NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology chapter 14 Ecosystem
These Solutions are part of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology chapter 14 Ecosystem
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Decomposers like fungi and bacteria are
(i) autotrophs
(ii) heterotrophs
(iii) saprotrophs
(iv) chemoautotrophs.
Choose the correct answer.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (ii)
Answer:
(c) : Decomposers like bacteria and fungi are heterotrophs because they are dependent on others for their food as they cannot make their own food. They are also called saprotrophs because they feed on dead and decaying organic matter.
Question 2.
The process of mineralisation by micro organisms helps in the release of
(a) inorganic nutrients from humus
(b) both organic and inorganic nutrients from detritus
(c) organic nutrients from humus
(d) inorganic nutrients from detritus and formation of humus.
Answer:
(a) : Mineralisation is the release of inorganic substances, both non-mineral (e.g., CO2, H2O) and minerals (e.g., Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, NH4+) from organic matter. The process is slow because of trapping of these nutrients in humus and their immobilisation in decomposers/detritivores. It prevents their washing out or leaching. Nutrients get immobilised in decomposer microbes and detritivores are again exposed to humification and mineralisation after the death of these organisms. its productivity. It is measured as weight (e.g., g/m2/yr) or energy (e.g., kcal/m2/yr). Hence, only unit (iv) is correct.
Question 3.
Productivity is the rate of production of biomass expressed in terms of
(i) (kcal m-3)yr-1
(ii) gyr-1
(iii) g-1 yr-1
(iv) (kcal m-2) yr-1
(a) (ii)
(b) (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer:
(None of the options is correct):
The rate of synthesis of energy containing organic matter or biomass by any trophic level per unit area in unit time is described as
Question 4.
An inverted pyramid of biomass can be found in which ecosystem?
(a) Forest
(b) Marine
(c) Grassland
(d) Tundra
Answer:
(b) : Biomass basically depends upon reproductive potential and age of individuals. In an aquatic ecosystem, producers have least biomass and this value gradually shows an increase towards the apex of the pyramid, thus making the pyramid inverted in shape.
Question 5.
Which of the following is not a producer?
(a) Spirogyra
(b) Agaricus
(c) Volvox
(d) Nostoc
Answer:
(b) : Spirogyra, Volvox and Nostoc are chlorophyll containing organisms and thus prepare their own food. Agaricus is a fungus (Basidiomycetes), it is a chlorophyllous and not a producer. It possesses saprotrophic mode of nutrition.
Question 6.
Which of the following ecosystems is most productive in terms of net primary production?
(a) Deserts
(b) Tropical rainforests
(c) Oceans
(d) Estuaries
Answer:
(b) : Tropical rainforests have an average net primary productivity (NPP) of 1,500 g/m2/ yr. Open oceans and deserts have average NPP of 125 and 90g/m2/yr respectively. Algal beds and reefs ecosystem have average NPP of 2,500 g/m2/yr.
Question 7.
Pyramid of numbers is
(a) always upright
(b) always inverted
(c) either upright or inverted
(d) neither upright nor inverted.
Answer:
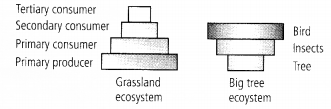
(c) : Ecological pyramids are pictorial representation of relationship between organisms at different trophic levels, regarding energy, biomass or number. Pyramid of numbers can be either upright or inverted. For example in a grassland ecosystem, number of primary consumers are less than primary producers and that of secondary consumers are less than primary consumers and so on. On the other hand, if a single big tree ecosystem is taken into consideration, pyramid of number will be inverted.
Question 8.
Approximately how much of the solar energy that falls on the leaves of a plant is converted to chemical energy by photosynthesis?
(a) Less than 1%
(b) 2-10%
(c) 30%
(d) 50%
Answer:
(b) : 50% of the solar energy incident over earth is present in PAR (photosynthetically active radiation). About 1-5% of total incident solar energy or 2-10% of PAR is captured by the photosynthetic organisms for photosynthesis.
Question 9.
Among the following, where do you think the process of decomposition would be the fastest?
(a) Tropical rainforest
(b) Antarctic
(c) Dry arid region
(d) Alpine region
Answer:
(a) : Tropical rainforests are the richest and most productive ecosystem in the world. Consequently, the rate of decomposition is also high, as the conditions of moisture and temperature are optimum.
Question 10.
How much of the net primary productivity of a terrestrial ecosystem is eaten and digested by herbivores?
(a) 1%
(b) 10%
(c) 40%
(d) 90%
Answer:
(b) : Energy flow in the ecosystem follows the ten percent law (put forth by Lindemann in 1942).
From the level of primary producers onwards, only 10% of energy is stored at the higher trophic level and 90% is lost (as heat or in respiration etc). This energy transfer forms the basis of life.
![]()
Question 11.
During the process of ecological succession the changes that take place in communities are
(a) orderly and sequential
(b) random
(c) very quick
(d) not influenced by the physical environment.
Answer:
(a) : Biotic or ecological succession is the natural development of a series of biotic communities at the same site, one after the other till a climax community develops which does not change further because it is in perfect harmony with the environment of the area. The change is orderly and sequential. The first biotic community which develops in a bare area is called pioneer community. It has very little diversity. Climax community is a stable, self perpetuating and final biotic community that develops at the end of biotic succession.
Question 12.
Climax community is in a state of
(a) non-equilibrium
(b) equilibrium
(c) disorder
(d) constant change.
Answer:
(b) : The process of sequential establishment of various plant communities in any habitat is called plant succession. Finally that community is established which is in complete equilibrium with the prevailing environment. This stage is called climax stage and its establishment is called stabilisation.
Question 13.
Among the following biogeochemical cycles which one does not have losses due to respiration?
(a) Phosphorus
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Sulphur
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) : Phosphorus, nitrogen and sulphur do not have losses due to respiration because they are not particularly involved in gaseous exchange.
Question 14.
The sequence of communities of primary succession in water is
(a) phytoplankton, sedges, free-floating hydrophytes, rooted hydrophytes, grasses and trees
(b) phytoplankton, free-floating hydrophytes, rooted hydrophytes, sedges, grasses and trees
(c) free-floating hydrophytes, sedges, phyto-plankton, rooted hydrophytes, grasses and trees
(d) phytoplankton, rooted submerged hydro-phytes, floating hydrophytes, reed swamp, sedges, meadow and trees.
Answer:
(d) : Primary succession in water is also called as hydrarch, which will lead from hydric to mesic conditions. Phytoplanktons (autotrophic) are generally the first to appear. Later zooplanktons feeding on phytoplanktons also appear. Next stage is characterised by the soft mud on the bottom having organic matter favouring the growth of rooted submerged plants. They are then replaced by free floating hydrophytes (Lenina, Woljfia etc). Rapid growth of these plants build up bottom so that water becomes shallow on periphery. In this shallow water, comes the reed swamp stage (e.g. Typha). They produce abundant organic matter. Next stages are sedge and meadow stage which transpire rapidly and build up soil, on which the next stage, trees can grow.
Question 15.
The reservoir for the gaseous type of biogeo-chemical cycle exists in
(a) stratosphere
(b) atmosphere
(c) ionosphere
(d) lithosphere.
Answer:
(b) : Biogeochemical cycles can be grouped into 3 types:
- Gaseous cycle (material involved in circulation are gases or vapours and the reservoir pool is the atmosphere or hydrosphere) e.g., nitrogen cycle.
- Sedimentary cycle (Materials involved in circulation are non-gaseous and the reservoir pool is lithosphere) e.g. phosphorus, calcium and magnesium cycles.
- Mixed cycle (materials involved in circulation has both gaseous and non- gaseous state), e.g., sulphur cycle.
Question 16.
If the carbon atoms fixed by producers already have passed through three species, the trophic level of the last species would be
(a) scavenger
(b) tertiary producer
(c) tertiary consumer
(d) secondary consumer.
Answer:
(c) : Length of a food chain i.e. number of trophic levels is limited by the efficiency of energy transfer i.e. 10% law.
Producers —> 1° consumers —> 2°consumers —> 3° consumers
If the carbon atoms fixed by producers already have passed through three species then the trophic level of the last species (i.e. third species) would be tertiary consumer. Scavengers (e.g. vultures) can be tertiary consumers, but they can be at other trophic levels too.
Question 17.
Which of the following type of ecosystem is expected in an area where evaporation exceeds precipitation, and mean annual rainfall is below 100mm?
(a) Grassland
(b) Shrubby forest
(c) Desert
(d) Mangrove
Answer:
(c) : Deserts have been variously classified as true deserts, having less than 120 mm annual rainfall, or extreme deserts showing less than 70 mm annual rainfall. In desert biomes, evaporation from soil always exceeds rainfall by 7 to 50 times.
Question 18.
The zone at the edge of a lake or ocean which is alternatively exposed to air and immersed in water is called
(a) Pelagic zone
(b) Benthic zone
(c) Lentic zone
(d) Littoral zone.
Answer:
(d) : Littoral zone is the shallow coastal zone. Light is available upto bottom in this zone. Therefore, producers are found throughout from surface to bottom in this zone. Rooted vegetation occurs along shores. Consumers are also available throughout i.e., from surface to the bottom in this zone.
Question 19.
Edaphic factor refers to
(a) water
(b) soil
(c) relative humidity
(d) altitude.
Answer:
(b) : Edaphic factors are classified under the abiotic factors affecting an ecosystem. Edaphic factors include factors of soil e.g. soil texture, substratum, topography, mineral composition, pH etc. These factors can influence the distribution and interrelationships of organisms, as well as rate of decomposition.
Question 20.
Which of the following is an ecosystem service provided by a natural ecosystem?
(a) Cycling of nutrients
(b) Prevention of soil erosion
(c) Pollutant absorption and reduction of the threat of global warming
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) : The products of ecosystem processes which have environmental, aesthetic and indirect economic value are named as ecosystem services. Soil formation and soil protection are the major ecosystem services accounting for nearly 50% of their total worth. Plant cover protects the soil from drastic changes in temperature. There is little wind or water erosion as soil particles are not exposed to them. The soil remains spongy and fertile. There are no landslides and no floods. Plant cover of natural ecosystem absorbs polluting gases, causes settling of suspended particulate matter, removes C02 and releases 0:. Purified air becomes available. There is no overall depletion of nutrients as the same are repeatedly circulated and recirculated. This keeps the fertility of soil intact.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name an organism found as secondary carnivore in an aquatic ecosystem.
Answer:
Large fish, catfish, water snake.
Question 2.
What does the base tier of the ecological pyramid represent?
Answer:
If Producers represent the base tier of the ecological pyramid.
Question 3.
Under what conditions would a particular stage in the process of succession revert back to an earlier stage?
Answer:
If At any time during primary or secondary succession, natural or human induced disturbances like fire, deforestation etc. can convert a particular seral stage of succession to an earlier stage.
Question 4.
Arrange the following as observed in vertical stratification of a forest: Grass, Shrubby plants, Teak, Amaranthus.
Answer:
Vertical stratification of forest are grass, Amaranthus, shrubby plants, teak.
Question 5.
Name an omnivore which occurs in both grazing food chain and the decomposer food chain.
Answer:
Crow is omnivore and occur in both grazing food chain and decomposer food chain.
Question 6.
Justify the pitcher plant as a producer.
Answer:
Leaf lamina in pitcher plant is modified into pitcher and consists of chlorophyll. It also undergoes photosynthesis, therefore pitcher plant is a producer.
Question 7.
Name any two organisms which can occupy more than one trophic level in an ecosystem.
Answer:
If Man and sparrow occupy more than one trophic level in an ecosystem.
Question 8.
In the North East region of India, during the process of Jhum cultivation, forests are cleared by burning and left for regrowth after a year of cultivation. How would you explain the regrowth of forest in ecological term?
Answer:
In Jhum cultivation, farmers cut down the trees of the forest and burn the plant remains. The ash is used as a fertiliser and land is used for farming or cattle grazing. After cultivation the area is left for several years so as to allow its recovery. This regrowth of forest is called secondary succession.
Question 9.
Climax stage is achieved quickly in secondary succession as compared to primary succession. Why?
Answer:
If Secondary succession occurs on a fertile land where living matter is already existing, whereas primary succession begins on a barren sterile area with no living matter present in it.
Question 10.
Among bryophytes, lichens and ferns which one is a pioneer species in a xeric succession?
Answer:
Crustose lichens are the pioneer species in xeric succession.
Question 11.
What is the ultimate source of energy for the ecosystems?
Answer:
Sun is the ultimate source of energy for the ecosystem.
Question 12.
Is the common edible mushroom an autotroph or a heterotroph?
Answer:
Edible mushroom is a heterotroph, as it is without chlorophyll and does not perform photosynthesis.
Question 13.
Why are oceans least productive?
Answer:
- Oceans have high salinity i.c., 3.5%.
- Low concentration of dissolved nutrients especially nitrogen.
- Deep abyssal zone in ocean has no producers.
Question 14.
Why is the rate of assimilation of energy at the herbivore level called secondary productivity?
Answer:
Herbivores are primary consumers and depend on plants to obtain biomass. Plants are producers and herbivores gain biomass from them by primary productivity. Rate of assimilation of primary productivity at the herbivore level is therefore, called secondary productivity.
Question 15.
Why are nutrient cycles in nature called biogeochemical cycles?
Answer:
The nutrients move from living organisms to environment in a cyclic manner and similarly back to the organism. Therefore, nutrient cycles in nature are called biogeochemical cycles.
Question 16.
Give any two examples of xerach succession.
Answer:
- L ithosere – Succession on a rock.
- Psammosere – Succession on a sandy area.
Question 17.
Define self sustainability.
Answer:
Self sustainability is the utilisation of natural resources in a way that their rate of consumption is equal to the rate of regeneration, so that same amount becomes available to the next generation. It is possible by judicious utilisation and avoiding wastage.
Question 18.
Given below is a figure of an ecosystem. Answer the following questions.
(1) What type of ecosystem is shown in figure.
(2) Name any plant that is characteristic of such ecosystem.

Answer:
- It is a desert biome.
- Xerophytic plants like cactus, Euphorbia.
Question 19.
What is common to earthworm, mushroom, soil mites and dung beetle in an ecosystem.
Answer:
All are decomposers involved in decomposition of organic remains.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Organisms at a higher trophic level have less energy available. Comment.
Answer:
This is because of 10% (ten percent) law which was proposed by Lindemann 1942. According to this law, during transfer of energy from lower trophic level to higher trophic level 90% of energy is lost, and only 10% of energy is transferred to next trophic level. As the trophic level increases, the available energy goes on decreasing.
Question 2.
The number of trophic levels in an ecosystem are limited. Comment.
Answer:
The amount of energy made available in a trophic level goes on decreasing from lower level to higher level. The transfer of energy follows 10% law. According to this a stage comes when energy available is too less to sustain the trophic level. Therefore number of trophic levels in an ecosystem remain limited.
Question 3.
Is an aquarium a complete ecosystem?
Answer:
Yes, a balanced aquarium is a artificial ecosystem consisting of both biotic and abiotic components. Water, oxygen supply source, light source are abiotic factors, whereas aquatic plants, small animals and decomposers serve as biotic components.
Question 4.
What could be the reason for the faster rate of decomposition in the tropics?
Answer:
Tropics mostly have temperature above 25°C, along with humid conditions, which is suitable environment for growth and multiplication of decomposers. That is why rate of decomposition is faster in tropics.
Question 5.
Human activities interfere with carbon cycle. List any two such activities.
Answer:
Human activities that are adding CO2 to the atmosphere are
- Excessive burning of fossil fuels.
- Deforestation.
Question 6.
Flow of energy through various trophic levels in an ecosystem is unidirectional and non- cyclic. Explain.
Answer:
Ultimate source of energy is sun. Green plants (producers) produce food by using solar energy. This food is consumed by herbivores (Primary consumers) to get energy. The energy is further transferred to next levels of consumers i.e., secondary consumers and tertiary consumers. During transfer of energy about 90% of it is wasted or consumed up in respiration and only 10% becomes part of the higher trophic level. The energy cannot be transferred from consumers to producers and even to the sun. Therefore, energy transfer is always unidirectional and non-cyclic accompanied by decrease in usable energy.
Question 7.
Apart from plants and animals, microbes form a permanent biotic component in an ecosystem. While plants have been referred to as autotrophs and animals as heterotrophs, what are microbes referred to as? How do the microbes fulfil their energy requirements?
Answer:
Microorganisms like bacteria and fungi are heterotrophs and are known as decomposers. They fulfil their energy needs by decomposition, which involves break down of complex organic matter into simple compounds. They absorb these simplified compounds and use them during their metabolism.
Question 8.
Poaching of tiger is a burning issue in today’s world. What implication would this activity have on the functioning of the ecosystem of which the tigers are integral part?
Answer:
Tigers and lions are top carnivores and play an important role in maintaining the stability of an ecosystem. Excessive poaching of tigers will lead to increase in population size of herbivores which in turn will damage the crops in abundance. This will create an imbalance in the ecosystem and will make it unstable.
Question 9.
In relation to energy transfer in ecosystem, explain the statement “10 kg of deer’s meat is equivalent to 1 kg of lion’s flesh”.
Answer:
The statement is very true, because lion is a predator which eats deer. According to 10% energy transfer law only 10% of energy will be made available to the lion from deer, and 90% of the energy will be lost in the atmosphere during transfer.
Question 10.
Primary productivity varies from ecosystem to ecosystem. Explain?
Answer:
Primary productivity is the amount of energy accumulation in green plants as biomass or organic matter per unit area over a time period through the process of photosynthesis. Primary productivity in an ecosystem depends on number of factors like photosynthetic capacities of producers, environmental factors like temperature, sunlight intensity, rainfall and availability of nutrients. These factors are different in different ecosystems, therefore productivity varies from ecosystem to ecosystem. In tropical rainforest primary productivity is high 20 tones/hectare/year whereas in desert it is low 0.7 tones /hectare/year.
Question 11.
Sometimes due to biotic/abiotic factor the climax remain in a particular seral stage (pre climax) without reaching climax. Do you agree with this statement. If yes give a suitable example.
Answer:
Yes, this statement is right. Sometimes certain biotic or abiotic factors do not let a seral stage to reach climax, and process of succession may get arrested at pre-climax stage. This may be due to certain reasons like forest fires, land slide, change in soil characteristic, increase in herbivore population and overgrazing etc.
Question 12.
What is an incomplete ecosystem? Explain with the help of suitable example.
Answer:
lf any essential component of an ecosystem is absent in an ecosystem, it is said to be an incomplete ecosystem. E.g., an ecosystem at the bottom of fish tank or deep aphotic zone of the ocean. In both cases producers are absent, therefore both are the examples of incomplete ecosystem.
Question 13.
What are the shortcomings of ecological pyramids in the study of ecosystem?
Answer:
Shortcoming of ecological pyramids are:
- It does not take into account the same species belonging to two or more trophic levels.
- It assumes simple food chain, that almost never exists in nature.
- It does not accommodate food web.
- Saprophytes are not given any place in ecological pyramids, even though they play a vital role.
Question 14.
How do you distinguish between humification and mineralisation?
Answer:
Humification – The process by which detritus is changed into dark-coloured amorphous substance called humus, which acts as a reservoir of nutrients.
Mineralisation – The process by which inorganic substances (water, CO2) and minerals (Ca, Mg’1″, KT NH4+) are released in the soil.
Question 15.
Fill in the trophic levels (1, 2, 3 and 4) in the boxes provided in the figure.
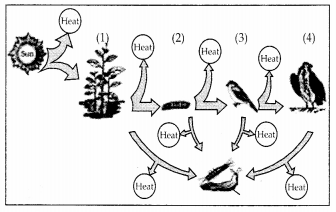
Answer:
(1) is T1 first trophic level i.e., producers
(2) is T2 – Second Trophic level i.e., herbivore (Primary consumer)
(3) is T3 – Third trophic level i.e., small carnivorous bird (Secondary consumers)
(4) is T4– Fourth Trophic level i.e., large carni-vorous bird (tertiary consumers)
Question 16.
The rate of decomposition of detritus is affected by the abiotic factors like availability of oxygen, pH of the soil substratum, temperature etc. Discuss.
Answer:
Breakdown of complex organic compounds of dead bodies of plants and animals and wastes of animals by microbial action into simple substances is known as decomposition.
It depends on various factors like –
- Temperature – Higher temperature i. e., above 25°C increases the rate of decomposition. Low temperature at high altitude and latitude decreases the metabolism of microbes.
- Availability of oxygen – Rate of decomposition of detritus is faster in presence of oxygen i.e., in aerobic conditions, while absence of oxygen or anaerobic conditions (anaerobiosis) reduces decomposition and causes piling up of detritus.
- pH of soil substratum – Neutral and slightly alkaline soils are rich in detritivores and favour decomposition. Increase in acidity decreases the rate of decomposition.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
A farmer harvests his crop and expresses his harvest in three different ways.
(a) I have harvested 10 quintals of wheat.
(b) I have harvested 10 quintals of wheat today in one acre of land.
(c) I have harvested 10 quintals of wheat in one acre of land, 6 months after sowing.
Do the above statements mean one and the same thing. If your answer is yes, give reasons. And if your answer is ‘no’ explain the meaning of each expression.
Answer:
NO, the above three statements do not mean one and the same thing because –
- Statement (a) indicates total productivity of wheat but does not indicate the extent of area.
- Statement (b) indicates the productivity of wheat/acre/on a specific day.
- Statement (c) indicates productivity of wheat/acre/specific period.
The third statement (c) is most accurate as it expresses the productivity of wheat per unit time and per unit area.
Question 2.
Justify the following statement in terms of ecosystem dynamics.”Nature tends to increase the gross primary productivity, while man tends to increase the net primary productivity”.
Answer:
Gross primary productivity of an ecosystem is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis. Nature always tend to increase gross primary productivity. Ecological succession is the natural development of a series of biotic communities at the same site, one after the other till a climax community develops which does not change further because it is in perfect harmony with the environment of the area.
In ecological succession there is tendency to increase species diversity, complexity of organisms, and gross primary productivity as higher serai communities have higher photosynthetic efficiency.
Net primary productivity is the available biomass for the consumption to heterotrophs. It is equal to the rate of organic matter created by photosynthesis minus the rate of respiration and other losses.
NPP = GPP – R
Human always tries to increase net primary productivity by cultivating food and crops, which are important for our survival.
Question 3.
Which of the following ecosystems will be more productive in terms of primary productivity? Justify your
A young forest, a natural old forest, a shallow polluted lake, alpine meadow.
Answer:
Primary productivity is the rate of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period by green plants during photosynthesis. Primary productivity depends upon the type of ecosystem. The ecosystem which has more producers, will be more productive in terms of primary productivity. A young forest will be more productive than an old forest. It is because the rate of total photosynthesis will be highest in it, due to fully grown vegetation, more number and large surface area of the leaves and higher quantum number. On the other hand, a shallow polluted lake will have low oxygen content and an alpine area is at high altitude where low temperature inhibits productivity.
Question 4.
What are the three types of ecological pyramids. What information is conveyed by each pyramid with regard to structure, function and energy in the ecosystem.
Answer:
An ecological pyramid is a graphic representation of an ecological parameter like number of individuals present in various trophic levels of a food chain with producers forming the base and top carnivores the tip. Each trophic level represents a functional level.
There are three types of ecological pyramids.
(1) Pyramid of numbers
(2) Pyramid of biomass
(3) Pyramid of energy
(1) Pyramid of numbers : It is a graphic representation of the number of individuals per unit area of various trophic levels stepwise with producers being kept at the base and top carnivores kept at the tip. In most cases the pyramid of number is upright with members of successive higher trophic level being fewer than the previous one.
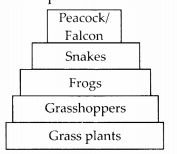
In a grassland, a larger number of grass plants or herbs support a fewer number of grasshoppers that support a still smaller number of frogs, the latter still smaller number of snakes and the snakes very few peacocks or falcons. This is, however, not applicable in all the cases.
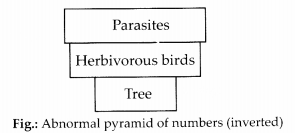
A single large sized producer like tree can, however, provide nourishment to several herbivores (e.g., birds). The birds may support a still larger population of ectoparasites. Such a pyramid shall be inverted.
(2) Pyramid of biomass : The amount of living organic matter is called biomass. It is measured both as fresh and dry- weight. Pyramid of biomass is a graphic representation of biomass present sequence-wise per unit area of different trophic levels with producers at the base and top carnivores kept at the tip.
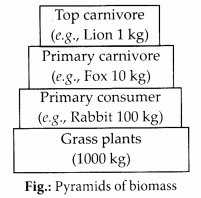
Maximum biomass occurs in producers. There is a progressive reduction of biomass found in herbivores, primary carnivores, secondary carnivores, etc. It is found that about 10-20% of the biomass is transferred from lower trophic level to higher trophic level.
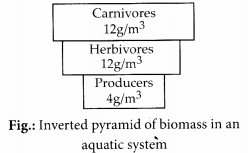
Pyramid of biomass is upright for terrestrial habitats. Inverted or spindle¬shaped pyramids are obtained in aquatic habitats where the biomass of a trophic level depends upon reproductive potential and longevity of its members,
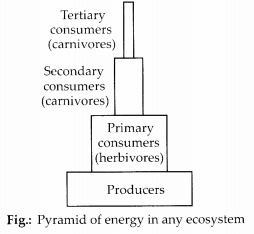
(3) Pyramid of energy – It is graphic representation of amount of energy trapped per unit time and area in different trophic levels of food chain. It is always upright as the amount of energy always decreases from lower to higher trophic level of food chain and follows 10% energy transfer law.
Question 5.
Write a short note on pyramid of numbers and pyramid of biomass.
Answer:
Re/er answer 4.
Question 6.
Given below is a list of autotrophs and heterotrophs. With your knowledge about food chain, establish various linkages between the organisms on the principle of’eating and being eaten’. What is the this inter-linkage established known as?
Algae, Hydrilla, grasshopper, rat, squirrel, crow, maize plant, deer, rabbit, lizard, wolf, snake, peacock, phytoplankton, crustaceans, whale, tiger, lion, sparrow, duck, crane, cockroach, spider, toad, fish, leopard, elephant, goat, Nymphaea, Spirogyra.
Answer:
A straight line sequence of ‘who eats whom’ or eating and being eaten in an ecosystem is called a food chain. A network of cross connecting food chains involving producers, consumers and decomposers are termed as a food web.
Lion, tiger, leopard, whale – Top carnivore (Top trophic level)
Spider, cockroach, lizard, wolf, snake, toad, fish, crow, sparrow, crane, duck, peacock – Secondary consumers (IIIrd trophic level).
Crustaceans, grasshopper, deer, rat, squirrel, rabbit, elephant, goat – Primary consumer (IInd trophic level). Phytoplankton, algae, Hydrilla, maize plant, Nymphaea, Spirogyra – Producers (Ist trophic level).
Question 7.
“The energy flow in the ecosystem follows the second law of thermodynamics”. Explain.
Answer:
Second law of thermodynamics, also called law of entropy, states that energy transfer or energy transformation is never cent percent. It involves degradation or dissipation of energy from a concentrated to a dispersed form as is used to maintain the metabolism. So only a part of energy is stored in the biomass. When a producer (plant) traps radiant energy for photosynthesis, only 2-10% of PAR (only 1-5% of incident solar radiations) is used for photosynthesis called GPP. About 0.2 to 1% of incident radiations is used by plants for respiration and 0.8 to 4% of incident radiations is used to produce biomass called NPP.
When a herbivore eats a producer about 90% of energy will be dissipated and only 10% of energy is available for producing biomass. It will be repeated when herbivore will be eaten by a carnivore. It is called 10% (ten percent) law which was proposed by Lindemann, 1942.
Question 8.
What will happen to an ecosystem if:
(a) All producers are removed;
(b) All organisms of herbivore level are eliminated; and
(c) All top carnivore population is removed.
Answer:
(a) In food chain plants occupy the place of producers. They are the source of food or energy for every organism. If plants producers are removed there will be reduction in primary productivity. No biomass will be available for consumption to higher levels of organisms and they all will die.
(b) If all herbivores are eliminated, there will be increase in primary productivity because of lack of consumers. Carnivores population will starve to death due to unavailability of food.
(c) ‘If all top carnivores are removed, the population of herbivores will increase. They will consume more producers, which can lead to desertification.
Question 9.
Give two examples of artificial or man made ecosystems. List the salient features by which they differ from natural ecosystems.
Answer:
Artificial or man-made ecosystem is created and maintained by human beings. Agriculture, garden, aquarium are artificial
ecosystems.
In artificial ecosystem, biotic and abiotic components are maintained artificially e.g., feeding, cleaning and supply of oxygen to fishes in aquarium.
A natural ecosystem is one which develops in nature without human support or interference i.e., forest, marine ecosystem.
In natural ecosystem, biotic and abiotic components are maintained naturally like light, nutrient cycle, self-sustainability, etc.
Question 10.
The biodiversity increases when one moves from the pioneer to the climax stage. What could be the explanation?
Answer:
The biodiversity increases in an ecological succession when one moves from pioneer community to climax stage due to following reasons –
- Environmental conditions become more and more favourable for survival of different organisms.
- Variety of ecological niches increases and become available to many organisms.
- Biomass and standing crop of organic matter increases with succession. According to Odum, the increase in amount of and the change in organic structure are two of the main factors bringing about succession of species. The enlargement of organic structure is of course, related in a cause-and-effect manner to increase in species diversity.
Question 11.
What is a biogeochemical cycle. What is the role of the reservoir in a biogeochemical cycle. Give an example of a sedimentary cycle with resefvoir located in earth’s crust.
Answer:
Biogeochemical cycles are cyclic pathways through which chemical elements move from environment to organism and back to the environment. Biogeochemicals are essential elements required by the organism for their body building and metabolism, which are provided by earth and return to earth after their death and decay.
Reservoir pool is the reservoir of biogenetic nutrients from which the latter are slowly transferred to cycling pool e.g., phosphates in rocks. The function of reservoir is to meet deficient of nutrient which occurs due to differences in rate of influx and efflux. Atmosphere acts as reservoir pool for carbon and nitrogen cycles.
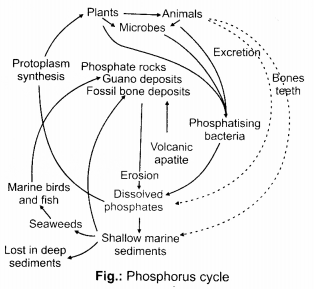
Phosphorus cycle is an example of sedi-mentary cycle.Phosphate present in the soil may occur in the insoluble form, which is dissolved by chemicals secreted by microbes and plant roots. The dissolved phosphate when absorbed by the plant as orthophosphate ions change to organic form and is then transferred to consumers and decomposer through food chain. Animal excretion and dead bodies when acted upon by decomposer, releases phosphorus, which is recycled/reutilised again. Leaching, erosion and mining also releases phosphate and make it available to plants. In aquatic environment, phosphate is taken from water by phytoplankton, consumed by zooplankton, which in turn excrete it into water.
- It is a an imperfect cycle as the biological processes (teeth and bones formation and excretion) account for considerable losses of phosphorus.
- It also shows one way flow : Phosphate rock —» land ecosystem > oceans ocean sediment.
It, causes eutrophication and pollution when its concentration increases in natural water.
Question 12.
What will be the P/R ratio of a climax community and a pioneer community. What explanation could you offer for the changes seen in P/R ratio of a pioneer community and the climax community.
Answer:
The species that invade a bare area are called pioneer species. These are generally lichens. A pioneer community has maximum number of producers. The rate of production P is higher than rate of respiration R. Therefore P/R ratio of pioneer community is more than 1. This increases the biomass. But with the progress in succession i.e., advancement towards climax community biomass of organisms increases and P/R ratio becomes equal to 1. This shows stability of the ecosystem.
When number of organisms increases by reaching climax community, rate of respiration increases greater than rate of production and community is dominated by heterotroph, where P/R ratio become less than 1.
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology chapter 14 Ecosystem help you. If you have any query regarding .NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology chapter 14 Ecosystem, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.