Check the below Online Education NCERT MCQ Questions for MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution with Answers Pdf free download. https://ncertmcq.com/mcq-questions-for-class-10-science-with-answers/
Class 10 Science Biology Chapter 9 MCQ With Answers
Biology Class 10 Chapter 9 MCQs On Heredity and Evolution
Heredity And Evolution Class 10 MCQ Question 1.
In peas, a pure tall plant (TT) is crossed with a pure short plant (tt). The ratio of pure tall plants to pure short plants in F2 generation will be:
(a) 1: 3
(b) 3:1
(c) 1:1
(d) 2:1
Answer:
(c) 1:1
Explanation: The genotype ratio of F2 generation is: TT: Tt: tt = 1: 2: 1. Therefore, the ratio of TT and tt plants of F2 generation will be the same.
Heredity Class 10 MCQ Question 2.
Two pink-colored flowers on crossing resulted in 1 red, 2 pink, and 1 white flower progeny. The nature of the cross will be:
(a) Double fertilization
(b) Self-pollination
(c) Cross-fertilization
(d) No fertilization
Answer:
(c) Cross-fertilization
Explanation: The nature of the cross will be cross fertilization, which is the transfer of pollen from one plant to the stigma of flower; borne on a different plant of the same species.
Related Theory:
- Self-pollination: Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower of the same plant.
- Cross-pollination: Transfer of pollen grains from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower.
- Double fertilization: This process occurs when one male nucleus fertilizes (fuses) with the egg cell to form a zygote cell and the other male nucleus fuses (fertilizes) with two polar nuclei to cause triple fusion. These two types of fertilization take place at the same time in the ovule of the plant.
Heredity And Evolution MCQ Question 3.
In human males, all the chromosomes are paired perfectly except one. These unpaired chromosomes are:
(I) Large chromosome
(II) Small chromosome
(III) Y chromosome
(IV) X chromosome
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (III) and (II)
(c) (III) and (IV)
(d) (II) and (IV)
Answer:
Class 10 Heredity And Evolution MCQ Question 4.
Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) For every hormone there is a gene.
(b) For every protein there is a gene.
(c) For production of every enzyme there is a gene.
(d) For every molecule of fat there is a gene.
Answer:
(d) For every molecule of fat there is a gene. Explanation: A section of DNA that provides information for one protein is called the gene for that protein. Hormones and enzymes are proteins, and the formation of any particular protein is controlled by a particular gene. Fat biosynthesis occurs through metabolic reaction. They are not related to genes.
![]()
MCQ On Heredity And Evolution Question 5.
Which one is a possible progeny in F2 generation of purebred tall plant with round seed and dwarf plant with wrinkled seeds?
(a) Tall plant with round seeds
(b) Tall plant with wrinkled seeds
(c) Dwarf plant with round seed
(d) All of the above
Heredity And Evolution MCQ Questions Question 6.
If a round, green-seeded pea plant (RR yy) is crossed with wrinkled, yellow seeded pea plant, (rr YY), the seeds production in the F1 generation are:
(a) Round and yellow
(b) Round and green
(c) Wrinkled and green
(d) Wrinkled and yellow
Answer:
(a) Round and yellow
Explanation: The cross between RR yy and rr YY seeds will obtain RrYy offspring which will exhibit round and yellow phenotype, as these traits are the dominant ones.
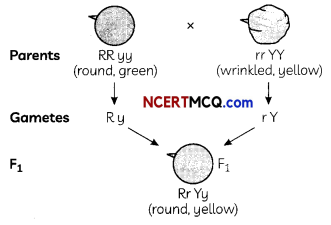
MCQ Questions On Heredity And Evolution Class 10 Question 7.
A zygote which has an X chromosome inherited from the father will develop into a:
(a) Boy
(b) Girl
(c) X chromosome does not determine the sex of a child
(d) Either boy or girl
Answer:
(b) Girl
Explanation: Humans follow XX- XY mechanism of sex determination i.e., women are XX while men are XY. All children will inherit an X chromosome from their mother regardless of whether they are boys or girls. Thus, the sex of the children will be determined by what they inherit from their father. A child who inherits an X chromosome from her father will be a girl and the one who inherits a Y chromosome from him will be a boy.
Heredity MCQ Class 10 Question 8.
Select the incorrect statement:
(a) The frequency of certain genes in a population change over several generations resulting in evolution.
(b) The reduction in the weight of an organism due to starvation is genetically controlled.
(c) Low weight parents can have heavy weight progeny.
(d) Traits which are not inherited over generations do not cause evolution.
Answer:
MCQ Questions For Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Question 9.
Select the correct statement:
(a) The tendril of a pea plant and the phylloclade of Opuntia are homologous.
(b) The tendril of a pea plant and the phylloclade of Opuntia are analogous.
(c) The wings of birds and the limbs of lizards are analogous.
(d) The wings of bird and the wings of bats are homologous.
Answer:
![]()
MCQs On Heredity And Evolution Class 10 Question 10.
If the fossil of an organism is found in the deeper layers of earth, then we can predict that:
(a) The extinction of the organism occurred recently.
(b) The extinction of the organism occurred thousands of years ago.
(c) The fossil position in the layers of Earth is not related to its time of extinction.
(d) The time of extinction cannot be deter¬mined.
Answer:
(b) The extinction of the organism occurred thousands of years ago.
Explanation: If we dig into the earth and start finding fossils, the fossils we find closer to the surface are more recent than the fossils we find in deeper layers.
Related Theory
Depth of each stratum signifies the relative age of fossils present in it. The deeper the stratum, the older the rock and the fossils present in it
Class 10 Science Chapter 9 MCQ Question 11.
A trait in an organism is influenced by:
(a) Paternal DNA only
(b) Maternal DNA only
(c) Both maternal and paternal DNA
(d) Neither paternal nor maternal DNA
Answer:
(c) Both maternal and paternal DNA
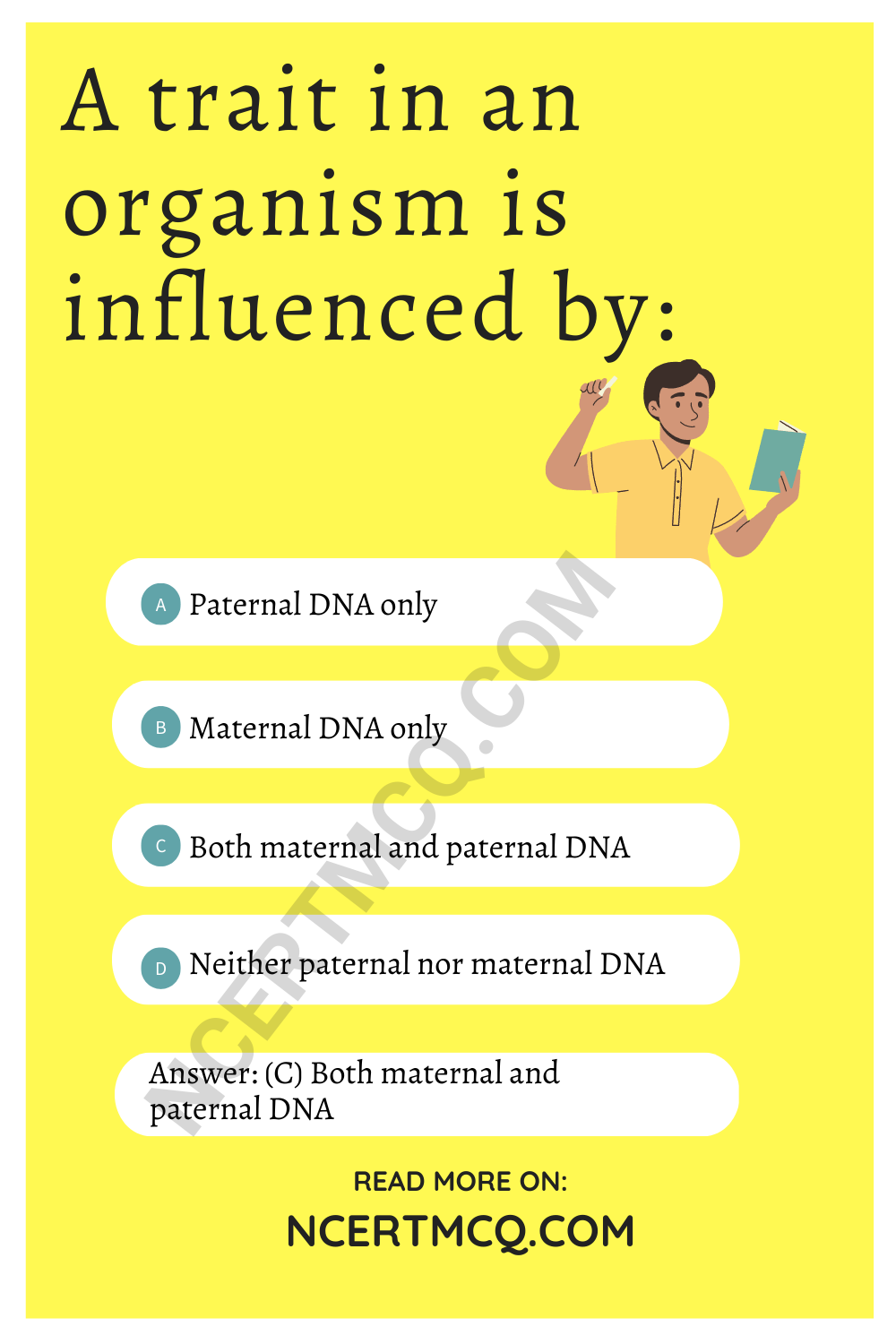
Explanation: DNA is contributed to an offspring by both the parents; hence, traits are influenced by both maternal and paternal DNA. During sexual reproduction, both mother and father pass their genes to their children, thus determining their traits; or characteristic features.
MCQ Of Heredity And Evolution Question 12.
New species may be formed if:
(I) DNA undergoes significant changes in germ cells.
(II) The chromosome number changes in the gamete.
(III) There is no change in the genetic material.
(IV) Mating does not take place.
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (I) and (III)
(c) (II), (III) and (IV)
(d) (I), (II) and (III)
Answer:
![]()
MCQ On Heredity And Evolution Class 10 Question 13.
which of the following statements is not true with respect to variation?
(a) All variations in a species have equal chances of survival.
(b) Change in genetic composition results in variation.
(c) Selection of variants by environmental factors forms the basis of evolutionary processes.
(d) Variation is minimum in asexual reproduction.
Answer:
Heredity And Evolution Class 10 MCQ With Answers Question 14.
According to the evolutionary theory, for¬mation of a new species is generally due to:
(a) Sudden creation by nature.
(b) Accumulation of variations over several generations.
(c) Clones formed during asexual reproduction.
(d) Movement of individuals from one habitat to another.
Answer:
Heredity And Evolution Class 10 MCQ Learn Cbse Question 15.
The theory of the evolution of species by natural selection was given by:
(a) Mendel
(b) Darwin
(c) Morgan
(d) Lamarck
Answer:
Question 16.
Some dinosaurs had feathers although they could not fly but birds have feathers that help them to fly. In the context of evolution this means that:
(a) Reptiles have evolved from birds.
(b) There is no evolutionary connection between reptiles and birds.
(c) Feathers are homologous structures in both the organisms.
(d) Birds have evolved from reptiles.
Answer:
Question 17.
Select a set of homologous organs from the following:
(a) Wings of a bat and wings of a butterfly
(b) Wings of a pigeon and wings of a bat
(c) Wings of a butterfly and wings of a pigeon
(d) Forelimbs of a duck, forelimbs of a cow and forelimbs of a lizard
Answer:
(d) Forelimbs of a duck, forelimbs of a cow and forelimbs of a lizard
Explanation: Wings of a bat and wings of a butterfly (A), Wings of a pigeon and wings of a bat (B) and Wings of a butterfly and wings of a pigeon (C) are analogous organs as they all use wings for flying but the wings have different structures.
Bat wings consist of flaps of skin stretched between the bones of the fingers and arm, wings of pigeon consist of feathers extending all along the arm whereas butterfly wings are covered in scales.
On the other hand, Forelimbs of a duck, forelimbs of a cow and forelimbs of a lizard are homologous organs as they all have similar structures which have been modified to perform different functions.
![]()
Question 18.
Select the correct statements regarding monohybrid cross between a pure tall pea plant and pure short pea plant performed by Mendel:
(I) All plants of the F1 generation were tall.
(II) The tall plants in the F1 generation were exactly the same as the tall plants of the parent generation
(III) One-quarter of the F2 progeny of the F1 tall plants were short.
(IV) Both the tallness and shortness traits were inherited in the F1 plants
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) (I), (II) and (III)
(d) (I), (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(d) (I), (III) and (IV)
Explanation: When a pure tall pea plant is crossed with a pure short plant, it was observed that all plants of the F1 generation were tall. But the tall plants in the F1 generation were not exactly the same as the tall plants of the parent generation. The genotype of the pure tall plant is TT, whereas the genotype of the tall plant in the F1 generation was Tt. The ratio of the tall and short plants in the F2 generation was 3:1. As 25 % of the pea plants in the F2 generation were tall, it means that both the shortness (t) and tallness (T) trait were inherited in the FI plants.
Question 19.
Which of the following are acquired traits?
(I) Attached or free earlobe
(II) Muscular body of a wrestler
(III) Body weight of starving animals
(IV) Brown and curly hair
(a) Both (I) and (III)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (I) and (IV)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 20.
Consider the plants the pitcher plant, venus fly trap, poinsettia and cactus.
Select the row containing incorrect information regarding the leaves of these plants in terms of evolutionary relationships.
| (a) Leaves of these plants are homologous organs | The leaves are structurally similar but modified to perform different functions |
| (b) Leaves of these plants are analogous organs | The leaves are structurally dissimilar but perform similar functions |
| (c) Leaves of these plants are vestigial organs | Leaves are homologous to
similar leaves in other plants |
| (d) Leaves of these plants are neither homologous nor analogous | The leaves have no structural or functional similarity |
Answer:
Question 21.
Study the organs and evolutionary relationship mentioned alongside. Select the row containing incorrect information.
| Organs Relationship | Evolutionary |
| (a) limbs of human being and frog | Homologous organs |
| (b) wings of bird and bat | Analogous organs |
| (c) Thorns and spines in plants | Analogous organs |
| (d) Tendril of pea plant and grape plant | Homologous organs |
Answer:
(d) Organs: Tendril of pea plant and grape plant; Evolutionary Relationship: Homologous organs
Explanation: Thorn is modification of stem and spine is modification of leaf. Tendrils in plant show similar function but they are different in origin. Pea plant has Leaf tendril whears. Grape plant has Stem tendril
Question 22.
which of the statements regarding evolution is correct?
(a) One species is always eliminated in order to give rise to a new species.
(b) The newly formed species are better than the old species.
(c) Evolution is the generation of diversity and the shaping of the diversity by environmental selection.
(d) More and more complex body designs have emerged over time as the older designs are ineffcient.
Answer:
Question 23.
which of the following cannot be an outcome of Mendel’s Experiment on crossing a tall pea plant with a short pea plant?
(a) 3 tall 1 short plant
(b) 4 tall plants and 1 medium height plant.
(c) 24 tall and 8 short plants
(d) 8 tall and 0 short plants
Answer:
![]()
Question 24.
Which of the following have a perfect pair of sex chromosomes?
(a) Only Girls
(b) Only Boys
(c) Both girls and boys
(d) It depends on many other factors
Answer:
(a) Only Girls
Explanation: Girls have a perfect paired 23rd chromosome, which is XX, whereas boys have a mismatched 23rd pair of chromosomes, which is XY.
Question 25.
Select the incorrect option.
Genetic drift is:
(a) A mechanism of evolution in which allele frequencies of a population remain constant over generations.
(b) It occurs in all populations of non-infinite size, but its effects are strongest in small populations.
(c) It may result in the loss of some alleles.
(d) It can have major effects when a population is sharply reduced in size by a natural disaster.
Answer:
Question 26.
Select the group which shares the maximum number of common characters:
(a) Two individuals of a species
(b) Two species of a genus
(c) Two genera of a family
(d) Two genera of two families
Answer:
Question 27.
Select the statements that describe the characteristics of genes:
(I) Genes are specific sequence of bases in a DNA molecule.
(II) A gene does not code for proteins.
(III) In individuals of a given species, a specific gene is located on a particular chromosome.
(IV) Each chromosome has only one gene.
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (I) and (III)
(c) (I) and (IV)
(d) (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(b) (I) and (III)
Explanation: Genes are units of heredity and are responsible for inheritance. Genes control the expression of a trait or a character in an organism. Genes are located on the chromosomes, which is present inside the nucleus of the cell in the crytoplasm.
Question 28.
The number of pair(s) of sex chromosomes in the zygote of humans is:
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Four
Answer:
Assertion Reasoning questions Class 10 Science Chapter 9
For the following questions, two statements are given: one Labeled Assertion (A) and the other Labeled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Question 29.
Assertion (A): The wing of an insect and wing of a bird are analogous organs
Reason (R): The organs which are quite different in fundamental structure and origin but perform the same function in different species are called analogous organs
Answer:
![]()
Question 30.
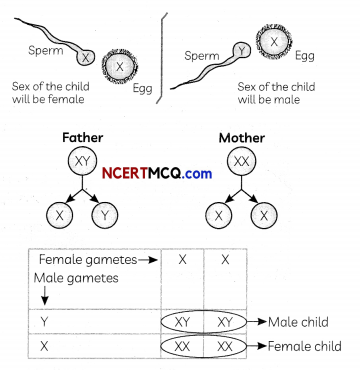
Assertion (A): The sex of a child in human beings will be determined by the type of chromosome he/ she inherits from the father.
Reason (R): A child who inherits ‘X‘ chromosome from his father would be a girl (XX), while a child who inherits a ‘Y‘ chromosome from the father would be a boy (XY).
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is correct explanation of the (A).
Explanation: Human beings have 23 pairs of chromosomes. Out of which one pair is sex chromosomes and 22 pairs are autosomes. In men, sex chromosome pair is mismatched pair ‘XY‘, ‘X‘ is normal sized and Y is shorter than ‘X‘ chromosomes. Human females have ‘XX chromosomes. Males produce two types of sperms whereas females produce only one ovum having ‘X’ chromosomes. A child who inherits the ‘X’ chromosome from a father would be a girl ‘(XX)’.
While a child who inherits a Y chromosome from the father would be a boy (XY).
Question 31.
Assertion: A geneticist crossed a pea plant having violet flowers with a peaplant with white flowers, he got all violet flowers in first generation.
Reason: White colour gene is not passed on to next generation.
Answer:
Question 32.
Assertion (A): New combination of traits are observed in F2 offspring when tall plants with round seeds are crossed with short plants with wrinkled seeds.
Reason (R): Tallness and round seed are both dominant traits.
Answer:
(Competency Based Questions (CBQs))
Question 1.
Lokesh was very fond of dogs. So, one day his friend called him to show a white dog and a black dog which he had recently got from his friend. Lokesh was wondering as to how different dogs have different colours!

Dogs having black coat colour when crossed with dogs having same colour, produced 200 offsprings. Out of this 150 were black and 50 were white. The genotype of dogs is:
(a) BB and bb (B: Black; b: white)
(b) Bb and bb (B: Black; b: white)
(c) Bb and Bb (B: Black; b: white)
(d) BB and Bb (B: Black; b: white)
Answer:
(a) BB and bb (B: Black; b: white)
Explanation: As the ratio of black: white dogs = 150 : 50 = 3 :1, black coat colour is dominant over white. Further, both black and white dogs are homozygous (BB and bb).
![]()
Question 2.
A giant 70 million year old fossil of a fish that lived amongst dinosaurs has been discovered in Argentine Patagonia, a team of researchers said on Monday.Argentine paleontologists “found the remains of a predator fish that was more than six meters long,” the researchers said in a statement.The discovery was published in the scientific journal Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology.The fish “swam in the Patagonian seas at the end of the Cretaceous Period, when the temperature there was much more temperate than now,” the statement said.

Mention any two methods of estimating life of a fossil.
Answer:
The two methods of estimating the life of a fossil are:
(1) By digging the earth and start finding fossils. The fossils found closer to the surface are more recent as compared to the fossils found in deeper layers.
(2) By detecting the ratios of different isotopes of a radioactive element in the fossil material, such as Carbon-14.
Question 3.
Inheritance from the previous generation provides both a common basic body design, and subtle changes in it, for the next generation. The original organism at the top will give rise to two individuals, similar in body design, but with subtle differences. Each of them, in turn, will give rise to two individuals in the next generation. Each of the four individuals in the bottom row will be different from each other. While some of these differences will be unique, others will be inherited from their respective parents, who were different from each other. Selection of variants by environmental factors forms the basis for evolutionary processes.
(A) If a trait A exists in 10% of a population of an asexually reproducing species and a trait B exists in 60% of the same population, which trait is likely to have arisen earlier?
Answer:
Trait B is likely to have arisen earlier because in asexual reproduction traits are carried from parents to offspring with least variations so since trait B has higher percentage it is likely to have arisen earlier.
(B) How does the creation of variations in a species promote survival?
Answer:
The Y chromosome in the zygote
Explanation: A child who inherits an X chromo¬some from her father will be a girl and the one who inherits a Y chromosome from him will be a boy. Thus the maleness of a child is determined by the presence of the Y chromosome in the zygote inherited from the father.
(C) Give any one factor that could lead to the rise of a new species?
Answer:
The factors could lead to the rise of a new species are:
(1) Natural Selection
(2) Method of Genetic Drift
(3) Gene Variation on Mutation
(4) Geographical and environmental factors
Related Theory
Specialtion is the process by which new species form. It occurs when groups in a species become reproductively isolated and diverge.
(D) Which of the processes, sexual reproduction or asexual reproduction, brings about maximum variations in the offsprings?
Answer:
Question 4.
When Simran visited the hospital, maternity ward to see her little brother born just a day before, she was pleasantly surprised to see so many new born babies in the hospital nursery. So, she thought, how many of these are male babies and how many are female?
The genetic makeup of a male embryo is determined by
(a) The X chromosome in the zygote
(b) The Y chromosome in the zygote
(c) The cytoplasm of the germ cell which determines the sex
(d) Sex is determined by chance
Answer:
(b) The Y chromosome in the zygote
Explanation: A chiLd who inherits an X chromosome from her father wilt be a girL and the one who inherits a Y chromosome from him will be a boy. Thus the maleness of a chiLd is determined by the presence of the Y chromosome in the zygote inherited from the father.
![]()
Question 5.
In the F2 generation of a cross, progeny having different traits are produced in the ratio 3:1.
(A) State whether it is a monohybrid cross or a dihybrid cross? Give one example of such a cross.
(B) Exchange of genetic material takes place in:
(a) Vegetative reproduction
(b) Asexual reproduction
(c) Sexual reproduction
(d) Budding
Answer:
It is a monohybrid cross.
Example: when two hybrids tall Pea plants crossbreed with each other they will produce three tall plants and one dwarf planet in the F2 generation.
(C) A cross between a tall plant (TT) and short pea plant (tt) resulted in progeny that were all tall plants because:
(a) Tallness is the dominant trait
(b) Shortness is the dominant trait
(c) Tallness is the recessive trait
(d) Height of pea plant is not governed by gene ‘T’ or ‘t’
Answer:
Question 6.
Observe the ears of all the students in the class. The lowest part of the ear, called the earlobe, is closely attached to the side of the head in some of us, and not in others. Free and attached earlobes are two variants found in human populations.
Prepare a list of students having free or attached earlobes and calculate the percentage of students having each. Find out about the earlobes of the parents of each student in the class. Correlate the earlobe type of each student with that of their parents. Based on this evidence, suggest a possible rule for the inheritance of earlobe types.
The percentage of people having free earlobes and attached earlobes is shown below:
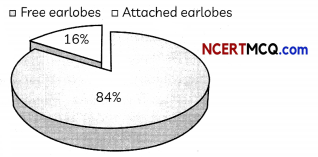
(A) Based on the findings in the NCERT activity, it can be concluded that:
(I) The gene responsible for free earlobes in dominant.
(II) The gene responsible for free earlobe may be dominant or recessive.
(III) The gene responsible for attached earlobe may be dominant or recessive.
(IV) The gene responsible for attached earlobe is recessive.
Select the correct statements.
(a) Both (I) and (III)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (I) and (IV)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(B) The earlobes of a child whose parents have free earlobes will be:
(a) Free earlobe
(b) Attached earlobe
(c) Can be free or attached earlobe
(d) Neither free nor attached
Answer:
(B) (c) Can be free or attached earlobe
Explanation: Parents with free earlobes can have both a copy of the dominant and recessive allele and they may give birth to a baby with free or attached earlobes.
(C) The shape of the earlobe in an offspring is determined by:
(a) Variation
(b) Chromosome
(c) DNA
(d) Gene
Answer:
(D) Mrs. and Mr. Sharma have six children. Three of them have attached eartobes Like their father, and the other three have free earlobes like their mother.
Taking F for free earlobes and f for attached earLobes, seLect the row containing the correct genotype of parents and children from the table below:

Answer:
(b) Mrs. Sharma: Ff; Mr. Sharma: Ff; Children with free earlobes: Ff; Children with attached earlobes: ff
Explanation: All of the individuals with attached earlobes must be ff. AIL of the individuals with free earlobes can be FF or ff. In this particular case, the parent having free earlobe has children who have attached earlobes, so that parent must have an f, and is thus Ff. And all of the children have one parent with attached earlobes, so they must also all have at Least one f, and are thus Ff. So the answer is, Mr. Sharma is ff, Mrs. Sharma is Ff. The three chiLdren with attached earlobes are ff, and the three with free earlobes are Ff.
(E) A child has attached earlobes.
Select the most appropriate statement regarding the earlobe of his/her parents.
(a) Earlobes of either parent may be attached or free.
(b) Both parents have attached earlobes.
(c) One parent has attached earlobes
(d) Cannot be determined.
Answer:
![]()
Question 7.
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations.
Charles Darwin popularized the term “natural selection”, contrasting it with artificial selection, which in his view is intentional, whereas natural selection is not.
Natural selection can cause microevolution (change in allele frequencies), with fitness-increasing alleles becoming more common in the population. Fitness is a measure of reproductive success (how many offspring an organism leaves in the next generation, relative to others in the group). Natural selection can act on traits determined by alternative alleles of a single gene, or on polygenic traits (traits determined by many genes). Natural selection on traits determined by multiple genes may take the form of stabilizing selection, directional selection, or disruptive selection.
(A) Which of the following are examples of natural selection?
(I) In an ecosystem, lizards that had long legs could climb better to avoid floods and reach food.
(II) Insects become resistant to pesticides very quickly, sometime in one generation and if an insect is resistant to the chemical, most of the offspring will also be resistant.
(III) Cultivation of wild cabbage as a food plant, and generation of different vegetables from it
(IV) Dog breeding for various desired characteristics.
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (I) and (III)
(c) Both (II) and (IV)
(d) (I), (II) and (III)
Answer:
(B) Natural selection acts on an organism’s:
(a) Environment
(b) Chromosome
(c) Phenotype
(d) Genotype
Answer:
(C) Imagine a population of brown and white rabbits, whose coat color is determined by dominant brown (B) and recessive white (b) alleles of a single gene. A predator such as a hawk can see white rabbits more easily than brown rabbits against the backdrop of a grassy field.
What is likely to happen? Select the incorrect answer:
(a) Brown rabbits are more likely than white rabbits to survive hawk predation.
(b) The b alleles may disappear from the population after several generations due to selection.
(c) The next generation will probably contain a higher frequency of B alleles.
(d) The next generation will probably contain a higher frequency of b alleles.
Answer:
(d) The next generation will probably contain a higher frequency of b alleles.
Explanation: Natural selection can shift allele and phenotype frequencies to make a population better-suited to its environment. If we imagine that half of the white rabbits (but none of the brown rabbits) are eaten by hawks, then the frequency of B allele will increase.
Natural selection acts on phenotypes, not genotypes, as a hawk can tell a brown rabbit from a white rabbit, but it can’t tell an BB rabbit from a Bb rabbit.
(D) Humans have, over more than two thousand years, cultivated wild cabbage as a food plant, and generated different vegetables from it by selection.
Select the row containing incorrect information.
|
Desirable Characteristic |
Name of Vegetable Evolved from Wild Cabbage |
| Short distances between leaves | Cabbage |
| For sterile flowers | Kale |
| For arrested flower development | Broccoli |
| For swollen parts | Kohlrabi |
Answer:
(b) Desirable characteristic: For sterile flowers: Name of vegetable evolved from wild cabbage: Kale
Explanation: For sterile flowers, man of made cauliflower and for leafy vegetable, made kale.
(E) In a habitat there are red bugs and green bugs. The birds prefer the taste of the red bugs, so soon there are many green bugs and few red bugs. The green bugs reproduce and make more green bugs and eventually there are no more red bugs.
The above is an example of:
(a) Natural selection
(b) Genetic drift
(c) Geographical isolation
(d) Speciation
Answer:
Question 8.
X-linked recessive inheritance is a mode of inheritance in which a mutation in a gene on the X chromosome causes the phenotype to be always expressed in males (who are necessarily homozygous for the gene mutation because they have one X and one Y chromosome) and in females who are homozygous for the gene mutation. Females with one copy of the mutated gene are carriers. X-linked inheritance means that the gene causing the trait or the disorder is located on the X chromosome.
In humans, inheritance of X-linked recessive traits follows a unique pattern as shown below:
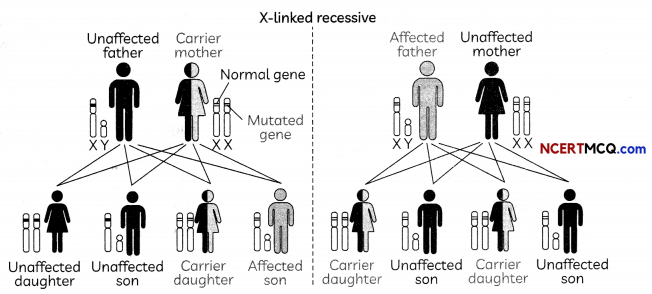
The first is that affected fathers cannot pass x-linked recessive traits to their sons because fathers give Y chromosomes to their sons. Second, x-iinked recessive traits are more commonly expressed in males than females.
This is due to the fact that males possess only a single X chromosome, and therefore require only one mutated X in order to be affected. The last pattern seen is that x-linked recessive traits tend to skip generations, meaning an affected grandfather will not have an affected son, but could have an affected grandson through his daughter.
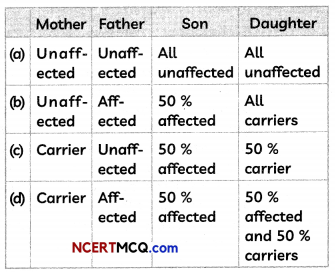
(A) In the cross shown above, if the father is unaffected and mother is also unaffected, but mother is a carrier (X-linked recessive allele present), then which of the following statements are correct about their children:
(I) Both sons will be unaffected but will be carriers.
(II) One son will be unaffected and one son will be affected.
(III) Both daughters will be unaffected
(IV) One daughter will be unaffected and one daughter will be affected.
(a) Both (I) and (III)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (I) and (IV)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(b) Both (II) and (III)
Explanation: Females have two X chromosomes while males have one X and one Y chromosome. Carrier females who have only one copy of the mutation do not usually express the phenotype. So, the son who receives the X chromosome containing the dominant allele will be unaffected whereas the son who receives X chromosome containing the recessive allele will be affected. Both daughters will be unaffected, but the daughter who receives the recessive allele from her mother will be carrier.
This means that males affected by an x-linked recessive disorder inherited the responsible X chromosome from their mothers.
Women possess two X chromosomes and thus must receive two of the mutated recessive X chromosomes (one from each parent). A popular example showing this pattern of inheritance is that of the descendants of Queen Victoria and the blood disease hemophilia.
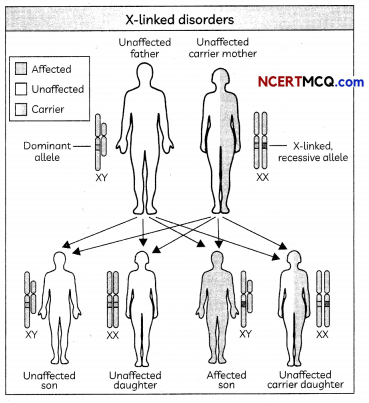
(B) Study the cross shown above and select the row containing incorrect information:
Answer:
(C) Sex-linked genetically inherited traits:
(a) can appear in both males and females
(b) are only found in males
(c) are only found in females
(d) appear only in F2 generation
Answer:
(D) X-linked recessive traits are more commonly expressed in males than females because:
(a) Females have both X chromosomes which will be mutated at the same time
(b) Males possess a Y chromosome which can be mutated
(c) Males possess only a single X chromosome, and therefore require only one mutated X in order to be affected
(d) Chances of mutation of both X chromosomes in females is very low
Answer:
(E) Insects also follow an XY sex- determination pattern and like humans, Drosophila males have an XY chromosome pair and females are XX. Eye color in Drosophila was one of the first X-linked traits to be identified. In fruit flies, the wild-type eye color is red (XW) and is dominant to white eye color (Xw).
In a cross between a white-eyed female fruit fly and red-eyed male, what percent of the female offspring will have white eyes? (White eyes are X-linked, recessive)
(a) 100 %
(b) 50 %
(c) 25 %
(d) 0 %
Answer:
(d) 0%
Explanation: The genotype of a white-eyed female fruit fly will be XWXW and of red-eyed male will be XWY. When we cross them, the genotype of offspring will be:
XWXW (Red eyed female), X (White-eyed male), XWXW (Red-eyed female) and XWY (white-eyed male).
All of the females are thus red-eyed and heterozygous. All of the males are white-eyed and hemizygous.
![]()
Question 9.
In mice, black coat colour (B) is dominant over brown coat colour (b), and a solid pattern (S) is dominant over white spotted (s). Colour and spots are controlled by genes that assort independently. A homozygous (both alleles identical) black, spotted mouse is crossed with a homozygous brown, solid mouse.
(A) The genotypes of the parents is:
(a) Bbss and bbSS
(b) BBss and bbSs
(c) BbSs and BbSs
(d) BBss and bbSS
Answer:
(B) Select the incorrect statements regarding the F1 progeny obtained:
(I) Phenotype of all mice of F1 generation is brown coat with solid pattern.
(II) Phenotype of all mice of F1 generation is black coat with solid pattern.
(III) Genotype of all mice of F1 generation is BbSs.
(IV) Genotype of all mice of F1 generation is BBSs.
(a) Both (I) and (III)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (II) and (IV)
(d) Both (I) and (IV)
Answer:
(d) Both (I) and (IV)
Explanation: Genotype of the homozygous black, spotted mouse is BBss and of the homozygous brown, solid mouse is bbSS.
When these are crossed, all F1 progeny will be black coat with solid pattern (BbSs) as gametes of homozygous black, spotted mouse will be Bs and of homozygous brown, solid mouse is bS.
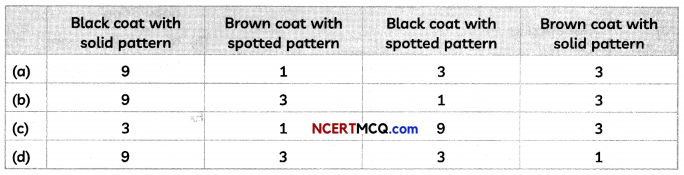
(C) The table below shows the phenotypic ratio of F2 generation when mice of F1 generation are crossed with each other.
Select the row containing correct information:
Answer:
(D) From the cross mentioned in (B) above, it can be concluded that:
(a) The phenotype of progeny is independent of inherited genes.
(b) The black/brown colour of coat and solid/spotted pattern are inherited independently.
(c) The genotype of progeny does not decide the phenotype.
(d) The phenotype and genotype of progeny are independently inherited.
Answer:
(b) The black/brown colour of coat and solid/spotted pattern are Inherited independently.
Explanation: The genes responsible for coLour (black or brown) and spotting (solid pattern or spotted) are assorted independently.
(E) Suppose a test cross is carried out by mating FI mice with brown, spotted mice. The percentage of progeny having black coat with solid pattern will be;
(a) 75 %
(b) 50 %
(c) 25 %
(d) 0 %
Answer:
Question 10.
Remember the Hindi film Ghajini where Aamir Khan had sported a new hairstyle? It became a rage and later, several boys started to experiment with their hairstyle in unique ways.

From the list given below, select the character which can be acquired but not inherited:
(a) Colour of eyes
(b) Colour of skin
(c) Size of body
(d) Nature of hair
Answer:
![]()
Question 11.
A big challenge with species conservation is trying to limit and reduce the negative genetic effects of small or isolated populations. Founder’s effect or bottleneck effect can lead to small populations which are highly susceptible to genetic drift. This means there is a serious reduction in genetic variation within the population, making that population less able to adapt to new selective pressures (“Bottleneck and founder effects”). Even if the species’ numbers were to rebound, the new generations would only carry the limited set of alleles passed down by the small population.
A population bottleneck is an event that drastically reduces the size of a population. The bottleneck may be caused by various events, such as an environmental disaster, the hunting of a species to the point of extinction, or habitat destruction that results in the deaths of organisms. The population bottleneck produces a decrease in the gene pool of the population because many alleles, or gene variants, that were present in the original population are lost. Due to the event, the remaining population has a very low level of genetic diversity, which means that the population as a whole has few genetic characteristics.
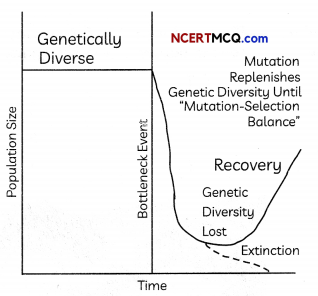
(A) Select the correct statements:
(I) A population bottleneck decreases genetic variation in a species or subspecies.
(II) Gene flow increases genetic diversity by introducing new alleles into the population.
(III) Mutation decreases genetic diversity in a population.
(IV) Species can become extinct if genetic diversity recovers after the bottleneck.
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (I) and (III)
(c) Both (II) and (III)
(d) (I), (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(B) Which of the following statements is true?
(a) Gene pool frequencies do not change as a result of migrations in or out of a population.
(b) Gene flow occurs only as a result of migrations.
(c) Gene flow can cause new alleles to enter a population’s gene pool.
(d) Gene flow is possible only in aquatic ecosystem.
Answer:
(c) Gene flow can cause new alleles to enter a population’s gene pool.

Explanation: Since gene flow alters the recipient population’s gene pool, it causes evolution independent of any other evolutionary mechanism.
(C) Which of the following is not true of genetic drift?
(a) It can lead to alleles being fixed in a population
(b) It results from the random transmission of alleles from parents to offspring in a population
(c) It can lead to loss of alleles from a population
(d) It can increase the genetic diversity of a population
Answer:
(D) In a population where the allele frequency shifts by random chance, the mechanism of evolution at work is:
(a) mutation
(b) genetic drift
(c) natural selection
(d) migration
Answer:
(b) genetic drift
Explanation: Genetic drift occurs as a result of chance events causing changes in the allele frequency of a population. It doesn’t favor the fittest individuals, but occurs at random.
(E) Mutation may be described as:
(a) Continuous genetic variation
(b) Phenotypic change
(c) Discontinuous genetic variation
(d) Change due to hybridization
Answer:
![]()
Question 12.
When a friend showed Uma two photographs and asked her to identify the relation between the persons shown in the photograph, she immediately replied that the photographs are of identical twins as they had identical features. But to her surprise, the photograph was of a father when he was a kid and of his daughter. The similarity in their features was remarkable!

Answer:
Cellular DNA is the information source for making proteins in the cell. As genes are responsible for controlling various processes in an organism and are made up of DNA, we can say that DNA is the carrier of basic genetic information in organisms.
Question 13.
Speciation, the formation of new and distinct species in the course of evolution. Speciation involves the splitting of a single evolutionary lineage into two or more genetically independent lineages. Speciation occurs when a group within a species separates from other members of its species and develops its own unique characteristics. The demands of a different environment or the characteristics of the members of the new group will differentiate the new species from their ancestors.
There are many hypotheses about how speciation starts, and they differ mainly in the role of geographic isolation and the origin of reproductive isolation (the prevention of two populations or more from interbreeding with one another).
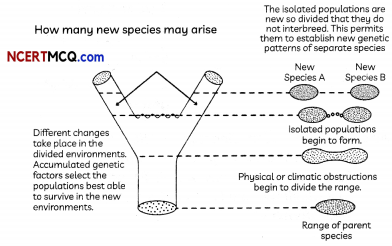
(A) Select the incorrect statement.
Speciation is possible in isolated populations of the parent species because:
(a) There will be an accumulation of different changes in each sub-population due to genetic drift.
(b) Natural selection may operate differently in these different geographic locations.
(c) isolated populations are no longer able to interbreed.
(d) Increased gene flow
Answer:
(d) Increased gene flow
Explanation: Speciation is possible when the parent species is subdivided into subpopulations. Each sub-population has a different gene pool and accumulation of different changes due to genetic drift. Moreover, different variations may be selected in the subpopulations by environmental factors. Eventually, the organisms belonging to the sub-populations may no longer be able to interbreed. However, if gene flow decreases, then the groups will evolve along separate paths.
(B) Two separate squirrel species inhabit the north and south rims of the canyon when Arizona’s Grand Canyon formed. This is an example of:
(a) Genetic Drift
(b) Geographical isolation
(c) Natural selection
(d) Variation
Answer:
(C) New species may be formed if
(I) DNA undergoes significant change in germ cells
(II) Chromosome number changes in the gamete
(III) There is no change in the genetic material
(IV) Mating is no longer possible
(a) Both (I) and (III)
(b) Both (II) and (IV)
(c) (I), (II) and (III)
(d) (I), (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(d) (I), (II) and (IV)
Explanation: New species may be formed due to significant change in DNA such that the organisms are no longer able to inter breed. Then, a new species is said to have been formed.
(D) Wild cabbage has evolved into new varieties like cabbage, broccoli and cauliflower by
(a) genetic drift
(b) natural selection
(c) reproductive isolation
(d) artificial selection
Answer:
(E) Imagine a situation in which a population extends over a broad geographic range, and mating throughout the population is not random. Individuals in the far west would have zero chance of mating with individuals in the far eastern end of the range.
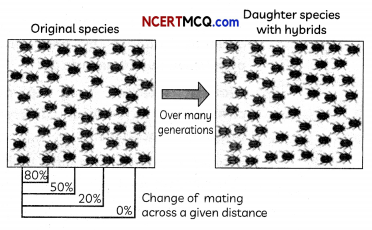
Which of the following can lead to the formation of a new species in such a situation?
Select the most appropriate answer in the given context.
(a) Geographical isolation
(b) Reduced gene flow
(c) Increased gene flow
(d) Genetic drift
Answer:
![]()
Question 14.
When Priyanka went to the market to buy some pulses, she was quite surprised when the shopkeeper mentioned the different varieties of pea. There was green and round variety as well as yellow and wrinkled and also yellow and round varieties!
Round and green seeds of pea plant were crossed with wrinkled and yellow seeds. Progeny of F1 generation were all having round and green seeds. These F1 progenies were used to generate F2 progeny. Select the row containing incorrect observation or remarks:
|
Observation |
Remarks |
| (a) Genotype of parents of F1 progeny was RRyy (Round, green) and rrYY (Wrinkled, yellow) | Roundness and yellow were dominant as all F1 progeny had round and yellow seeds |
| (b) Genotype of 50% F1 progeny was RRYY and RrYy for the remaining 50% F1 progeny. | As alt F1 progeny had round/yellow seeds, roundness and yellow were dominant. |
| (c) Some F2 progeny showed new combinations | The round seed/ wrinkled seed trait and yellow! green trait are independently inherited. |
| (d) Phenotype ratio of F2 progeny was 9:3:3:1 | 9 (round/yellow) |
| 3 (round green) | |
| 3 (wrinkled yellow) | |
| 1 (wrinkled green) |
Answer:
(b) Observation: Genotype of 50% F1 progeny was RRYY and RrYy for the remaining 50% F1 progeny: Remarks: As all F1 progeny had round/yellow seeds, roundness and yellow were dominant.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Mendel took tall pea plants and short pea plants and produced F1 progeny through cross-fertilisation. What did Mendel observe in the F1 progeny?
Answer:
When Mendel cross-fertilized tall pea plants and short pea plants, he observed that all plants in the F1 progeny were tall.
Related Theory
- When these F1 progeny are self crossed, he observed that the F2 progeny are not all tall. The ratio of tall plants to dwarf plants comes to be approximately 3:1.
- This indicates that both the tallness (T) and shortness (t) traits were inherited in the F1 plants, but only the tallness trait was expressed.
- Above experiment led Mendel to propose that two copies of factor (now called genes) controlling traits are present in sexually reproducing organisms.
- Traits like T which are expressed are called dominant traits, while traits like’t’ are called recessive traits.
Question 2.
How is the normal number of chromosomes restored in the progeny of sexually reproducing organisms?
Answer:
Each cell has two copies of each chromosome, one each from the male and female parents. Each germ cell or gamete takes one chromosome from each pair and when two germ cells combine, the original number of chromosomes is restored in the progeny.
![]()
Question 3.
Do all variations in a species have equal chances of surviving in the environment in which they find themselves?
Answer:
No, all variations in a species do not have equal chances of surviving in the environment in which they find themselves. Depending upon the nature of variations, each individual would have different advantages of survival.
