Class 10 Science Chemistry Chapter 3 MCQ With Answers
Chemistry Class 10 Chapter 3 MCQs On Metals and Non-metals
Metals And Non Metals Class 10 MCQ Question 1.
Which of the following properties is generally not shown by metals?
(a) Electrical conduction
(b) Sonorous in nature
(c) Dullness
(d) Ductility
Answer:
(c) Dullness
Explanation: Metals generally do not show dullness. Metals such as gold and silver are usuaLly shiny rather than dull.
Related Theory:
Conduction: Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity as they have free electrons. Silver and copper are the best conductors of heat, whereas lead and mercury are poor conductors of heat. Sonorous: Metals that produces a sound on striking a hard surface.
Metallic lustre: Metal, in its pure state, has a shining surface. This property is known as metallic lustre. Ductility: The ability of metals to be drawn into thin wires. Cold is the most ductile metal.
Metal And Non Metals Class 10 MCQ Question 2.
The solution of one of the following compounds will not conduct electricity. This compound is:
(a) NaCl
(b) CCl4
(c) MgCl2
(d) CaCl2
Answer:
Metals And Nonmetals Class 10 MCQ Question 3.
Which one of the following metals does not react with cold as well as hot water?
(a) Na
(b) Ca
(c) Mg
(d) Fe
Answer:
![]()
Class 10 Metals And Non Metals MCQ Question 4.
An aluminium strip is kept immersed in freshly prepared ferrous sulphate solution taken in a test tube, the change observed is that:
(a) Green solution slowly turns colourless
(b) Lower end of test tube becomes slightly warm
(c) A colourless gas with the smell of burning sulphur is observed
(d) Light green solution changes to blue
Answer:
Class 10 Science Chapter 3 MCQ Question 5.
Which of the following oxide(s) of iron would be obtained on the prolonged reaction of iron with steam?
(a) FeO
(b) Fe2O3
(c) Fe3O4
(d) Fe2O3 and Fe3O4
Answer:
(c) Fe3O4
Metals And Non Metals MCQ Question 6.
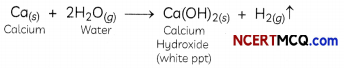
What happens when calcium is treated with water?
(I) It does not react with water.
(II) It reacts violently with water.
(III) It reacts Less violently with water.
(IV) Bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of calcium.
(a) (I) and (IV)
(b) (II) and (III)
(c) (I) and (II)
(d) (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(d) (III) and (IV)
Explanation: When calcium is treated with water, it reacts vigorously with water and to produce a cloudy white precipitate of calcium hydroxide and hydrogen gas is released as bubbles.
‘Related Theory
Sometimes hydrogen bubbles get stuck to the surface of calcium metaL making it tight arid thus calcium starts floating. Reaction of calcium with water is exothermic but the heat produced in this reaction is not sufficient so that hydrogen can catch
Ch 3 Science Class 10 MCQ Question 7.
Which of the foLLowing are not ionic compounds?
(I) KCl
(II) HCl
(III) CCl4
(IV) NaCl
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (II) and (III)
(c) (III) and (IV)
(d) (I) and (III)
Answer:
![]()
Class 10 Science Ch 3 MCQ Question 8.
Generally, non-metals are not Lustrous. Which of the following non-metals is lustrous?
(a) Sulphur
(b) Oxygen
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Iodine
Answer:
(d) Iodine
Explanation: Iodine is a non-metal with a lustrous appearance and exists in solid state.
Related Theory
Graphite is another non-metaL that is shiny and Lustrous.
MCQ On Metals And Non Metals Class 10 Question 9.
2 mt each of conc. HCL, HNO3, and a mixture of conc. HCL and conc. HNO3 in the ratio of 3:1 were taken in test tubes labelled as A, B and C. A small piece of metal was put in each test tube. No change occurred in test tubes A and B but the metaL got dissolved in test tube C. The metal could be:
(a) Al
(b) Au
(c) Cu
(d) Pt
Metal And Non Metals MCQ Class 10 Question 10.
An element A is soft and can be cut with a knife. This is very reactive to air and cannot be kept ¡n open air. It reacts vigorously with water. Identify the element from the following:
(a) Mg
(b) Na
(c) P
(d) Co
Answer:
(b) Na
Explanation: Na (sodium) possesses all the above properties. It is too soft and can be cut with a knife. It is also very reactive and reacts with oxygen or moisture present in air and produces sodium hydroxide, which is a highly exothermic reaction producing a lot of heat. It also reacts with water and burns due to the vigorous formation of hydrogen gas. That is why sodium is stored in kerosene oil to prevent any reaction.
MCQ On Metals And Non Metals Question 11.
Which among the following statements is incorrect for magnesium metal?
(a) It burns in oxygen with a dazzling white flame.
(b) It reacts with cold water to form magnesium oxide and evolves hydrogen gas.
(c) It reacts with hot water to form magnesium hydroxide and evolves hydrogen gas.
(d) It reacts with steam to form magnesium hydroxide and evoLves hydrogen gas.
Answer:
![]()
Metal And Non Metal Class 10 MCQ Question 12.
The electronic configurations of three elements X, Y and Z are X – 2, 8; Y – 2, 8, 7 and Z – 2, 8, 2. Which of the following ¡s correct?
(a) X is a metal
(b) Y is a metaL
(c) Z ¡s a non-metal
(d) Y is a non-metaL and Z is a metaL
MCQ Questions For Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Question 13.
In the given reaction,
Al2O3 + NaOH → X + H2O.
What is element X?
(a) NaAlO2
(b) Na3Al
(c) Na2O3
(d) NaAl2O3 [Diksha]
MCQ Of Metal And Nonmetal Class 10 Question 14.
Sandhya took three beakers A, B and C containing zinc sulphate, silver sulphate and iron(ll) sulphate solutions respectively. Copper pieces were added to each beaker. The solution will appear blue in the case of:
(a) Beaker A
(b) Beaker B
(c) Beaker C
(d) Beakers B and C [Diksha]
Answer:
(b) Beaker B
Explanation: The solution will appear blue in Beaker B. Let us see how.
When pieces of copper metal are kept immersed in silver sulphate solution for some time, the solution gradually becomes blue and a shiny greyish-white deposit of silver metal is formed on the copper strip.
In this reaction, copper metal is displacing silver from silver sulphate solution, forming copper sulphate and silver metal. The solution becomes blue due to the formation of copper sulphate. The reason behind this displacement reaction is that copper is more reactive than silver.
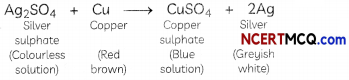
On the other hand, copper metal is less reactive than iron and zinc and hence cannot displace them from their respective salt solutions.
Chapter 3 Science Class 10 MCQ Question 15.
Arrange the following metal in the decreasing chemical activity series.
(I) Potassium
(II) Magnesium
(III) Gold
(IV) Iron
Correct options are:
(a) (I), (II), (III) and (IV)
(b) (I), (III), (IV) and (II)
(c) (I), (II), (IV) and (III)
(d) (I), (IV), (II) and (III)
Question 16.
Which metal can be displaced by copper from Its salt solution?
(I) Silver
(II) Magnesium
(III) iron
(IV) Iron
Correct options are:
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (I) and (III)
(c) (II) and (III)
(d) (I) and (IV)
Answer:
(d) (I) and (IV)
Silver and mercury are less reactive than copper and as copper will displace those metals from its salt solution which are less reactive than it, the correct option is (d).
![]()
Question 17.
Metals are refined by using different methods. Which of the following metals are refined by electrolytic refining?
(I) Au
(II) Cu
(III) Na
(IV) K
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (IV) and (III)
(c) (II) and (III)
(d) (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(a) (I) and (II)
Explanation: Gold (Ag) and copper (Cu) obtained after extraction are in impure form. So, metals Au (gold) and Cu (copper) are refined by electrolytic refining. Other than gold and copper, electrolytic refining is used for metals such as Zn and Ag. Sodium (Na) and potassium (K) are extracted by electrolytic reduction. Metals obtained after electrolytic reduction are in pure form.
Related Theory
Alkali metals are very reactive, so they cannot be refined with the help of the electrolytic refining process.
Question 18.
Galvanisation is a method of protecting iron from rusting by coating it with a thin layer of:
(a) Gallium
(b) Aluminium
(c) Zinc
(d) Silver
Answer:
(c) Zinc
Explanation: Zinc (Zn) metal is used to protect iron surfaces from rusting.
Related Theory
Galvanization is basically coating iron or steel with a layer of zinc to prevent it from rusting. Water pipes are also galvanized to prevent corrosion.
Question 19.
Stainless steel is a very useful material in our life, in stainless steel, iron is mixed with:
(a) Mi and Cr
(b) Cu and Cr
(c) Mi and Cu
(d) Cu and Au
Answer:
(a) Ni and Cr
Explanation: Stainless steel is an alloy of iron (74%), nickel (8%) and chromium (18%).
Related Theory
‘Alloying elements enhance the structure and properties such as durability, strength and toughness of the metal. It makes them corrosion-resistant.
![]()
Question 20.
If copper is kept in the open air, it slowly loses its shining brown surface and gains a green coating. It is due to the formation of:
(a) CuSO4
(b) CuCO3
(c) CU(NO3)2
(d) CuO
Answer:
Question 21.
Which of the following metals are obtained by electrolysis of their chlorides in a molten state?
(I) Na
(II) Ca
(III) Fe
(IV) Cu
(a) (I)and(IV)
(b) (III) and (IV)
(c) (I) and (III)
(d) (I) and (II)
Answer:
Question 22.
An electrolytic cell consists of:
(I) Positively charged cathode
(II) Negatively charged anode
(III) Positively charged anode
(IV) Negatively charged cathode
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (III) and (IV)
(c) (I) and (III)
(d) (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(b) (III) and (IV)
Explanation: There is a positively charged anode and a negatively charged cathode in an electrolytic cell. Positively charged ions (cations) are deposited at the negatively charged cathode. Negatively charged ions (anions) are deposited at the positively charged anode.
Question 23.
During electrolytic refining of zinc, it gets:
(a) Deposited on the cathode
(b) Deposited on the anode
(c) Deposited on the cathode as well as anode
(d) Remains in the solution
Answer:
Question 24.
Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of a metal with a metal or non-metal. Which among the following alloys contains non-metal as one of its constituents?
(a) Brass
(b) Bronze
(c) Amalgam
(d) Steel
Answer:
(d) Steel
Explanation: SteeL contains non-metal as one of its constituents. Steel is an alloy made by combining iron and other elements, mainly carbon. Carbon gives strength to iron. It is used to make buildings, ships, automobiles, machines, and appliances.

Related Theory
- Brass – Copper and zinc
- Bronze – Copper and tin
- Amalgam – Mercury with other metal
- Steel – Iron with carbon
Question 25.
Which among the following alloys contains mercury as one of its constituents?
(a) Stainless steel
(b) Alnico
(c) Solder
(d) Zinc amalgam
Answer:
![]()
Question 26.
Which one of the following figures correctly describes the process of electrolytic refining?
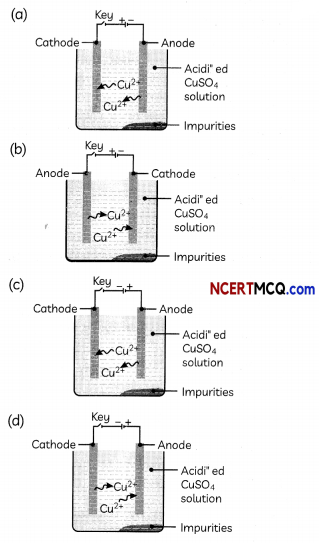
Answer:
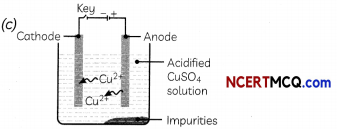
Explanation: In the electrolytic refining process, impure metal forms the anode, which is the positive electrode, whereas pure metal forms the cathode which is the negative electrode.
Figure (c) shows the process of electrolytic refining of copper metal. Copper from impure anode dissolves into the solution. Copper ions (Cu2+) from the solution are deposited on the cathode and impurities settle down below the anode as anode mud.
Question 27.
Select the incorrect statements):
(I) Solder is an alloy of lead and copper
(II) Solder is an alloy of lead and tin
(III) Melting point of solder is low
(IV) Melting point of solder is high
(a) Only (I)
(b) Both (I) and (III)
(c) Both (II) and (IV)
(d) Both (I) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 28.
All ionic compounds:
(a) Have high melting point but the low boiling point
(b) Are generally soluble in kerosene
(c) Are generally brittle
(d) Conduct electricity in solid-state
Answer:
Question 29.
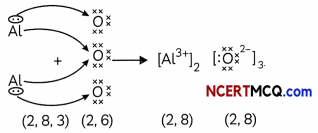
The cations and anions present in aluminium oxide are:
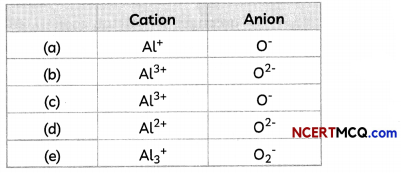
Answer:
(b) Cation: Al37; Anion: O2-
Explanation: Aluminium oxide or Al2O3 is formed by the transfer of electrons from aluminium atoms to oxygen atoms.
Aluminium (Atomic number = 13) has 3 valence electrons whereas oxygen (atomic number = 8) has 2 valence electrons.
So, each aluminium atom donates its 3 valence electrons to the oxygen atoms and forms cations [Al3+], whereas each oxygen atom gains two electrons and forms anions [O2-].
Question 30.
The metals which have very low melting points are:
(a) Gallium and caesium
(b) Gallium and sodium
(c) Caesium and potassium
(d) Sodium and potassium
Assertion Reasoning questions Class 10 Science Chapter 3
For the following questions, two statements are given – one labelled Assertion (A) and other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
![]()
Question 31.
Assertion (A): Alkali metals like sodium and potassium can be cut with a knife.
Reason (R): They have high densities.
Answer:
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false.
Explanation: Alkali metals like sodium and potassium are so soft that they can be cut with a knife as they have low densities.
Question 32.
Assertion (A): Magnesium is less reactive than sodium.
Reason (R): Sodium reacts more vigorously with oxygen than magnesium.
Answer:
Question 33.
Assertion (A): In the following reaction between calcium and water, calcium starts floating.
Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2
Reason (R): Calcium hydroxide is lighter than water.
Answer:
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false.
Explanation: In the reaction between calcium and water, calcium starts floating because the bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of calcium metal.
Question 34.
Assertion (A): Hydrogen gas is evolved when a metal reacts with nitric acid.
Reason (R): Nitric acid is a strong oxidizing agent.
Answer:
Question 35.
Assertion (A): The compound MgCl2 will not conduct electricity in a solid-state.
Reason (R): Movement of ions in ionic compounds is not possible in solid-state.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are. true but (R) is not the correct explanation of the (A).
Explanation; The compound MgCl2 is an ionic compound as it is formed by the transfer of electrons between magnesium and chlorine. It will not conduct electricity in solid-state as the movement of ions in ionic compounds is not possible in a solid-state.
Question 36.
Assertion (A): The metals and alloys are good conductors of electricity.
Reason (R): Bronze Is an alloy of copper and tin and it is not a good conductor of electricity.
Answer:
(d) (A) is false but (R) is true.
Explanation: All the metals and alloys are not always good conductors of electricity like bronze is not a good conductor of electricity, its constituents are copper and tin. Copper is a good conductor whereas tin is not a good conductor of electricity. Alloy nichrome is a good conductor of electricity.
Related Theory
- Metals are good conductors of electricity because they.
- have a large number of free electrons.
- Possess small resistivity in the range of 10-8 W m to 10-6 W m. Whereas alloys have more resistivity.
(Competency Based Questions (CBQs))
Question 1.
The exact date that humans first began to mine gold is unknown, but some of the oldest known gold artefacts were found in the Varna Necropolis in Bulgaria. The graves of the necropolis were built between 4700 and 4200 BC, indicating that gold mining could be at least 7000 gears old. In the area of the Kolar Gold Fields in Bangarpet Taluk, Kolar District of Karnataka state, India, gold was first mined prior to the 2nd and 3rd century AD by digging small pits. (Golden objects found in Harappa and Mohenjo-daro have been traced to Kolar through the analysis of impurities — the impurities include 11% silver concentration, found only in KGF ore.

In nature, aluminium is found in a combined state whereas silver/gold is found in Freestate. Give reason.
Answer:
Silver and gold are least reactive metals and are often found in their native or free state. Aluminium is a very reactive metal and is never found in free state, but in combined state.
![]()
Question 2.
Dhanteras, also known as Dhanatrayodashi, is the first day that marks the festival of Diwali in India. Dhanteras is the worship of lord Dhanvantari. Fundus considers this an extremely auspicious day for making new purchases, especially of gold or silver articles and new utensils. It is believed that new “Dhan” (wealth} or some item made of precious metal is a sign of good. luck. In modern times, Dhanteras has come to be known as the most: auspicious occasion for buying gold, silver, and other metals, especially kitchenware. Palak, along with her mother, purchased some kitchenware articles made of stainless steel on this occasion.
How does alloying of iron change its properties?
Answer:
Pure iron is very soft arid stretches easily when hot but if iron ismixed with a small amount of carbon (about 0.05 %), it becomes hardand strong. When iron is mixed with nickel and chromium, we getstainless steel, which is hard and does not rust. Thus, if iron is mixedwith some other substance, its properties change.
Question 3.
Have you ever imagined what would happen if all the electrical wires used in our homes, offices and other places were without any covering? Well, people handling them would die of electrical chock and there would be short-circuiting leading to electrical fires all around us!

Electrical wires have a coating of an insulating material. The material, generally used is:
(a) Sulphur
(b) Graphite
(c) PVC
(d) All can be used
Answer:
(c) PVC
Explanation: An insulating substance is required to coat the electrical wire such as PVC, PVC is a polymer and a bad conductor of electricity, it is the most common insulating material used to insulate electrical conductors from electric charge, thus preventing direct human contact with electricity.
Graphite is a good conductor of electricity. Hence, it cannot be used as insulating material. Sulphur, although a bad conductor of electricity, is brittle in nature. So, it cannot be used as an insulating material.
Question 4.
Analyse the following reactivity series given below and answer the questions that follow:
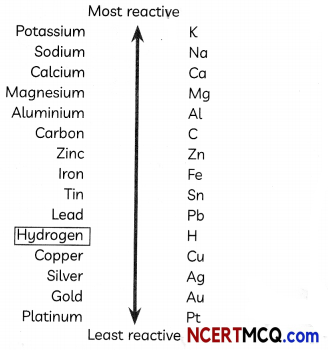
(A) Which of the two metals is more reactive: copper or silver?
Answer:
(B) What will happen if a strip of zinc is immersed in o solution of copper sulphate?
Answer:
When a strip of zinc metal is put in copper sulphate solution, then the blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades gradually and red-brown coating of copper is deposited on zinc strip.
![]()
This is an example of displacement reaction.
Explanation: Zinc is more reactive than copper so it will displace copper from its salt solution so displacement reaction takes place.
(C) If copper is kept open in air, it slowly Loses its shining brown surface and gains a green coating. It is due to the formation
(a) Acidic CuSO4
(b) Basic CuCO3
(c) Acidic Cu(NO3)2
(d) Basic CuO
Answer:
(D) Which one of the following four metals would be displaced from the soLution of its softs by other three metals?
(a) Mg
(b) Ag
(c) Zn
(d) Cu
Answer:
(b) Ag
Explanation: Least reactive metal can be displaced from its solution by other three metals. Silver is least reactive out of the given four metals.
Related Theory
Basic copper carbonate is an undesired layer formed on the surface of the copper and the process is known as corrosion.
![]()
Question 5.
Aqua regia is a yellow-orange (sometimes red) fuming liquid, so named by alchemists because it can dissolve the noble metals gold and platinum, though not all metals.

The composition of aqua-regia is:
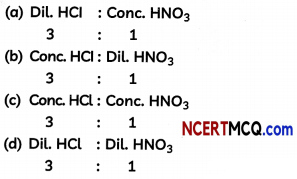
Answer:
![]()
Explanation: Aqua-regia is a mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid and concen¬trated nitric acid in the ratio of 3:1. Aqua-regia, being a strong acid, dissolves gold.
Question 6.
Atoms that gain electrons and therefore have a net negative charge are known as anions. Conversely, atoms that lose electrons and therefore have a net positive charge are called cations. Cations tend to be metals, while anions tend to be non-metals. Ions may also be single atoms or multiple, complex groups of atoms. When we talk about ions, it’s true that opposites attract.
The opposite negative and positive charges of the ions hold together in ionic bonds, forming ionic compounds, which are just what they sound like: compounds made of ions. The loss or gain from one atom matches the loss or gain of the other, so one atom essentially ‘donates’ an electron to the other atom it pairs up with. Two positive or two negative ions will not join together because they have the same charge. But one positive and one negative will happily join together to make an ionic compound.
(A) Explain the formation of MgO. (Atomic No. of O = 8, Mg = 12).
Answer:
Electronic configuration of Mg: 2, 8, 2 and that of O: 2, 6.
Magnesium atom loses its two valence electrons to form Mg2+ ion and oxygen atom gains two electrons to form O2 ion thereby achieving their nearest inert gas configuration.
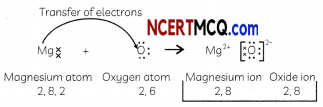
(B) Will the aqueous solution of MgO conduct electricity? If yes, give reasons for your answer?
Answer:
(C) Name a solvent in which ionic compounds are soluble and a solvent in which they are insoluble.
Answer:
Ionic compounds are soluble in water and insoluble in kerosene.
(D) Why do ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points?
Answer:
![]()
Question 7.
When Rohan was suffering from fever, the doctor had asked his parents to check his temperature every 2 hours and also to keep a record. He was a thermometer that has a certain metal in a liquid state inside it

Generally, metals are soLid in nature. Which one of the following metals is found in Liquid state at room temperature?
(a) Na
(b) Fe
(c) Cr
(d) Hg
Answer:
(d) Hg
Explanation: At room temperature, mercury (Hg) is the only metal found in a liquid state.
Related Theory
All other metals are solid at room temperature. Hg also has the lowest melting point.
Question 8.
Collect the samples of the following metals aluminium, copper, iron, lead, magnesium, zinc and sodium. Hold each of the samples above with a pair of tongs and try burning over a flame. It would be better if students wear eye protection and perform this activity with assistance from the teacher. Repeat with the other metal samples.
(A) Select the incorrect statements).
(I) All metals burn easily.
(II) Not all metals burn easily.
(III) Magnesium burns easily.
(IV) Copper and aluminium take time to burn.
(a) Only (I)
(b) Only (II)
(c) Both (I) and (III)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(B) The student performing this activity noted the following observations on the colour of flame observed when the metal is burnt.
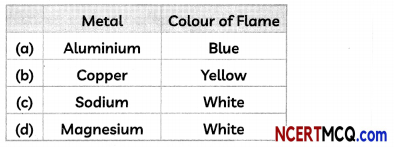
Select the correct observation.
Answer:
(d) Metal: Magnesium; Colour of Flame: White
Explanation: The colour of flame observed when the given metals are heated is given below:
Aluminium: Silvery white
Copper: Blue
Sodium: Yellow
Magnesium: White
(C) The correct arrangement of metaLs Al, Mg, Na and Zn in the decreasing order of their reactivity towards oxygen ¡s:
(a) Na > Al > Mg > Zn
(b) Na > Mg > Al> Zn
(c) Na > Al > Zn > Mg
(d) Mg > Na > Al > Zn
Answer:
(b) Na > Mg > Al > Zn
Explanation: Almost all metals combine with oxygen to form metal oxide. However, the reactivities of different metals towards oxygen are different. The most reactive of the given metals is Na followed by Mg, Al and Zn.
(D) Which of the following metal oxides are soluble in water?
(I) CuO
(II) Na20
(III) FeO
(IV) K20
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (I) and (III)
(c) Both (II) and (IV)
(d) Both (I) and (IV)
Answer:
(c) Both (II) and (IV)
Explanation: Most metal oxides are
insoluble in water but some of these dissolve in water to form alkalis. Sodium oxide and potassium oxide dissolve in water to produce alkalis as follows:
Na2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq)
K2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2KOH(aq)
(E) Metals such as sodium and potassium are kept immersed in:
(a) Kerosene oil
(b) Water
(c) Carbon disulphide
(d) Alcohol
Answer:
![]()
Question 9.
Pritha’s mother had lots of silver jewellery which she had kept in a jewellery box. One day, when she took them out to show them to her friends, she was surprised to see that most of them had a black coating over them.
Silver articles become black on prolonged exposure to air. This is due to the formation of:
(a) Ag3N
(b) Ag3O
(c) Ag2S
(d) Ag3S and Ag3N
Answer:
(c) Ag2S
Explanation: Silver metal reacts with atmos¬pheric sulphur compounds like H2S gas and forms a black coating of Ag2S over the surface. This reaction is as below:

Question 10.
Take samples of sodium chloride, potassium iodide, barium chloride or any other salt from the science laboratory. Take a small amount of a sample on a metal spatula and heat directly on the flame as shown in fig. Also try to dissolve the samples in water, petrol and kerosene.
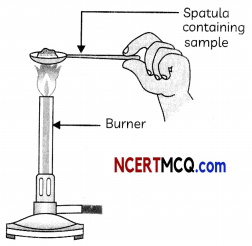
Heating a sail sample on a spatula
Make a circuit as shown in Fig. and insert the electrodes into a solution of one salt.
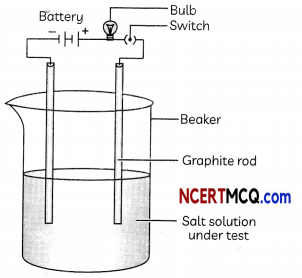
(A) The physical state and properties of the salt samples used in the activity is:
(I) All are crystalline solids
(II) All are brittle
(III) Not all are hard
(IV) Not all are brittle
Which of the statements above is correct?
(a) Both (I) and (III)
(b) Both (I) and (II)
(c) Both (II) and (III)
(d) Both (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(b) Both (I) and (II)
Explanation: All the salts are ionic compounds and are crystalline solids and hard due to the strong force of attraction between the positive arid negative ions. They are also brittle.
(B) Select the correct, observation when the salt sample is taken on a metal spatula and heated directly on the flame:
(a) The salts melt immediately
(b) The salts give out characteristics flame upon heating
(c) The salts do not melt easily
(d) The salts undergo sublimation
Answer:
(c) The salts do not melt easily
Explanation: The given salts are ionic compounds that have very high melting and boiling points as a large amount of energy is required to break the strong inter-ionic attraction.
(C) The solution of which of the following compounds will not conduct electricity?
(a) CCl4
(b) NaCl
(c) CaCl2
(d) KBr
Answer:
(D) A student noted the following observations with four compounds A, B, C and D.
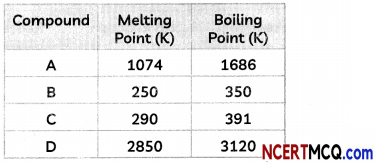
Which of the compounds A, B, C and D are ionic compounds?
(a) A and B
(b) B and C
(c) C and D
(d) A and D
Answer:
(E) Select the correct statement regarding the electrical conductivity of ionic compounds:
(a) The salt samples in the activity conduct electricity in their solid-state.
(b) The salt samples in the activity conduct electricity in a solution of water.
(c) The salt samples do not conduct electricity in a molten state.
(d) The salt samples do not conduct electricity in solution or in molten state.
Answer:
![]()
Question 11.
Displacement reactions are very important reactions of chemistry. They have many applications in various fields some of which are listed below:
(1) It is used in thermite welding.
(2) It is used in making alloy steel.
(3) It is used in the extraction of various metals.
(4) It is used in treating acid indigestion.
A thermite reaction is a single displacement reaction between iron oxide and aluminium which is also a highly exothermic reaction. The extreme heat released from this reaction is sufficient to melt the iron product.
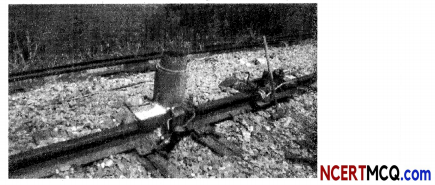
(A) The correct chemical equation describing the thermite process is:
(a) Fe2O3(s) + 2Al(s) + Heat → 2Fe(s) + Al2O3(l)
(b) Fe2O3(s) + 2Al(S) → 2Fe(l) + Al2O3(s) + Heat
(c) 3FeO(s) + 2Al(S) + Heat → 3Fe(l) + Al2O3(s)
(d) 3FeO(s) + 2Ai(s) → 3Fe(l) + Al2O3(s) + Heat
Answer:
(b) Fe2O3(s) + 2Al(s) → 2Fe(l) + Al2O3(s) + Heat
Explanation: Thermite reaction is the reaction between iron (III) oxide or Fe2O3 and aluminium. It is a highly exothermic process (shown by “+ Heat” in the product side) and iron is produced in the molten state. It is used to join is used tojoin railway tracks or cracked machine parts.
(B) What happens when zinc metal is added to G test tube containing Al2(SO4)3 solution?
(a) Zinc displaces aluminium from its salt solution
(b) No reaction takes place
(c) The solution becomes blue in colour
(d) The solution becomes colourless and aluminium metal is deposited.
Answer:
(b) No reaction takes place
Explanation: No reaction takes place as zinc is less reactive than aluminium and cannot displace aluminium from its salt solution, namely, Al2(SO4)3 solution.
(C) A student made the following observations after studying the following displacement reactions between a metal and a salt solution of a different metal:
(i) Mg + ZnSO4 → MgSO4 + Zn
(ii) Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
(iii) Co + MgSO4 → CaSO4 + Mg
Selsect the incorrect observation(s):
(i) Calcium will displace copper from copper sulphate solution.
(II) Magnesium will be displaced by both calcium and zinc
(II) The least reactive metal out of Mg, Ca, Cu and Zn are Zinc.
(IV) The most reactive metal out of Mg, Ca, Cu and Zn is calcium.
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (I) and (III)
(c) Both (II) and (III)
(d) Both (I) and (IV)
Answer:
(D) An activity was performed by a student to find the reactivity of four metals- A, B, C and D by taking salt solutions of four metals in four test tubes numbered 1 to 4 and adding the samples of each metal one by one to each of the test tubes.
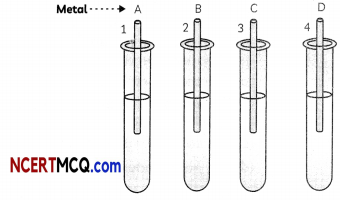
The observations recorded by the student are as given below:
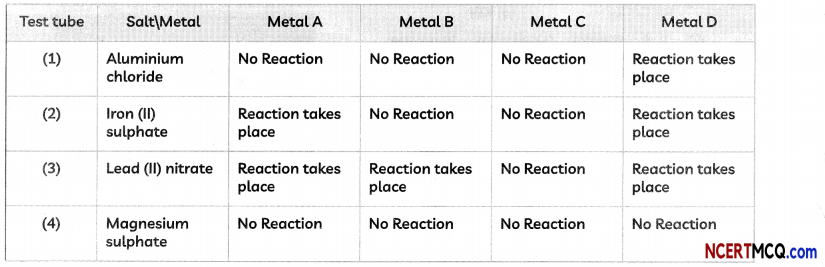
The correct arrangement of the given metals A, B, C and D in decreasing order of their reactivities is:
(a) C < B < A < D
(b) B < C < A < D
(c) C < B < D < A
(d)D < A < B < C
Answer:
(E) A student performed an experiment to study the displacement reaction of metals. He took two test tubes X and Y containing copper sulphate and silver nitrate solutions respectively.
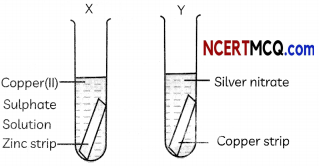
He dipped a strip of zinc in test tube X and copper strip in test tube Y and recorded his observations as shown below. Select the correct observation:
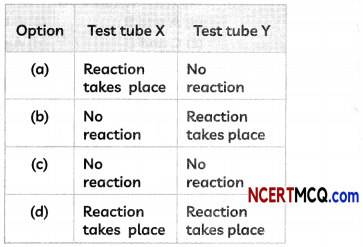
Answer:
(d) Test Tube X: Reaction takes place; Test Tube Y: Reaction takes place.
Explanation: Zinc is more reactive than copper and will displace copper from copper (II) sulphate solution in test tube X.
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
Also, copper is more reactive than silver and will displace silver from silver nitrate solution in test tube Y.
Cu + 2AgNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2Ag
Question 12.
A fusible metal alloy is used to create a permanent bond between metal workpieces. The alloy is melted in order to adhere to and connect the pieces after cooling, which requires that the alloy have a lower melting point than the pieces being joined. The alloy should also be resistant to oxidative and corrosive effects that would degrade the joint over time.
Name an alloy that is used for welding electrical wires together and also give its composition.
Answer:
Solder is an alloy that is used for welding electrical wires together. It is an alloy of lead and tin (Pb and Sn) and has a low melting point.
![]()
Question 13.
Sam went to the grocery store with his mother one day.
He observed that pickles, curds and other sour things are always stored in glass or plastic containers and never in any container made of a metal or alloy. He later found out that this is related to the chemical properties of metals as metals react with acids.

(A) Metals react with dilute acids to give:
(a) Salt and water
(b) Salt and hydrogen gas
(c) Salt and carbon dioxide gas
(d) Salt, water and carbon dioxide gas
Answer:
(b) Salt and hydrogen gas
Explanation: Most metals react with dilute acid to give the metal salt and hydrogen gas. Example:
Zn(s) + H2SO4 (aq) → ZnSO4(aq)) + H2(g)

(B) Which of the following metal will react with dilute hydrochloric acid?
(I) Cu
(II) Zn
(III) Al
(IV) Ag
(a) Only (I)
(b) Only (II)
(c) Both (I) and (IV)
(d) Both (II) and (III)
Answer:
(C) Which of the following oxides will not react with dilute sulphuric acid?
(a) CO2
(b) CuO
(c) MgO
(d) Na2O
Answer:
(D) Some students reacted an insoluble metal oxide with a dilute acid to form a soluble salt with a characteristic blue colour.
The insoluble metal oxide and the soluble salt could be:
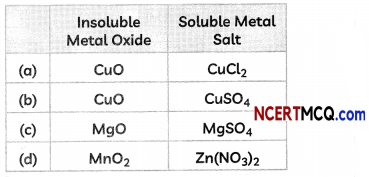
Answer:
(E) The correct arrangement of metals Mg, Zn, Fe and Al in decreasing order of their reactivity with dilute acids is:
(a) Al > Mg > Zn > Fe
(b) Al > Mg > Fe > Zn
(c) Mg > Al > Zn > Fe
(d) Mg > Al > Fe > Zn
Answer:
(c) Mg > Al > Zn > Fe
Explanation: Out of the metals Mg, Zn, Fe and Al, Mg will react most vigorously with dilute acid, followed by Al, Zn and Fe.
![]()
Question 14.
While walking along the roadside with his grandfather, Aman observed that many iron pipes had developed cracks on their surfaces.

(A) Metals react with dilute acids to give:
(a) Salt and water
(b) Salt and hydrogen gas
(c) SaLt ared carbon dioxide gas
(d) Salt, water and carbon dioxide gas
Answer:
(b) Salt and hydrogen gas
Explanation: Most metals react with dilute acid to give the metal salt and hydrogen gas.
Example:
Zn(s) + H2SO4 (aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
(B) Which of the following metal will react with dilute hydrochloric acid?
(I)Cu
(II)Zn
(III)AL
(IV)Ag
(a) Only (I)
(b) Only (II)
(c) Both (I) and (IV)
(d) Both (il) and (III)
Answer:
(C) Which of the following oxides will not react with dilute sulphuric acid?
(a)CO2
(b)CuO
(c) MgO
(d) Na2O
(D) Some students reacted an insoluble metal oxide with a dilute acid to form a soluble salt with a characteristic blue colour.
The insoluble metal oxide and the soluble salt couLd be:
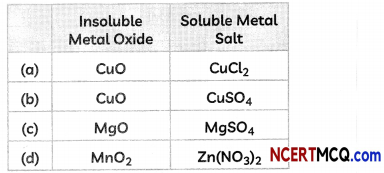
(E) The correct arrangement of metals Mg, Zn, Fe and AL in decreasing order of their reactivity with diLute acids is:
(a) Al > Mg > Zn> Fe
(b) Al > Mg> Fe > Zn
(c) Mg > Al> Zn > Fe
(d) Mg > Al > Fe > Zn
Answer:
(c)Mg > Al > Zn > Fe
Explanation: Out of the metals Mg, Zn, Fe and Al, Mg will react most vigorously with dilute acid, folLowed by At. Zn and Fe.
![]()
Question 15.
While walking along the roadside with his grandfather, Aman observed that many iron pipes had developed cracks on their surfaces.

Being inquisitive in nature and atso having Learned about the phenomenon of corrosion, Aman searched the internet for more information about corrosion and its prevention and found out that the most important factor in atmospheric corrosion, overriding pollution or lack of it, is moisture, either in the form of rain, dew, condensation, or high relative humidity (RH). In the absence of moisture, most contaminants would have little or no corrosive effect.
(A) Identify the correct statement:
(a) Rusting of iron is caused only by water.
(b) Rusting of iron is caused only by air,
(c) Rusting of iron is caused only by impurities.
(d) Rusting of iron is caused by both air and water.
Answer:
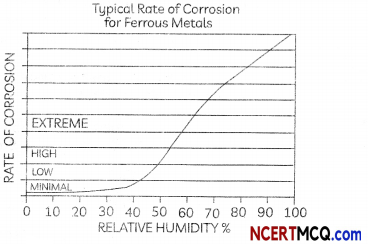
(B) Two students noted down the following observations after studying the graph showing the effect of reLative humidity on the rate of corrosion in iron
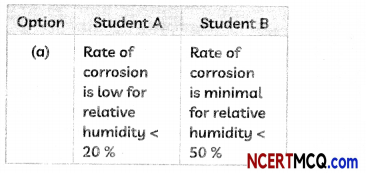
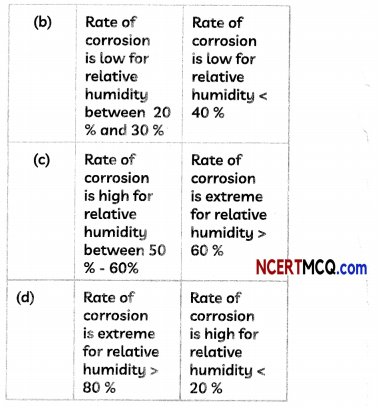
Select the correct option.
(C) Chemically rust is:
(a) Hydrated Iron (II) oxide
(b) Hydrated Iron (III) oxide
(c) Iron (III) sulphate
(d) Iron (III) oxide
Answer:
(c) Student A: Rate of corrosion is high for neiative humidity between 50% – 60%; Student B: Rate of corrosion… >60%.
Explanation: From the graph, we observe that the rate of corrosion depends upon the relative humidity and it increases with increase in the relative humidity.
Rate of corrosion is minimal for relative humidity < 40 %, is low for relative humidity between 40 % to 50 %. is high for relative humidity between 50% – 60 % and is extreme for relative humidity > 60 %.
(D) Which of the following statement is /are incorrect about corrosion?
(I) The black coating on silver articles is due to formation of basic silver oxide when silver reacts with oxygen present in air.
(II) The green coating on copper articles is due to formation of copper carbonate.
(III) The brown flaky substance formed on iron articles is due to the formation of rust.
(IV) The black coating on silver articles is due to formation of silver sulphide when silver reacts with hydrogen sulphide present in air.
(a) Only (I)
(b) Only (II)
(c) Both (I) and (III)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(a) Only (I)
(E) 0 Rusting of iron can be prevented by :
(a) Galvanisation only
(b) Alloying only
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer:
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
A metal combines with a non-metal to form a compound Y. Will it dissolve in an organic solvent or not?
Answer:
Metals combine with non-metals to form ionic compounds by transfer of electrons. Ionic compounds do not dissolve in organic solvents but are soluble in water.
Question 2.
An element E combines with 02 to form an oxide E20, which is a good conductor of electricity. Write the formula of the compound formed when it combines with chlorine?
Answer:
Question 3.
Why do ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten state?
Answer:
ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten state because the ions move freely in molten state since the electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions is overcome due to heat.
![]()
Question 4.
Why should the metal sulphides and carbonates be converted to metal oxides in the process of extraction of metal from them?
Answer:
Usually, metal sulphides and carbonates are converted to metal oxides in the process of extraction of metal. This is because extraction of a metal from its oxide is easier as compared to its extraction from its sulphides and carbonates. Metal oxides can easily reduce to metal with the help of a common reducing agent like coke.
Question 5.
From amongst the metal, sodium, calcium, aluminium, copper and magnesium, name the metal:
(A) Which reacts with water only on boiling.
(B) Another one which does not. react even with steam.
Answer:
(A) The metal which reacts with water only on boiling is magnesium as it does not react with cold water.
(B) The metal which does not react even with steam is copper.
Question 6.
An element ‘A’ form two oxides AO and AO2. The oxide AO is neutral whereas the oxide AO2 is acidic in nature. Would you call element ‘A’ a metal or a non-metal?
Answer:
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science with Answers
Class 10 Science Chemistry MCQ:
