Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Gymnosperms Various Types and its General Characteristics
Naked Seed Producing Plants
Michael Crichton’s Science Fiction is a book transformed into a Film of Steven Spielberg (1993) called Jurassic Park. In this film you might have noticed insects embedded in a transparent substance called amber which preserves the extinct forms. What is amber? Which group of plants produces Amber?

Amber is a plant secretion which is an efficient preservative that doesn’t get degraded and hence can preserve remains of extinct life forms. The amber is produced by Pinites succinifera, a Gymnosperm. In this chapter we shall discuss in detail about one group of seed producing plants called Gymnosperms.
Gymnosperms (Gr. Gymnos = naked; sperma = seed) are naked seed producing plants. They were dominant in the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods of Mesozoic era. The members are distributed throughout the temperate and tropical region of the world.
General Characteristic Features
- Most of the gymnosperms are evergreen, woody trees or shrubs. Some are lianas (Gnetum)
- The plant body is sporophyte and is differentiated into root, stem and leaves.
- A well developed tap root system is present. Coralloid roots of Cycas have symbiotic association with blue green algae. In Pinus the roots have mycorrhizae.
- The stem is aerial, erect and branched or unbranched (Cycas) with leaf scars.
- In conifers two types of branches namely branches of limited growth (Dwarf shoot) and Branches of unlimited growth (Long shoot) is present.
- Leaves are dimorphic, foliage and scale leaves are present. Foliage leaves are green, photosynthetic and borne on branches of limited growth. They show xerophytic features.
- The xylem consists of tracheids but in Gnetum and Ephedra vessels are present.
- Secondary growth is present. The wood may be Manoxylic (Porous, soft, more parenchyma with wide medullary ray – Cycas) or Pycnoxylic (compact with narrow medullary ray-Pinus).
- They are heterosporous. The plant may be monoecious (Pinus) or dioecious (Cycas).
- Microsporangia and megasporangia are produced on microsporophyll and megasporophyll respectively.
- Male and female cones are produced.
- Anemophilous pollination is present.
- Fertilization is siphonogamous and pollen tube helps in the transfer of male nuclei.
- Polyembryony (presence of many embryo) is present. The naked ovule develops into seed. The endosperm is haploid and develop before fertilization.
- The life cycle shows alternation of generation. The sporophytic phase is dominant and gametophytic phase is highly reduced.
- The photograph of some of the gymnosperms is given in Figure 2.8. Sporne (1965) classified gymnosperms into 3 classes, 9 orders and 31 families.
The Classes Include:-
- Cycadospsida
- Coniferopsida
- Gnetopsida.

Comparison of Gymnosperm with Angiosperms
Gymnosperms resemble with angiosperms in the following features:-
- Presence of well organised plant body which is differentiated into roots, stem and leaves.
- Presence of cambium in gymnosperms as in dicotyledons.
- Flowers in Gnetum resemble the male flower of the angiosperm. The zygote represent the first cell of sporophyte.
- Presence of integument around the ovule.
- Both plant groups produce seeds.
- Pollen tube helps in the transfer of male nucleus in both.
- Presence of eustele.
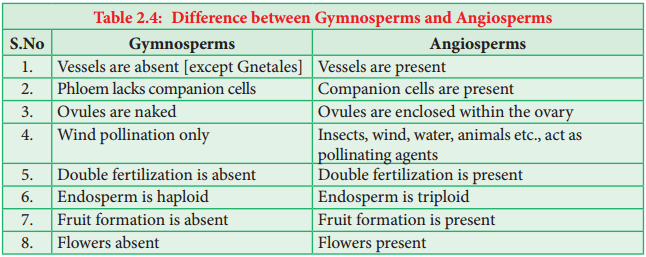
The difference between Gymnosperms and Angiosperms were given in Table 2.4.
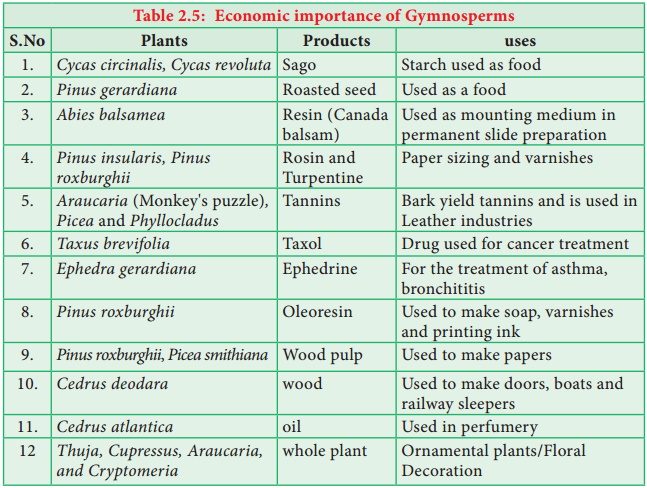
Economic Importance Of Gymnosperms
Palaeobotany in India
The National wood fossil park is situated in Tiruvakkarai, a Village of Villupuram district of Tamil Nadu. The park contains petrified wood fossils approximately 20 million years old. The term ‘form genera’ is used to name the fossil plants because the whole plant is not recovered as fossils instead organs or parts of the extinct plants are obtained in fragments. Shiwalik fossil park-Himachal Pradesh, Mandla Fossil park-Madhya Pradesh, Rajmahal Hills-Jharkhand, Ariyalur – Tamilnadu are some of the fossil rich sites of India.
Some of the Fossil Representatives of Different Plant Groups are Given Below:
- Fossil Algae – Palaeoporella, Dimorphosiphon
- Fossil Bryophytes – Naiadita, Hepaticites, Muscites
- Fossil Pteridophytes – Cooksonia, Rhynia, Baragwanthia, Calamites
- Fossil Gymnosperms – Medullosa, Lepidocarpon, Williamsonia, Lepidodendron
- Fossil Angiosperms – Archaeanthus, Furcula