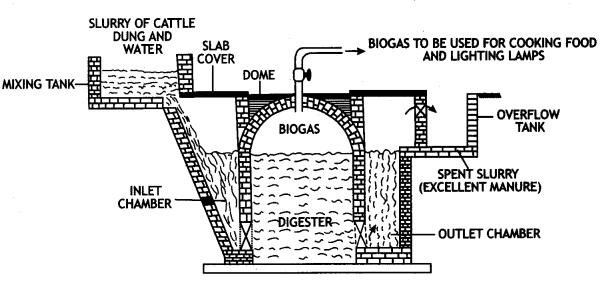
Biogas plant
- The plant consists of a well-like underground tank made of bricks. This tank is called a digester.
- The roof of the digester is dome-shaped made of cement and bricks. The dome of the digester tank acts as a gas holder (or storage tank for biogas). Thus, the gas holder in this type of gas-plant is fixed.
- There is a gas outlet at the top of the dome for the supply of biogas.
- On the one side of the digester tank, there is a slopping inlet tank and on the other side, there is a rectangular outlet tank or overflow tank. Both these tanks are made of cement and bricks.
- The mixing tank is connected with a slopping inlet chamber (or tank) while the outflow tank is connected with a rectangular outlet chamber (or tank).
- The inlet-chamber is for introducing fresh dung slurry into the main digester tank whereas the outlet chamber is for taking out spent dung slurry after extraction of biogas.