ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable MCQS
These Solutions are part of ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths. Here we have given ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable MCQS
More Exercises
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable Ex 5.1
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable Ex 5.2
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable Ex 5.3
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable Ex 5.4
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable Ex 5.5
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable MCQS
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable Chapter Test
Choose the correct answer from the given four options (1 to 15) :
Question 1.
Which of the following is not a quadratic equation ?
(a) (x + 2)2 = 2(x + 3)
(b) x2 + 3x = ( – 1) (1 – 3x)
(c) (x + 2) (x – 1) = x2 – 2x – 3
(d) x3 – x2 + 2x + 1 = (x + 1)3
Solution:
(a) (x + 2)2 = 2(x + 3)
⇒ x2 + 4x + 4 = 2x + 6
⇒ x2 + 4x – 2x + 4 – 6 = 0
⇒ x2 + 2x – 2
It is a quadratic equation.
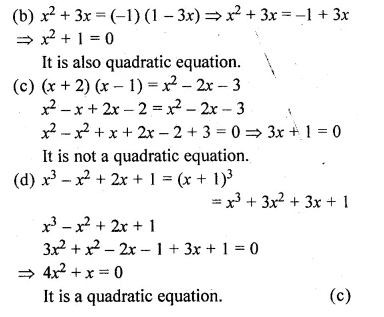
Question 2.
Which of the following is a quadratic equation ?
(a) (x – 2) (x + 1) = (x – 1) (x – 3)
(b) (x + 2)3 = 2x(x2 – 1)
(c) x2 + 3x + 1 = (x – 2)2
(d) 8(x – 2)3 = (2x – 1)3 + 3
Solution:
(a) (x – 2) (x + 1) = (x – 1) (x – 3)
⇒ x2 + x – 2x – 2 = x2 – 3x – x + 3
⇒ 3x + x – 2x + x = 3 + 2
⇒ 3x = 5
It is not a quadratic equation.
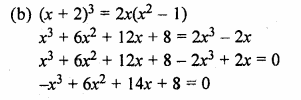
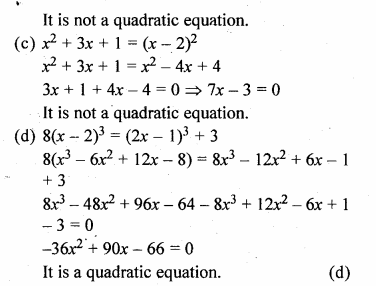
Question 3.
Which of the following equations has 2 as a root ?
(a) x2 – 4x + 5 = 0
(b) x2 + 3x – 12 = 0
(c) 2x2 – 7x + 6 = 0
(d) 3x2 – 6x – 2 = 0
Solution:
(a) x2 – 4x + 5 = 0
⇒ (2)2 – 4x2 + 5 = 0
⇒ 4 – 8 + 5 = 0
⇒ 9 – 8 ≠ 0
2 is not its root.
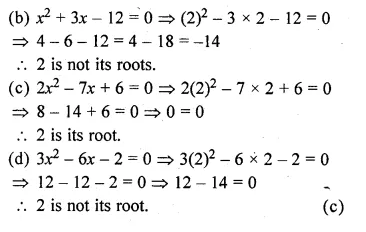
Question 4.
If \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) is a root of the equation x2 + kx – \(\\ \frac { 5 }{ 4 } \) = 0, then the value of k is
(a) 2
(b) – 2
(c) \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)
(d) \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)
Solution:
\(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) is a root of the equation
x2 + kx – \(\\ \frac { 5 }{ 4 } \) = 0
Substituting the value of x = \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) in the
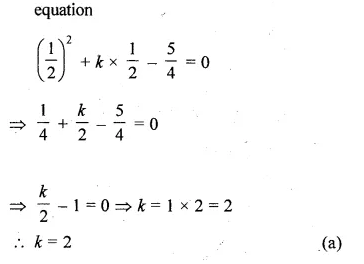
Question 5.
If \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) is a root of the quadratic equation 4x2 – 4kx + k + 5 = 0, then the value of k is
(a) – 6
(b) – 3
(c) 3
(d) 6
Solution:
\(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) is a root of the equation
4x2 – 4kx + k + 5 = 0
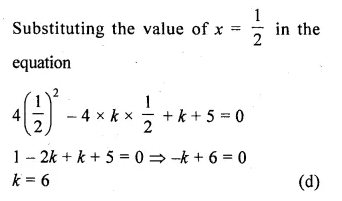
Question 6.
The roots of the equation x2 – 3x – 10 = 0 are
(a) 2,- 5
(b) – 2, 5
(c) 2, 5
(d) – 2, – 5
Solution:
x2 – 3x – 10 = 0
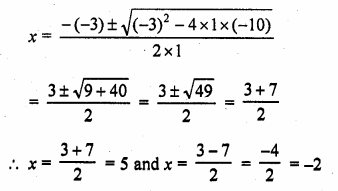
x = 5, – 2 or – 2, 5 (b)
Question 7.
If one root of a quadratic equation with rational coefficients is \(\frac { 3-\sqrt { 5 } }{ 2 } \), then the other
(a)\(\frac { -3-\sqrt { 5 } }{ 2 } \)
(b)\(\frac { -3+\sqrt { 5 } }{ 2 } \)
(c)\(\frac { 3+\sqrt { 5 } }{ 2 } \)
(d)\(\frac { \sqrt { 3 } +5 }{ 2 } \)
Solution:
One root of a quadratic equation is \(\frac { 3-\sqrt { 5 } }{ 2 } \)
then other root will be \(\frac { 3+\sqrt { 5 } }{ 2 } \) (c)
Question 8.
If the equation 2x² – 5x + (k + 3) = 0 has equal roots then the value of k is
(a)\(\\ \frac { 9 }{ 8 } \)
(b)\(– \frac { 9 }{ 8 } \)
(c)\(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 8 } \)
(d)\(– \frac { 1 }{ 8 } \)
Solution:
2x² – 5x + (k + 3) = 0
a = 2, b = -5, c = k + 3
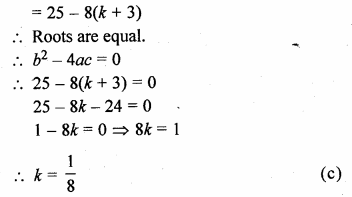
Question 9.
The value(s) of k for which the quadratic equation 2x² – kx + k = 0 has equal roots is (are)
(a) 0 only
(b) 4
(c) 8 only
(d) 0, 8
Solution:
2x² – kx + k = 0
a = 2, b = -k, c = k
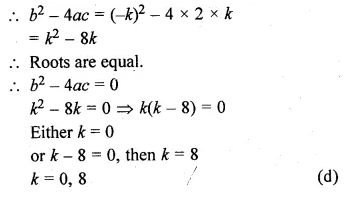
Question 10.
If the equation 3x² – kx + 2k =0 roots, then the the value(s) of k is (are)
(a) 6
(b) 0 Only
(c) 24 only
(d) 0
Solution:
3x² – kx + 2k = 0
Here, a = 3, b = -k, c = 2k
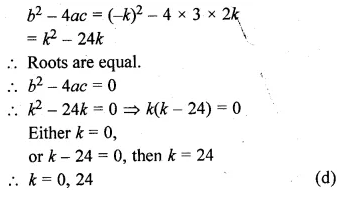
Question 11.
If the equation {k + 1)x² – 2(k – 1)x + 1 = 0 has equal roots, then the values of k are
(a) 1, 3
(b) 0, 3
(c) 0, 1
(d) 0, 1
Solution:
(k + 1)x² – 2(k – 1)x + 1 = 0
Here, a = k + 1, b = -2(k – 1), c = 1
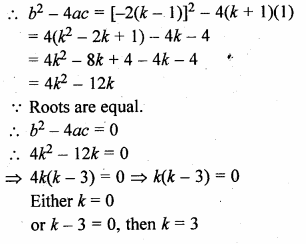
k = 0, 3 (b)
Question 12.
If the equation 2x² – 6x + p = 0 has real and different roots, then the values ofp are given by
(a)p < \(\\ \frac { 9 }{ 2 } \)
(b)p ≤ \(\\ \frac { 9 }{ 2 } \)
(c)p > \(\\ \frac { 9 }{ 2 } \)
(d)p ≥ \(\\ \frac { 9 }{ 2 } \)
Solution:
2x² – 6x + p = 0
Here, a = 2, b = -6, c = p
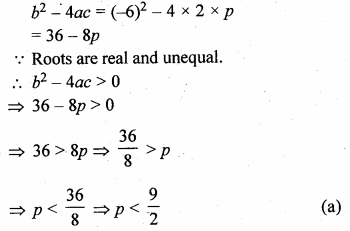
Question 13.
The quadratic equation 2x² – √5x + 1 = 0 has
(a) two distinct real roots
(b) two equal real roots
(c) no real roots
(d) more than two real roots
Solution:
2x² – √5x + 1 = 0
Here, a = 2, b = -√5, c = 1
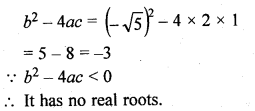
Question 14.
Which of the following equations has two distinct real roots ?
(a) 2x² – 3√2x + \(\\ \frac { 9 }{ 4 } \) = 0
(b) x² + x – 5 = 0
(c) x² + 3x + 2√2 = 0
(d) 5x² – 3x + 1 = 0
Solution:
(a) 2x² – 3√2x + \(\\ \frac { 9 }{ 4 } \) = 0
b² – 4ac = ( -3√2)² – 4 x 2 x \(\\ \frac { 9 }{ 4 } \) = 18 – 18 = 0
.’. Roots are real and equal.
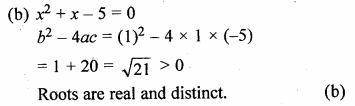
Question 15.
Which of the following equations has no real roots ?
(a) x² – 4x + 3√2 = 0
(b) x² + 4x – 3√2 = 0
(c) x² – 4x – 3√2 = 0
(d) 3x² + 4√3x + 4 = 0
Solution:
(a) x² – 4x + 3√2 = 0
b² – 4ac = ( -4)² – 4 × 1 × 3√2
= 16 – 12√2
= 16 – 12(1.4)
= 16 – 16.8
= -0.8
b² – 4ac < 0
Roots are not real. (a)
Hope given ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable MCQS are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.