Here we are providing Class 12 Biology Important Extra Questions and Answers Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease. Important Questions for Class 12 Biology are the best resource for students which helps in Class 12 board exams.
Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Important Extra Questions Human Health and Disease
Human Health and Disease Important Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What is health?
Answer:
It is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being of a person.
Question 2.
What is a disease?
Answer:
Malfunctioning of one or more organs characterised by signs and symptoms is called disease.
Question 3.
Write the role of interferons. (CBSE Delhi 2019(C))
Answer:
Role of interferon. These are glycoprotein released by virus-infected cells. They protect the adjoining cells from the attack of the virus.
Question 4.
Define autoimmunity.
Answer:
It is an abnormality which sometimes occurs in the immune system and instead of destroying foreign molecules, it attacks the body’s own cells.
Question 5.
A boy of ten years had chickenpox. He is not expected to have the same disease for the rest of his life. Mention how it is possible. (CBSE 2009)
Answer:
The body will acquire active immunity as the antibodies formed will protect him from the attack of microbes of chickenpox.
Question 6.
What is it that prevents a child to suffer from a disease he/she is vaccinated against? Give one reason. (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
- Antibodies
- These antibodies neutralise the action of antigens.
Question 7.
Name the pathogen which causes Typhoid. Name the test that confirms the disease. (CBSE Delhi 2019 (C))
Answer:
Causative pathogen: Salmonella typhi Test: Widal test
Question 8.
Name two types of cells in which the HIV multiplies after gaining entry into the human body. (CBSE 2008)
Answer:
- T-Lymphocytes
- White Blood Corpuscles (Macrophages).
Question 9.
Why is a secondary immune response more intense than the primary immune response in human? (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
It is because the human body appears to have more memory of the first encounter.
Question 10.
When does a human body elicit an anamnestic response? (CBSE (Outside Delhi) 2013)
Answer:
The primary immune response is of low intensity; a subsequent encounter with the same pathogen elicits a highly intensified anamnestic or secondary response.
Question 11.
Name the two intermediate hosts which the human liver fluke depends on to complete its life cycle so as to facilitate parasitisation of its primary host. (CBSE Delhi 2014)
Answer:
- Freshwater Snail
- Fish
Question 12.
Indiscriminate use of X-rays for diagnoses should be avoided. Give reason. (CBSE (Delhi) 2015)
Answer:
X-rays cause mutation thus may lead to cancer.
Question 13.
Give the scientific name of the source organism from which the first antibiotic was produced. (CBSE Sample paper 2018-19)
Answer:
Penicillium Notatum
Question 14.
Name two diseases whose spread can be controlled by the eradication of Aedes mosquitoes. (CBSE 2018)
Answer:
Dengue and chikungunya
Question 15.
How do cytokine barriers provide innate immunity in humans? (CBSE 2018)
Answer:
Cytokine barriers: Cytokines inhibit viral replication. Virus-infected cells secrete proteins called interferons which protect non-infected cells from virus.
Question 16.
Name two recent incidences of wide-spread diseases caused by Aedes mosquitoes. (CBSE Delhi 2008)
Answer:
- Dengue
- Chikungunya
Question 17.
How does the human body respond when haemozoin produced by Plasmodium is released in its blood? (CBSE Delhi 2019 (C))
Answer:
As haemozoin is released in the blood, the patient shows symptoms of malaria such as restlessness, sleeplessness, muscular pain and chilliness. In response to chill, the body temperature rises.
Question 18.
How does saliva act in body defence? (CBSE Delhi 2004)
Answer:
Human saliva contains lysozyme, a lytic enzyme, which kills the germs in the food.
Question 19.
Name the type of cells that produce antibodies. (CBSE 2004)
Answer:
Lymphocytes which is a form of leucocytes (white blood cells) produce antibodies.
Question 20.
Why sharing injection needles between two individuals is not recommended? (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Sharing of injection needles between two individuals may cause the transmission of AIDS and Hepatitis B.
Question 21.
How do monocytes act as a cellular barrier in humans to provide innate immunity? (CBSE Delhi 2018C)
Answer:
Monocytes kill bacteria by the process of phagocytosis.
Human Health and Disease Important Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Make a list of common infectious diseases.
Answer:
Common infectious diseases: Depending on the pathogen, infectious diseases are as follows:
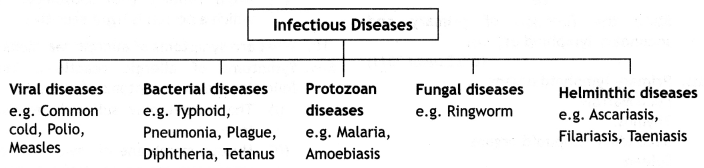
Question 2.
Given below are pairs of pathogens and diseases caused by them. Which of these is not a matching pair and why?
(i) Virus Common Cold
(ii) Salmonella Typhoid
(iii) Microsporum Filariasis
(iv) Plasmodium Malaria
Answer:
- (iii) is not matching.
- Microsporum is a fungus which causes ringworm disease. Filariasis is caused by Wuchereria bancrofti and W. Malayi (roundworm).
Question 3.
Differentiate between antibodies and interferons.
Answer:
Differences between antibodies and interferons:
| Antibodies | Interferons |
| 1. They are slow-acting and long-lasting. | 1. They are quick acting and temporary. |
| 2. They act outside the cells. | 2. They act inside the cells. |
| 3. They act against bacterial and viral infections. | 3. They act against the virus only. |
Question 4.
(i) Name the source plants of heroin drug. How is it obtained from the plants?
Answer:
Papaver somniferum is the source plant of heroin drug. It is obtained by acetylation of morphine, which is extracted from the latex of poppy plant (Papaver somniferum).
(ii) Write the effects of heroin on the human body. (CBSE 2018)
Answer:
Heroin is depressant and slows down body functions.
Question 5.
Mention one application for each of the following:
(i) Passive immunisation
Answer:
(i) Passive Immunisation: When ready¬made antibodies are introduced into the body, it is called passive immunisation. Passive immunisation provides a quick immune response in the body.
(ii) Antihistamine
Answer:
Anti-Histamines: Anti-Histamines are the chemicals which are given against allergic reactions.
(iii) Colostrum (CBSE 2017, 2019)
Answer:
Colostrum: Colostrum is the yellow fluid produced during the initial days of lactation. It is rich in antibodies and is essential to develop resistance in a newborn baby.
Question 6.
What is a vaccine? (CBSE Delhi 2019 C)
Answer:
Vaccine: It is a preparation of dead or altered (weakened) germs of a disease which on entry into the body of a healthy person provide temporary or permanent active/passive immunity by inducing antibody formation. Thus antibody provoking agents are called vaccines. The vaccine provides artificial active immunity.
Question 7.
Name the primary and secondary lymphoid organs. (CBSE Delhi 2019 C)
Or
State the function of primary and secondary lymphoid organs. (CBSE Delhi 2011)
Answer:
Primary lymphoid organs:
- Bone Marrow
- Thymus.
Secondary lymphoid organs:
- Spleen
- Lymph nodes
- Tonsils
- Peyer’s Patches of the small intestine.
Or
Primary lymphoid organs are the sites where immature lymphocytes differentiate and become antigen-sensitive mature lymphocytes.
However, secondary lymphoid organs provide site/location for mature lymphocyte & antigen interaction.
Question 8.
Explain what is meant by metastasis. (CBSE 2009)
Answer:
Metastasis. Small pieces of primary tumour break off and are carried to other body parts by the blood or lymph where these form the secondary tumours. This process is called metastasis. So metastasis is the process of transference of cancerous cells from the site of origin to distant parts of the body. The most frequent sites of metastasis are lymph nodes, lungs, long bones, liver, skin and brain. Metastasis is the most feared property of malignant tumours.
Question 9.
A person shows strong unusual hypersensitive reactions when exposed to certain substances present in the air. Identify the condition. Name the cells responsible for such reactions. What precaution should be taken to avoid such reactions?
Answer:
The condition is called allergy. Mast cells are responsible for such reactions. To avoid such reactions, the following precautions must be taken:
- Use of drugs like antihistamine, adrenalin and steroids quickly reduces the symptoms.
- Avoid contact with substances to which a person is hypersensitive.
Question 10.
What are the symptoms of allergic reactions?
Answer:
Symptoms of allergic reactions.
The following are the symptoms of allergies:
- The person may suffer from high fever
- The mucous membrane of the lower part of the respiratory tract gets affected which leads to cough and asthma.
- Reddening of the skin, the appearance of blisters on the skin.
- Accumulation of tissue fluid below the skin.
- Watering of eyes and inability to breathe.
- Sneezing, running nose, etc.
Question 11.
In the metropolitan cities of India, many children are suffering from allergy asthma. What are the main causes of this problem? Give some symptoms of allergic reactions.
Answer:
- Allergy is the exaggerated (hypersensitive) response of the immune system to certain antigens present in the environment. These certain antigens are called allergens. Our immune system responds to it by releasing histamines and serotonin from mast cells. Common allergens are mites in the dust, pollens and animal dander (material shed from animals),
- Lifestyle in metro cities is making them sensitive to allergens.
- The symptoms are sneezing, watery eyes, running nose and difficulty in breathing.
Question 12.
Drugs and alcohol give short-term ‘high’ and long-term ‘damages’. Discuss.
Answer:
Mostly stimulant drugs (caffeine) and alcohol (depressant) give a feeling of intoxication and euphoria for only a brief period soon after use. However, prolonged use for long-term causes permanent damage to vital body parts like liver, kidneys, lungs, cardiovascular system, etc.
Question 13.
List any two adaptive features evolved in parasites enabling them to live successfully on their hosts. (CBSE Delhi 2008)
Answer:
Adaptations of parasites:
- Presence of adhesive organs or suckers to cling to the host.
- Loss of unnecessary sense organs.
Question 14.
What is dengue fever? List two symptoms.
Answer:
Dengue fever: Dengue fever is caused by an RNA containing arbovirus of flavivirus group which also causes yellow fever (not found in India). Thus, the virus which causes dengue fever is a mosquito-borne flavi-ribo virus. The virus of dengue fever is transmitted by the bite of Aedes aegypti (mosquito). The incubation period is 3-8 days.
Symptoms:
- Abrupt onset of high fever.
- Severe frontal headache and pain behind eyes which worsens with eye movement.
Question 15.
Why is the structure of an antibody molecule represented as H2L2? Name any two types of antibodies produced in humans. (CBSE Delhi 2018C)
Answer:
- The antibody molecule is made up of four peptide chains-two small chains are called light chains and two longer chains are called heavy chains. Hence it is represented as H2L2.
- Ig G, Ig A, Ig M. and Ig E are the antibodies produced in humans.
Question 16.
What are the preventive measures of dengue fever? Is there any vaccine available?
Answer:
Prevention and treatment:
- Mosquitoes and their eggs should be eliminated. Put wire mesh on doors and windows.
- No specific treatment is available.
- Symptomatic care including bed rest, intake of adequate fluid and pain killer medicines are recommended.
- Do not take Aspirin and Aspirin. Give plenty of liquids to the patient.
- No vaccine for Dengue fever is available.
Question 17.
Differentiate between the roles of B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes in generating immune responses. (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Role of B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes in the immune response:
- B-cells (B-lymphocytes) and T-cells (T lymphocytes) comprising the immune system are produced in the bone marrow. T-cells differentiate in the thymus.
- B-lymphocytes produce antibodies in response to foreign substances (antigens) such as pathogens and pollen. Antibodies are immunoglobulins. They are specific for each antigen. There is more than one antibody for an antigen. Antibodies bind antigens but do not destroy them. This is attacked through other mechanisms. Allergens which are weak antigens cause allergy.
- T-cells respond to pathogens by producing three types of cells: killer T-cells, helper T-cell and suppressor T-cells. T lymphocytes either help B-lymphocytes to produce antibodies or kill the pathogen directly (killer T-cells). Both B- and T-cells produce memory cells when stimulated. These have long lives and form the basis of acquired immunity.
Question 18.
Why is tobacco smoking associated with rising in blood pressure and emphysema? Explain. (CBSE Outside Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Nicotine, an alkaloid present in tobacco, stimulates the adrenal gland to release adrenaline and nor-adrenaline into blood circulation. Both these hormones increase blood pressure and heart rate.
Smoking causes emphysema. Tobacco smoke damages the air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs. Thus surface area for exchange of gases becomes less and disorder emphysema is caused.
Question 19.
Write the scientific names of the causal organisms of elephantiasis and ringworm in humans. Mention the body parts affected by them. (CBSE DeLhi 2012)
Answer:
| Name of disease | Causative organism | Organ affected |
| 1. Elephantiasis | (i) Wuchereria bancrofti (ii) Wuchereria malayi Fungi namely |
Genital organs, swelling of lower limbs. |
| 2. Ringworm | (i) Microsporum (ii) Trichophyton (iii) Epidermophyton |
Skin, nails and scalps. |
Human Health and Disease Important Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
(i) How and at what stage does Plasmodium enter a human body?
Answer:
Sporozoite stage enters human body aLong with saLiva of female anopheLes mosquito as ii
bites to suck bLood.
(ii) With the help of a flow chart only shows the stages of asexual reproduction in the life cycle of the parasite in the infected human.
Answer:
Asexual phases of the life history of plasmodium in the body of a human
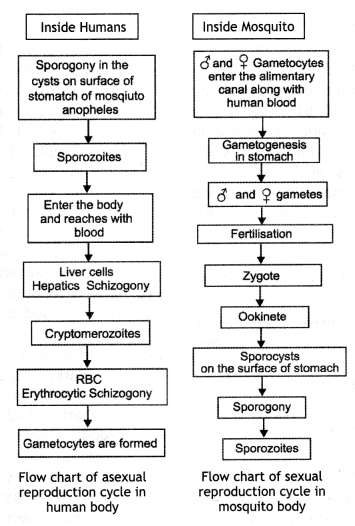
(iii) Why does the victim show symptoms of high fever? (CBSE Delhi 2008, 2013)
Answer:
When the parasite attacks red blood cells, it leads to its rupture with the release of haemozoin, which is a toxin. As the haemozoin is released into blood, symptoms (high fever) of malaria appear.
Question 2.
What is Immune system? Mention the two types of the immune system. (CBSE Delhi 2011)
Answer:
The system which protects our body from pathogens and other foreign invaders is called the immune system. It is of two types.
- Innate
- Acquired
Innate immunity is non-specific and is present by birth. It includes physical barriers, physiological barriers, cellular and cytokinin barriers.
Acquired immunity is pathogen-specific and is obtained with experience. It is of two types- Humoral and cell-mediated
Question 3.
Distinguish between B-cells and T-cells.
Answer:
Differences between B-cells and T-cells:
| B-cells | T-cells |
| 1. They are produced in cells of bone marrow and remain there and later migrate to lymphoid tissues. | 1. They are produced in cells of bone marrow and migrate to the thymus and differentiate under the influence of thymus. |
| 2. These crafts produce plasma cells, once triggered off by the antigens. | 2. These cells are responsible for recognising a specific antigen and attack it by releasing chemicals. |
| 3. They are part of a humoral system. | 3. They are part of the cell-mediated immune system. |
| 4. They act against viruses and bacteria and do not react against transplants and cancer cells. | 4. They act against pathogenic microorganism, organ transplants and cancer cells. |
| 5. No inhibitory effect on the immune system. | 5. Suppressor cells inhibit the immune system. |
Question 4.
(i) Name the infective stage of Plasmodium which Anopheles mosquito takes in along with the blood meal from an infected human.
Answer:
Gametocytes
(ii) Why does the infection cause fever in humans?
Answer:
Due to the release of haemozoin toxin in the blood.
(iii) Give a flow chart of the part of the life cycle of this parasite passed in the insect. (CBSE (Delhi) 2008, 2011)
Answer:

Question 5.
(i) Why do the symptoms of malaria not appear immediately after the entry of sporozoites into the human body when bitten by female Anopheles? Explain.
Answer:
As the sporozoites enter the human body along with saliva of female anopheles mosquito, these parasites pass through hepatic schizogony in liver cells and erythrocytic schizogony in RBCs. Haemozoin present in unused cytoplasm of RBC is released, followed by the appearance of malarial symptoms. This period is also called the incubation period.
(ii) Give the scientific name of the malarial parasite that causes malignant malaria in humans. (CBSE 2009)
Answer:
Plasmodium falciparum. Causes malignant malaria in human.
Question 6.
Give the scientific name of the parasite that causes malignant malaria in humans. At what stage does this parasite enter the human body? Trace its life cycle in the human body. (CBSE 2009, 2012)
Answer:
- Plasmodium falciparum
- Sporozoites enter the human body along with saliva of the female anopheles mosquito.
- The life cycle of Plasmodium in the human body
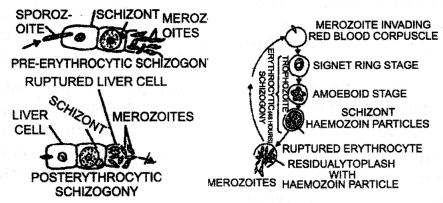 Life Cycle of Plasmodium
Life Cycle of Plasmodium
Question 7.
A 17-year-old boy is suffering from high fever with profuse sweating and chills. Choose the correct option from the following diseases which explains these symptoms and rule out the rest with adequate reasons.
(i) Typhoid
Answer:
If the boy is suffering from typhoid, then he should have sustained high fever (39° to40°C), weakness, stomach pain, constipation and headache. So it cannot be typhoid.
(ii) Viral Fever
Answer:
If the boy is suffering from viral fever, he will suffer from high fever, joint pain, weakness and headache. So it cannot be a viral fever.
(iii) Malaria (CBSE Sample paper 2018-19)
Answer:
If the boy is suffering from malaria, he should have high fever recurring with profuse sweating every three to four days associated with chills and headache. There is a possibility that he is suffering from malaria because high fever associated with chills is possible with malaria.
Question 8.
Medically it is advised to all young mothers that breastfeeding is the best for their newborn babies. Do you agree? Give reasons in support of your answer. (CBSE 2018)
Answer:
Yes, I do agree with the fact that breastfeeding is the best for newborn babies. Mammary glands start producing milk at the end of pregnancy. The milk produced during the initial few days of lactation is called colostrum which contains several antibodies. It helps in developing resistance for newborn baby against diseases. It helps the baby fight off viruses and bacteria. Thus breast milk is packed with a disease-fighting substance that protects newborn babies from illness. Breast milk also naturally contains many of the vitamins and minerals that a newborn requires. It is easily digested as well. There is no constipation, diarrhoea and upset stomach.
Question 9.
Name a human disease, its causal organism, symptoms (any three) and vector, spread by intake of water and food contaminated by human faecal matter. (CBSE 2017)
Answer:
- Amoebic dysentery [Amoebiasis]
- Causal Organism: Entamoeba historlytica, protozoa.
Symptoms:
- Abdominal pain
- Constipation
- Cramps.
Vector: Housefly.
Question 10.
(i) Why is there a fear amongst the guardians that their adolescent wards may get trapped in drug/alcohol abuse?
Answer:
Reasons for alcohol abuse in adolescents:
(a) Curiosity for adventure, excitement and experiment
(b) Social pressure
(c) To escape from stress, depression and frustration
(d) To overcome hardships of life
(e) Unstable or unsupportive family structure, etc.
(ii) Explain ‘addiction’ and dependence’ in respect of drug/alcohol abuse in youth. (CBSE 2017)
Answer:
Addiction is the psychological attachment to certain effects such as euphoria and a temporary feeling of well-being, associated with drugs and alcohol. The addicted person cannot manage him/herself without drug or alcohol.
Dependence: Dependence is the tendency of the body to manifest a characteristic and unpleasant withdrawal syndrome on abrupt discontinuation of a regular dose of drug/alcohol.
Question 11.
What is the basic principle of vaccination? How do vaccines prevent microbial infections? Name the organism from which the hepatitis B vaccine is produced.
Or
Principle of vaccination is based on the property of “memory” of the immune system. Taking one suitable example, justify the statement. (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Principle of vaccination is based on the property of ‘memory’ of the immune system.
In vaccination, a preparation of antigenic proteins of pathogens or inactivated/live but weakened pathogens is introduced into the body. The antigens generate a primary immune response by producing antibodies along with forming memory B-cells and T-cells. When the vaccinated person is attacked by the same pathogens, the existing memory B-cells and T-cells recognise the antigen and overwhelm the invaders with massive production of lymphocytes and antibodies. The hepatitis-B vaccine is produced from yeast.
Question 12.
Prior to a sports event blood and urine samples of sportspersons are collected for drug tests.
(i) Why is there a need to conduct such tests?
Answer:
Drugs are consumed by sportspersons to enhance their performance. It is necessary to test the blood and urine of sportspersons to analyse the presence of any performance-enhancing drug.
(ii) Name the drugs the authorities usually look for.
Answer:
Narcotic analgesics, anabolic steroids, diuretics.
(iii) Write the generic names of two plants from which these drugs are obtained. (CBSE Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(a) Cocaine is obtained from Erythroxylum coca
(b) Caffeine is obtained from Coffea arabica and narcotics from Papaver somniferum.
Question 13.
Explain the following terms:
(i) Benign tumour
Answer:
A benign tumour (Non-malignant tumour). Such tumours grow slowly but become quite large. It remains restricted to the place of origin and does not spread to other areas of the body. Most tumours are of this type and do not give rise to cancer.
(ii) Cancerous tumour
Answer:
A cancerous tumour (Malignant tumour): It begins as a small tumour growth at first, grows slowly in the starting and more rapidly later on. The tumour ultimately spreads to the neighbouring tissue like the roots of a tree. Later on, cancerous cells separate off from the original site and migrate through the blood to the other sites and they divide and redivide to form a secondary tumour.
(iii) Metastasis.
Answer:
Metastasis: The stage when the secondary tumour is formed and accumulated by repeated division, is called metastasis. This stage is fatal and causes death sooner or later.
Question 14.
Why cannabinoids are banned in sports and games?
Answer:
Cannabinoids are hallucinogenic chemicals obtained from leaves, resins and inflorescence of Hemp plant, Cannabis sativa. They are used by sportspersons to increase their athletic performance. Intake of cannabinoids results in rapid heartbeat decreased vital capacity of the lung. But their misuse is associated with a number of problems in both sportsmen and sportswomen, e.g. these cause masculinisation, increased aggressiveness, mood swings, abnormal menstrual cycles, enlarged clitoris in sportswomen, while their misuse in sportsmen is known to cause acne, mood swings, reduced testicular size, decreased spermatogenesis, enlarged breasts and prostate gland, dysfunctioning of liver and kidney, etc.
Question 15.
The outline structure of a drug is given below:
1. Which group of drugs does this represent?
2. What are the modes of consumption of these drugs?
3. Name the organ of the body which is affected by the consumption of this drug.
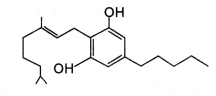
Answer:
- Cannabinoids.
- By smoking or oral ingestion.
- Cannabinoids generally affect the cardiovascular system of the body.
Question 16.
What is cannabis? List its main derivatives.
Answer:
Cannabis: It is the most ancient drug and is obtained from hemp plants.
The following three kinds of drugs are obtained from these plants (Derivative of Cannabis indica):
- Hashish or Charas is obtained from flowering tops of female plants.
- Bhang is obtained from dry leaves.
- Ganja is obtained from small leaves and bracts of inflorescence.
Marijuana is another drug obtained from Cannabis sativa. The common reaction of these drugs is relaxation, euphoria, laughing tendency and rise in blood sugar level.
Question 17.
Why is using tobacco in any form injurious to the health? Explain. (CBSE Delhi 2008, Outside Delhi 2011)
Answer:
Tobacco is injurious to health:
- Nicotine present in tobacco is toxic and addictive. It causes coronary diseases.
- Heat irritants and carcinogens cause mouth cancer and lung cancer.
- Tobacco leads to male infertility.
- in pregnant women, nicotine causes decreased foetal growth and development.
- Tobacco addiction often leads to gastric and duodenal ulcers.
- It is an expensive habit causing staining of teeth and fingers and making breath unpleasant.
- Swelling of respiratory tract leads to chronic bronchitis.
Question 18.
Give reasons for the following:
(a) Antibody-mediated immunity is called humoral immunity.
Answer:
(a) Antibodies produced by plasma cells are present in the blood, the response is called humoral, immunity response. Thus it is termed humoral immunity.
(b) How is a child protected from a disease for which he/she is vaccinated?
Answer:
The principle of vaccination is based on the property of the ‘memory’ of the immune system. As during vaccination, antigens are introduced in the body. In response to antigens, antibodies are produced in the body against them. They neutralise the pathogen during actual infection.
(c) Name the type of cells the AIDS virus enters after getting into the human body. (CBSE Outside Delhi 2019)
Answer:
HIV enters macrophages. Simultaneously HIV enters T helper- Lymphocytes.
Question 19.
(a) Write the scientific names of the source plants from where opioids and cannabinoids are extracted.
Answer:
Opioids are obtained from the opium plant Papaver somniferous. Cannabinoids are extracted from Cannabis sativa.
(b) Write their receptor sites in the human body. How do these drugs affect human beings? (CBSE Outside Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Receptors of opioids are present on the central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract. They are a depressant and slow down the body functions. Receptors of cannabinoids are present in the brain. They affect the cardiovascular system of the body.
Question 20.
Briefly describe the life history of the malarial parasite.
Answer:
- Malarial parasite (Plasmodium) completes its life cycle in two hosts., i.e. female anopheles mosquito and humans.
- Sporozoites are the infective stage.
- The sporozoites enter the human body, reach the liver through blood and multiply within the liver cells.
- Such liver cells burst and release the parasites (Cryptomerozoites) into the blood.
- Then they attack RBCs, multiply and cause their rupture.
- The rupture of RBCs is associated with the release of a toxin called haemozoin, which is responsible for the high recurring fever and the chill/ shivering and causing malaria.
- Sexual stages (gametocytes) develop in the red blood cells.
- The parasite then enters the female Anopheles mosquito along with the blood when it bites the infected person.
- Further development occurs in the stomach wall of the mosquito.
- The gametes fuse to form a zygote. It takes the worm-like shape called ookinete as it pierces the wall of the stomach.
- The zygote undergoes further development in the body of the mosquito to form sporozoites.
- Sporozoites are transported to and stored in the salivary glands of mosquitoes and are transferred to a human body during the bite of the mosquito.
- Female mosquito sucks human blood because it requires blood proteins for the development of its eggs.
Question 21.
Describe the effects of drug and alcohol abuse.
Answer:
Effects of drug/alcohol abuse:
- The immediate effects of drugs/ alcohol abuse are manifested as reckless behaviour, vandalism and violence.
- Excess doses can lead to coma and death due to cerebral haemorrhage, respiratory and heart failure.
- A combination of drugs or their intake of alcohol leads to death.
- The most common warning signals of drug/alcohol abuse include:
(a) Drop in academic performance.
(b) Lack of interest in personal hygiene.
(c) Withdrawal and isolation from family and friends.
(d) Aggressive and rebellious behaviour.
(e) Lack of interest in hobbies.
(f) Change in sleeping and eating habits.
(g) Fluctuations in weight, etc.
Question 22.
Name the type of immunity that is present at the time of birth in humans. Explain any two ways by which it is accomplished. (CBSE 2008)
Answer:
Innate immunity: It is also called inborn or non-specific immunity. It is the first line of defence. It is composed of the following steps:
1. Anatomic barriers: The skin and mucous membranes secrete certain chemicals which dispose of pathogens. Specific cases of this defence are cited below: The oil and sweat secreted by sebaceous and sudoriferous glands contain lactic acid and fatty acids, which make the skin surface acidic (pH 3 to 5). This does not allow the microorganisms to establish.
2. Physiological barrier: Body temperature, pH and various body secretions like saliva prevent the growth of many pathogenic microorganisms. Pyrogens and interferons aid in fighting infections.
Question 23.
On what basis diagnosis of cancer is made?
Answer:
Diagnosis of cancer:
- Blood and bone marrow tests are done for increased cell counts in case of leukaemia.
- Histopathological study or biopsy: In a biopsy, a piece of the suspected tissue cut into thin sections is stained and examined under a microscope by a pathologist.
- Radiography: X-rays are used to detect cancer of the internal organs
- Computed tomography: It uses X-rays to generate a three-dimensional internal image of an object.
- Resonance imaging: Non-ionising radiation and strong magnetic field are used in MRI to accurately detect pathological and physiological changes in the living tissue.
- Monoclonal antibodies: Antibodies against cancer-specific antigens are also used for the detection of certain cancers.
Question 24.
Explain with the help of sketch the action of HIV in the body. (CBSE Delhi 2011)
Or
Name the cells HIV (Human Immuno Deficiency Virus) gains entry into after infecting the human body. Explain the events that occur in these cells. (CBSE Outside Delhi 2016)
Or
Trace the events that occur in the human body to cause immunodeficiency when HIV gains entry into the body. (CBSE 2011, 2014)
Answer:
The action of HIV in the body. After getting into the body of the person, the virus enters into macrophages where RNA genome of the virus replicates to form viral DNA with the help of the enzyme reverse transcriptase. This viral DNA gets incorporated into the host cell’s DNA and directs the infected cells to produce virus particles. The macrophages continue to produce virus and in this way acts as an HIV factory.
Simultaneously, HIV enters into helper (Th) T-lymphocytes (a type or subset of T-lymphocytes about which you have read above, in the immune system), replicates and produces progeny viruses. The progeny viruses released in blood attack other helper T-lymphocytes. This is repeated leading to a progressive decrease in the number of helper T-lymphocytes in the body of the infected person.
During this period, the person suffers from bouts of fever, diarrhoea and weight loss. Due to the decrease in the number of helper T-lymphocytes, the person starts suffering from an infection due to bacteria such as Mycobacterium, viruses, fungi and even parasite Toxoplasma. The patient becomes so much immunologically deficient and unable to fight against such infections.
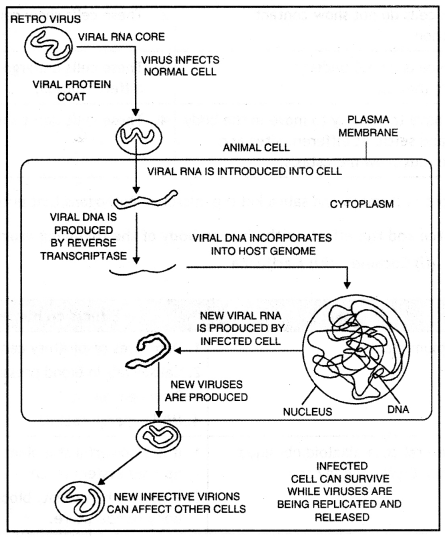 The action of HIV in the body cells.
The action of HIV in the body cells.
Question 25.
(a) If a patient is advised anti-retroviral drug, name the possible infection he/ she is likely to be suffering from. Name the causative organism.
Answer:
The person may be suffering from AIDS. It is caused by HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus).
(b) How do vaccines prevent subsequent microbial infection by the same pathogen?
Answer:
Antibody-provoking agents are called a vaccine. They prevent microbial infection by initiating production of antibodies to act against antigens to neutralise the pathogenic agents during later actual infection.
The vaccine also generates memory B-cells and T-cells that actually recognise the pathogen quickly in case of infection at later stages of life.
(c) How does a cancerous cell differ from a normal cell?
Answer:
Differences between the cancerous cell and normal cell:
| Cancerous cells | Normal cells |
| 1. These cells divide in an uncontrolled manner and rate of division is high. | 1. These cells divide in a regulated and controlled manner. |
| 2. These cells do not show contact inhibition. | 2. These cells show contact inhibition. |
| 3. These cells do not undergo differentiation. | 3. These cells undergo programmed differentiation. |
| 4. They have the ability to move in the body fluid and settle at different sites and divide thus show metastasis. | 4. These cells don’t show metastasis. |
(d) Many microbial pathogens enter the gut of humans along with food. Name the physiological barrier that protects the body from such pathogens. (CBSE Sample Paper 2020)
Answer:
The acid present in the stomach and saliva kills the microbial pathogens that enter along with food.
Question 26.
Write the source and the effect on the human body of the following drugs:
(i) Morphine
(ii) Cocaine
(iii) Marijuana (CBSE Delhi 2011)
Answer:
| Name of drug | Source | Effects on the human body |
| 1. Morphine | Opium plant | 1. Depresses respiratory centre. 2. Causes fall in blood pressure. 3. Slow heartbeat. 4. Mild hyperglycaemia |
| 2. Cocaine | Natural coca alkaloid obtained from Erythroxylon coca | 1. It is a powerful stimulant of the central nervous system (CNS) 2. Increases heartbeat, blood pressure and body temperature. |
| 3. Marijuana | Dried flowers and top leaves of female plant of Cannabis Sativa | 1. It causes psychosis 2. Raises blood sugar and increases the frequency of urination |