ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable Ex 5.5
These Solutions are part of ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths. Here we have given ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable Ex 5.5
More Exercises
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable Ex 5.1
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable Ex 5.2
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable Ex 5.3
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable Ex 5.4
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable Ex 5.5
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable MCQS
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable Chapter Test
Question 1.
(i) Find two consecutive natural numbers such that the sum of their squares is 61.
(ii) Find two consecutive integers such that the sum of their squares is 61.
Solution:
Let the first natural number = x
then second natural number = x + 1
According to the condition, (x)² + (x + 1)² = 61

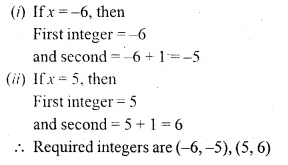
Question 2.
(i) If the product of two positive consecutive even integers is 288, find the integers.
(ii) If the product of two consecutive even integers is 224, find the integers.
(iii) Find two consecutive even natural numbers such that the sum of their squares is 340.
(iv) Find two consecutive odd integers such that the sum of their squares is 394.
Solution:
(i) Let first positive even integer = 2x
then second even integer = 2x + 2
According to the condition,
2x × (2x + 2) = 288
⇒ 4x² + 4x – 288 = 0
⇒ x² + x – 72 = 0 (Dividing by 4)
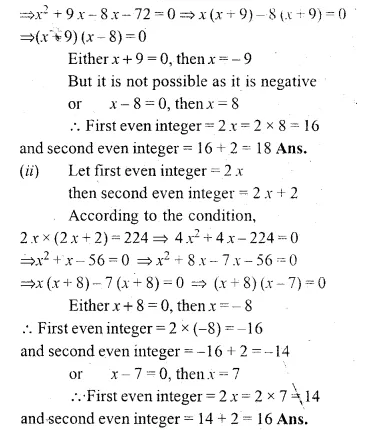

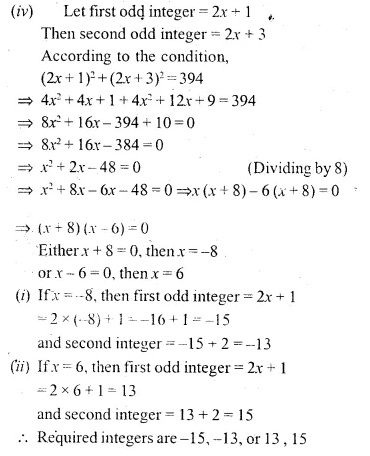
Question 3.
The sum of two numbers is 9 and the sum of their squares is 41. Taking one number as x, form ail equation in x and solve it to find the numbers.
Solution:
Sum of two numbers = 9
Let first number = x
then second number = 9 – x
Now according to the condition,
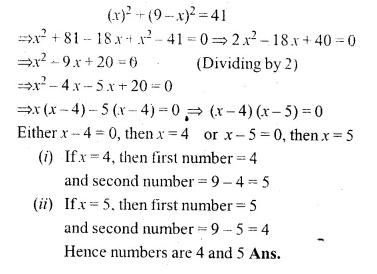
Question 4.
Five times a certain whole number is equal to three less than twice the square of the number. Find the number.
Solution:
Let number = x
Now according to the condition,
5x = 2x² – 3
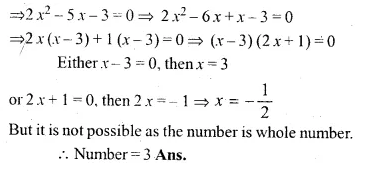
Question 5.
Sum of two natural numbers is 8 and the difference of their reciprocal is 2/15. Find the numbers.
Solution:
Let x and y be two numbers
Given that, x + y = 8 ……(i)
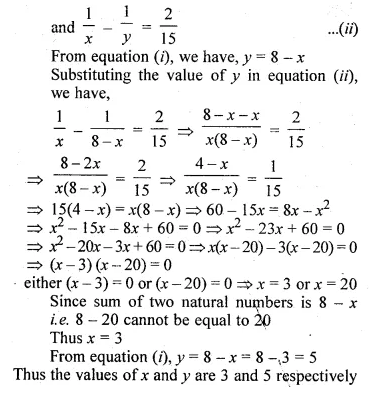
Question 6.
The difference between the squares of two numbers is 45. The square of the smaller number is 4 times the larger number. Determine the numbers.
Solution:
Let the larger number = x
then smaller number = y
Now according to the condition,

Question 7.
There are three consecutive positive integers such that the sum of the square of the first and the product of other two is 154. What are the integers?
Solution:
Let the first integer = x
then second integer = x + 1
and third integer = x + 2
Now according to the condition,
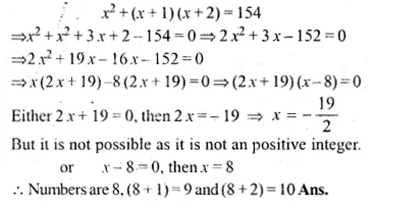
Question 8.
(i) Find three successive even natural numbers, the sum of whose squares is 308.
(ii) Find three consecutive odd integers, the sum of whose squares is 83.
Solution:
(i) Let first even number = 2x
second even number = 2x + 2
third even number = 2x + 4
Now according to the condition,

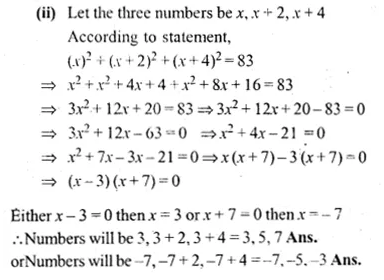
Question 9.
In a certain positive fraction, the denominator is greater than the numerator by 3. If 1 is subtracted from both the numerator and denominator, the fraction is decreased by \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 14 } \). Find the fraction.
Solution:
Let the numerator of a fraction = x
then denominator = x + 3
then fraction = \(\\ \frac { x }{ x+3 } \)
Now according to the condition,
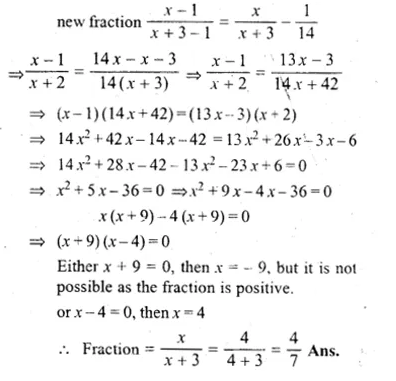
Question 10.
The sum of the numerator and denominator of a certain positive fraction is 8. If 2 is added to both the numerator and denominator, the fraction is increased by \(\\ \frac { 4 }{ 35 } \). Find the fraction.
Solution:
Let the denominator of a positive fraction = x
then numerator = 8 – x
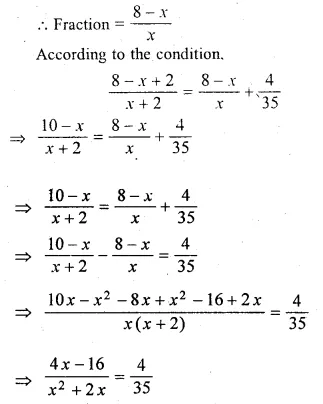
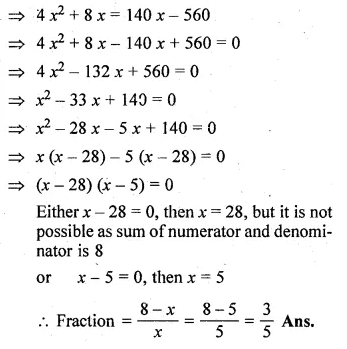
Question 11.
A two digit number contains the bigger at ten’s place. The product of the digits is 27 and the difference between two digits is 6. Find the number.
Solution:
Let unit’s digit = x
then tens digit = x + 6
Number = x + 10(x + 6)
= x + 10x + 60
= 11x + 60

Question 12.
A two digit positive number is such that the product of its digits is 6. If 9 is added to the number, the digits interchange their places. Find the number. (2014)
Solution:
Let 2-digit number = xy = 10x + y
Reversed digits = yx = 10y + x
According to question,
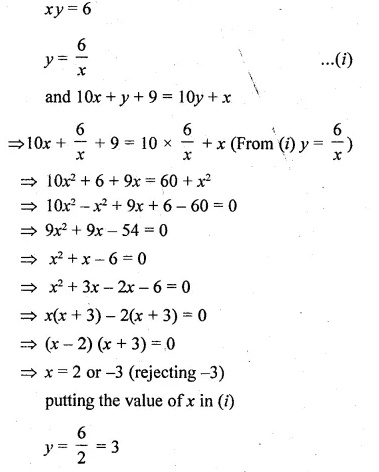
![]()
Question 13.
A rectangle of area 105 cm² has its length equal to x cm. Write down its breadth in terms of x. Given that the perimeter is 44 cm, write down an equation in x and solve it to determine the dimensions of the rectangle.
Solution:
Perimeter of rectangle = 44 cm
length + breadth = \(\\ \frac { 44 }{ 2 } \) = 22 cm
Let length = x
then breadth = 22 – x
According to the condition,
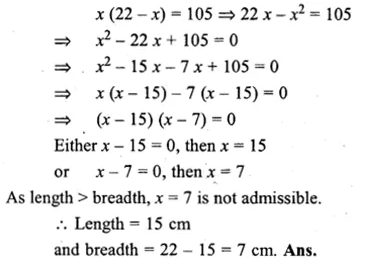
Question 14.
A rectangular garden 10 m by 16 m is to be surrounded by a concrete walk of uniform width. Given that the area of the walk is 120 square metres, assuming the width of the walk to be x, form an equation in x and solve it to find the value of x. (1992)
Solution:
Length of garden = 16 m
and width = 10 m
Let the width of walk = x m
Outer length = 16 + 2x
and outer width = 10 + 2x
Now according to the condition,
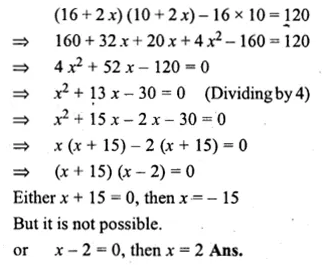
Question 15.
(i) Harish made a rectangular garden, with its length 5 metres more than its width. The next year, he increased the length by 3 metres and decreased the width by 2 metres. If the area of the second garden was 119 sq m, was the second garden larger or smaller ?
(ii) The length of a rectangle exceeds its breadth by 5 m. If the breadth were doubled and the length reduced by 9 m, the area of the rectangle would have increased by 140 m². Find its dimensions.
Solution:
In first case,
Let length of the garden = x m
then width = (x – 5) m
Area = l x b = x(x – 5) sq. m
In second case,
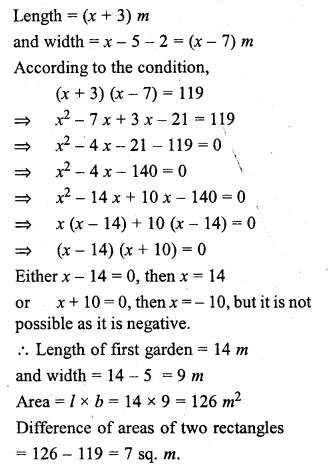
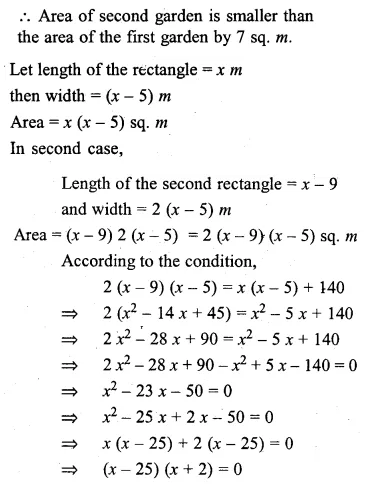
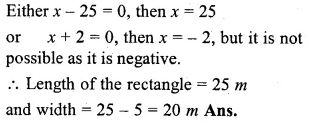
Question 16.
The perimeter of a rectangular plot is 180 m and its area is 1800 m². Take the length of the plot as x m. Use the perimeter 180 m to write the value of the breadth in terms of x. Use the values of length, breadth and the area to write an equation in x. Solve the equation to calculate the length and breadth of the plot. (1993)
Solution:
The perimeter of a rectangular field = 180 m
and area = 1800 m²
Let length = x m

Question 17.
The lengths of the parallel sides of a trapezium are (x + 9) cm and (2x – 3) cm and the distance between them is (x + 4) cm. If its area is 540 cm², find x.
Solution:
Area of a trapezium = \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)
(sum of parallel sides) x height
Lengths of parallel sides are (x + 9) and (2x – 3)
and height = (x + 4)
According to the condition,
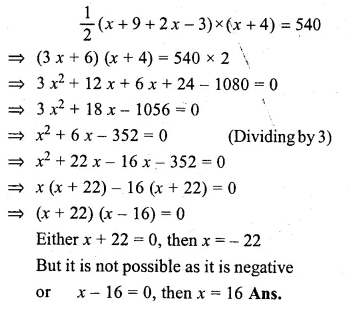
Question 18.
If the perimeter of a rectangular plot is 68 m and the length of its diagonal is 26 m, find its area.
Solution:
Perimeter = 68 m and diagonal = 26 m
Length + breadth = \(\\ \frac { 68 }{ 2 } \) = 34 m
Let length = x m
then breadth = (34 – x) m
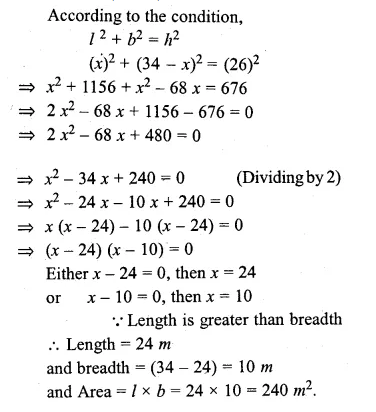
Question 19.
If the sum of two smaller sides of a right – angled triangle is 17cm and the perimeter is 30cm, then find the area of the triangle.
Solution:
The perimeter of the triangle = 30 cm.
Let one of the two small sides = x
then, other side = 17 – x
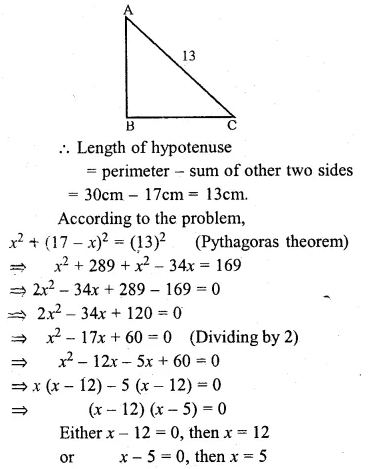

Question 20.
The hypotenuse of grassy land in the shape of a right triangle is 1 metre more than twice the shortest side. If the third side is 7 metres more than the shortest side, find the sides of the grassy land.
Solution:
Let the shortest side = x
Hypotenuse = 2x + 1
and third side = x + 7
According to the condition,
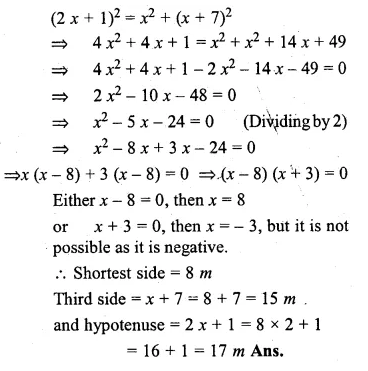
Question 21.
Mohini wishes to fit three rods together in the shape of a right triangle. If the hypotenuse is 2 cm longer than the base and 4 cm longer than the shortest side, find the lengths of the rods.
Solution:
Let the length of hypotenuse = x cm
then base = (x – 2) cm
and shortest side = x – 4
According to the condition,

Question 22.
In a P.T. display, 480 students are arranged in rows and columns. If there are 4 more students in each row than the number of rows, find the number of students in each row.
Solution:
Total number of students = 480
Let the number of students in each row = x
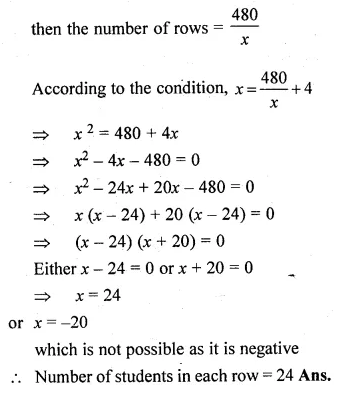
Question 23.
In an auditorium, the number of rows are equal to the number of seats in each row.If the number of rows is doubled and number of seats in each row is reduced by 5, then the total number of seats is increased by 375. How many rows were there?
Solution:
Let the number of rows = x
then no. of seats in each row = x
and total number of seats = x × x = x²
According to the condition,
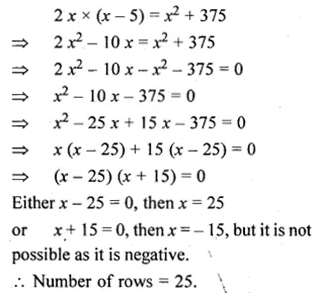
Question 24.
At an annual function of a school, each student gives the gift to every other student. If the number of gifts is 1980, find the number of students.
Solution:
Let the number of students = x
then the number of gifts given = x – 1
Total number of gifts = x (x – 1)
According to the condition,
x (x – 1) = 1980
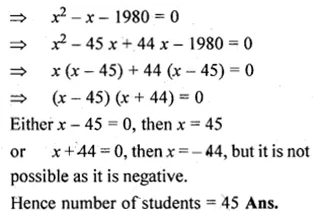
Question 25.
A bus covers a distance of 240 km at a uniform speed. Due to heavy rain, its speed gets reduced by 10 km/h and as such it takes two hours longer to cover the total distance. Assuming the uniform speed to be ‘x’ km/h, form an equation and solve it to evaluate x. (2016)
Solution:
Distance = 240 km
Let speed of a bus = x km/hr


Question 26.
The speed of an express train is x km/hr and the speed of an ordinary train is 12 km/hr less than that of the express train. If the ordinary train takes one hour longer than the express train to cover a distance of 240 km, find the speed of the express train.
Solution:
Let the speed of express train = x km
Then speed of the ordinary train = (x – 12) km
Time is taken to cover 240 km by the express
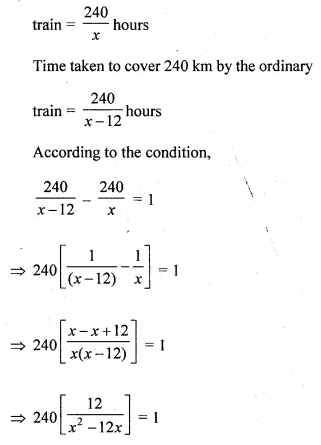

Question 27.
A car covers a distance of 400 km at a certain speed. Had the speed been 12 km/h more, the time taken for the journey would have been 1 hour 40 minutes less. Find the original speed of the car. (1996)
Solution:
Let the original speed of the car = x km/h.
Distance covered = 400 km
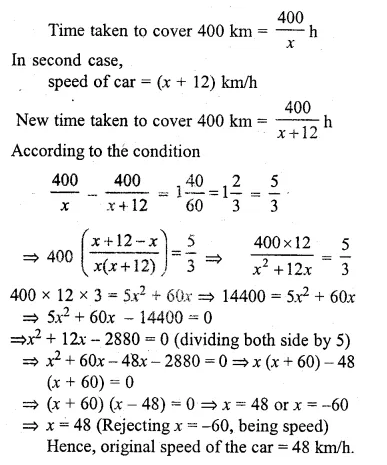
Question 28.
An aeroplane travelled a distance of 400 km at an average speed of x km/hr. On the return journey, the speed was increased by 40 km/hr. Write down an expression for the time taken for
(i)the onward journey,
(ii) the return journey.
If the return journey took 30 minutes less than the onward journey, write down an equation in x and find its value. (2002)
Solution:
Distance = 400 km
Speed of aeroplane = x km/hr
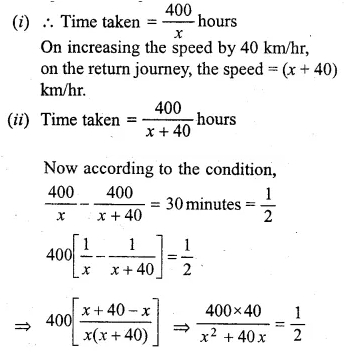
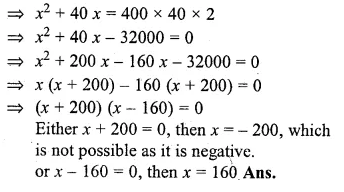
Question 29.
The distance by road between two towns A and B, is 216 km, and by rail it is 208 km. A car travels at a speed of x km/hr, and the train travels at a speed which is 16 km/hr faster than the car. Calculate :
(i) The time taken by the car, to reach town B from A, in terms of x ;
(ii) The time taken by the train, to reach town B from A, in terms of x ;
(iii) If the train takes 2 hours less than the car, to reach town B, obtain an equation in x and solve it.
(iv) Hence find the speed of the train. (1998)
Solution:
The distance by road between A and B = 216 km
and the distance by rail = 208 km
speed of car = x km/hr
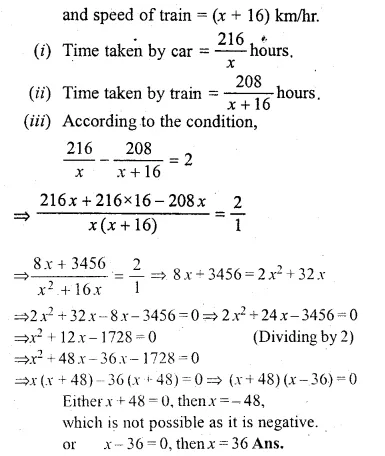

Question 30.
An aeroplane flying with a wind of 30 km/hr takes 40 minutes less to fly 3600 km, than what it would have taken to fly against the same wind. Find the planes speed of flying in still air.
Solution:
Let the speed of the plane in still air = x km/hr
Speed of wind = 30 km/hr
Distance = 3600 km
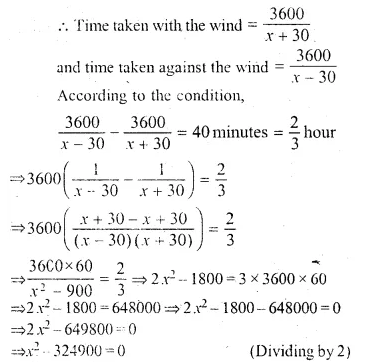
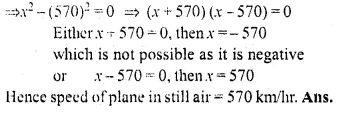
Question 31.
A school bus transported an excursion party to a picnic spot 150 km away. While returning, it was raining and the bus had to reduce its speed by 5 km/hr, and it took one hour longer to make the return trip. Find the time taken to return.
Solution:
Distance = 150 km
Let the speed of bus = x km/hr

Question 32.
A boat can cover 10 km up the stream and 5 km down the stream in 6 hours. If the speed of the stream is 1.5 km/hr. find the speed of the boat in still water.
Solution:
Distance up stream = 10 km
and down stream = 5 km
Total time is taken = 6 hours
Speed of stream = 1.5 km/hr
Let the speed of a boat in still water = x km/hr
According to the condition,
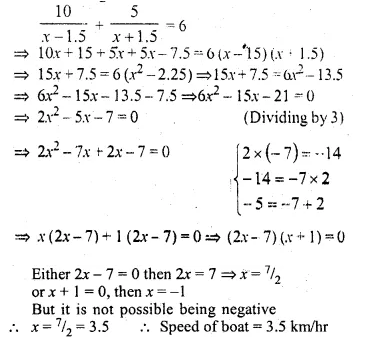
Question 33.
Two pipes running together can fill a tank in \({ 11 }^{ 1/9 }\) minutes. If one pipe takes 5 minutes more than the other to fill the tank, find the time in which each pipe would/fill the tank.
Solution:
Let the time taken by one pipe = x minutes
Then time taken by second pipe = (x + 5) minutes
Time taken by both pipes = \({ 11 }^{ 1/9 }\) minutes
Now according to the condition.
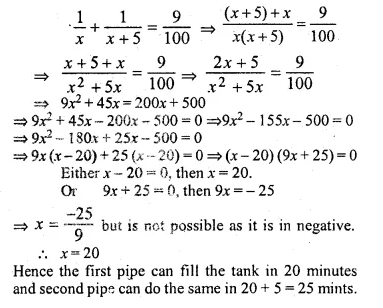
Question 34.
(i) Rs. 480 is divided equally among ‘x’ children. If the number of children was 20 more then each would have got Rs. 12 less. Find ‘x’.
(ii) Rs. 6500 is divided equally among a certain number of persons. Had there been 15 more persons, each would have got Rs. 30 less. Find the original number of persons.
Solution:
(i) Share of each child = Rs \(\\ \frac { 480 }{ x } \)
According to the question
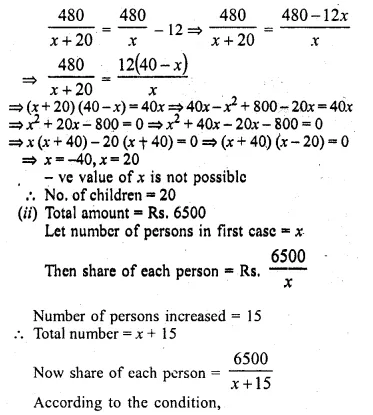
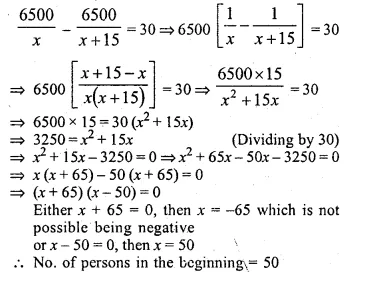
Question 35.
2x articles cost Rs. (5x + 54) and (x + 2) similar articles cost Rs. (10x – 4), find x.
Solution:
Cost of 2x articles = 5x + 54
Cost of 1 article = \(\\ \frac { 5x+54 }{ 2x } \) ….(i)
Again cost of x + 2 articles = 10x – 4
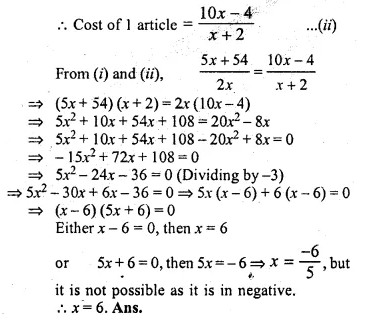
Question 36.
A trader buys x articles for a total cost of Rs. 600.
(i) Write down the cost of one article in terms of x. If the cost per article were Rs. 5 more, the number of articles that can be bought for Rs. 600 would be four less.
(ii) Write down the equation in x for the above situation and solve it to find x. (1999)
Solution:
Total cost = Rs. 600,
No. of articles = x
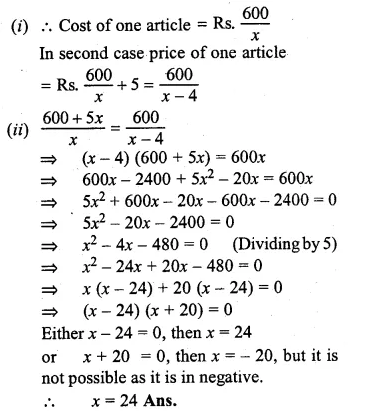
Question 37.
A shopkeeper buys a certain number of books for Rs 960. If the cost per book was Rs 8 less, the number of books that could be bought for Rs 960 would be 4 more. Taking the original cost of each book to be Rs x, write an equation in x and solve it to find the original cost of each book.
Solution:
Let original cost = Rs x
No. of books bought = \(\\ \frac { 960 }{ x } \)
New cost of books = Rs (x – 8)

Question 38.
A piece of cloth costs Rs. 300. If the piece was 5 metres longer and each metre of cloth costs Rs. 2 less, the cost of the piece would have remained unchanged. How long is the original piece of cloth and what is the rate per metre?
Solution:
The total cost of cloth piece = Rs. 300
Let the length of the piece of cloth in the beginning = x m

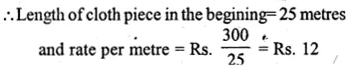
Question 39.
The hotel bill for a number of people for an overnight stay is Rs. 4800. If there were 4 more, the bill each person had to pay would have reduced by Rs. 200. Find the number of people staying overnight. (2000)
Solution:
Let the number of people = x
Amount of bill = Rs. 4800

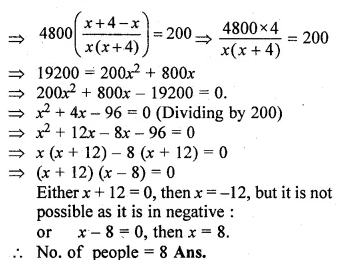
Question 40.
A person was given Rs. 3000 for a tour. If he extends his tour programme by 5 days, he must cut down his daily expenses by Rs. 20. Find the number of days of his tour programme.
Solution:
Let the number of days of tour programme = x
Amount = Rs. 3000
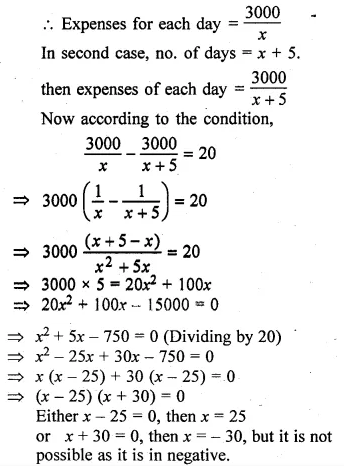
![]()
Question 41.
Ritu bought a saree for Rs. 60 x and sold it for Rs. (500 + 4x) at a loss of x%. Find the cost price.
Solution:
The cost price of saree = Rs. 60x
and selling price = Rs. (500 + 4x)
Loss = x%
Now according to the condition
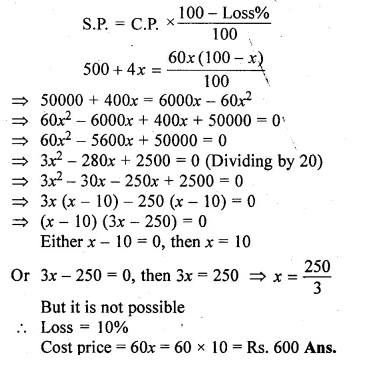
Question 42.
(i) The sum of the ages of Vivek and his younger brother Amit is 47 years. The product of their ages in years is 550. Find their ages. (2017)
(ii) Paul is x years old and his father’s age is twice the square of Paul’s age. Ten years hence, the father’s age will be four times Paul’s age. Find their present ages.
Solution:
(i) Let Vivek’s present age be x years.
His brother’s age = (47 – x) years
According to question,
x(47 – x) = 550
⇒ 47x – x² = 550
⇒ x² – 47x + 550 = 0
⇒ x² – 25x – 22x + 550 = 0
⇒ x(x – 25) – 22(x – 25) – 0

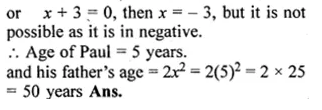
Question 43.
The age of a man is twice the square of the age of his son. Eight years hence, the age of the man will be 4 years more than three times the age of his son. Find the present age.
Solution:
Let the present age of the son = x years
then, the present age of the man = 2x² years.
8 years hence,
The age of son will be = (x + 8) years and the
age of man = (2x² + 8) years
According to the problem,
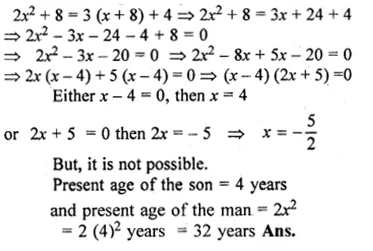
Question 44.
Two years ago, a man’s age was three times the square of his daughter’s age. Three years hence, his age will be four times his daughter’s age. Find their present ages.
Solution:
2 years ago,
Let the age of daughter = x
age of man = 3x²
then present age of daughter = x + 2
and mean = 3x² + 2
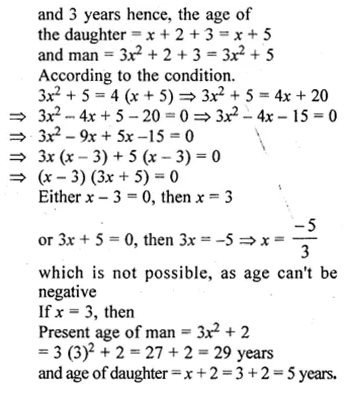
Question 45.
The length (in cm) of the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle exceeds the length of one side by 2 cm and exceeds twice the length of another side by 1 cm. Find the length of each side. Also, find the perimeter and the area of the triangle.
Solution:
Let the length of one side = x cm
and other side = y cm.
then hypotenues = x + 2, and 2y + 1

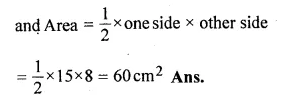
Question 46.
If twice the area of a smaller square is subtracted from the area of a larger square, the result is 14 cm². However, if twice the area of the larger square is added to three times the area of the smaller square, the result is 203 cm². Determine the sides of the two squares.
Solution:
Let the side of smaller square = x cm
and side of bigger square = y cm
According to the condition,
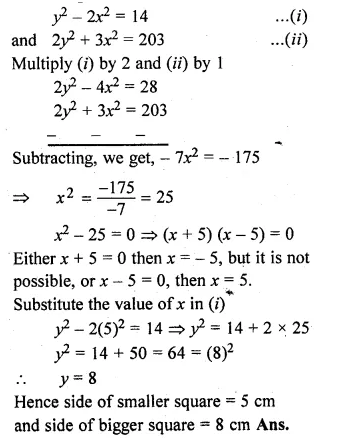
Hope given ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable Ex 5.5 are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.