Here we are providing Class 12 Biology Important Extra Questions and Answers Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications. Important Questions for Class 12 Biology are the best resource for students which helps in Class 12 board exams.
Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Important Extra Questions Biotechnology and its Applications
Biotechnology and its Applications Important Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What is a transgenic organism?
Answer:
An organism that carries a foreign functional gene in its genome is termed a transgenic organism.
Question 2.
Write two applications of biotechnology.
Answer:
- Treatment of diseases.
- Preparation of processed fortified food.
Question 3.
What are probes?
Answer:
It is a single-stranded DNA or RNA, tagged with a radioactive molecule, which is complementary to the DNA in a clone of cells. It is used for detecting the presence of nucleotides complementary to the probe.
Question 4.
Name two diseases that can be treated by producing biological compounds in transgenic animals.
Answer:
Cystic fibrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, and emphysema.
Question 5.
Name the toxin produced by Bacillus Thurinsiensis.
Answer:
Bt Toxin.
Question 6.
What is the utility of the Bt-toxin gene?
Answer:
Bt-Toxin gene provides Bt-toxin which is involved in providing resistance to cotton plants against insects.
Question 7.
Bt-toxin protein exists in which form?
Answer:
Inactive protoxins.
Question 8.
How is inactive Bt-toxin converted into active form? (CBSE Outside Delhi 2019)
Answer:
The inactive toxin is converted into active form due to the alkaline pH of the gut of insects which solubilizes the crystal converting the toxin to its active form.
Question 9.
How does Bt toxin cause the death of insects?
Answer:
Activated Bt toxin binds to the surface of midgut epithelial cells and creates pores in it that cause cell swelling and lysis. It finally leads to the death of the insect.
Question 10.
Name a few forms of cry gene.
Answer:
cry I Ac, cry II Ab, cry III Ab, and cry III Bb.
Question 11.
List the specific insects killed by:
(i) cry I Ac and
(ii) cry II Ab.
Answer:
cry I Ac, cry II Ab-both control cotton bollworm.
Question 12.
Name the insects killed by proteins coded by cry III Ab and cry III Bb.
Answer:
- Colorado potato beetle
- corn rootworm.
Question 13.
What is unique about transgenic animals?
Answer:
Animals that have their DNA manipulated to possess and express a foreign gene are known as transgenic animals. e.g. Rabit, sheep, cows, fish, etc.
Question 14.
How infestation of Meloidogyne incognita was prevented in the Tobacco plant?
Answer:
An infestation of Meloidogyne incognita was prevented on the basis of RNA interference. This method involves the silencing mRNA by complementary dsRNA molecule that binds to mRNA and prevents its translation.
Question 15.
What is the silencing of mRNA?
Answer:
The binding of single-stranded mRNA with complementary and double-stranded RNA to prevent translation of mRNA is called silencing of mRNA.
Question 16.
What is the source of the complementary strand in mRNA silencing?
Answer:
- Viruses having RNA genomes.
- Mobiles genetic elements (transposons).
Question 17.
How is dsRNA prepared?
Answer:
Reverse transcription.
Question 18.
Name the genetically engineered insulin.
Answer:
Humulin.
Question 19.
Write the name of the transgenic protein used to treat emphysema.
Answer:
Alpha-1-antitrypsin.
Question 20.
How is Indian basmati unique?
Answer:
It is unique for its aroma and flavor.
Question 21.
What is complementary DNA (cDNA)?
Answer:
DNA synthesized on RNA template with the help of reverse transcriptase.
Question 22.
Mention the chemical change that proinsulin undergoes, to be able to act as mature insulin. (CBSE 2018)
Answer:
The proinsulin is cleaved to remove extra stretch called the C-peptide to form mature insulin having only A-chain and B-chain joined by a disulfide bond.
Question 23.
What is the application of genetically engineered bacterium namely Pseudomonas Putidal?
Answer:
Pseudomonas putida is used for scavenging oil spills by digesting hydrocarbons of crude oil.
Question 24.
How did the first transgenic cows Rosie differ from other cows with respect to the quality of milk? (CBSE 2008)
Answer:
Rosie produced a human protein (alpha-lactalbumin) enriched milk which is nutritionally a more balanced product for human babies.
Question 25.
State the role of C-peptide in human insulin. (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
C-peptide maintains its nature as pro-hormone (pro-insulin) and during maturation, it is removed. Thus proinsulin matures into insulin.
Biotechnology and its Applications Important Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
List three critical research areas of biotechnology.
Answer:
Three critical research areas of biotechnology are:
- Providing the best catalyst in the form of an improved organism usually a microbe or pure enzyme.
- Creating optimal conditions through engineering for a catalyst to act, and
- Downstream processing technologies to purify the protein/organic compound.
Question 2.
Give the few characteristics of GMOs. (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Genetically modified organisms:
- They are capable of producing pharmaceutically useful proteins.
- They are capable of producing en¬hanced, modified, or new metabolites.
- They can be used for crop protection by control of insects, fungal diseases, frost damage, etc.
- They degrade non-biological wastes and detoxify toxic wastes.
- They show enhanced nitrogen fixation.
Question 3.
List a few transgenic organisms and their potential application. (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Transgenics and their potential applications:
| Transgenics | Useful Applications |
| Bt Cotton | Pest resistance, herbicide tolerance, and high yield |
| Flavr Savr Tomato | Increased shelf life (delayed ripening) and better nutrient quality. |
| Golden Rice | Vitamin A-rich |
| Cattles (cow, sheep, goat) | Therapeutic human proteins in their milk |
| pig | Organ transplantation without risk of rejection. |
Question 4.
In view of the current food crisis, it is said that we need another green revolution. Highlight the major limitations of the earlier green revolution.
Answer:
- Excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides which are polluting the water bodies, soil, and food items.
- It was related to better management practices that can improve food availability to a limited extent.
- Genetic cap for improvement in food yield.
Question 5.
Differentiate between diagnostics and therapeutics. Give one example for each category.
Answer:
Difference between diagnostics and therapeutics:
| Diagnostics | Therapeutics |
| 1. It finds out the cause and nature of the disease. | 1. It treats patients to cure them of the disease. |
| 2. It provides a logical basis for treatment. Example: ELISA test or HIV. | 2. It provides relief from the disease. Example: Antibiotic for bacterial infection. |
Question 6.
Gene therapy can cure important genetic disorders in humans. Comment.
Answer:
Through the “human genome project,” most human genes and sequences have been identified, genetic disorders such as Eczema, cancer, hemophilia, thalassemia, and cystic fibrosis can be cured by the insertion of correct genes into these patients.
Question 7.
What are the advantages of molecular diagnostic over conventional methods?
Answer:
Advantages of molecular diagnostics:
- Early diagnosis is not possible using conventional methods, but by using rDNA technology and PCR, early diagnosis is possible.
- It is also a powerful technique to identify many genetic disorders.
- It is used to detect mutations in suspected cancer patients.
Question 8.
List two uses of cloned genes in molecular diagnostics.
Answer:
- Cloned genes, when expressed to pro¬duce recombinant proteins, help in developing sensitive diagnostic techniques.
- Cloned genes are used as probes to detect the presence of its complementary DNA strand; mutated genes will not hybridize with the probe and hence do not appear on the photographic film.
Question 9.
How is early detection of infectious diseases possible by molecular diagnostics?
Answer:
Molecular diagnostic of early detection of infectious diseases:
- A low concentration of viral or bacterial DNA in a host body can be detected (much before the symptoms of the disease appear) by polymerase chain reaction (amplification).
- Clones of genes can be used as probes to detect the presence of complementary (normal) strands of DNA in a mutant-clone. Hybridization does not occur and hence the radioactivity does not appear in the (autoradiography) photographic films.
Question 10.
How was insulin obtained before the advent of rDNA technology? What were the problems encountered?
Answer:
Before the advent of rDNA technology, insulin was obtained from slaughtered cattle and pigs.
Problems:
- Insulin obtained from slaughtered cattle and pigs was slightly different from human insulin. It had a harmful effects over long periods.
- The drug has been eliciting an immune response in some patients.
Question 11.
Why has the Indian Parliament cleared the second amendment of the country’s patents bill?
Answer:
The major change in the patent regime achieved through the second amendment is not in the area of medicine and drugs but in the area of seeds and plants, especially genetically engineered seeds. It has opened the flood gates for patenting genetically engineered seeds.
Question 12.
Give any two reasons why the patent on Basmati should not have gone to an American Company.
Answer:
- In India, Basmati rice is being cultivated for several years.
- American company by producing hybrids of this scented (basmati) rice cannot claim to have the patent rights.
Question 13.
What is a gene library?
Answer:
Gene Library: Several clones of cells each containing one of a few foreign genes are finally obtained, representing almost all the genes of an organism, it is termed the gene library of that organism. From that gene library, it is possible to identify a clone containing the gene of interest.
In order to obtain the gene library of an organism, its genome is first to cut into smaller DNA fragments containing one or a few genes, and such fragments can be cloned in the cell where such a cell multiplies to form a group of cells, all cells have same foreign DNA and are termed clone.
Question 14.
What is a reporter or marker gene?
Answer:
A reporter or marker gene produces a phenotype that is either easily and specifically detected or which allows a differential multiplication of the cells.
Question 15.
Why is the use of probes considered better than conventional diagnostic tools for disease diagnosis?
Answer:
Probes are better than conventional diagnostic tools because:
- They are highly specific, relatively rapid, and much simpler.
- They are extremely powerful especially when combined with PCR, even a single molecule in the test sample can be detected.
- Since the culture of microbe is not required, the risk of accidental infection to laboratory personnel is eliminated.
Question 16.
Name different transfection methods.
Answer:
Calcium phosphate precipitation, direct microinjection, retrovirus infection, lipofection, particle gun delivery, and electroporation.
Question 17.
Why mice are considered the most suitable animals for transgenic production?
Answer:
The mouse is preferred for studies of gene transfers due to its many favorable features like a short estrous cycle and gestation period, production of several offspring per pregnancy, convenient in vitro fertilization, production, and maintenance of embryonic stem cell lines.
Question 18.
Define ‘Germline gene therapy.
Answer:
It is a therapy in which germ cells, i.e. sperms or eggs (even zygotes) are modified by the introduction of functional genes which are ordinarily integrated into their genomes. Therefore, the change due to therapy is heritable and passed on to later generations.
Question 19.
Write the advantages of recombinant therapeutics. How many of them have been approved the world over for human use and how many are available in the Indian market?
Answer:
Advantages of Recombinant Therapeutics:
- The recombinant therapeutics do not induce unwanted immunological responses like similar products of non-human origin.
- About 30 recombinant therapeutics have been approved the world over.
- 12 of them are being marketed in India.
Question 20.
What is interest-sensitive speciesism? Is it one of the ethical issues related to transgenic animals?
Answer:
The use of animals in biotechnological research causes greater suffering to the animals. But most people seem to accept some animal suffering to serve the basic interest and welfare of mankind; this attitude has been termed as interest-sensitive speciesism. It is one of the most common ethical issues.
Question 21.
Name a few useful products obtained from animal cell lines.
Answer:
Useful products obtained from animal cell lines:
- Production of vaccines for influenza, measles, and mumps from chick embryo fluid.
- Production of vaccines for rabies and rubella from duck embryo fluid.
Question 22.
Can you suggest a method to remove oil (hydrocarbon) from seeds based on your understanding of DNA technology and the chemistry of oil?
Answer:
The genes for the formation of oil in the seed should be identified. The specific gene can be removed by using enzyme restriction endonucleases. Such DNA molecules should be treated with DNA ligases to seal at the broken ends. These cells when grown in a minimum nutrient medium, under aseptic conditions will differentiate into a new plant whose seeds will not have oil in them.
Question 23.
Find out from the Internet what is Golden Rice.
Answer:
Golden Rice. It is genetically engineered rice rich in Vitamin A. It was prepared by introducing three genes involved in the biosynthetic pathway for carotenoid, the precursor of vitamin A. The color of golden rice is yellow due to the synthesis of provitamin A in the entire grain.
Question 24.
Describe the responsibility of GEAC, set up by the Indian Government. (CBSE 2009)
Answer:
- Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC) makes decisions regarding the validity of GM research.
- It also ensures the safety of introducing GM organisms for public services.
Question 25.
Why insulin is being extracted from bacteria rather than animal sources?
Or
Name the source from which insulin was extracted earlier. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
Insulin for the use of diabetic patients was earlier extracted from the pancreas of slaughtered cows and pigs. It caused allergy and other reactions in patients, due to foreign proteins. So these days insulin is being extracted from bacteria.
Question 26.
What are embryonic stem cells? What stages of early embryonic development are important for generating embryonic stem cells?
Answer:
Embryonic stem cells, as their name suggests, are derived from embryos. Most embryonic stem cells are derived from embryos that develop from eggs that have been fertilized in vitro-in an in vitro fertilization clinic and then donated for research purposes with the informed consent of the donors. They are not derived from eggs fertilized in a woman’s body. Embryonic stem cells are obtained from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst stage of the embryo.
Question 27.
Name the first transgenic cow developed and state the improvement in the quality of the product produced by it. (CBSE Sample Paper 2018)
Answer:
- Name of the first transgenic cow developed: Rosie
- Advantage: It produced human protein-enriched milk (2.4 grams per liter).
Question 28.
What are cry genes? In which organism are they present? (CBSE 2017)
Answer:
Cry genes code for a toxin that is poisonous to some insects thus making plant insect resistant. They are present in the bacterium Bacillus Thuriengiensis.
Question 29.
Name one toxin gene isolated from B. Thuringiensis and its target pest. (CBSE Delhi 2019 C)
Answer:
Cry I AC is a toxin isolated from B. Thuringiensis and its target pest is cotton bollworm.
Question 30.
Why does the toxin produced by B. Thuringiensis not kill the Bacillus? (CBSE Delhi 2019 C)
Answer:
The toxin produced is in inactive form as protoxin. It does not kill the bacteria and attacks only its target pest because protoxin is activated in the optimum pH medium of the gut of insect pest.
Biotechnology and its Applications Important Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Expand GMO. How is it different from a hybrid?
Answer:
- GMO – Genetically modified organism.
- Differences between GMO and Hybrid.
| GMO | Hybrid |
| 1. Formation of GMO does not require crossing between different organisms. | 1. It is formed as a result of crossing between two different organisms. |
| 2. One or more foreign genes are incorporated into GMOs. | 2. It contains complete genomes of two different organisms. |
| 3. A completeLy new trait has been introduced. | 3. OnLy the existing traits are improved. |
Question 2.
Mention any six fields of application of biotechnology for human welfare.
Answer:
Applications of Biotechnology:
- Therapeutics
- Genetically modified crops
- Molecular diagnostics
- Processed food items
- Bioremediation
- Biological waste treatment
- Energy production.
Question 3.
“Specific Bt Toxin gene is incorporated into the cotton plant so as to control the infestation of Bollworm”. Mention the organism from which the gene was isolated and explain its mode of action. (CBSE Sample paper 2019-20)
Answer:
- Specific Bt toxin genes isolated from Bacillus Thuringiensis are incorporated into cotton. Cry I AC and Cry II AC control the bollworm.
- Bt gene forms protein crystals that contain a toxin insecticidal protein.
- It is in an inactive state.
- The inactive toxin is converted into active form due to the alkaline pH of the gut which solubilizes the crystal.
- Activated Bt-toxin binds to the surface of midgut epithelial cells and creates pores that cause cell swelling and lysis. It finally leads to the death of the insect.
Question 4.
How is the ELISA test carried out?
Answer:
ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Test):
- It is a technique of detecting a very small amount of protein (antibody or antigen) with the help of enzyme peroxidase or alkaline phosphatase and stain-producing substrates like 5-aminosalicylic acid or orthophenylene diamine.
- The serum is sorbed to the surface of the ELISA plate.
- An antibody is specific to the antigen for diagnosis placed over an immobilized antigen.
- The spot is washed to remove the free antibody.
- Antibody bound to the enzyme is poured over the spot so as to react with com¬plex antibody.
- The area is washed again to remove the free antibody-enzyme complex.
- Chromagen is added. It will produce a stain showing the antigen was present.
- ELISA is a quick method of diagnosis of pregnancy (by detection hCG in urine), AIDS, hepatitis, STDs, thyroid disorder, and Rubella virus.
Question 5.
While creating genetically modified organisms, genetic barriers are not respected. How this can be dangerous in the long run?
Answer:
- Genetic pollution. The ecological imbalance may occur due to transferring of transgenes from one organism to another.
- Formation of Superweeds. Due to the introduction of weedicide genes in crops, there is a danger that any such crop may itself become superweed.
- Formation of super insecticides.
- Foreign proteins formed with foreign genes may get attacked by the defense system of the organism leading to the formation of defective biochemicals,
- Transgenes may exhibit changes in their expressivity after attaining certain age and change in environment.
Question 6.
Explain the structure of Insulin. How insulin is synthesized in humans (or mammals)? (CBSE Outside Delhi 2011) Answer:
(i) Insulin is made up of two short polypeptide chains; A and chain B which are linked together by disulfide bridges.
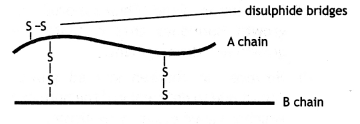
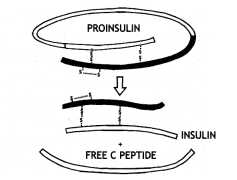
(A), (B) Conversion of proinsulin after removal of C-peptide.
(ii) Insulin is synthesized as pro-hormone (i.e. which is to be processed before becoming functional) which contains an extra stretch called C-peptide which is usually removed during the maturation of insulin.
Question 7.
Explain the social, economical, and environmental implications of genetic engineering techniques.
Answer:
- Genetically prepared human insulin and edible vaccines will be readily available and also will be economical.
- Transgenic crop plants for human consumption may cause concern for safety due to unwanted properties they may have.
- Some people believe that transgenic plants and animals can solve many human problems especially hunger and disease.
Question 8.
Write a short note on:
(i) Production of human growth hormone by E. coli.
Answer:
Production of human growth hormone by E. coli. The Human growth hormone is produced commercially by transgenic Escherichia coli. The pituitary gland of humans produces growth hormones that regulate growth and development. However, in children stunted growth occurs due to deficiency of the hormone called pituitary dwarfism. For this, the hGH is now available as a recombinant protein.
The high-coding DNA sequence is linked with the bacterial signal sequence of E. coli. The hGH is secreted into the periplasmic space of bacterial cells by the signal peptides wherefrom the protein is purified.
(ii) Animals as organ donors for humans.
Answer:
Animals as organ donors for humans. Organ transplantation from animals to humans is called xenotransplantation. The first experiment was done in 1906 by French Surgeon Mathieu Jaboulay who implanted a pig’s kidney into one woman and a goat’s liver into another woman, but it was not successful.
Though now, organ transplantation from animals has been made possible in America and the United Kingdom. Of all, baboons and pigs have favored xenotransplant donors. Pig organs have been transplanted to humans several times in the last few years. Baboons are genetically close to humans, so they are most often used. Six baboon kidneys were transplanted into humans in 1964. Today, however, xenotransplantation is still experimental and there is a serious risk to the procedures.
(iii) Plant Variety Protection and Farmers’ Right Act.
Answer:
Plant Variety Protection and Farmers’ Right Act. This act provides the establishment of an effective system for the protection of plant breeder’s rights. It gives concurrent attention to the right of farmers, breeders and researchers, and the protection of public interest. Public interest is related to issues like compulsory licensing of rights and to the import of varieties incorporating Genetic Use Restriction Technology.
Question 9.
Explain the following terms in one or two sentences: intellectual property rights, humulin, and biofortified foods.
Answer:
1. Intellectual Property Rights: It is the general term covering patents, copyright, trademark, industrial designs, geographical indications, protection of layout designs of integrated circuits, and protection of undisclosed information (trade secrets).
2. Humulin: It is a crystalline suspension of human insulin. It is made using a chemical process called recombinant DNA technology and is of various types (Humulin R, U, N, L, 70/30, 50/50) depending on the percentage of insulin present in suspension. Humulin does not come from human beings, but they are synthesized in special non¬disease producing special lab strains of E. coli which are genetically altered by the addition of the gene for human insulin production. Humulin is identical in chemical structure to human insulin and is made in a factory by recombinant DNA technology.
3. Biofortified foods: They are the modified food rich in nutritional values. Biofortification is the process of breeding food crops that are rich in bioavailable micronutrients. These crops fortify themselves, they toad high levels of minerals and vitamins in their seeds and roots, which are harvested and eaten.
Question 10.
What are transgenic bacteria? Illustrate using any one example.
Answer:
Those bacteria whose DNA is manipulated to possess and express an extra (foreign) gene are known as transgenic bacteria.
Example: Human Growth hormone production by transgenic Escherichia coli.
- The pituitary gland of humans produces growth hormones that regulate growth and development.
- However, in children stunted growth occurs due to deficiency of the hormone which is called pituitary dwarfism.
- For this, the hGH is now available as a recombinant protein.
- The hGH-coding DNA sequence is linked with the bacterial signal sequence of E. coli.
- The hGH is secreted into the periplasmic space of bacterial cells by the signal peptides wherefrom the protein is purified.
Question 11.
Write properties of stem cells. How is the population of stem cells maintained?
Answer:
Properties of stem cells:
The classical definition of a stem cell requires that it possess two properties:
- Self-renewal: The ability to go through numerous cycles of cell division while maintaining the undifferentiated state,
- Potency: The capacity to differentiate into specialized cell types. In the strictest sense, this requires stem cells to be either totipotent or pluripotent- to be able to give rise to any mature cell type, although multipotent or unipotent progenitor cells are sometimes referred to as stem cells. Apart from this, it is said that stem cell function is regulated in a feedback mechanism.
1. Self-renewal:
Two mechanisms exist to ensure that a stem cell population is maintained:
- Obligatory asymmetric replication: A stem cell divides into one mother cell that is identical to the original stem cell, and another daughter cell that is differentiated.
- Stochastic differentiation: When
one stem cell develops into two differentiated daughter cells, another stem cell undergoes mitosis and produces two stem cells identical to the original.
2. Totipotency
They have the potential to develop into any cell found in the human body.
Question 12.
Show with a simple sketch the location of stem cells and their role in treatment.
Answer:
Stem cells:
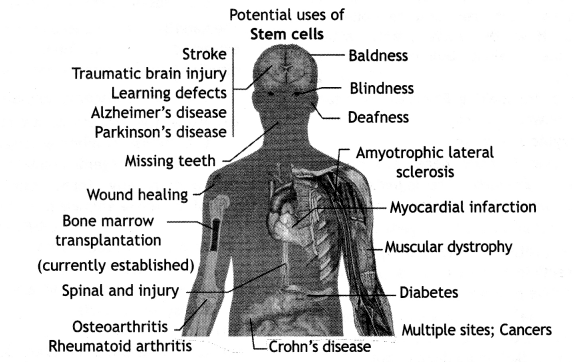
Diseases and conditions where stem cell treatment is being investigated.
Question 13.
(i) Why are transgenic animals so called?
Answer:
Animals that have had their DNA manipulated to possess and express (foreign) genes are called transgenic animals.
Example: Transgenic mice, transgenic rabbits.
(ii) Explain the role of transgenic animals in (a) vaccine safety (b) biological products with the help of an example for each.
Answer:
(a) Role of transgenic animals in vaccine safety:
- Transgenic mice are being developed for use in testing the safety of vaccines before they are used on humans.
- Transgenic mice are being used to test the safety of the polio vaccine.
(b) Role of transgenic animals in biological products: In 1997, the first transgenic cow, Rosie, produced human protein-enriched milk of 2.4 gm per liter. The milk contained the human alpha-lactalbumin and was a more balanced product for human babies.
Question 14.
Name the genes responsible for making Bt cotton plants resistant to bollworm attack. How do such plants attain resistance against bollworm attacks? Explain. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
- Genes for making Bt cotton resistant to bollworm attack:
1. acrylic
2. cry IIAb - Specific Bt toxin genes are isolated from Bacillus Thurinsiensis and incorporated into the cotton plant.
- The toxin is coded by a gene name cry.
- The protein synthesized by these is insecticidal protein. It is present as an inactive protoxin.
- Once the insect ingests the protoxin it is converted into the active form of toxin due to the alkaline medium of the gut.
- The activated toxin binds to the surface of midgut epithelial cells and creates pores in them.
- It causes swelling and breakdown and eventually leads to the death of the insect.
Question 15.
Explain the various steps involved in the production of artificial insulin. (CBSE 2017)
Or
Explain how Eli Lilly, an American company, produced insulin by recombinant DNA technology. (CBSE Delhi 2018C)
Answer:
Genetically engineered insulin:
- Insulin contains two short polypeptide chains: chain A and chain Blinked together by disulfide bridges.
- In mammals, insulin is synthesized as a pro-hormone. It contains an extra stretch called C-peptide.
- C-peptide is absent in the mature insulin and is removed during maturation into insulin.
- Production of insulin by rDNA techniques was achieved by an American company, Eli Lilly in 1983. It prepared two DNA sequences corresponding to A and B, chains of human insulin, and introduced them in plasmids of E. coli for production.
- The Aand B chains produced were separated, extracted and combined, by creating disulfide bonds to form human insulin.
Question 16.
(i) What are transgenic animals?
Answer:
Animals whose DNA has been manipulated to possess and express an extra/foreign gene are known as transgenic animals.
(ii) Name the transgenic animal having the largest number amongst all the existing transgenic animals.
Answer:
Mice
(iii) Mention any three purposes for which these animals are produced. (CBSE Delhi 2018C)
Answer:
(a) Transgenic animals are designed to allow the study of how genes are regulated and how they affect the normal functions of the body and its developments, e.g. information is obtained as to how insulin has a role as a growth factor.
(b) Transgenic animals are designed to increase our understanding of how genes control the development of diseases; they serve as models for human diseases.
(c) Transgenic mice are being developed to test the safety of vaccines, e.g. polio vaccine has been tested on mice.
Question 17.
Explain the following terms in not more than 70 words.
(i) Single-cell proteins (SCP)
Answer:
Cells from different kinds of organisms such as bacteria, filamentous fungi, yeast, and algae are treated in different ways so that they are used as food or feed, are called single-cell protein. The biomass is obtained from both unicellular and multicellular microorganisms. The common substrate used for preparing such food containing SCP ranges from whey sawdust, and paddy straw. SCP provides a valuable protein-rich supplement in the human diet.
(ii) Biopatent
Answer:
A patent is a right granted by a Government to an inventor to prevent others to make commercial use of such an invention. At present patents that are granted for biological entities and the various products obtained from these organisms, are termed as biopatent.
Biopatents are being granted for the following:
(1) Strains of microorganisms
(2) Cell lines
3) Genetically modified strains of living organisms
(4) DNA sequences
(5) The proteins prepared by DNA sequences
(6) Biotechnological process
(7) Production process
(8) Products
(9) Product application.
(iii) Bioethics
Answer:
Bioethics is a set of standards that may be used to regulate our activities in relation to biological works.
The major bioethical concerns are as follows:
(a) Introduction of transgenes from one species to another violates the integrity of species.
(b) Transfer of human genes to other animals and vice versa is against ethics.
(c) Making of the clone.
(d) May cause risk to biodiversity.
(e) Suffering from animals used in biotechnology will increase.
(iv) Biopiracy
Answer:
The exploitation of patent biological resources without proper permission is called biopiracy. The collection of such material without a benefit-sharing agreement is likely to find its way into the list of criminal violations in many countries.
(v) Genetically modified food
Answer:
The food prepared from the production of genetically modified crops is called genetically modified food (GM food). It contains proteins produced by a transgene.
Question 18.
Briefly explain why are Transgenic animals produced? (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Transgenic animals:
Transgenic animals are produced for the following purposes:
- Transgenic animals are designed to allow the study of how genes are regulated and how they affect the normal functions of the body and its developments, e.g. information is obtained as to how insulin has a role as a growth factor.
- Transgenic animals are designed to increase our understanding of how genes control the development of diseases; they serve as models for human diseases.
- Transgenic animals that produce useful biological compounds are created by introducing a portion of the DNA that codes for that product, e.g. a-1 antitrypsin is produced for curing emphysema.
- Transgenic mice are being developed to test the safety of vaccines, e.g. polio vaccine has been tested on mice.
- Transgenic animals with more sensitivity to toxic substances are being developed to test the toxicity of drugs.
Question 19.
Describe the hazards of transgenic animals.
Answer:
Hazards of transgenic animals:
- Proteins: Genes introduced in various organisms operate through the synthesis of polypeptide proteins and enzymes. However, foreign proteins are generally attacked by the defense system resulting in damaged biochemicals which may prove harmful and in the long term produce allergy.
- Human organs: Replaceable human organs like kidneys, liver, heart, pancreas, etc. can be obtained only from autografts and isografts. Will it be ethical to grow the human body, human body organs for obtaining the required organs?
- Human cloning: This can solve the problem of infertility. However, such a method of human reproduction will destroy the family system, fine human feelings, and the fabric of human society.
- Recreation: It is not only a fancy but also the desires of numerous children, adults, and elders to see dinosaurs live.
Question 20.
Compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of the production of genetically modified crops.
Or
Write advantage of GM crops. (CBSE Outside Delhi 2019)
Answer:
The advantages of the production of genetically modified crops are:
- They have proved to be extremely valuable tools in studies on plant molecular biology, regulation of gene action, identification of regulatory/ promontory sequences.
- Genetically modified crops have improved agronomic and other features such as resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses.
- Over-ripening losses can be reduced, e.g. flavor saves tomato.
- Nutritional values are improved, e.g. Golden rice has high vitamin A content.
- Viral resistance can be introduced.
- The number of pharmaceuticals like insulin, interferon, blood clotting factors are improved.
- Insect resistance can be introduced, e.g. cry gene can be introduced into cotton, wheat, and rice from Bacillus Thuringiensis.
The main disadvantages of the production of genetically modified crops are:
- Many transgenes are expressed at low levels which usually limit their usefulness.
- Sometimes, the expression of transgenes is suppressed in transgenic plants, this is called gene silencing.
- The undesirable features are also carried along with desirable features in transgenic plants such as necrosis, reduced growth, sterility, etc.
- Genetic pollution can be there.
- Weeds also become resistant.
- Bt cotton, Bt wheat also destroy pollinators and disseminators.
- The product of transgene may be allergic or toxic.
Question 21.
Why is the introduction of genetically engineering lymphocyte into an ADA deficiency patient, not a permanent cure? Suggest a possible permanent cure. (CBSE 2010, 2011)
Or
Explain how a hereditary disease can be corrected? Give an example of the first successful attempt made towards this objective. (CBSE 2011, 2019 C)
Or
Explain enzyme replacement therapy to treat ADA deficiency. (CBSE Outside Delhi 2016, 2019 C)
Or
What is gene therapy? Illustrate using the example of adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency? (CBSE Delhi 2011, 2013, 2016)
Or
Two children A and B aged 4 and 5 years respectively visited a hospital with a similar genetic disorder. Girl A was provided enzyme-replacement therapy and was advised to revisit periodically for further treatment. Girl B was, however, given therapy that did not require a revisit for further treatment.
(a) Name the ailments the two girls were suffering from.
(b) Why did the treatment provided to girl A require repeated visits?
(c) How was girl B cured permanently? (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Gene Therapy. It is defined as the introduction of a normal functional gene into cells that contain the defective allele of the concerned gene with the objective of correcting a genetic disorder or an acquired disorder.
Treatment of ADA deficiency:
- Gene therapy was used to correct the genetic disorder called Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) syndrome produced by adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
- In this, Normal ADA gene copies were produced by cloning.
- Packed into a retrovirus, most of the viral genes were replaced by the ADA gene.
- Lymphocytes were isolated from the patients.
- Recombinant DNA of the recombinant retroviruses was used to infect the lymphocytes.
- The infected cells expressing the ADA gene were injected back into the patients.
- The normal ADA gene was then expressed in the patients and ADA deficiency is partially corrected. If the gene isolated from bone marrow cells producing ADA is introduced into embryonic cells at early stages, it could provide a permanent cure.
Question 22.
How is the transgenic tobacco plant protected against Meloidogyne incognita? Explain the process? (CBSE 2009)
Or
Explain the process of RNA interference. (CBSE Delhi 2011, 2016)
Or
How has the use of Agrobacterium as vectors helped in controlling Meloidogyne incognita infestation in tobacco plants? Explain in the correct sequence. (CBSE 2018, Sample paper 2020)
Answer:
Protection of tobacco plant against Nematodes, Meloidogyne incognita:
- A nematode Meloidogyne incognita infects tobacco plants and reduces their yield.
- The specific genes (in the form of cDNA) from the parasite are introduced into the plant using Agrobacterium as the vector.
- The genes are introduced in such a way that both sense/coding RNA and antisense RNA (Complementary to the sense/coding RNA) are produced.
- Since these two RNAs are complementary, they form a double-stranded RNA (ds RNA)
- This neutralizes the specific RNA of the nematode, by a process called RNA- interference.
- As a result, the parasite cannot live in the transgenic host, and the transgenic plant is protected from the pest.
Question 23.
What are the ethical concerns of biotechnology?
Answer:
- Biotechnology is producing newer genotypes. Some of them can be extremely harmful due to intragenomic interactions and mutations.
- It introduces unfamiliar proteins into transgenics which may react to form toxins and allergens.
- The genes introduced into crops can pass into weeds through pollen transfer. It will produce superweeds.
- It is going to cause genetic pollution which is likely to disturb natural balance in a big way.
- Animals employed in experiments of biotechnology are made to suffer.
- Animals being used to produce particular structures and pharmaceutical proteins are reduced to the status of factories.
- As a gene is introduced from outside into an organism, its integrity as a species is violated.
- Transfer of genes from human beings to specific animals or vice-versa violates the concept of humanness.
- Biotechnology has no respect for living beings. Its only goal is to exploit them for commercial use in benefitting human society.
- In their race to gain supremacy over others, companies and individuals are rushing for biopatents even of those products which are produced through the traditional knowledge of tribals, communities, and societies.
Question 24.
The Green Revolution succeeded in increasing the yield of crops but it is not sufficient to feed the growing human population. Thus there is a need for another green revolution.
(i) Name the technique which will help in increasing the yield of crops.
Answer:
Genetic engineering (Recombinant DNA technology).
(ii) Name any two genetically modified crops.
Answer:
(a) Bt cotton
(b) ‘Flavr Savr Tomato’
(iii)What is golden Rice’?
Answer:
Golden rice is a transgenic variety of rice (Oryza sativa) that contains good quantities of (3-carotene (provitamin A – inactive state of vitamin). Since the grains of the rice are yellow in color due to [3-carotene, the rice is called golden rice.
(iv) Name a natural genetic engineer.
Answer:
Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
Question 25.
How have transgenic animals proved to be beneficial in:
(i) Production of biological products
(ii) Chemical safety testing. (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
(i) Production of biological products:
(a) Medicines required for treating human diseases are obtained by genetic engineering.
(b) a-1-antitrypsin used to treat emphysema.
(c) Transgenic cow ‘Rosie’ produces human-protein enriched milk.
(ii) Chemical safety (Toxicity/safety testing) Transgenic animals are made that carry genes that make these more sensitive toxic substances than non-transgenic animals.
Question 26.
List the disadvantages of insulin obtained from the pancreas of slaughtered cows and pigs.
Answer:
- A slaughtered animal produces very little hormone so that the demand was always higher than the supply.
- It is unethical to slaughter animals for obtaining the drug.
- Contamination was quite common.
- The immune response is common.
Question 27.
List the advantages of recombinant insulin.
Answer:
- Recombinant insulin is exactly similar to human insulin and is, therefore, also called humulin.
- It is available in pure form with little chances of contamination.
- There is no slaughtering of animals.
- There is no immune response or any other side effect.
- There is enough manufacturing capacity so that the chances of short supply are few.
Question 28.
Explain the process of synthesis of insulin.
Answer:
Production of human insulin: Gene transfer involves essentially the following stages:
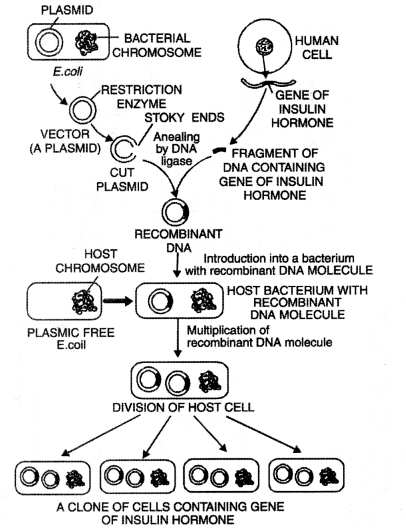
Steps involved in gene transfer for the production of human insulin:
- Isolation of donor or DNA segment. A useful DNA segment is isolated from the donor organism.
- Formation of Recombined DNA (rDNA). Both the vector and donor DNA segments are cut in the presence of restriction endonuclease. In the presence of ligase DNA segments of both are joined to form rDNA.
- Production of Multiple Copies of rDNA. The next step in the process is the production of multiple copies of this recombinant DNA.
- Introduction of rDNA in the recipient organism. This rDNA is inserted into a recipient organism.
- Screening of the transformed cells. The recipient (host) cells are screened for the presence of rDNA and the product of the donor gene. The transformed cells are separated and multiplied, using an economical method for its mass production.