Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 Science Important Questions with Answers PDF will help you in scoring more marks in your exams.
Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 Important Questions and Answers Science Chapter 15
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
From where do plants acquire the following nutrients— Nitrogen, Hydrogen. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
(a) Nitrogen. From soil (as nitrate, ammonia, urea)
(b) Hydrogen. From water.
More Resources
- Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science
- Value Based Questions in Science for Class 9
- HOTS Questions for Class 9 Science
Question 2:
Give technical terms for milk producing females and farm labour animals. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Milk Producing Females. Milch animals.
Farm Labour Animals. Draught animals.
Question 3.
Distinguish between a Mullet and Prawn.
(CCE 2010)
Answer:
Mullet is an edible fish while Prawn is an edible arthropod.
Question 4.
How does Catla differ from Mrigal ? (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Catla is a surface feeder that feeds on small animals. Mrigal is a bottom feeder that feeds on detritus and decaying vegetation.
Question 5.
State the reason for introducing Italian bee variety in bee farms. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Italian Bee (Apis millifera) is high honey collecting gende bee with less swarming and with ability to protect itself from enemies.
Question 6.
How does Bombay Duck differ from Common Carp ?
(CCE 2010)
Answer:
Bombay Duck is a marine fish while common carp is a fresh water fish.
Question 7.
Name one micronutrient and one macronutrient which ( plants take from soil. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Micronutrient: Iron/Zinc/Copper.
Macronutrient: Nitrogen/Phosphorus/Potassium.
Question 8.
How does Bos indicus differ from Bos bubalis ?
(CCE 2010)
Answer:
Bos indicus is cow while Bos bubalis is buffalo.
Question 9.
Name two vitamins which are added to poultry feed.
(CCE 2010)
Answer:
Vitamins A and K.
Question 10.
Why do we eat Pea and Groundnut ? (CCE 2010)
Answer:
They are rich in proteins. Groundnut is also rich in fat.
Question 11.
Name two breeds of cows selected for long lactation/ period. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Jersey, Brown Swiss.
Question 12.
State the meaning of mixed cropping ? (CCE 2010)
Answer:
It is a method of growing two or more different crops simultaneously in the same field.
Question 13.
Define hybridisation. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Hybridisation is crossing of two different varieties and breeds in order to obtain a progeny that has good traits of both of them.
Question 14.
What is vermicompost ? (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Vermicompost is a manure rich in worm castings and pulverised organic matter that is prepared by allowing earthworms, (e.g. Drawida willisi) to feed on organic remains.
Question 15.
Write four methods of weed control. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Mechanical, cultural, chemical and biological.
Question 16.
Mention any two activities for improvement of crop yield. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
- Crop variety improvement,
- Crop production improvement by providing optimum nutrients.
Question 17.
State one importance of photoperiod in agriculture.
(CCE 2010)
Answer:
Photoperiod or duration of sunlight determines the timing of flowering of crop plants and hence distinction of kharif and rabi crops.
Question 18.
List two desirable traits of fodder crops. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
- Good height, juicy stems and profuse branching.
- Good growth of foliage.
Question 19.
State one demerit of composite fish culture system.
(CCE 2010)
Answer:
Only some selected high yielding and economically important breeds are reared. Other breeds, varieties and species are being ignored so that natural biodiversity has come under threat.
Question 20.
State the two major categories of dairy animal feed in animal husbandry. (CCE 2010, 2013)
Answer:
- Maintenance feed
- Lactation period feed.
Question 21.
Write two examples of rabi crop. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Wheat, Gram, Mustard.
Question 22.
State the kinds of nutrients provided by vegetables and fruits. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Vitamins, minerals, roughage, small quantity of carbohydrates, proteins and oils.
Question 23.
Based on photoperiod, what type of crops are Mustard and Wheat ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Rabi crops.
Question 24.
We have no major scope for increasing the area of land under cultivation in India. Why ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
More land can be obtained only through deforestation which is already high causing large scale floods, landslides and soil erosion.
Question 25.
Distinguish between intervarietal and interspecific hybridisation of crop plants.
(CCE 2013)
Answer:
Intervarietal hybridisation is development of hybrid through crossing between two varieties of the same species. Interspecific hybridisation is development of hybrid through crossing between two species.
Question 26.
Mention two climatic conditions essential for different crops for growth and completion of their life cycle.
(CCE 2013)
Answer:
Temperature and photoperiod.
Question 27.
Mention any method of incorporating desirable characters into a crop variety. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Hybridisation.
Question 28.
A farmer grows gram crop between two cereal crops. Which agricultural practice is being followed here ?
(CCE 2013)
Answer:
Crop rotation.
Question 29.
Fertilizers have disturbed the ecology upto a large extent. State two alternatives that may be practised to overcome this problem. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Use of manures and biofertilizers.
Question 30.
Name a farming system with no use of chemical fertilizers.
(CCE 2013)
Answer:
Organic farming.
Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
Question 1.
List any two advantages of crop rotation. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
1. Maintenance of Soil Health. Crop rotation maintains the health of the soil by leaving roots of harvested crops at different levels and withdrawal of nutrients by plants from different layers.
2. Weed and Pest Control. Crop specific weeds, pests and pathogens decline in number because of the longer interval between two similar crops.
Question 2.
The shorter the duration of the crop, the more economical is the variety. Justify the statement. (CCE2010, 2013)
Answer:
Shorter duration crops are more economical as
(i) They require lesser inputs (irrigation, nutrients, manure, fertilizer, pesticide),
(ii) The land becomes available for growing another crop.
Question 3.
What are rabi crops ? State any two examples.
(CCE 2010)
Answer:
Rabi crops are winter season crops that grow between November and April, e.g., Wheat, Gram, Mustard.
(a) Name any one bottom feeder that can be grown in composite fish culture.
(b) What are the problems faced in such a culture.
Question 4.
How are they overcome ? (CCE 2010)
Answer:
(a) Mrigal/Common Carp.
(b) Problems,
- Avoiding competition and fighting amongst different types of fish by selecting the ones which have different feeding habits and tolerance to other fish nearby,
- Maintenance of water fertility or food at different levels in the same pond.
Question 5.
What is the major problem in fish farming ? How is this problem overcome ? (CCE 2010, 2013)
Answer:
The major problem in fish farming is breeding of fish which occurs naturally during monsoon of technique of induced breeding by injecting pituitary hormones (hypophysation).
Question 6.
Farmers use beekeeping as an additional income generating activity. Give two reasons. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
- It requires low investment,
- Beekeeping helps in cross pollination of crops as honey bees transfer pollen grains from one flower to another while collecting nectar.
Question 7.
List two characteristics each of roughage and concentrate in relation to animal feed. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Roughage:
- Coarse, fibrous feed that has low nutrient content,
- Roughage is mainly made of cellulose which is digested by catde and other herbivores with the help of cellulose digesting bacteria present in stomach of animals.
- They down grade the quality of produce.
Concentrate:
- It is nutrient rich component of animal feed,
- Concentrate has little fibrous matter.
Question 8.
What are weeds ? List two disadvantages of weeds.
(CCE 2010, 2015)
Answer:
Weeds are unwanted plants which grow along with cultivated crop plants in the same field.
Disadvantages:
- Weeds compete with and deprive crop plants of nutrients, water, space and light,
- They often spread crop pests and diseases,
- They down grade the quality of produce.
Question 9.
“Removal of weeds from cultivated fields during the early stages of growth of crops is essential for a good harvest.” Justify the statement. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
- Removal of weeds during the early stages of growth of crops is essential as it will allow the crop plants to grow and spread properly obtaining all the inputs (which are robbed by the weeds if they are present)
- Destruction of weeds in early stages prevent them to produce seeds and multiply.
Question 10.
List two demerits of the continuous use of fertilizers.
(CCE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
- Fertilizers change soil chemistry by making it either too alkaline or too acidic.
- They pollute both ground and surface waters. Surface waters receive fertilizers from runoff from fields. They undergo eutrophication (excessive growth of algae and other plants) that later kills aquatic animals and make water unfit for human consumption. .
Question 11.
List any two methods adopted in farming for the health of catde. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
- Vaccination against various diseases.
- A clean, spacious shelter, regular grooming of animals and good nutritive food.
Question 12.
Hari Ram wanted to add fertilizers in his vegetable garden to get healthy plants while his brother wanted to do organic farming.
(a) List two important differences between manure and fertilizers,
(b) What is organic farming system ? (CCE 2016)
Answer:
(a)

(b) Organic Fanning System. It is the practice of raising unpolluted crops through the use of manures, biofertilizers and biopesticides.
Short Answer Questions (3 Marks)
Question 1.
How is green manure prepared ? When is it added to the crop plants ? What is the advantage of this type of manure ? (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Green manure is prepared in situ by ploughing back young green crop plants into soil.
When Added. Green manure is added to the soil before seeding it for new crop.
- Organic Matter. Manure provides a lot of organic matter (like humus) to the soil which increases water retention capacity in sandy soils and drainage as well as aeration in clayey soils. It also improves the physical characteristics of the soil.
- Nutrients. Manure enriches the soil with nutrients.
- Soil Organisms. It provides food for soil organisms like soil friendly bacteria and earthworm. Earthworm helps in making soil porous and making nutrients available to plants.
- By using biological waste materials as a manure, we recycle the wastes and protect our environment from chemicals (fertilizers).
- It contains substances that stimulate plant growth and seed germination.
Question 2.
List six facilities that must be provided to cattle to ensure their good health and production of clean milk.
(CCE 2010)
Answer:
- It should be spacious enough to provide a proper space for each animal to stay comfortably and avoid overcrowding. A cow requires 6 square metre space while a buffalo needs little more space.
- The shelter should be clean, dry, airy and well-ventilated. It should get adequate sunlight during the day.
- There should be proper arrangement for the hygienic disposal of animal wastes (urine and excreta).
- It should have arrangement for fresh, clean drinking water. Water should also be available for cleaning the shelter and bathing of the animals. They require regular brushing to remove dirt and loose hairs.
- The shelter should protect the animals from rain, storm, heat, cold and predators. It should also safeguard animals from various diseases.
- Cattle shed should be properly covered, with cemented floors having slope for quick drainage. The shed is partitioned to house different categories of cattle (calves, bull, cows are kept separately).
Question 3.
(a) List three factors on which cultivation practices and crop yield are related.
(b) Name three stages involved in farming practices.
(CCE 2010, 2013)
Answer:
(a) Factors Controlling Cultivation Practices and Crop Yield.
- Climate
- Soil
- Genetic potentiality of crop variety.
(b) Stages Involved in Farming Practices.
- Crop variety improvement,
- Crop production improvement,
- Crop protection management.
Question 4.
(a) Black and blue dots in the picture below are an indication of two different types of crop plants. Identify the cropping pattern in figures A and B.
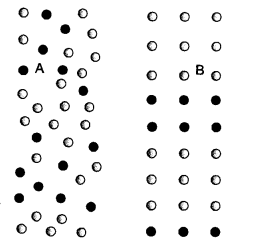
(b) Mention any two advantages of such cropping patterns. (CCE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
(a) A—Mixed cropping.
B—Inter-cropping.
(b) Advantages:
- Higher yield especially when a leguminous crop is sown alongwith a non-leguminous crop,
- Maintenance of soil health and reduced pest infestation.
Question 5.
Broiler production is indeed a solution to increase the , production of nutritious animal protein food. Enumerate the factors that need to be considered for broiler production. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
- A proper, spacious, airy, ventilated shelter/shed which is cleaned properly and regularly.
- Vaccination of the young birds.
- A proper quick growing breed
- Vitamin (A and K) and protein rich, some fat containing feed.
Question 6.
What is composite fish culture ? State one merit and demerit of such a system. (CCE 2010, 2012)
Answer:
Composite fish culture is a practice of growing 5-6 species , in the same culture pond with different food habits so that there is no competition amongst them, e.g., Catla (surface feeder on small animals). Silver Carp (surface feeder or phytoplankton) Rohu (middle zone), Grass Carp (water weeds), Mrigal (bottom feeder on detritus) and Common Carp (bottom feeder, omnivorous).
Merit. Yield is very high.
Demerit. Reduction in biodiversity.
Question 7.
What is manure ? How is it prepared ? State its role in changing the quality of soil of a field having excess of
- Sand
- Clay. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Manure: It is a partially decomposed organic matter derived from plant and animal wastes which is added to the soil to increase its fertility.
Preparation: Organic remains (e.g., crop residue, excreta of animals, litter and other organic wastes) are dumped in pit. Microbial action causes decomposition. Organic matter is changed into dark amorphous mass in 1-3 months. It is called manure.
- Sandy Soil: Manure provides mineral nutrients and increases water retention capacity.
- Clay Soil: Manure improves drainage and aeration.
Question 8.
A farmer cultivated soyabean in the field of Maize in well planned rows. Name the method of cultivation ?
Explain the method. What are the advantages of this agricultural practice ? (CCE 2010)
Answer:
- It is taking a plant or new variety from an area where it grows naturally to a region where it does not occur before for
- Ornamental purposes.
- Increasing yield of food, fruit or economic product.
- Improvement in local varieties.
- New food or commercial product.
Initial introduction is carried out in those areas which have similar climatic and soil conditions. Slowly its area is allowed to spread when it gets acclimitised to local conditions. Introduction is the oldest method of crop improvement.
- It is picking up plants with better traits for further multiplication. Selection by human beings is also called artificial selection.
- Crop improvement by developing better varieties of crop plants through hybridisation forms the backbone of modern agriculture. In order to obtain an improved variety, following steps should be taken :
- Choice of Parents. Two older varieities of crop having different desirable characteristics, are selected. For example, if we want to obtain a variety having higher yield as well as disease resistance, we should select two existing varieties of crops, one having higher yield and the other having more resistance to diseases.
- Cross-breeding The Two Parents. Pollen grains of plants of one variety are dusted over the stigmas of plants of the other variety and vice-versa. It produces a new variety which has good chacateristics of both the parents. The process of crossing plants of two varieties having different traits to produce a hybrid having good traits of both is called The crossing may be intervarietal (between different varieties), intergeneric (between different genera) or interspecific (between different species of the same genus). The most common type of breeding is intervarietal.
Question 9.
Artificial selection operating over long time spans can give rise to varieties strikingly different from starting generation. For example, broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower and other varieties have been obtained through artificial selection from Wild
(a) What suggestions can you give to an agriculturalist to combine fish culture in his crop field ?
(b) What is mariculture ? What can be grown by this method ?
(CCE 2010)
Answer:
(a) Quick growing edible fish (e.g., Mtigil, Lates, Mystus species) can be grown in paddy fields. Catching and marketing of fish would give an extra income to the farmer.
(b) Mariculture: Culture fisheries in sea water include fin fisheries (like mullets, pearl spots, bhetki, etc.), shell fisheries (like mussel, oysters, prawns, pearl culture) and sea weeds. Culture of marine fin fishes, shell fishes and sea weeds is called mariculture.
Question 10.
List any six factors for which variety improvement in crops is done. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
- Higher yield.
- Improved quality.
- Biotic and abiotic resistance.
- Change in maturity duration.
- Desirable agronomic traits.
- Wider adaptability.
Question 11.
A farmer observed Parthenium plant growing alongwith wheat crop. What is Parthenium ? What should he do to protea his crop ? Why ? (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Parthenium. (Gajar Ghas) is a serious weed of rabi crops which is also toxic to catde as well as humans.
Protection of Crop. Removal of Parthenium and burning it. Growth of Cassia near the field can prevent spreading of Parthenium.
Why ? Weeds rob the crop of its nutrients, water and other necessities. They are also toxic.
Question 12.
Explain mixed cropping method with the help of an example. Give any one advantage of using such a method.
Answer:
Mixed cropping is the technique of growing two or more different crops together in the same field, e.g., Groundnut and Sunflower, Wheat and Gram/Mustard. The component crops do not compete with each other as they have diffèrent growth patterns and root patterns which obtain their water and nutrients from different soil layers but otherwise requiring common type of fertilizers. Advantage. Mixed cropping eliminates chances of complete crop failure, reduces pest infestation, improves soil fertility and increases yield.
Question 13.
State three advantages of shorter duration of the crop from sowing to harvesting. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
- Change in sowing time reduces the chances of weed, pest and pathogen infestation.
- There is lesser requirement of inputs like irrigation and fertilizer.
- An early harvesting time ensures proper ripening of crop, reduced moisture content of seeds/grains, proper marketing and storage while giving enough time for preparing the field for the next crop.
Question 14.
Define manure. What are its three kinds ? State two limitations of manures. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Manure: It is a partially decomposed organic matter derived from plant and animal wastes which is added to the soil to increase its fertility.
Kinds:
- Compost
- Vermicompost
- Green Manure.
Limitations:
- Bulk: Manure is quite bulky. It cannot be transported over long distances.
- Storage: Manure cannot be stored beyond 1 -2 months.
Question 15.
What are weeds ? Why is removal of weeds essential ? Name any two measures of weed control.
(CCE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
Weeds: Weeds are unwanted plants which grow alongwith cultivated crop plants in the same field.
Why Removal: Removal of weeds during the early stages of growth of crops is essential as it will allow the crop plants to grow and spread properly obtaining all the inputs (which are robbed by the weeds if they are present)
8 under disadvantages: Measures of Weed Control. Mechanical, cultural, chemical and biological method.
Question 16.
What is meant by bee-keeping ? Name
(a) The variety commonly used for commercial honey production,
(b) The variety having high honey collection capacity. State how is pasturage related to honey production. (CCE 2010, 2013)
Answer:
Bee Keeping or Apiculture. It is rearing, care and management of honey bees for obtaining honey, wax and other substances.
(a) Variety Commonly Liked. Apis mettifera. (Italian Bee)
(b) High Honey Collection. Apis mellifem (Italian Bee)
Pasturage. It is area covered by crops and other flowering plants from where honey bee can collect honey. The quantity and quality of honey depends upon pasturage.
Question 17.
Name any three methods of irrigation and briefly describe them. (CCE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
1. Canal system. 2. Wells. 3. Drip and Sprinkle system.
- Canal System. Canals take irrigation water from dams, barrages, lakes and rivers to agricultural lands. For irrigation, a canal divides into branch canals. Each branch canal divides into distributaries with each distributary passing into a group of fields.
- Wells. They can be dug wells or tube wells. Water is
lifted from them by means of various devices. The lifted water is passed to the fields with the help of narrow channels. - Drip and Sprinkler System. Water lifted from tube well is passed to over head pipes for spraying (drip system) or sprinkler system for spraying water over the fields.
Question 18.
What is animal husbandry ? Differentiate between milch and draught animals. What do the following supply to dairy animals :
- Roughage
- Concentrate ?
(CCE2010, 2011, 2013)
Answer:
Animal husbandry is a branch of agriculture that deals with feeding, shelter, health, breeding and utilisation of domestic animals.
Milch animals are the ones which are raised mainly for milk as they are high milk yielders. They generally lack stamina and strength to do strenuous physical work, e.g., Sahiwal, Red Sindhi.
Draught animals are strong and sturdy animals that can undertake strenuous physical work like ploughing and transporting e.g., Halikar, Mahi.
- Roughage. It supplies cellulose rich fibrous diet to the dairy animal.
- Concentrate. It is nutrient rich low fibre component of catde feed.
Question 19.
Define hybridsation. List any two benefits.
(CCE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
Hybridisation is crossing of two different varieties and breeds in order to obtain a progeny that has good traits of both of them.
Benefits. Hybridization is a technique of crop variety improvement for
- Better yield (higher yield, improved quality),
- Disease resistance.
Question 20.
List any three ways by which insect pests attack the plants. (CCE 2010, 2011, 2012)
Answer:
- Chewing/Cutting, e.g., locusts, hoppers, caterpillars, grubs.
- Sucking plant sap, e.g., aphids, plant bugs, leaf hoppers.
- Boring into stem, roots, fruits and seeds, e.g., top borer, shoot borer, pod borer, boll weevil, gràin weevil.
Question 21.
Distinguish between intercropping and mixed cropping with examples. List any two advantages of intercropping over mixed cropping. (CCE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
Difference:

Advantages of Intercropping,
(i) Non-mixing. There is no mixing of the produce of different crops.
(ii) Easier Operations. Fertilizer and pesticide application, sowing and harvesting can be undertaken separately and easily for each crop.
Question 22.
What is green manuring ? List any two green manuring crops and name two macrenutrients provided by green manure. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
Green manuring is the practice of ploughing back young / green crop plants into soil for improving its fertility.
Green Manuring Crops. Guar (Cluster Bean), Sunn Hemp.
Macronutrients in Green Manure. Nitrogen, Phosphorus.
Question 23.
What is crop rotation ? Tabulate two differences between . intercropping and mixed cropping. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
(a) Crop Rotation. It is growing of different crops in a preplanned succession in the same field, e.g., Rice and Wheat ; Maize, Potato, Sugarcane and Pea.
(b)

Question 24.
Explain that livestock production needs to be improved. Why is there necessity of animal husbandry ?
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
With the increase in population and rise in living standards, the demand for milk, eggs, fish, meat and their preparations is growing up continuously. Therefore, there is a constant need to improve livestock production. This is achievable through scientific breeding programme, proper feeding, hygiene, regular grooming and disease control. Improvement, management, utilisation and care of animal livestock is called animal husbandry.
Necessity of Animal Husbandry. Being an important source of food products to humanity, improvement, care, management and utilisation of animal livestock or animal husbandry is necessary.
Question 25.
(a) Define macronutrients and micronutrients.
(b) Pick out two micronutrients : Zinc, Calcium, Iron, Nitrogen, Potassium.
(c) Name three processes in plants which are affected by deficiency of nutrients. (CCE2011, 2012, 2013, 2014)
Answer:
(a) Macronutrients are essential elements required for growth and reproduction of plants which are needed in larger quantities forming more than 1 mg/g of dry matter, e.g., nitrogen, potassium. Micronutrients are essential elements that are needed by plants in minute quantities forming quite less than lmg/g of dry matter.
(b) Micronutrients. Zn, Iron.
(c) Processes Affected by Deficiency,
- Formation of organic molecules like chlorophyll,
- Development of osmotic potential.
- Functioning of enzymes. Inorganic nutrients are. therefore, required in growth, metabolism and reproduction.
Question 26.
(a) Describe any two irrigation systems adopted in India to supply water to agricultural lands.
(b) Write two advantages of building check dams.
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Irrigation Systems.
- Canal System. Canals take irrigation water from dams, barrages, lakes and rivers to agricultural lands. For irrigation, a canal divides into branch canals. Each branch canal divides into distributaries with each distributary passing into a group of fields.
- Wells. They can be dug wells or tube wells. Water is
lifted from them by means of various devices. The lifted water is passed to the fields with the help of narrow channels. - Drip and Sprinkler System. Water lifted from tube well is passed to over head pipes for spraying (drip system) or sprinkler system for spraying water over the fields.
(b) Advantages of Building Check Dams. Check dams are small sediment storage dams built in channels to stabilise channel bed and stop the rain water from flowing away,
- Check dams prevent soil erosion,
- They increase ground water level.
Question 27.
Distinguish between
(a) Inland fishery and marine fishery.
(b) Culture fishery and capture fishery,
(c) Apiculture and aquaculture. – (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
(a) Inland fishery is exploitation of fish resources of inland waters (fresh and brackish waters) while marine fishery is exploitation of fish resources of sea. Inland fishery is mosdy culture fishery while marine fishery is mosdy capture fishery.
(b) Culture fishery is raising of fish in ponds, tanks, sea enclosures, etc. and exploitation of the same. Capture fishery is catching of fish from natural water without seeding them.
(c) Apiculture is rearing of honey bees for obtaining honey and wax. Aquaculture is rearing and harvesting of fish, other animals and plants in water bodies.
Question 28.
Mention the type of Honey Bee you will prefer to rear if you are running an apiary. Give any three reasons for your choice. List any two factors on which the quality of honey depends. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
(a) Like Italian Bee, Apis mellifera.
(b) Reasons:
- Gentleness in nature,
- Good honey collection.
- Prolific queen,
- Less swarming,
- Ability to protect itself from enemies, e.g. Italian Honey Bee (Apis mellifera).
(c) Factors: Quality of honey depends upon
- Pasturage having flowers with nectar and pollen,
- Kind of flowers.
Question 29.
(a) What is the basis of classifying manure ?
(b) What are vernicompost and green manure ?
(c) Name the nutrients which are supplied by green manure to the soil. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Manure is classified on the basis of organic matter used and the process of its formation-farmyard manure, compost, vermicompost and green manure.
(b)
- Vermicompost is a manure rich in worm castings and pulverised organic matter that is prepared by allowing earthworms, (e.g. Drawida willisi) to feed on organic remains.
- Green Manure. It is manure formed in the soil by mulching of young green crop plants ploughed back into soil.
(c) Nitrogen, Phosphorus and minor quantities of other nutrients.
Question 30.
(a) Name the months during which khariff crop is grown
(b) List any four factors for which crop variety improvement is done. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) June to October (rainy season), e.g., Maize, Cotton, Paddy, Soyabeen.
(b)
- Higher yield.
- Improved quality.
- Biotic and abiotic resistance.
- Change in maturity duration.
Question 31.
(a) Give an example of exotic and indigenous breeds of poultry and milch catde.
(b) Name two shell fish. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Poultry. Exotic-Leghorn. Indigenous-Aseel.
Milch Cattle. Exotic—Jersey. Indigenous-Sahiwal.
(b) Shell Fish. Crustaceans (e.g., prawn, crab) and molluscs (e.g. mussels and oysters).
Question 32.
State three preventive and control measures taken for storage of agricultural produce. (CCE 2011, 2014)
Answer:
Preventive Measures.
- Proper cleaning the produce before storage,
- Dry the produce first in sunlight and then in shade.
Control Measures. Fumigation with methyl bromide or other fumigant.
Question 33.
(a) State three ways by which pests attack the plants.
(b) Name the chemical used to control pests,
(c) Explain why excessive use of these chemicals should be avoided.
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a)
- Chewing/Cutting, e.g., locusts, hoppers, caterpillars, grubs.
- Sucking plant sap, e.g., aphids, plant bugs, leaf hoppers.
- Boring into stem, roots, fruits and seeds, e.g., top borer, shoot borer, pod borer, boll weevil, gràin weevil.
(b) The pesticide used is malathion (cutting insects) or dimethoate (sucking insects).
(c) Excessive use of pesticides is harmful as they are toxic to humans, other animals and cause environmental pollution. They also make the crop produce toxic. Distinguish between fertilizers and manures.
Question 34.
Write any two advantages of manures and any two disadvantages of fertilizers. (CCE 2011, 2013)
Answer:
Fertilizers are chemical formulations that are added in small quantities to the soil for providing nutrients to crop plants. Manures are semidecomposed organic matter that are added in large quantity to the soil for enriching the soil with both inorganic nutrients as well as organic matter.
Advantages of Manure,
- Manure increases water holding capacity of soil, even in sandy soils,
- It improves soil aeration as in clay soils,
- It increases activity of soil microorganisms some of which are required for solubilisation of heavy minerals.
Disadvantages of Fertilizers,
- Repeated use of fertilizers tends to change pH of soil, making it acidic or alkaline.
- It destroys soil structure.
- It causes pollution of soil, crop plants, ground water and nearby surface waters.
Question 35.
A farmer wants to store his agriculture produce,
(a) What are the factors that he should check before storing it.
(b) What are the control measures that he should take ?
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a)
- Proper cleaning of the produce,
- Proper drying the produce in sun and shade,
- Disinfection of gunny bags.
(b) Control Measures,
- Cleaning and fumigation of godown.
- Periodic check of stored grains,
- Keeping temperature and humidity under check,
- Spray of insecticides, fungicides or fumigation if required.
Question 36.
Broiler production is indeed a solution to increase the production of nutritious animal protein food. List six factors that need to be considered for broiler production.
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
Broilers are fast growing young chicken of 6-10 weeks age which are known for the good quality and taste of their meat.
Layers are sexually mature hens which are raised for egg laying.
Broilers are given diet rich in protein, with adequate fat, vitamins A and K. They are provided with best of space, hygiene and temperature. Layers are given inferior quality feed. Light is required for good egg laying. Temperature variations may occur to some degree.
Factors,
- Diet rich in protein with adequate fat.
- Vitamin A and K supplement,
- Maintenance of feathering and carcass quality,
- Spacious hygienic rat proof shelter,
- Maintenance of temperature at 34° – 38° C.
- Vaccination against all important diseases.
Question 37.
(a) What are pesticides ?
(b) Why do excessive use of pesticides not advisable ?
(c) Name two preventive measures against pests.
(CCE 2011, 2012, 2013)
Answer:
(a) Pesticides. They are chemicals toxic to pests and eliminate them. Pesticides can be insecticides (against insects), fungicides (against fungi), weedicides (against weeds), rodenticides (against rats), etc.
(b) Excessive Use of Pesticides: Excessive use of pesticides is harmful as they are toxic to humans, other animals and cause environmental pollution. They also make the crop produce toxic. Distinguish between fertilizers and manures.
(c) Preventive Measures,
- Summer ploughing,
- Use of clean seeds.
- Use of resistant varieties.
Question 38.
List six facilities that must be provided to cattle to ensure their good health and production of clean milk.
(CCE 2011, 2013)
Answer:
- Grooming. Regular grooming removes dust, loose hair and external parasites.
- Shelter. It should be clean, dry, well ventilated, spacious with sloping floor and protection from rain.
- Separation of Sick Animals. There should be space to keep the sick animals separate from healthy ones. Provision for proper medical aid is also a must.
- Clean Drinking Water,
- Proper Feed.
- Vaccination against different bacterial and viral diseases.
Question 39.
What are kharif and rabi crops ? Name two kharif and two rabi crops. State two ways of incorporating desired characters in crop plants. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Kharif Crops. They are summer or rainy season crops which grow between June and October, e.g., Maize, Cotton, Paddy, Onion.
Rabi Crops. They are winter or non-rainy season crops which grow between November and April, e.g., Wheat, Gram, Mustard.
Incorporation of Desired Characters. Two ways :
- Hybridisation
- Introduction of specific genes.
Question 40.
(a) List two characteristics each of roughage and concentrate in relation to animal feed. Give one example of each,
(b) Which method is commonly used for improving catde breeds ? (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
(a) Roughage
- High fibre content rich in cellulose.
- Poor content of protein, fat and other nutrients.
Example. Pounded straw, hay, silage, green and dry fodder.
Concentrate,
- It is rich in nutrients — proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals.
- Fibre content is low. Example. Oil cakes, grains, bran.
(b) Improvement of Cattle Breeds: Excessive use of pesticides is harmful as they are toxic to humans, other animals and cause environmental pollution. They also make the crop produce toxic. Distinguish between fertilizers and manures.
Question 41.
(a) Why are manures and fertilizers used in the fields ?
(b) A farmer irrigated his field exessively just after applying fertilizers. Explain why this is not a correct practice.
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Manures and fertilizers are added to fields mainly to replenish minerals which get depleted due to withdrawal by crop plants and leaching down to lower strata of soil.
- Manures add small quantity of all minerals to the soil. They improve soil hydration, soil aeration and activity of soil micro-organisms, some of which are required for solubilisation of heavy minerals.
- Fertilizers are nutrient specific which contain one or more minerals in concentrated form. They meet the immediate and complete mineral requirement of high yielding varieties. However, they harm soil structure and cause pollution of crops, soil, ground water and nearby surface waters. A combination of both manure and fertilizer is highly useful.
(b) Excessive irrgation soon after application of fertilizer will be
- wastage of fertilizer as the same would be either washed away or percolate down into ground without being absorbed by the crop,
- It will lead to water pollution.
Question 42.
Define
(a) Cattle farming
(b) Composting
(c) Organic farming. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
(a) Cattle Farming (Cattle Husbandry). It is raising of cattle for yield of milk by females and draught labour by males.
(b) Composting. It is the process of preparing semidecomposed organic matter derived from all sources like garbage, vegetable waste, animal refuse, domestic waste, sewage sludge, eradicated weeds, etc by placing them in large pits, moistened and covered with thin layer of earth.
(c) Organic Farming. It is the practice of raising unpolluted crops by using only manures, biofertilizers and biopesticides for nutrient enrichment and control of pests and weeds.
Question 43.
Explain the meanings of desirable factors for crop improvement :
(a) Biodc and abiotic resistance
(b) Wider adaptability
(c) Desirable agronomic traits. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Biotic and Abiotic Resistance. It is resistance to living and non-living factors, which tend to decrease crop yield. Biotic Factors. Pathogens (bacterial, fungal, viral), nematodes, insects. Abiotic Factors. Flood, drought, water logging, frost, lodging.
(b) Wider Adaptability. Ability to grow and mature under different climatic, weather and soil conditions. Such plants are insensitive to variations in light duration and temperature.
(c) Desirable Agronomic Traits. They are plant traits which are most suitable to the crop, e.g., dwarfness in cereals, more pods and hence branching in pulses, more foliage branching and soft stems in fodder crops.
Question 44.
(a) What is crop rotation ? How is it different from intercropping ?
(b) What are the two main factors that decide the choice of crop to be cultivated after one harvest.
(CCE 2011, 2013)
Answer:
(a) Crop Rotation: It is growing of different crops in a preplanned succession in the same field, e.g., Rice and Wheat ; Maize, Potato, Sugarcane and Pea.
(b) Differences: In crop rotation only one crop is grown in the field at one time while in intercropping two or more crops are grown at the same time in the same field, of course, in different rows.
Availability of moisture, irrigation facility, soil fertility and season determine the crop to be sown after one harvest.
Question 45.
(a) From where do plants acquire
(i) Nitrogen
(ii) Hydrogen,
(b) Why should fertilizers be applied in proper dose and at proper time ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a)
(i) Nitrogen from nitrate/ammonia/urea of soil.
(ii) Hydrogen from water.
(b) Fertilizers are commercially produced chemical formulations that immediately provide nutrients to crop plants. They should be applied to crops only at that time when they are required. The amount should be just enough that meets the need of crop. Any excess or wrong time application will pollute the soil, crop, ground water and surface water (due to run-off).
Question 46.
(a) What are the food requirements of dairy animals ?
(b) Why do external and internal parasites living on and in the cattle can be fatal ? (CCE 2011, 2013)
Answer:
(a) Food requirement of dairy animals is of two types
- Maintenance requirement for supporting metabolic activity and healthy life,
- Milk producing requirement for supporting and enhancing milk production during lactation period, e.g, feed additives like minerals, vitamins, more protein and fat.
(b) External parasites live on the skin and cause diseases. Internal parasites like worms live within the body and affect stomach and intestine while flukes damage liver. If untreated, the parasites may prove fatal because skin diseases often invite attack of other pathogens, especially of contagions diseases. Similarly, internal parasites not only reduce vitality of the animal themselves but make it more prone to other diseaes that are fatal.
Question 47.
(a) Give two examples of fodder crops raised as food for livestock.
(b) State any two advantages of using manure.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Fodder Plants. Berseem, Sudan Grass, Sorghum.
(b) Uses of Manure. See under Advantages in question 36 above.
Question 48.
(a) Using the symbols given below make a diagrammatic representation of intercropping, Crop A – 0, Crop B-A.
(b) Give two examples of crops selected for intercropping. Mention two benefits that a farmer gets by following this cropping pattern.
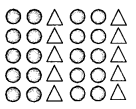
Answer:
(a) Figure of intercropping –
(b) Examples. Soyabean and Maize;
Finger Millet and Cow Pea.
Benefits:
- Optimum Utilisation. It helps in optimum utilization of the soil.
- Reduced Pest Infestation. The chances of pest infestation are reduced because the pest of one crop rarely
Question 49.
Explain how compost is made. What makes it good manure ? What is vermicompost ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Preparation of Compost. Vegetable waste, galbage, sewage sludge, animal refuse, domestic waste, straw, eradicated weeds, etc. are dumped in large pits, moistened and covered by a thin layer of earth. Compost is ready within 3-6 months. Good Manure. Compost is a better manure as it is richer in minerals as compared to farmyard manure (1-4% instead of 0-5% N2O,1.0% instead of 0-2% P2O5, 1-4% instead of 0-5% K2O).
Vermicompost is a manure rich in worm castings and pulverised organic matter that is prepared by allowing earthworms, (e.g. Drawida willisi) to feed on organic remains.
Question 50.
(a) What are the difference between broilers and layers ?
(b) Which exotic breeds of fowl are popular in India ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a)
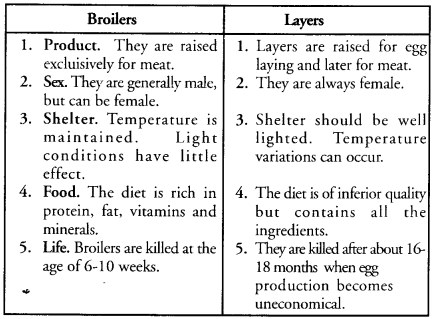
(b) Exotic Breeds Popular in India. White Leghorn, Rhode Island Red, Plymouth, Black Minorca.
Question 51.
There is a water reservoir near the village and a river flows near the village. Due to insufficient rain, farmers are worried about their crops. Suggest and explain the irrigation practice that can be adopted to supply water to entire agriculture land in the village. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Adoption of river lift system. Pumps are used to draw water from the river and pour the water either in the village reservoir or directly to the fields through narrow channels.
Question 52.
Name two exotic and two local breeds of cattle that the students have observed when they visited a livestock farm. List two desirable qualities that you would expect in the progeny when they undergo cross breeding.
(CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
Exotic Breeds. Jersey, Brown Swiss. Local Breeds. Sahiwal, Red Sindhi.
Desirable Qualities in Hybrid Progeny (e.g., Karan Swiss, Frieswal).
- Long lactation period with high milk yield.
- Disease resistance and acdimitisation to local climate.
Question 53.
In what way is green manure different from compost ?
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Green manure is prepared in situ while compost is prepared away from the field.
- Green manure does not contain any contaminant of sewage and other ingredients of composing.
- It is richer in nitrogen as green manure is generally prepared from leguminous plants.
Question 54.
Based on the kind of biological material used, what are the two kinds of manures ? How are they prepared ?
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
The two types of manures based on biological material used are (t) Green manure {it) Nongreen manure. Nongreen manure is of further two kinds, compost and verimicompost.
Green Manure. It is formed inside the soil from 6-8 week old green plants ploughed back into soil. Green manure becomes ready after 1-2 months.
Nongreen Manure. It is manure formed in pits or dumps from organic remains like farm waste, animal excreta, vegetable waste, domestic waste, sewage waste, straw, eradicated weeds, etc. Microbial action for its decomposition is called composting. Earthworms are used to hasten the process of composting when it is called vermicomposting. Manure prepared exclusively from farm refuse is called farmyard manure.
Question 55.
List two products of bee keeping and mention one use of each. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
1. Honey. It is viscous, sweet syrup used as sweetener in confectionary and other items besides helping in digestion, curing dysentery, vomiting, stomach and liver ailments.
2. Bees Wax. It is used in cosmetics, creams and ointments.
Question 56.
(a) Name two factors which bring about loss of food grains during storage. Write one example for each.
(b) List two preventive and control measures that are used before grains are stored for future use.
(CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
(a) (i) Humidity (Abiotic Factor). Higher humidity of godown or higher moisture content of stored grains causes discolouration and breaking due to growth of fungi and bacteria causing rise in temperature.
(à) Insects (Biotic Factor). They eat the grains causing their cutting, powdering and producing holes.
(b) Prevention and Control Measures.
- Cleaning of produce.
- Proper drying, first is sun and then in shade.
- Cleaning and disinfecting the godowns and stores.
- Disinfection of gunny bags and mixing dried grains with pesticides.
Question 57.
Give two examples of crops that yield source of carbohydrate, protein and fat respectively.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
Carbohydrate. Rice, Wheat, Potato.
Protein. Gram, Soyabean, Pea.
Fat. Mustard, Sunflower, Groundnut (also protein).
Question 58.
Write two aims of poultry forming. Name one indigenous and one exotic breeds of hen. (CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
- To increase availability of eggs and meat both of which are cheap source of animal proteins,
- To increasingly convert low fibre food stuff unfit for human consumption into highly nutritions animal protein. Indigenous Breed. Aseel. Exotic Breed. Leghorn.
Question 59.
What is organic farming ? Write its four advantages. (CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
Organic farming is the practice of raising unpolluted crops (free from pesticides and excess salts) through use of manures, biofertilisers and biopesticides.
Advantages:
- There is no pollution of the environment.
- The food is free from chemicals and pesticides.
- The form wastes are recycled,
- It controls weeds and pests naturally through biocontrol measures.
Question 60.
Name the programme which contributed to increased food grain production in our country. What are its highlights? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Green revolution. Highlights.
- Development of high yielding dwarf varieties of wheat (in Mexico) and semidwarf varieties of rice (in Philippines).
- Acclimitisation of these varieties to Indian conditions.
- Mutation breeding of triple dwarf Mexican wheat varieties to Indian liking
- Large scale supply of seeds to farmers,
- Higher inputs like fertilizers, manures and irrigation.
Question 61.
Why should we choose strains of crops with wider adaptability? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
- It will help in sowing the improved variety over wider area.
- Strain with wider adaptability is able to tolerate variations in soil, temperature, moisture and light conditions.
- The strain is insensitive to photoperiods and thermoperiods so that it can be grown in any season.
Question 62.
“The nutritional requirements of broilers are different from those of egg layers”. Mention the three different nutrient requirements. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Broilers require
- Easily digestible clean poultry feed for quick growth,
- The feed should be rich in protein as well as good amount of fat.
- Feed additions rich in vitamins, trace minerals and anticoccidial drug are added.
Question 63.
“Efforts are always made to improve production from agriculture and animal husbandry. Why is it necessary? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
- Rise in Population. Human population is continuously rising. There is always a need to increase yield from agriculture and animal husbandry to feed the extra individuals being added to population.
- Checking Malnutrition. A large section of human population is suffering from malnutrition due to deficient food. Extra food is required to check malnutrition.
- Food Components. Food articles require improvement to provide all the ingredients required by humans (e.g., protein in Rice and Potato) and remove antinutritional chemicals.
Question 64.
“Cross breeding between indigenous breeds and exotic breeds of dairy animals is done on which three desired qualities of animals.” (CCE 2013, 2015)
Answer:
- Higher milk yield in exotic breeds
- Longer lactation period in exotic breeds.
- Acdimitation to local conditions and hardiness or disease resistance in local breeds.
Question 65.
(a) Name a crop which can be grown in combination of fish culture,
(b) Mention the feeding zones of Catla, Rohu, Mrigal and Common Carp. (CCE 2013, 2015)
Answer:
(a) Paddy,
(b) Catla (surface feeder on small animals),
Rohu (middle zone),
Mrigal (bottom feeder on detritus) and
Common Carp (bottom feeder, omnivorous).
Question 66.
List any three management practices while designing a shelter for catde. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
- Space. It should provide proper space to each animal and a small enclosure for sick animals.
- Protection. It should protea the animals from rain, storm, heat, cold and predators.
- Hygiene. There should be proper arrangement for hygienic disposal of urine and excreta like cemented floor with slope, drains and water supply.
Question 67.
“Green revolution” and “white revolution” indicate that our natural resources are getting used more intensively. What can be harmful effea of this ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Intensive use of natural resources is causing degradation of forests, soil and water.
- Ground water has depleted at several places so that arid conditions are spreading due to non-availability of water for irrigation and human use.
- Water bodies and soil have become polluted with chemicals.
- Soil is turning water-logged, saline and infertile.
- Forests have depleted. It is causing flash floods, landslides and soil erosion.
Question 68.
(a) Why is organic farming considered beneficial for crop production ?
(b) Why is it called ecofriendly process ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Organic farming is the practice of raising unpolluted crops (free from pesticides and excess salts) through use of manures, biofertilisers and biopesticides.
Advantages:
- There is no pollution of the environment.
- The food is free from chemicals and pesticides.
- The form wastes are recycled,
- It controls weeds and pests naturally through biocontrol measures.
(b) Ecofriendly Process. Organic farming does not pollute the environment and crop because it does not use chemical fertiizers and pesticides. Rather it utilises the organic remains and cleanse the environment.
Question 69.
Compare the requirements of low cost farming and high cost farming in crop production. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
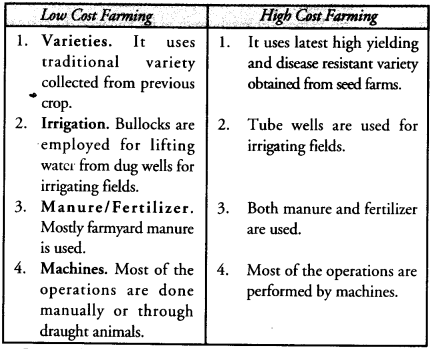
Question 70.
(a) How can poultry farming be integrated with crop production ?
(b) How improved poultry breeds are developed in poultry farming ?
(CCE 2013, 2015, 2016)
Answer:
(a) Farmers have sufficient time and materials to integrate agriculture with poultry (bee keeping and animal husbandry). A lot of agricultural waste can be used as poultry feed so that expenditure on poultry is reduced.
(b) Poultry breeds are improved for smaller size of parents, larger and more eggs, resistance to diseases and better conversion of low fibre organic matter. For this hybridisation is carried out between seleaed breeds and new varieties obtained, e.g., HH-260.
Question 71.
Ravi started poultry farming and brought few poultry fowls. Every year he added more and more poultry fowls. After some time, he observed that health of the birds started deteriorating and their egg production went down. Also very often the birds started suffering from diseases.
(a) Suggest three ways by which he can improve general health of birds.
(b) Suggest one measure to prevent the occurrence of infectious diseases.
(c) What values will Ravi learn if he follows your suggestions. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Proper space, nourishment and hygienic conditions for the fowls.
(b) Vaccination to immunise birds against common infections and diseases.
(c) Values,
- Overcrowded areas are unhealthy.
- Hygienic conditions are essential for healthy living and protection against diseases,
- A well balanced proper diet is essential for good health,
- A proper vaccination is essential for protection against outbreak of diseases.
Question 72.
Excessive use of chemicals such as insecticides and pesticides causes a threat to ecology. Explain with reason.
(CCE 2013)
Answer:
Chemical insecticides and pesticides are biocides which are capable of destroying most of the organisms. They disperse in air, soil and pass into water bodies. They enter the food chains and undergo biomagnification, becoming more and more toxic with rise in trophic level. The result is that most of the biota is harmed. Humans are harmed the maximum because we use all types of foods and from all trophic levels.
Question 73.
Name three Indian varieties of Honey Bee that are used in honey produaion. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Apis cerana indica (Indian Bee). Apis dorsata (Rock Bee), Apis florae (Little Bee).
Question 74.
Kiran is a manager of a poultry farm. What steps will she take to enhance the produaion of eggs ?
(CCE 2013)
Answer:
- Selection of chicken variety which yields higher quantity and good quality eggs for maximum number of days.
- Hygienic condition of shelter with floor covered with dry litter, proper slope, proper illumination and temperature.
- Timely vaccination of birds.
- Proper low fibre feed rich in vitamins, minerals and micronutrients.
- Drinking water.
Question 75.
“Green revolution of 1960s is a boon by itself.” List three steps that may be initiated to increase crop production. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
- Continuous improvement of crop varieties for higher yield, better quality, biotic and abiotic resistance, desirable agronomic traits, etc.
- Proper nutrients in the form of manures and fertilizers
- Proper irrigation
- Protection from weeds and pests.
Question 76.
Karan’s father was practising apiculture with farming . On the advice of Karan, he introduced Italian bee which yields an average of 50-200 kg of honey per year. He encouraged others to adopt the same as he believed that the pasturage there was suitable for bee keeping.
- State two desirable traits of bee varieties suitable for honey production.
- Give the scientific name of Italian bee commonly used for commercial honey production.
- State two values shown by Karan. (CCE 2014, 2016)
Answer:
-
- Gentleness in nature,
- Good honey collection.
- Prolific queen,
- Less swarming,
- Ability to protect itself from enemies, e.g. Italian Honey Bee (Apis mellifera).
- Apis mellifera.
- Every farmer can augment his income by adopting apiculture
- Apiculture helps in better yield of crops pollinated by bees.
Question 77.
Explain intensive fish farming with the help of one example. Write two advantages of this practice.
(CCE 2014)
Answer:
Intensive fish farming is a pisciculture practice which uses high stocking density of fish that take up maximum amount of feed from their environment. Water is replenished at intervals to maintain oxygen level and remove wastes. An example of intensive fish farming is composite fish farming.
Composite Fish Farming: Composite fish culture is a practice of growing 5-6 species , in the same culture pond with different food habits so that there is no competition amongst them, e.g., Catla (surface feeder on small animals). Silver Carp (surface feeder or phytoplankton) Rohu (middle zone), Grass Carp (water weeds), Mrigal (bottom feeder on detritus) and Common Carp (bottom feeder, omnivorous).
Advantages:
- The food available in all zones is fully utilized .
- Yield is high.
Question 78.
Ravi visited his village during vacation of school. He » observed that elders of the village always talked about different cropping systems like mixed cropping, intercropping and crop rotation. But they did not know the scientific reason behind these practices. Ravi explained them the scientific reason so that they could use the practices more gainfully.
(i) What do we call the kind of farming system with minimal or no use of chemical ?
(ii) Write the basis of selection of crops for intercropping
(iii) Village elders appreciated Ravi. Give two possible reasons. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(i) Organic farming
(ii)
- Different nutrient requirement
- Different sowing and harvesting times e.g., Soya Bean and Maize.
(iii) Appreciation,
- Villagers became aware of the utility of different cropping patterns,
- They could understand how to maintain soil fertility and maximise output with minimum inputs.
Question 79.
State the difference between ‘mixed farming’ and ‘mixed cropping’ (CCE 2014)
Answer:
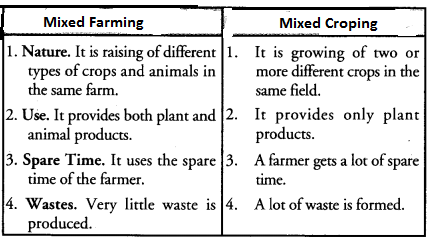
Question 80.
In summer vacation, the students of IX standard were given an investigating project. They were asked to visit a dairy farm and note down their observations. Vinay took information from internet and made the project. Sakshi visited a dairy, saw how and what cattle were fed with and how much milk they gave per day. She also learned about diseases they suffer from and how they are cleaned and taken care of.
(i) To increase the milk production, what kind of feed is given to cattle.
(ii) Write down two symptoms of a sick animal.
(iii) Write two values which Sakshi possesses while Vinay lacks. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(i) Feed additives like minerals, vitamins, more proteins and fats.
(ii)
- The animal looks tired, inactive and tries to remain isolated,
- Urine is often coloured while dung is loose or watery. .
(iii) Values,
- Sakshi went in for knowing the ground reality which is a must for any investigatory project.
- The difference between theoretical and practical parameters are known, (c) With her knowledge of the project Sakshi could suggest improvement in the working of the dairy and care of the animals.
Question 81.
Spraying pesticides and fungicides on stored food grains should be avoided because these chemicals may enter the food chain.
(i) What are fungicides ?
(ii) What can be alternative to fungicides.
(iii) Mention any two advantages of the alternative.
(CCE 2014)
Answer:
(i) Fungicides are chemicals capable of killing and hence curing of fungal infestation.
(ii) Alternative. Fungi flourish in humid hot conditions. It is, therefore, essential that the godown of stored grains should be kept dry, air with low humidity and moderate temperature. Certain chemicals which are harmless to human beings are also . useful, e.g., calcium chloride, thyme oil.
(iii) Advantages:
- Fungal infestation is avoided
- Harmful effect of fungicides is avoided
Question 82.
“Application of fertilizers increases crop productivity but it destroys the soil fertility”. State three disadvantages of using fertilizers. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Use of excess fertilisers will cause :
- Mineral loading of underground water.
- Excess minerals in the crop plants.
- Salination of soil.
- Run off from fertilizers rich soil, will cause eutrophication of water bodies.
Question 83.
Vishnu’s father had two healthy Sahiwal cows. Vishnu told that the lactation period of cows can be increased by cross breeding catde with foreign breeds and also it was possible artificially. In this way if villagers participated in cross breeding, they would have higher milk yield .
- What is meant by lactation period ?
- Name two exotic cattle breeds with long lactation period
- What values are exhibited by Vishnu. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
- Lactation Period. It is period of milk production after birth of a young one lasting generally upto next pregnancy.
- Exotic Breeds with Long Lactation Period. Holstein ffiesian (365 days), Jersey (351 day).
- Values
- Social Responsibility. Vishnu undertook his social responsibility of sharing useful knowledge with his father and other villagers,
- Artificial insemination protects the cattle from infection while making semen available in remote areas,
- Higher and better yield will give farmers more income.
Question 84.
What is necessity of proper cleaning, sanitation and , spraying disinfectants in poultry farms ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Cleaning, sanitation and spraying disinfectants are meant for providing a germ free, healthy, spacious environment to the poultry birds for their proper growth, activity
and functioning. Chances of catching diseases become minimum. Healthy birds are able to convert feed better and more efficiently into body mass and egg laying.
Question 85.
Teacher mentioned about organisms which enrich the soil with nutrients. Rahila was curious to know more about them. So she searched internet and came to know about Rhizobium bacteria and cyanobacteria,
- What are biofertilizers ?
- Explain how any one of the organisms mentioned above enrich the soil with nutrients.
- Write two values shown by Rahila. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
- Biofertilizers. They are microorganisms which enhance the availability of nutrients to the crop plants, e.g., nitrogen fixing bacteria and cyanobacteria, mycorrhiza.
- Rhizobium (a symbiotic bacterium in root nodules of legumes) and cyanobacteria are nitrogen fixing , microorganisms. They pick up gaseous nitrogen from their environment and convert it into ammonia and then amino acids. The fixed nitrogen later becomes available to soil partly or completely. Soil is thus enriched.
- Values,
- Use of biofertilizers will reduce the dependance on chemical fertilizers,
- Biofertilizers are nonpollutant
- Very little cost is involved in their use.
Question 86.
In Raghvan’s village there was a large pond. But he observed that villagers were not rearing fish in it. He gathered villagers and told them that by having selected species of fish they can get good yield of fish. His suggestion helped to eradicate malnutrition in the village.
- State the basis of selecting the different species of fish in this method of fishery,
- Name this method of intensive fish culture,
- What values of Raghvan helped to combat malnutrition in his village ? (Write any two). (CCE 2014)
Answer:
- Basis of Selection. Species which feed at different levels and do not compete with one another as they have different feeding habits.
- Composite fish culture is a practice of growing 5-6 species , in the same culture pond with different food habits so that there is no competition amongst them, e.g., Catla (surface feeder on small animals). Silver Carp (surface feeder or phytoplankton) Rohu (middle zone), Grass Carp (water weeds), Mrigal (bottom feeder on detritus) and Common Carp (bottom feeder, omnivorous).
- Values;
- Raghvan helped villagers to overcome malnutrition as they could get protein rich fish diet almost free,
- He used his knowledge to inculcate sense of cooperation amongst the villagers.
Question 87.
When the grains are harvested the disposal of agricultural byproducts which were unfit for human consumption was a problem. Trilok suggested his father that they should have a poultry farm. Farmers took a collective loan from a government bank to set up the poulty farm.
- What was the advantage of suggestion to set up a poultry farm ?
- Why is poultry farming done ? Give two reasons .
- Write two values of Trilok due to which he was motivated to help villagers. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
- Advantages of Suggestion. Utilisation of agricultural byproducts unfit for human consumption.
- Obtaining, (a) Eggs (b) Meat.
- Values:
- Increasing income of the farmers
- Utilisation of spare time of farmers,
- Preventing rotting of form byproducts unfit for human consumption.
Question 88.
Now-a-days incorporating desirable characters in plants or animals to improve the quality has become essential. Discuss three processes by which this can be facilitated.
Answer:
A number of desirable characters must be incorporated in crop plants and animals for meeting ever increasing human requirement, e.g., higher yield, improved quality, wider adaptation, shorter maturity duration, resistance to adverse abiotic and biotic factors, etc.
This is carried out by
- Hybridisation between selected varieties.
- Incorporation of traits from the wild
- Transfer of genes through DNA recombination technology.
Question 89.
A farmer had a plot just beside the bank of a river. Each time he planted kharif crop, the crop got damaged due to floods. He consulted the agricultural scientist who gave him a special variety of seeds and also advised him to practise fish farming,
(i) What was the speciality of seed grains ?
(ii) What name can be given to this type of fish farming ?
(iii) What is the benefit of mixing crop production with fish farming ?
(CCE 2014, 2015, 2016)
Answer:
(i) Paddy seeds
(ii) Rice-Fish culture,
(iii) It increases the income of the farmer.
Question 90.
Why is organic farming considered beneficial for crop production management ? Why is it called ecofriendly process ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
The conventional foods are raised using chemical fertilizers and chemical pesticides. These agrochemicals pass into conventional foods in small traces. Repeated use of conventional foods increases the concentration of agrochemicals in our bodies. They become toxic. As a result a number of ailments and harms can occur to us.
On the other hand, organic foods are free from any traces ol agrochemicals as they are raised by using manures, biofertilizers and biopesticides. Being nontoxic, organic foods should be preferred over conventional foods. Agrochemicals used in raising conventional foods are highly pollutants. They pollute soil, ground water and surface waters. Eutrophication of ponds and lakes is due to them. Manure used in raising organic foods is environmentally clean method of disposing off and recycling organic wastes.
Question 91.
What are Xanthium, Parthenium and Cyperinus rotundus ? How do they harm the crop production ?
(CCE 2014)
Answer:
They are weeds or unwanted plants which grow alongwith cultivated crop plants in the same field. Harm.
Weeds are unwanted plants which grow alongwith cultivated crop plants in the same field.
Disadvantages:
- Weeds compete with and deprive crop plants of nutrients, water, space and light,
- They often spread crop pests and diseases,
- They down grade the quality of produce.
Question 92.
State the meaning of layers. Why limestone is added in their diet ? Name the other dietary requirement of poultry birds. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Layers. They are female poultry birds which are raised for egg laying.
Limestone. It is added in the feed of layers to provide extra calcium for formation of egg shells.
Other dietary requirement of poultry birds is low fibre nutritions feed having all constituents of food, vitamins, minerals and water.
Question 93.
Define ‘rain water harvesting’ and ‘water shed management’. State one advantage of each.
(CCE 2014)
Answer:
- Rain Water Harvesting: It is use of rain water to either recharge the ground water or filling ponds.
- Water Shed Management: It is increasing percolation of water into ground by building small check dams in areas of run off.
Increased availability of ground water and pond water is used for providing irrigation facility in nonrainy season.
Question 94.
State the conditions essential for production of best quality of honey. Name a product other than honey which is obtained through honey bee keeping. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(i) Pasturage. Quality, taste and quantity of honey depends upon pasturage available for nectar and pollen collection,
(ii) Apiary Location. Number of beehives and distance from pasturage.
(iii) Honey Flow Period. Period when nectar is available,
(iv) Variety of Bee. It should be good collector and shows less swarming. Other Product. Bees wax. It is used in cosmetics, creams and ointments besides special candles.
Question 95.
Malti felt that women of her village need to be liberated so that they can also contribute to the society. Malti told them that they can increase the milk production of the cattle by mating them with species having long lactation period and taking care of the balanced ration of the catde.
- Which method is commonly used for improving cattle breed.
- One of the women asked Malti how it is possible to get their cattle mate with foreign breeds. Suggest how is it done ?
- What values are inculcated by Malti in the women of the village ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
- The common method for improving cattle breed is cross breeding or hybridisation.
- Artificial insemination. Semen from males of high milk yielding and long lactation period is collected and cryopreserved. It is sent throughout the country for artificial insemination of low milk yielding and short lactation period cows.
- Values,
- Self awareness
- Co-operation
- Mutual respect
- Women empowerment.
Name the environmental factors related to cultivation practices and crop yield.
Question 96.
Explain how they are related to crop yield. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Broadly there are two cultivation practices :
(i) Summer season or kharif (June to October) when water, temperature and fight are available in plenty, e.g., Paddy, Maize.
(ii) Winter season or rabi (November to April) when water availability is less, temperature is low and days are shorter, e.g., wheat, mustard. Crop yield is influenced by weather, water and soil conditions.
- Weather. Excess heat, frost and cold reduce the metabolic activities and therefore, yield of the crop. However, optimum temperature and photoperiod as per season and crop help in obtaining good yield.
- Water. Both excess water (water logging) and water scarcity reduce yield. Excess water or water logging reduces soil aeration and hence growth of roots. An optimum water with optimum aeration are required for good crop yield.
- Soil. Most crops require loam soils. However, some plants prefer sandy loams (e.g., Groundnut). Soil salinity, soil acidity and soil alkalinity reduce crop yield.
Question 97.
The practices involved in farming like the choice of seeds for planting, nurturing the crop plants and then protection of growing and harvested crops from loss are important. These all things were known to Guddi’s father but still he was facing a loss in crops. Guddi told him about a new TV channel. ‘Kisan Channel’ by which he was able to understand his problem. A lapse at any stage can have a major effect at the crop yield,
(i) List two useful characteristics of crops for which their hybridisation is done,
(ii) “Removal of weeds from cultivated fields during early stages of crop growth is essential for a good harvest”. Justify the statement.
(iii) How Guddi’s father found the solution of his problem ?
(CCE 2015)
Answer:
(i) Benefits.
- Hybridization is a technique of crop variety improvement for
- Better yield (higher yield, improved quality), (it) Disease resistance.
(ii)
- Removal of weeds during the early stages of growth of crops is essential as it will allow the crop plants to grow and spread properly obtaining all the inputs (which are robbed by the weeds if they are present)
- Destruction of weeds in early stages prevent them to produce seeds and multiply.
(iii) Guddi’s father found that he was not eradicating the weeds from the field. They not only decreased the yield but also deteriorated the quality of produce.
Question 98.
What are the desirable agronomic characteristics for crop improvement ?
Answer:
They are different for different crops.
Cereals should be dwarf but with large ears. Dwarfness makes their stem stronger. They can withstand lodging effect of strong winds. Nutrient requirement is also less. Large ears produce more grains.
Legumes should have more pods which generally develop in relation to stem branching. Therefore, more branching and good foliage increase their productivity.
Fodder crops meant for feeding catde must have profuse branching, good foliage, juicy stems and large size.
Question 99.
What management practices are common in dairy and poultry farming ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
- Proper shelter, its hygiene, aeration and lighting.
- Proper feed and feed additives.
- Proper drinking water.
- Health care including vaccination.
Question 100.
Write three advantages of each inter-cropping and crop rotation. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Advantages of Crop Rotation,
- Incidence of disease, pest infestation and growth of weeds is reduced.
- There is lesser requirement of nitrogen fertilizers,
- It improves soil fertility
- There is optimum use of soil nutrients as different crops remove the same from different layers,
- Yield is improved.
Question 101.
Shekhran was planning to transplant paddy. His son Raman told him that he can have fish along with paddy in the same field. He told him about the species of fish that are able to five in shallow water of paddy fields. His father, shared the information with his friend and both of them adopted this practice.
(i) Name this mode of obtaining fish,
(ii) Which method is used to get pure fish seed ?
(iii) Which values of Raman prompted his father adopt this practice ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(i) Mixed farming, agriculture with culture fishery.
(ii) Induced breeding through hypophysation can give pure seeds of fish.
(iii)
(a) Awareness
(b) Welfare of the family,
(c) Co-operation.
Question 102.
Differentiate between manure and fertilizers. Write any three points of difference. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
| Manure | Fertilizer |
| Nature. Manure is semidecomposed organic matter. | Fertilizer is a chemical formulation. |
| Preparation. It is prepared from natural materials like plant residues and animal residues. | It is synthetic being formed from chemical salts. |
| Mineral Content. It contains only a small quantity of mineral salts. | Fertilizers contain pure mineral salts or their precursors. |
| Specificity. It is not nutrient specific. | It is nutrient specific. |
| Organic Matter. It adds organic matter to the soil. | There is no addition oforganic matter. |
| Quantity. It is required in large quantity. | It is required in small quantity. |
| Nutrient Availability. Nutrient availability is moderate. Nutrients are released slowly. | Fertilizer possesses readily available plant nutrients. |
| Transport. Manure is bulky. It is very difficult to transport it to longer distances. | It has smaller bulk. Fertilizers can, therefore, be transported easily to long distances. |
| Storage. Manure cannot be stored for long. | Fertilizers can be stored for long duration. |
| Soil. It helps in maintaining soil texture, its hydration and aeration. | It can harm soil texture and other soil characters. |
| Excess. Excess manure is not much harmful. | Excess fertilizer is harmful to plants. It also causes pollution. |
Question 103.
India is a country with three fourth of the population engaged in agriculture. Even though financial conditions of some farmers do allow them to take higher level of farming practices and improved agriculture technology, yet they are hesitant to use HYV seeds with traits such as resistance to disease and pests, high quality that would result finally in higher yield. The Government’s ‘Kisan channel’ solved all their apprehensions,
(i) What is meant by genetically modified crop ?
(ii) What are two desired agronomic characters for fodder and cereal crops ?
(iii) In your opinion what should be done so that the modern agriculture technology is adopted by most of farmers ?
(CCE 2015)
Answer:
(i) Genetically modified crops are crop varieties in which genes of other organisms have been incorporated so as to enhance their quality, yield and resistance to various biotic and abiotic stresses,
(ii)
- Fodder Crops. Tall plants, juicy stems, profuse branching and good foliage.
- Cereal Crops. Dwarfness so as ro consume less nutrients and prevent lodging, longer ears.
(iii) Wider publicity of technology, its uses, facilities for purchase and subsidies.
Question 104.
Explain river lift system. Where is this system applicable ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
It is taking up water directly from river with the help of pumps and pouring the same into irrigation channel or canal. It is used in places where ground water is insufficient and canals do not occur. In areas, where the land is at a higher level than the irrigation channels, lift system is also used.
Question 105.
Dunichand was good in studies and his parents wanted him to continue further. When he came to the village during vacation he pursuaded villagers to adopt modern methods of irrigation and genetically modified seeds. And the villagers saw tremendous increase in the yield.
(i) Why the modern methods of irrigation are better than the traditional ones ?
(ii) What is meant by genetically modified seeds ?
(iii) Why Dunichand returned to his village in holidays ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(i) The modern method of irrigation is drip and sprinkler system. It is more natural, saves a lot of water and prevents water logging of soil,
(ii) Genetically modified crops are crop varieties in which genes of other organisms have been incorporated so as to enhance their quality, yield and resistance to various biotic and abiotic stresses.
(iii) Returning to village during vacation is keeping one’s roots intact, meeting and sharing the experiences with the family members and friends.
Question 106.
Define organic farming. Name two cropping system where organic farming is practiced. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Organic farming is the practice of raising unpolluted crops through the use of manures, bio-fertilizers and biopesticides instead of chemical fertilizers and pesticides. Two cropping patterns where organic farming can be practised are crop rotation and intercropping.
Question 107.
Kishore’s mother treated their cattle as their family members. She took care of proper cleaning and shelter facilities, provided balanced ration but despite this one day she observed that one of the cows stopped taking food and did not have normal posture. She was sad and felt guilty. Kishore pacified her and explained to her that it was not her fault,
(i) Mention two possible reasons of illness of cattle,
(ii) State how farm animals can be protected against diseases,
(iii) State two values in Kishore’s mother’s behaviour that should be imbibed by all. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(i) Drinking polluted water during grazing.
Infected grass and other foliage.
(ii) Protection. Regular vaccination and grooming. Protection agianst entry of flies, ticks, mice and rats into
animal shelter.
(iii) Values,
(a) Compassion
(b) Analytical approach.
Question 108.
Mention three advantages of using manures and green manures over the use of fertilizers. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
- Organic Matter. Manure provides a lot of organic matter (like humus) to the soil which increases water retention capacity in sandy soils and drainage as well as aeration in clayey soils. It also improves the physical characteristics of the soil.
- Nutrients. Manure enriches the soil with nutrients.
- Soil Organisms. It provides food for soil organisms like soil friendly bacteria and earthworm. Earthworm helps in making soil porous and making nutrients available to plants.
- By using biological waste materials as a manure, we recycle the wastes and protect our environment from chemicals (fertilizers).
- It contains substances that stimulate plant growth and seed germination.
Question 109.
List the management practices needed for good production of poultry birds. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
- Shed. Poultry shed should be kept clean, dry, well ventilated, well spaced and well illuminated,. Rats and cats should not be able to enter the shed.
- Protection from Pests and Diseases. All the poultry birds should be vaccinated against common diseases, Disinfectants and insecticidal solutions are sprayed at intervals to prevent infestation by pests.
- Temperature, Temperature of the shed is maintained
between 34°—38°C. - Poultry Feed. It should contain all essential constituents of food including vitamins, minerals and clean water.
- Variety. A high yielding quick growing variety should be maintained.
Question 110.
Afzal was taking care of his poultry farm for years now.
His son Abdul visited central Poultry Breeding farm to seek advice on certain improved breeds. When he introduced HH 260 cross breed, the egg and meat production increased,
(i) List four desirable traits for which variety improvement or cross breeding is done
(ii) Why did Abdul obtain information on improved breeds. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
(i)
- High er Yield
- Limited cropping area.
- Improved Quality
- Biotic and Abiotic Resistance
- Change in Maturity Duration
- Desirable Agronomic Traits
- Wider Adaptability.
(ii) Abdul obtained information on improved breeds for increasing yield of poultry, summer adaptation and better immunity with low maintenance.
Question 111.
(a) The desirable agronomic characteristic in cereals is dwarfness of plants. Why ?
(b) Why do farmers prefer to grow crops with shorter maturity duration ?
(c) What are macronutrients ? Name any one macronutrient required by plants that is obtained from soil.
(CCE 2016)
Answer:
(a) Dwarfhess of Cereals. It reduces lodging and requires lesser inputs.
(b) Shorter duration crops are more economical as
- They require lesser inputs (irrigation, nutrients, manure, fertilizer, pesticide),
- The land becomes available for growing another crop.
(c) Macronutrients are essential elements required for growth and reproduction of plants which are needed in larger quantities forming more than 1 mg/g of dry matter, e.g., nitrogen, potassium. Micronutrients are essential elements that are needed by plants in minute quantities forming quite less than lmg/g of dry matter.
Question 112.
While teaching importance of food management, teacher , told her class that due to heavy rains in 2010, tonnes of grains got damaged because sufficient precaution was not taken for storage in government ware houses. Because of this, the prices of commodities went sky high. Shekhar felt very angry with the persons responsible for food storage.
(i) Write two factors that may be responsible for losses to grains during storage,
(ii) Governments decision to let the grains rot in the ware-houses was not right. What do you think should have been done at that time to reduce loss.
(iii) List any two values in the décision making officials that are required to avoid such situations again .(CCE 2016)
Answer:
(i)
(a) Seepage of rain water
(b) Excessive humidity of air
(c) Rotting of grains and infestation by insects, worms and microorganisms.
(ii) The government should have asked the officials to prevent wetting of grains by sealing the godowns, checking use of exhausts, raising the level of gunny bags by placing wooden platforms below them.
(iii) Values:
(a) Regular inspection of the godowns
(b) Efforts to save the grains from spoilage.
(c) Consciousness of their duty.
Question 113.
Bhola and Rajni, who are studying in class IX were travelling in a train. Rajni observed a field with two crops growing simultaneously in a definite pattern. While Bhola was busy in playing with video game, Rajni noticed that rows of Bajra and Lobia were grown in alternate rows. She asked her grand father why Bajra and Lobia are grown together ?
(i) On what basis are the two crops selected in this pattern ?
(ii) How does this practice benefit the farmer ?
(iii) State any two values in Rajni’s behaviour here that differentiate her from Bhola. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
The practice of growing two crops in alternate rows is called intercropping.
(i) Basis. Different nutrient requirements, different sowring and harvesting dates.
(ii) Advantages of Intercropping.
- It ensures higher productivity per unit area,
- Soil erosion is checked as field is seldom left uncovered.
- It saves time and labour of the farmer.
- Sowing and harvesting of different crops can be undertaken separately.
- Curiosity to know what is happening in our surroundings,
(iii) Utilising the spare time in nature study and enhancing knowlege.
Question 114.
Neetu was much distrurbed by reading a report that in 2010 fields of farmers in the Kathua district was hit by a swarm of crop destroying grasshoppers which damaged corn, paddy, fodder and barley crops. The agriculture department supplied pesticide spray at subsidised rate. Since she knew that excessive use of pesticide is harmful to human health and soil fertility, she decided to bring awareness about it amongst villagers,
(i) How do insect pests attack the plants ?
(ii) As chemical, pesticides can be harmful for human health, mention two biopesticides which can be used in their place
(iii) What do you learn from the above situation ? (CCE 2016)
Answer:
(i) Insects attack plants for feeding. (They can be chewing, sucking or borer).
(ii) Neem, pyrethrum.
(iii) We should resort to organic farming where pests are kept under control by their natural predators and use of biopesticides.
Question 115.
Mention two problems of culture fishing. How can they be overcome ? (CCE 2016)
Answer:
Culture fishing is raising of fish in ponds and other water bodies and exploitation of the same. The major problems of culture fishing.
Selection of fish. High yielding fish of 5-6 types which do not compete with one another have to be selected. These fish feed in different strata and on different articles. The phenomenon is called composite fish culture. Obtaining Seeds. In nature, fish breed in particular season (rainy season in inland fishery). To obtain fish seed throughout the year, suitable mates are selected,given injection of ovaprim, ovatide or nova and kept in breeding hapas. The eggs are collected, allowed to hatch, care of hatchlings, fries and fingerlings before introducing into fish ponds.
Question 116.
Ashok read a newspaper report that we in India have had the green revolution which contributed to increased food production, white revolution which led to increased availability of milk and blue revolution to increased fish yield. Yet after 69 years of independence in our country, problem of malnutrition and hunger persists. He was much agitated on reading the report.
(i) What does food security mean ?
(ii) “We should increase the food production without degrading the environment”. Give reasons to support the statement.
(iii) What can Ashok do at the individual level to combat the problem of hunger in our country ? (CCE 2016)
Answer:
(i) Food Security. It is ensuring availability of proper quantity and quality of food to every individuaal of the country. For this the government supplies cereals and pulses to poor persons at highly subsidised rate. Efforts are also afoot to provide employment to most of the people so that they can easily purchase their minimum requirements.
(ii) Nondegtadation of Environment. For increasing food output, more area is brought under agriculture by clearing forests, more canals are dug up, and more fertilizers and pesticides are used. All of these disturb the balance of nature and degrade the environment. Therefore, stress should be laid on genetic improvement of crop plants and adopting sustainable agriculture or organic forming.
(iii) Ashok should form an NGO who would see to it that all poor people get subsidised ration and minimum employment to sustain themselves.
Question 117.
Give the term used for rearing and caring of animal livestock. Explain three major aspects of this practice.
(CCE 2016)
Answer:
Animal husbandry.
Major Aspects. Shelter, vaccination and proper diet.
Good animal husbandry practices keep the animals healthy and more productive. There is higher yield of animal products— milk, eggs, meat.
- Shelter: Diseases spread if the animal shelters are dingy and crowded. If they are spacious, hygienic and well lighted, the animals remain healthy.
- Vaccination: Vaccination of young animals prevents the occurrence of common diseases.
- Segregation of Sick Animals: When sick animals are noticed, they are immediately segregated. Cleanliness drive is undertaken and the remaining animals are given prophylactic doses of medicines to prevent the spread of disease. The livestock remains healthy and productive.
- Proper Diet: A proper optimum diet with feed additives enhances growth and yield of animals.
- Breeding: Breeding for more milk, longer lactation period, more egg laying, better convertibility of food and other good characteristics have allowed various branches of animal husbandry to give better yield.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
(a) What are weeds ? Give an example.
(b) Why should weeds be removed from cultivated fields ?
(c) List five preventive methods that help in weed control. (CCE 2010, 2011, 2012)
Answer:
(a) Weeds. They are unwanted plants which grow alongwith cultivated crop plants in the same field, e.g., Phalaris, Convolvulus, Xanthium, Parthenium.
(b)
Removal of weeds during the early stages of growth of crops is essential as it will allow the crop plants to grow and spread properly obtaining all the inputs (which are robbed by the weeds if they are present)
- Destruction of weeds in early stages prevent them to produce seeds and multiply.
- Some weeds produce toxins.
- During harvesting, weeds get mixed with crop to downgrade its quality.
(c) Preventive Methods. Proper seed bed preparation. 2. Clean cultivation. 3. Summer ploughing. 4. Timely sowing of crops. 5. Crop rotation and inter-cropping.
Question 2.
(a) A former found that Xanthium and Parthenium are also growing alongwith paddy in the field. What are such plants called ? How the presence of these crops affect the crop yield ?
(b) List any four methods for controUing and preventing the growth of such plants. (CCE 2011, 2012, 2016)
Answer:
(a) Weeds. They rob the crop of nutrients, water, space and light. Weeds also spread crop pests and pathogens. Therefore, crop yield is reduced. The quality of crop yield also becomes poor due to the presence of weed seeds.
(b) The four methods of preventing and controlling weeds are mechanical, cultural, chemical and biological
- Mechanical Methods. Removal of weeds as soon as they appear in the field by hand or trowel
- Cultural Methods. Summer ploughing, proper seed bed preparation, timely sowing of crop, inter-cropping and crop rotation.
- Chemical Methods. Spraying weedicides like 2, 4-D, butachlor, atrazine.
- Biological methods. Natural predator of weed, e.g., Mexican Beede for Parthenium.
Question 3.
(a) List the different ways in which biotic and abiotic factors affect stored food grains,
(b) What preventive and controlling measures need to be taken before and after storing the grains ? (CCE 2011, 2016)
Answer:
(a)
- Degradation of quality,
- Loss of weight.
- Discolouration,
- Poor germinability.
- Infestation and contamination.
(b) Preventive Measures,
- Cleaning of produce.
- Proper drying, first is sun and then in shade.
- Cleaning and disinfecting the godowns and stores.
- Disinfection of gunny bags and mixing dried grains with pesticides.
Control Measures,
- Spraying of pesticide over gunny bags,
- Fumigation of godown.
- Systematic management with periodic inspection.
Question 4.
(a) How is culture of Pomphret and Mackeral different from that of Cada and Rohu ?
(b) Give an example each of
- Fresh water prawn
- Marine water prawn. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Pomphret and Mackeral are marine fish which are reared in sea water or mariculture. Catla and Rohu are fresh water fish which are reared in inland fisheries (ponds, canals, rivers, reservoirs).
(b)
- Freash Water Prawn — Macrobrachium rosenbergii
- Water Prawn —Peneaus monodon.
Question 5.
(a) Define animal husbandry. List any three basic aspects covered by animal husbandry,
(b) Mention any two basic requirements of shelter facilities for animals so that their health is not affected,
(c) Give two examples of exotic breeds of cows which are selected for long lactation period. (CCE 2011, 2013),
Answer:
(a)
(i) Animal husbandry is a branch of agriculture that deals with scientific management of animal livestock.
(ii) The basic aspects of animal husbandry are rearing (feeding, shelter and breeding), health care and utilisation of animal livestock.
(b)
(i) The shelter should be clean, dry, well-ventilated, spacious with gentle slope.
(ii) It should protect the animals from rain, heat, cold.
(c) Jersey, Brown Swiss, Holstein-Friesian.
Question 6.
(a) Why is irrigation important for crops ?
(b) Describe in brief any four different kinds of irrigation systems adopted to supply water to agricultural lands. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
(a) Irrigation is the process of supplying water to crop plants as per their requirements through human efforts.
(b) Importance,
(i) Water is made available to crops throughout their development. There is no dependence on rainfall alone,
(ii) It has enabled humans to grow crops throughout the year.
Irrigation Systems:
1. Tanks. They are small reservoirs which store run-off rain.
2. Canal System. It takes water from reservoirs and rivers to agricultural fields by means of distributaries.
3. Wells. They are of two types, dug-wells and tube wells. Lifting devices are used to bring water to the surface for supply to fields.
4. Drip and Sprinkler Systems. Drip system uses overhead pipes while sprinkler system uses a rotating fountain system.
Question 7.
How are cultivation practices and crop yield related to weather ? Describe any three factors for which variety improvement is done.
Answer:
Different crops require different climatic conditions, water regimes, temperature and photoperiods for their growth, maturation and hence yield. Broadly speaking there are two seasons of crop growth, kharif and rabi. Kharif or summer season crops grow between June and October, e.g., Paddy, Maize, Groundnut. Rabi or winter season crops grow between November and April, e.g., Wheat,
Gram, Mustard.
Variety Improvement Factors:
- Improved quality and higher yield,
- Abiotic and biotic resistance,
- Wider adaptability.
Question 8.
(a) What is lactation period. Name two breeds of cattle which are selected for long lactation period. Why are they crossed with local breeds ?
(b) What are roughages and concentrates ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Lactation Period. It is period of milk production after birth of a calf. Higher yield and longer lactation period are preferred traits of dairy animals, e.g., Brown Swiss,
Jersey. The cattle with long and high yield lactation period are exotic breeds which are not acdimitised to our climatic conditions. They are crossed with local breeds to produce hybrids having prolonged lactation, adopted to local environment and resistant to diseases, e.g. Frieswal.
(b) Roughage: It supplies cellulose rich fibrous diet to the dairy animal.
Concentrate: It is nutrient rich low fibre component of catde feed.
Question 9.
(a) A student visited a fish farm where he found Catla, Rohu, Mrigal, Common Carp and Grass Carp cultured in the same pond. Name the type of fish farming observed by the student.
(b) Mention the advantages of such farming system.
(c) What is the main problem in such fish farming ?
How do formers overcome such problem ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Composite fish forming.
(b) Advantages:
- There is no competition and fighting among the fish,
- Food available in all parts of the pond is properly used,
- The yield is high,
(c) Problem.
- Avoiding competition and fighting amongst different types of fish by selecting the ones which have different feeding habits and tolerance to other fish nearby,
- Maintenance of water fertility or food at different levels in the same pond.
Question 10.
(a) How are new varieties of poultry birds with desired traits produced ?
(ib) Mention any four desirable traits for which new varieties are produced.
(c) List the management practices that are common between dairy and poultry farming.
(CCE 2011, 2012, 2013)
Answer:
(a) Varieties with requisite traits are first marked out. They are generally exotic and local or previously improved varieties. Birds of varieties having different desirable traits are crossed, self-bred and back crossed till a new variety with all desired traits is produced.
(b)
- Smaller sized birds with larger sized eggs.
- Ability to utilise more fibrous, cheaper diet using agricultural by products,
- Tolerance to higher temperature or summer adaptation.
- Develop dwarf broiler parents for commercial chick production.
(c)
- Proper shelter, its hygiene, aeration and lighting.
- Proper feed and feed additives.
- Proper drinking water.
- Health care including vaccination.
Question 11.
Explain five different factors for which varietal improvement is carried out by the farmers.
(CCE 2011, 2013, 2015)
Answer:
- Higher Yield. More grains in cereals, more seeds and pods in pulses, more tubers in tuber crops, etc.
- Improved Quality. More desirable characters like good baking and taste is wheat, more protein and vitamins in Rice, protein quality in pulses, more unsaturated oils in oil crops, better storage taste and flavour of fruits, etc.
- Biotic and Abiotic Resistance. Resistance to pests, pathogens, flooding, drought, firost, lodging, etc.
- Wider Adaptability. Development of insensitivity to photoperiods and thermoperiods.
- Desirable Agronomic Traits. Dwarf food plants that consume less nutrients and are resistant to lodging. Large and profuse branching with softer stems are required for fodder plants.
Question 12.
(a) Identify and define the cropping pattern shown in the figure.

(b) On. what basis the selection of different crop as shown in the figure carried out.
(c) List the advantages of growing crops in this pattern. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Intercropping.
(b)
| Mixed cropping | Intercropping |
| Seeds. Seeds of different crops are mixed before sowing. | Seeds of different crops are not mixed. They are sown separately. |
| Pattern. There is no pattern of sowing. | The different crops are sown in separate rows or strips. |
| Target. It minimises the risk of crop failure. | It increases crop productivity per unit area. |
| Fertilizers. Only a common type of fertilizer can be added. | Specific fertilizers can be provided to each crop. |
| Pesticides. Crop sepecific pesticides cannot be sprayed. | Crop specific pesticides can be sprayed without difficulty. |
| Harvesting. Harvesting of early maturing crop provides a lot of difficulty. | There is little difficulty in harvesting individual crops. |
| Produce. There is some mixing of the produce of different crops. | There is no mixing of produce of different crops. |
| Inputs. Lesser inputs of irrigation and nutrients are required. | Requirement of inputs is comparatively more. |
| Ex. Barley/wheat and gram/mustard. | Ex. Soya bean and Maize, Finger Millet and Cow Pea. |
(c)
- Attack by insects and fungi is minimized because different pests are associated with different crops. By varying the crops, the insects and fungi associated with a particular crop usually disappear.
- Rotation of crops helps in weed control. This is because weeds are associated with specific crops. When the crop is changed, the weeds associated with the previous crop usually disappear.
- Rotation of crops improves the fertility of the soil and hence brings about an increase in the production of food grains.
- It saves a lot of nitrogenous fertilizer, because growing leguminous crop during the rotation fixes atmospheric nitrogen with the help of their nitrogen fixing bacteria and there is no need to add nitrogenous fertilizer to the soil.
- The chemical nature of the soil is not altered as different crops require different types of fertilizers.
Question 13.
(a) What is meant by ‘sustainable agriculture’,
(b) Give an example to explain the meaning of integrated farming practice.
(c) List three major groups of activities to be followed to increase the crop yield. (CCE 2011, 2012, 2013)
Answer:
(a) Sustainable Agriculture. It is technique of farming that maximises agriculture yield without disturbing the balance of nature and degrading environment.
(b) Integrated Farming Practice. It is a combination of farming practices that includes raising of crop plants, livestock, poultry, fishery and beekeeping. The practice keeps the farmer busy throughout the year. One procedure supports the other. For example, bees help in pollination. Agriculture waste is used in poultry. Animal
excreta is source of manure and biogas. Manure enriches the crop fields.
(c) Activities for Increasing Crop Yield.
- Development of high yielding varieties (HYV).
- Proper crop production management with proper timely irrigation and nutrient supply while keeping the soil structure intact.
- Crop protection mangement by removing weeds, keeping pests and pathogens under check.
Question 14.
(a) A farmer wants to improve the catde breed for getting higher yield and for resistance to diseases. Name the method he should adopt to get animals of desired qualities. Illustrate it for cows.
(b) Name the two types of food requirements of dairy animals.
(c) Differendate roughage and concentrate in animal food.
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Cross-breeding high milk yielding long lactation period exotic breed animal (e.g., Jersey, Brown Swiss) with disease resistant local bread (e.g. Sahiwal, Red Sindhi). The hybrid (e.g. Frieswal, Karan-Swiss) has the desired traits required by the farmer.
(b) Food requirement of dairy animals is of two types
- Maintenance requirement for supporting metabolic activity and healthy life,
- Milk producing requirement for supporting and enhancing milk production during lactation period, e.g, feed additives like minerals, vitamins, more protein and fat.
(c) Roughage
- Fibre Content. It has high fibre content and is coarse in nature.
- Cellulose. Roughage is largely cellulose in nature.
- Nutrients. Carbohydrate content is good. Other nutrients are poor.
Ex. Hay, pounded straw, green fodder.
Concentrate
- There is less fibre content. Coarseness is also low.
- Cellulose content is low.
- It is rich in carbohydrate, protein, fat, mineral and vitamins.
Ex. Grains, seeds, oil cakes, bran.
Question 15.
(a) Give two types of food requirements of dairy animals.
(b) Mention two forms of animal feed.
(c) State the role of feed additives like micronutrients that are added in the food of dairy animals. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a)
- Maintenance requirement for supporting metabolic activity and healthy life,
- Milk producing requirement for supporting and enhancing milk production during lactation period, e.g, feed additives like minerals, vitamins, more protein and fat.
(b) Forms of Animal Feed. Two, fibre-rich nutrient poor roughage and fibre-poor, nutrient rich concentrate.
(c) Micronutrients. They are required in enhancing , metabolic activity connected with milk prodution and health of animals.
Question 16.
(a) Farmer ‘X’ planted Soya Bean + Maize + Cow Pea in the same field simultaneously in a set row pattern. Farmer ‘Y’ planted cereal crop in one season and leguminous crop is next season on the same piece of land in pre¬planned succession. Name the cropping patterns used by “X’ and ‘Y’.
(b) What are the advantages of different cropping patterns followed by the farmers ‘X’ and ‘Y’ (any four points).
(c) Differentiate between mixed cropping and mixed farming. (CCE 2011, 2013)
Answer:
Farmer’ X. Intercropping. Farmer ‘Y’ Crop rotation.
(b) Advantages of Intercropping.
- It ensures higher productivity per unit area,
- Soil erosion is checked as field is seldom left uncovered.
- It saves time and labour of the farmer.
- Sowing and harvesting of different crops can be undertaken separately.
Advantages of Crop Rotation,
- Incidence of disease, pest infestation and growth of weeds is reduced.
- There is lesser requirement of nitrogen fertilizers,
- It improves soil fertility
- There is optimum use of soil nutrients as different crops remove the same from different layers,
- Yield is improved.
(c) Mixed cropping is growing of two or more crops simultaneously in the same field at the same time. Mixed farming is the practice of raising of livestock as well as growing crops together on the same farm.
Question 17.
(a) Differentiate between broilers and layers including their management. (CCE 2013)
(b) Give an example each for indigenous and exotic breeds of poultry,
(c) What management practices are common in dairy and poultry farming ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Differences.
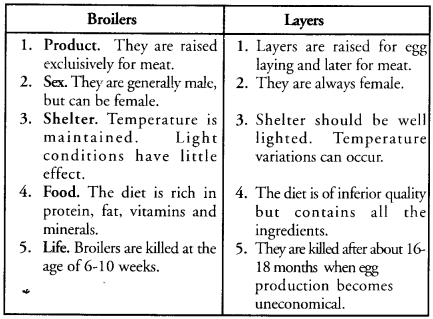
(b) Indigenous. Aseel. Exotic. Leghorn.
(c)
- Proper shelter, its hygiene, aeration and lighting.
- Proper feed and feed additives.
- Proper drinking water.
- Health care including vaccination.
Question 18.
(a) Mention any two desirable agronomic characters for crop improvement,
(b) Explain how farmers get desired characters incorporated into new varieties produced,
(c) List two conditions necessary for the new varieties to be accepted. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Agronomic Characters for Improvement.
(i) Dwarfness in food crops (e.g. cereals) so that they do ‘ not undergo lodging with wind and consume lesser nutrients,
(it) Good height, profuse branching and softer stems in fodder plants.
(b) Incorporation of Desired Characters.
(c) Acceptance of New Varieties by Farmers.
(i) Availability of good quality pure seeds that show simultaneous germination,
(ii) Wider adaptability to weather and soil conditions.
Question 19.
(a) List any two benefits of using fertilizers. What will happen when they are used continuously and excessively ?
(b) What materials are used in organic farming instead of chemical fertilizers ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Benefits of Fertilizers.
- Fertilizers are nutrient specific and readily absorbed so to benefit crop immediately.
- Being chemicals, they are compact, easily stored for long and transported to long distances.
(b) Materials Used in Organic Farming :
- Farmyard manure,
- Compost
- Vermioompost.
- Green manure.
- Biofertilizers like nitrogen fixing bacteria, cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) and mineral solubilising bacteria.
Question 20.
(a) How are cultivation practices and crop yield related to each other ?
(b) Describe any three factors for which variety improvement is done. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Cultivation practices depend upon climate, weather and soil conditions. Plants may require long moderate or short duration of sunlight, low moderate or high temperature, good more or low rainfall, loam clayey or sandy soil. A crop plant with good genetic potentiality will yield maximum if it is provided with optimum cultivation conditions. Early or late sowing will reduce the yield. Apple cannot be grown in plains. Rabi crop cannot be grown in summer. Groundnut yield will be poor in clayey or loam soil.
(b)
- Higher Yield: More grains in cereals, more seeds and pods in pulses, more tubers in tuber crops, etc.
- Improved Quality: More desirable characters like good baking and taste is wheat, more protein and vitamins in Rice, protein quality in pulses, more unsaturated oils in oil crops, better storage taste and flavour of fruits, etc.
- Biotic and Abiotic Resistance: Resistance to pests, pathogens, flooding, drought, firost, lodging, etc.
Question 21.
(a) Mention the different methods of growing crops to get maximum produce. Give one example of each method.
(b) List the characters which are taken into consideration while deciding the choice of crops for each method.
(CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
(a) Different Methods. Crop rotation, intercropping and mixed cropping.
- Crop Rotation: It is growing of different crops in a pre-planned succession in the same field, e.g., Rice and wheat, Maize, Potato Sugarcane and Pea. The choice is based on different requirements, availability of irrigation, nutrients and depth of the root system.
- Inter-cropping: It is growing of two or more crops simultaneously in the same field but in different row patterns. Crops are selected for intercropping on the basis of different nutrient requirement and different sowing and reaping times. eg. Soyabean.
- Mixed cropping: It is the technique of growing two or more different crops together in the same field, e.g., Groundnut and Sunflower.
(b) Characters for Selection of Crops,
- Timing of sowing and harvesting,
- Different depths of root systems,
- Types of crowns,
- Requirement of water.
- Requirment of nutrients,
- Different types of possible pests and pathogens.
Question 22.
(a) Define animal husbandry. Mention any two aspects.
(b) Specify the. two advantages that a farmer is looking
for when he crosses a Jersey cow (exotic breed) with a Sahiwal (local breed).
(c) Explain how parasites attack cattle. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Animal husbandry is branch of agriculture which deals with feeding, shelter, health and breeding of domesticated animals. Aspects,
(i) Proper feeding
(ii) Proper shelter
(iii) Proper breeding
(iv) Proper economic utilisation
(v) Proper health care.
(b) Develop hybrid breed having high yielding long lactation period with acclimitisation to local climate and resistance to common diseases, e.g., Karan Swiss, Frieswal.
(c) Parasites: External parasites live on the skin and cause diseases. Internal parasites like worms live within the body and affect stomach and intestine while flukes damage liver. If untreated, the parasites may prove fatal because skin diseases often invite attack of other pathogens, especially of contagions diseases. Similarly, internal parasites not only reduce vitality of the animal themselves but make it more prone to other diseaes that are fatal.
Question 23.
(a) Name any fresh water resource and one brackish water resource which are important fish reservoirs. Write the names of two scientific methods to detect large schools of fish.
(b) Explain composite fish culture system with example.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a)
- Fresh water ponds and estuaries
- Echosounders and satellite receptors (electronic devices).
(b) Composite fish culture is a practice of growing 5-6 species , in the same culture pond with different food habits so that there is no competition amongst them, e.g., Catla (surface feeder on small animals).
Question 24.
While cross breeding Indian and foreign poultry, list any three desirable traits that can be developed in new variety. List factors due to which health of poultry fowls is affected and also mention two steps to be taken to prevent it. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Desirable Traits: Varieties with requisite traits are first marked out. They are generally exotic and local or previously improved varieties. Birds of varieties having different desirable traits are crossed, self-bred and back crossed till a new variety with all desired traits is produced.
Factors Affecting Ffealth. Poultry feed, proper rat proof shelter, hygienic conditions, maintenance of temperature, proper light for layers, proper space, prevention and control of diseases and pests.
Steps,
- Quick and hygienic disposal of excreta and keeping the shelter bed dry, free from mosquitoes and pests,
- Vaccination.
Question 25.
(a) Mention one indigenous and exotic breed of cow
(b) Explain the food requirements of dairy animals
(c) Write two features of healthy cattle. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Indigenous Breed Sahiwal, Red Sindhi. Exotic Breed. Holstein-Friesian, Brown Swiss.
(b) Food requirement of dairy animals is of two types
- Maintenance requirement for supporting metabolic activity and healthy life,
- Milk producing requirement for supporting and enhancing milk production during lactation period, e.g, feed additives like minerals, vitamins, more protein and fat.
(c) Healthy Cattle.
- Feeds regularly
- Shows normal behaviour and posture.
Question 26.
(a) List six factors for which the variety improvement of crops is aimed at ? Explain two advantages of mixed cropping. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Factors
- Higher yield.
- Improved quality.
- Biotic and abiotic resistance.
- Change in maturity duration.
- Desirable agronomic traits.
- Wider adaptability.
(b) Advantages of Mixed Cropping
- There is no risk of complete crop failure,
- There is optimum utilisation of soil, besides improving its fertility,
- Pest infestation is low.
- Irrigation requirement is lower.
Question 27.
(a) Differentiate between capture fishery and culture fishery,
(b) Explain any two steps that are taken for increasing production in poultry, fisheries and bee keeping,
(c) Name any two Indian bees. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Differences.

(b) Steps for Increased Production
- Poultry: Proper feed, vaccination, improved variety and hygienic shelter
- Fisheries: Composite fish culture, proper natural feed.
- Bee Keeping: Good pasturage and protection from enemies.
(c) Indian Bees. Apis cerana indica (Indian Bee), Apis dorsata (Rock Bee).
Question 28.
(a) Name the process used for developing improved poultry breeds. Give its one example. Write any three desirable traits for which new varieties are developed,
(b) In a pond Catlas, Rohus, Mrigals, Common Carps and Grass Carps are cultured together. What is this system of fish culture called ? Explain its advantages.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Hybridisation of local breeds with exotic breeds, e.g, HH-260. Desirable Traits in Poultry
- Smaller size of birds,
- Increased number and larger size of eggs.
- Resistance to diseases.
(b) Composite Culture. Advantages,
- The different fishes do not compete with one another,
- The food available in all zones of pond is utilised,
- Only natural foods are consumed,
- As a number of fish are reared in the same pond, the yield is very high.
Question 29.
(a) Define composite or intensive fish culture, (b) State the advantage of this system by giving suitable examples.
(c) What is the major problem in composite fish farming ? How is this problem overcome ?
(CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
(a) Composite or Intensive Fish Culture. It is rearing of 5-6 different types of fish in the same pond. The different fish do not compete nor fight with one another as they have different feeding habits,
(b) Advantages:
- Only natural food is taken by the fish,
- The different fish feed at different levels, e.g., Cada (surface feeder on small animals). Silver Carp (surface feeder on phytoplankton). Rohu (middle zone), Grass Carp (feeds on water plants), Mrigal (bottom feeder on detritus) and Common Carp (bottom feeder, omnivorous). It prevents wastage of available water resources.
- The yield is very high.
(c) Major Problem. The fish used in composite culture breed only during monsoon. The seed collected from the wild is mixed with that of other species. The quality is also poor. The problem has been solved by Alikuhni (1957) by developing the technique of induced breeding. By this technique fish can be bred throughout the year. Through selection and hybridisation, the quality of fish has also been improved. For induced breeding fish are given pituitary hormone injections. The process is called hypophysation.
Question 30.
Define fumigation and fumigant. Give an example of fumigant. How does fumigation differ from spraying ? Give two points. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Fumigation. It is method of releasing lethal fumes (gas or smoke) in an enclosed area so as to kill all types of pests and pathogens.
Fumigant. It is a chemical compound which in its gaseous state acts as a pesticide or disinfectant. A fumigant can be solid (e.g,, aluminium phosphide), liquid (e.g., ethylene . dichlorine-carbon tetrachloride) or gas (e.g, methyl bromide).

Question 31.
What are pests ? How can pests be controlled ? In what way biopesticides are better than the chemical pesticides ? (CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
Pests. They are organisms (insects, rodents, nematodes, mites, weeds, pathogens) which cause damage to plants (and animals) and their products.
Control of Plant Pests. Plant pests can be controlled by either using chemical pesticides or biopesticides.
- Chemical Pesticides. They are chemical formulations which are toxic to pests and are used for killing them. Pesticides include insecticides (kill insects), weedicides (kill weeds), fungicides, rodenticides, nematicides, etc. Malathion, lindane and thiodon are sprayed over crops to control stem and leaf cutting insects. Sucking insects are controlled by systemic insecticides like dimethoate and metasystox. Roots are protected from pests by fumigants and insecticides like chloropyriphos.
- Biopesticides. They are biological agents or their products which are used to control pests. Beetle Zygogramma feeds selectively over Parthenium. Baculoviruses parasitise insect pests. Insect pests can also be killed by natural insecticides like azadirachtin and pyrethrum.
Biopesticides Better Than Chemical Pesticides. Chemical pesticides can directly harm us as they are toxic. They are often nonbiodegradable. Chemical pesticides pass into soil, plants and water bodies harming living beings every where. Biopesticides are better as they eliminate the .pests without harming crops, soil, water bodies and * human beings.
Question 32.
(a) “Removal of weeds from the cultivated fields during the early stages of crop growth is essential for good harvest”.
(i) What are weeds ? Give one example,
(ii) List any two reasons due to which it is essential to remove them during early stage of crop growth.
(iii) Mention any two methods by which weed growth can be controlled,
(b) Apart from weeds, mention two other factors that may adversely affect crops and briefly state how these affect crop yield.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a)
(i) Weeds: They are unwanted plants which grow alongwith cultivated crop plants in the same field, e.g., Phalaris, Convolvulus, Xanthium, Parthenium.
(ii) Removal in Early Stage.
- Removal of weeds during the early stages of growth of crops is essential as it will allow the crop plants to grow and spread properly obtaining all the inputs (which are robbed by the weeds if they are present)
- Destruction of weeds in early stages prevent them to produce seeds and multiply.
(iii) Methods:
The four methods of preventing and controlling weeds are mechanical, cultural, chemical and biological
- Mechanical Methods. Removal of weeds as soon as they appear in the field by hand or trowel
- Cultural Methods. Summer ploughing, proper seed bed preparation, timely sowing of crop, inter-cropping and crop rotation.
- Chemical Methods. Spraying weedicides like 2, 4-D, butachlor, atrazine.
- Biological methods. Natural predator of weed, e.g., Mexican Beede for Parthenium.
(b) Other Biotic Factors,
- Insect Pests. They damage and even destroy cultivated crop plants thus reducing quality and quantity of yield e.g., Gundhy Bug (Rice), Shoot Fly (Wheat), Shoot Borer (Sugarcane).
- Plant Pathogens. They cause diseases. The diseases reduce the growth and productivity of crops, e.g., Wheat Rust, Blast of Rice.
Question 33.
(a) Farmer A wants to grow fodder crops while farmer B wants to grow cereals. Mention the agronomic characteristics which the two farmers would desire in their respective crops,
(b) List any four other factors for which variety improvement is done,
(c) Name and define the process of incorporating desirable characteristics into crops. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a)
- Fodder Crops. Tall plants, juicy stems, profuse branching and good foliage.
- Cereal Crops. Dwarfness so as ro consume less nutrients and prevent lodging, longer ears.
(b) Other Factors,
- Higher yield
- Improved quality
- Biotic and abiotic resistance,
- Short duration
- Wider adaptability.
(c) Plant Breeding. Ir is the process of improving heredity of plants in relation to their economic use. Desirable characters can be incorporated into crops through
- Hybridisation
- Mutation breeding and
- DNA recombination technology.
Question 34.
(a) Explain four different kinds of irrigation systems adopted in India to supply water for agriculture.
(b) What is rain water harvesting and water shed management ? How are they useful for enhancing availability of water for agriculture. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Irrigation Systems: Irrigation is the process of supplying water to crop plants as per their requirements through human efforts.
(b)
- Rain Water Harvesting. It is use of rain water to either recharge the ground water or filling ponds.
- Water Shed Management. It is increasing percolation of water into ground by building small check dams in areas of run off.
- Increased availability of ground water and pond water is used for providing irrigation facility in nonrainy season.
Question 35.
How are manures different from fertilizers ? Give one example of each. What is poultry farming ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Manures and Fertilizers.
| Manure | Fertilizer |
| Nature. Manure is semidecomposed organic matter. | Fertilizer is a chemical formulation. |
| Preparation. It is prepared from natural materials like plant residues and animal residues. | It is synthetic being formed from chemical salts. |
| Mineral Content. It contains only a small quantity of mineral salts. | Fertilizers contain pure mineral salts or their precursors. |
| Specificity. It is not nutrient specific. | It is nutrient specific. |
| Organic Matter. It adds organic matter to the soil. | There is no addition oforganic matter. |
| Quantity. It is required in large quantity. | It is required in small quantity. |
| Nutrient Availability. Nutrient availability is moderate. Nutrients are released slowly. | Fertilizer possesses readily available plant nutrients. |
| Transport. Manure is bulky. It is very difficult to transport it to longer distances. | It has smaller bulk. Fertilizers can, therefore, be transported easily to long distances. |
| Storage. Manure cannot be stored for long. | Fertilizers can be stored for long duration. |
| Soil. It helps in maintaining soil texture, its hydration and aeration. | It can harm soil texture and other soil characters. |
| Excess. Excess manure is not much harmful. | Excess fertilizer is harmful to plants. It also causes pollution. |
Example for Fertilizer. Urea, NPK fertilizer.
Poultry Farming. It is rearing of chicken, ducks, turkey and geese for their meat and eggs.
Question 36.
How is variety improvement being done in animals ? What is animal husbandry ? What are its four important steps? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Variety Improvement in Animals. It is carried out through selective mating between animals of different breads like high milk yield and longer loctation period in Jersey and Brown Swiss cattle and disease resistance as well as acelimitisation to local conditions in Red Sindhi and Sahiwal cattle.
Animal Husbandly: Animal husbandry is a branch of agriculture that deals with scientific management of animal livestock.
Four Steps. Grooming, proper shelter, proper feeding and health care.
Question 37.
Define animal husbandary. Discuss feeding, breeding and controlling the diseases of cattle population in dairy farming. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Animal Husbandry: Animal husbandry is a branch of agriculture that deals with scientific management of animal livestock.
Feeding and Breeding of Catde: Cross-breeding high milk yielding long lactation period exotic breed animal (e.g., Jersey, Brown Swiss) with disease resistant local bread (e.g. Sahiwal, Red Sindhi). The hybrid (e.g. Frieswal, Karan-Swiss) has the desired traits required by the farmer.
Controlling Diseases of Cattle:
- Provison of hygienic spacious shelter,
- Separation of sick animals,
- Prompt medical aid to sick animals,
- Vaccination against all important diseases.
Question 38.
(i) State two types of food requirements of dairy animals.
(ii) List the various constituents of food of dairy animals.
(iii) Why do cattle need a balanced diet ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(i) Food requirement of dairy animals is of two types
- Maintenance requirement for supporting metabolic activity and healthy life,
- Milk producing requirement for supporting and enhancing milk production during lactation period, e.g, feed additives like minerals, vitamins, more protein and fat.
(ii) Roughage
- Fibre Content. It has high fibre content and is coarse in nature.
- Cellulose. Roughage is largely cellulose in nature.
- Nutrients. Carbohydrate content is good. Other nutrients are poor.
Ex. Hay, pounded straw, green fodder.
Concentrate
- There is less fibre content. Coarseness is also low.
- Cellulose content is low.
- It is rich in carbohydrate, protein, fat, mineral and vitamins.
Ex. Grains, seeds, oil cakes, bran.
(iii) Balanced Diet. Every component of food is required in proper quantity and proportion for healthy living of cattle, their maximum milk yield and protection from deficiency diseases.
Question 39.
(i) How many nutrients are essential for plants ?
(ii) What are macronutrients and micronutrients ?
(iii) List the nutrients supplied by air, water and soil.
(CCE 2013)
Answer:
(i) 16
(ii)
(a) Macronutrients are essential elements required for growth and reproduction of plants which are needed in larger quantities forming more than 1 mg/g of dry matter, e.g., nitrogen, potassium. Micronutrients are essential elements that are needed by plants in minute quantities forming quite less than lmg/g of dry matter.
(b) Micronutrients: Zn, Iron.
(iiî)
| Source | Nutrient | Type |
| 1 Air
2. Water 3. Soil |
Carbon, Oxygen
Hydrogen (i) Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulphur (ii) Iron, manganese, boron, zinc, copper, molybdenum, chlorine |
Macronutrients
Macronutrient Macronutrients Micronutrients |
Question 40.
(a) Mention the indications found in the grains that are stored in place of inappropriate moisture and temperature. State losses occurring due to these.
(b) State the preventive measures to be taken before the grains are stored for future use. (CCE 2013, 2014)
Answer:
(a) Moisture and temperature increase the respiration of grains, heat them up, reduce their keeping quality, invite microorganisms, fungi and insects to attack them. It causes rotting, discolouration, bad odour, damage to grains, contamination with webs, cocoons, excreta, dead remains and toxins of infesting organisms.
Loss. The infested grains lose their germination, get degraded in quality and become unfit for consumption or germination.
(b) Preventive Measure,
- Drying. The grains should be properly dried and cleaned prior to storage,
- Proper Godown. Godown should be cleaned, disinfected and dried before storing the grains,
- Gunny Bags. The containers and the gunny bags used for storing food grains should be clean, dry and properly funigated.
- Spray and fumigation of godown at intervals.
Question 41.
(a) What are milch and draught animals ? Give an example for each,
(b) Name two components of cattle feed,
(c) Name the method which is commonly used for improving cattle breed. Write name of one exotic breed which is selected. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Milch Animals. Animals where cows are high milk yielders and bullocks are poor draught animals, e.g., Sahiwal, Red Sindhi.
Draught Animals. They are animals where the males are strong and sturdy to carry out tough farming duties like ploughing, drawing water, carting, e.g., Halliker. j The females of draught animals yield less milk.
(b) Components of Cattle Feed. Two, roughage and j concentrate.
a) Roughage
- High fibre content rich in cellulose.
- Poor content of protein, fat and other nutrients.
- Example. Pounded straw, hay, silage, green and dry fodder.
Concentrate,
- It is rich in nutrients — proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals.
- Fibre content is low. Example. Oil cakes, grains, bran.
(c) Improving Cattle Breed: Cross breeding indigenous breeds with exotic breeds. Foreign or exotic breeds have higher milk yield and longer lactation period as compared to indigenous breeds. Therefore, indigenous breeds should be cross¬bred with exotic breeds. The local breeds are hardy and resistant to several diseases. There are two methods of cross breeding — natural and artificial insemination. Artificial insemination is preferred as frozen semen can be transported, required in small quantity and protects the cows from contagious diseases.
Question 42.
(a) List two desirable characteristics for which crop variety improvement is done,
(b) Name the Italian bee variety commonly used for commercial honey production. List its three advantages,
(c) Name and differentiate between two -components of food required by catde. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Higher yield, improved quality, wider adaptability.
(b) Apis mellifera.
- Gentle in nature
- Good honey collection ability,
- Less swarming.
(c) Roughage and concentrate.
Roughage
- Fibre Content. It has high fibre content and is coarse in nature.
- Cellulose. Roughage is largely cellulose in nature.
- Nutrients. Carbohydrate content is good. Other nutrients are poor.
Ex. Hay, pounded straw, green fodder.
Concentrate
- There is less fibre content. Coarseness is also low.
- Cellulose content is low.
- It is rich in carbohydrate, protein, fat, mineral and vitamins.
Ex. Grains, seeds, oil cakes, bran.
Question 43.
(a) Define weed. Give two examples.
(b) Why is it essential to remove weeds from agricultural fields ?
(c) What are weedicides ? (CCE 2013, 2014)
Answer:
(a) Weeds: They are unwanted plants which grow alongwith cultivated crop plants in the same field, e.g., Phalaris, Convolvulus, Xanthium, Parthenium.
(b)
- Removal of weeds during the early stages of growth of crops is essential as it will allow the crop plants to grow and spread properly obtaining all the inputs (which are robbed by the weeds if they are present)
- Destruction of weeds in early stages prevent them to produce seeds and multiply.
- Some weeds produce toxins.
(c) Weedicides. They are chemicals which specifically kill weeds without harming the crop plants, e.g., 2, 4-D, butachlor, atrazine, isoproturon.
Question 44.
“Biotic and abiotic factors both influence the productivity of crops in a particular geographical area”. Illustrate the statement with suitable examples. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Biotic Factors. They are living organisms that reduce crop yield. Biotic factors are pests, pathogens and weeds. Weeds: They are unwanted plants which grow alongwith cultivated crop plants in the same field, e.g., Phalaris, Convolvulus, Xanthium, Parthenium.
Pests. They are small animals which damage cultivated plants, e.g, insects like aphids, hoppers.
Pathogens. A number of fungi, bacteria and viruses attack crop plants and cause diseases, e.g., rust of wheat, blast of Rice, mosaics.
Abiotic factors are non-living components of environment that affect growth of crop plants like excess of water (water-logging), scarcity of water (drought), salinity, heat, cold or frost. Water logging reduces aeration of soil which is harmful to growth and functioning of roots. In drought, water is not available to meet the requirement of the plants for transpiration, growth and photosynthesis. Frost, cold and heat reduce or inhibit metabolic activities and are, therefore, harmful.
Question 45.
Define genetically modified crops. How are they made ? Explain the significance of genetically modified crops with suitable example. (CCE 2014, 2015)
Answer:
Genetically modified crops are varieties that have been formed by taking genes form other organisms . They are also called transgenic crops.
The desired genes are searched. They are removed from their DNA with the help of special enzymes called restriction endonucleases. The genes are either incorporated into vectors like plasmids (e.g.,Ti) of bacteria or artificial chromosomes. They can also be injected directly into nuclei of cells of crop plant. The modified cells are multiplied and then made to develop into plants through tissue culture.
Examples of genetically modified crops are vitamin A rich Golden Rice, protein rich Potato and insect resistant Bt cotton. Bt cotton is grown extensively in India as it does not require costly insecticides to protect
the crop from bollworms.
Question 46.
List major factors for which the crop variety improvement is done. Illustrate any two of them. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
- Higher Yield. More grains in cereals, more seeds and pods in pulses, more tubers in tuber crops, etc.
- Improved Quality. More desirable characters like good baking and taste is wheat, more protein and vitamins in Rice, protein quality in pulses, more unsaturated oils in oil crops, better storage taste and flavour of fruits, etc.
- Biotic and Abiotic Resistance. Resistance to pests, pathogens, flooding, drought, firost, lodging, etc.
- Wider Adaptability. Development of insensitivity to photoperiods and thermoperiods.
- Desirable Agronomic Traits. Dwarf food plants that consume less nutrients and are resistant to lodging. Large and profuse branching with softer stems are required for fodder plants.
Question 47.
Describe the different types of irrigation systems adopted in India to supply water to the fields, (b) Mention the modern initiative undertaken in this respect. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(a) Irrigation Systems: Irrigation is the process of supplying water to crop plants as per their requirements through human efforts.
(b)
- Rain Water Harvesting. It is use of rain water to either recharge the ground water or filling ponds.
- Water Shed Management. It is increasing percolation of water into ground by building small check dams in areas of run off.
- Increased availability of ground water and pond water is used for providing irrigation facility in nonrainy season.
Question 48.
Write descriptive notes on
(i) Mariculture
(ii) Aquaculture
(iii) Inland fisheries. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(i) Mariculture: It is rearing and harvesting of selected fin fishes, shell fishes and sea weeds in special enclosures in sea. The important fin fishes grown in mariculture are mullets, bhetki and pearl spots. Shell fishes include mussels, oysters and pearl oysters.
(ii) Aquaculture: Growing and harvesting of various types of aquatic organisms in water bodies is called aquaculture. It includes fin fish, shell fish,other aquatic animals and plants. Water body can be fresh water, brackish and coastal waters (mariculture).
(iii) Inland Fisheries: They are fisheries found in fresh and brackish waters over land. Fresh water occurs in rivers, canals, reservoirs, lakes and ponds. Brackish water is found in estuaries, lagoons and some lakes. Inland fisheries are again of two types, capture and culture. The yield from capture fisheries is not much. Inland culture fisheries provide more than 60% of our fish yield. Composite fish culture is quite popular amongst farmers.
Question 49.
Mention the basis of crop selection in intercropping and crop rotation. Write the advantages of these two types of cropping patterns. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Inter-cropping: It is growing of two or more crops simultaneously in the same field but in different row patterns. Crops are selected for intercropping on the basis of different nutrient requirement and different sowing and reaping times. eg. Soyabean
Crop Rotation: It is growing of different crops in a pre-planned succession in the same field, e.g., Rice and wheat, Maize, Potato Sugarcane and Pea. The choice is based on different requirements, availability of irrigation, nutrients and depth of the root system.
Advantages of Intercropping:
- It ensures higher productivity per unit area,
- Soil erosion is checked as field is seldom left uncovered.
- It saves time and labour of the farmer.
- Sowing and harvesting of different crops can be undertaken separately.
Advantages of Crop Rotation:
- Incidence of disease, pest infestation and growth of weeds is reduced.
- There is lesser requirement of nitrogen fertilizers,
- It improves soil fertility
- There is optimum use of soil nutrients as different crops remove the same from different layers,
- Yield is improved.
Question 50.
Define crop rotation. How is it done to increase the yield of crops? Why is it called environment friendly ?
(CCE 2014)
Answer:
Rotation of crops is a method of crop production which ensures high yield. Crop rotation is growing of different crops on the same piece of land in a preplanned succession. Crop rotation is done for one year, two year and three year cycle. Crops chosen are such that they withdraw nutrients from different layers of the soil. Crop rotation involving a leguminous crop ensures that the soil gets naturally enriched with nitrogen.
Crop rotation is useful in
- Weed control,
- Reduction in pest infestation,
- Elimination of soil borne diseases,
- Saving of nitrogen fertilizer
- Improving soil structure and fertility,
- Raising of 2-4 crops in a year from the same land giving higher returns to the farmer,
- Yield of individual crops is also higher due to improved soil structure, soil fertility, fewer weeds, fewer insects and diseases.
One Year Rotation : Rice—Wheat, Maize—Mustard
Two Year Rotation : Maize-Potato-Sugarcane-Pea
Three Year Rotation : Rice-Wheat-Mung-Mustard-Sugarcane-Burseem
Environment Friendly. Crop rotation is ecoffiendly as it uses minimum weedicides, pesticides and very little amount of nitrogen fertilizers. It also improves soil structure.
Question 51.
Define weeds. Name two common weeds. Illustrate the different methods of controlling weeds in a crop field.
(CCE 2014)
Answer:
Weeds: They are unwanted plants which grow alongwith cultivated crop plants in the same field, e.g., Phalaris, Convolvulus, Xanthium, Parthenium.
The four methods of preventing and controlling weeds are mechanical, cultural, chemical and biological
- Mechanical Methods. Removal of weeds as soon as they appear in the field by hand or trowel
- Cultural Methods. Summer ploughing, proper seed bed preparation, timely sowing of crop, inter-cropping and crop rotation.
- Chemical Methods. Spraying weedicides like 2, 4-D, butachlor, atrazine.
- Biological methods. Natural predator of weed, e.g., Mexican Beede for Parthenium.
Question 52.
State the purpose for which cattle husbandry is done.
Name the method which is commonly used for improving cattle breeds and why ? Name one exotic and one , indigenous breed of cow with long lactation period.
(CCE 2014)
Answer:
Purpose of Cattle or Animal Husbandry:
Animal husbandry is branch of agriculture which deals with feeding, shelter, health and breeding of domesticated animals. Aspects,
- Proper feeding
- Proper shelter
- Proper breeding
- Proper economic utilisation
- Proper health care.
Methods for Improving Breeds:
Variety Improvement in Animals. It is carried out through selective mating between animals of different breads like high milk yield and longer loctation period in Jersey and Brown Swiss cattle and disease resistance as well as acelimitisation to local conditions in Red Sindhi and Sahiwal cattle.
Long Lactation:
- Exotic Breed. Holstein freiesian — 365 days.
- Indigenous Breed. Sahiwal — 300 days.
Question 53.
In a fresh water composite fish culture, mention the basis of selection of varieties of fishes. Name any four varieties of fishes selected along with their zones. Write one advantage and one problem of composite fish culture. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Basis and Varieties: Composite fish culture is a practice of growing 5-6 species , in the same culture pond with different food habits so that there is no competition amongst them, e.g., Catla (surface feeder on small animals). Silver Carp (surface feeder or phytoplankton) Rohu (middle zone), Grass Carp (water weeds), Mrigal (bottom feeder on detritus) and Common Carp (bottom feeder, omnivorous).
Advantages:
- Only natural food is taken by the fish,
- The different fish feed at different levels, e.g., Cada (surface feeder on small animals). Silver Carp (surface feeder on phytoplankton). Rohu (middle zone), Grass Carp (feeds on water plants), Mrigal (bottom feeder on detritus) and Common Carp (bottom feeder, omnivorous). It prevents wastage of available water resources.
- The yield is very high.
Question 54.
(a) Explain how biotic and abiotic factors influence storage of agricultural produce.
(b) Mention the preventive and control measures used before storing food grains for future use.
(CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Both abiotic and biotic factors damage stored grains.
Abiotic Factors
- Moisture Content of Grains: Moisture content of grains is generally higher than optimum 14%. Higher moisture content of grains increases their respiration, which heats the grains and reduces their keeping quality. Microorganisms, fungi and insects attack such grains.
- Dampness and Humidity of Air: Dampness of godowns and humidity of air cause growth ol moulds over and inside the grains.
- Temperature: Temperature of 30°C and above is harmful to stored grains due to activity of microorganisms, insects, pests and activation of enzymes of the grains.
Biotic Factors
- Rodents: Six rats consume food equivalent to an average human being. They damage 5-6 times more grains by cutting and contamination (by urine, hair and excreta).
- Birds: Birds are often seen in large number around godowns. They are able to puncture bags and eat the stored grains. The birds also contaminate the stored grains with their excreta and feathers. Bird excreta often contains Salmonella, the bacterium causing food poisoning.
- Insects and Worms: Insects and their larvae feed on stored grains either internally (internal feeders like Pulse Beetle, Rice Weevil, Lesser Grain Borer) or externally (external feeders, e.g., Khapra Beetle, Rust Red Flour Beetle). They damage the grains, decrease their quality and cause contamination with webs, cocoons, excreta, dead remains and toxins.
- Microorganisms: Bacteria, yeasts and moulds attack stored grains and cause their rotting. Rotting brings about discolouration, loss of weight, bad odour and aflatoxin contamination of grains which also lose their ability to germinate.
(b) Preventive Measures,
- Cleaning of produce.
- Proper drying, first is sun and then in shade.
- Cleaning and disinfecting the godowns and stores.
- Disinfection of gunny bags and mixing dried grains with pesticides.
Control Measures,
- Spraying of pesticide over gunny bags,
- Fumigation of godown.
- Systematic management with periodic inspection.
Question 55.
(a) What is meant by composite fish culture ?
(b) What is the basis of selecting the different species of fish? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Composite or Intensive Fish Culture. It is rearing of 5-6 different types of fish in the same pond. The different fish do not compete nor fight with one another as they have different feeding habits,
(b) Basis:
- Only natural food is taken by the fish,
- The different fish feed at different levels, e.g., Cada (surface feeder on small animals). Silver Carp (surface feeder on phytoplankton). Rohu (middle zone), Grass Carp (feeds on water plants), Mrigal (bottom feeder on detritus) and Common Carp (bottom feeder, omnivorous). It prevents wastage of available water resources.
- The yield is very high.
(c) Pure Seed: The fish used in composite culture breed only during monsoon. The seed collected from the wild is mixed with that of other species. The quality is also poor. The problem has been solved by Alikuhni (1957) by developing the technique of induced breeding. By this technique fish can be bred throughout the year. Through selection and hybridisation, the quality of fish has also been improved. For induced breeding fish are given pituitary hormone injections. The process is called hypophysation.
Question 56.
(a) Differentiate between roughage and concentrate as components of animal feed,
(b) Explain briefly any three factors for which variety improvement is done in crops. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Roughage
- Fibre Content. It has high fibre content and is coarse in nature.
- Cellulose. Roughage is largely cellulose in nature.
- Nutrients. Carbohydrate content is good. Other nutrients are poor.
Ex. Hay, pounded straw, green fodder.
Concentrate
- There is less fibre content. Coarseness is also low.
- Cellulose content is low.
- It is rich in carbohydrate, protein, fat, mineral and vitamins.
Ex. Grains, seeds, oil cakes, bran.
(b) Factors for Variety Improvement
- Higher yield.
- Improved quality.
- Biotic and abiotic resistance.
- Change in maturity duration.
- Desirable agronomic traits.
- Wider adaptability.
Question 57.
Excessive use of fertilizer and chemical pesticides is harmful-Justify the statement. How can this problem be solved ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Excessive Use of Fertilizers:
- They cause change in soil chemistry making it either too alkaline or too acidic.
- They harm soil micro-organisms.
- Crumb structure of soil is destroyed. It effects both hydration and aeration of soil.
- They cause nutrient enrichment of lakes and other water bodies due to run olf from fields. Eutrophication, water blooms and killing of aquatic animals occur.
- Fertilizers percolate alongwith the gravitational water into ground water causing salt enrichment of the ground water.
- There is excessive salt load in the farm produce.
Excessive Use of Chemical Pesticides:
- They are biocides and kill all types of living organisms including soil microbes.
- Pesticides enter plants and their seeds, causing harm to animals and humans who feed on them.
- They pollute both soil and ground water.
- During run off pesticides reach the water bodies, polluting water, aquatic plants and killing many animals.
- Pesticides enter food chains and cause harm to higher trophic level organisms.
- They directly harm the persons engaged in spraying pesticides.
Remedy. More and more use of manure, biofertilizers and biopesticides, i.e., organic farming.
Question 58.
(a) Write two characteristics of good cattle shelter.
(b) What should be the components of balanced ration for catde ?
(c) Write two symptoms of a sick animal. ( CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Cattle Shelter
- Space. It should provide proper space to each animal and a small enclosure for sick animals.
- Protection. It should protea the animals from rain, storm, heat, cold and predators.
- Hygiene. There should be proper arrangement for hygienic disposal of urine and excreta like cemented floor with slope, drains and water supply.
(b) Balanced Ration. Roughage, concentrate and feed additives (minerals, vitamins, proteins, fat. if lacking in concentrate).
(c) Symptoms of Sick Animals
- Looks tired, inactive and tries to remain isolated,
- Little interest in taking food.
Question 59.
(i) What do you understand by genetically modified crops ?
(ii) What are the desired agronomic characters for fodder and cereal crops ?
(iii) What are the advantages of having improved varieties by hybridisation ? (CCE 2016)
Answer:
(i) Genetically modified crops are varieties that have been formed by taking genes form other organisms . They are also called transgenic crops.
The desired genes are searched. They are removed from their DNA with the help of special enzymes called restriction endonucleases. The genes are either incorporated into vectors like plasmids (e.g.,Ti) of bacteria or artificial chromosomes. They can also be injected directly into nuclei of cells of crop plant. The modified cells are multiplied and then made to develop into plants through tissue culture.
(ii)
- Fodder Crops. Tall plants, juicy stems, profuse branching and good foliage.
- Cereal Crops. Dwarfness so as ro consume less nutrients and prevent lodging, longer ears.
(iii) Benefits: Hybridization is a technique of crop variety improvement for
- Better yield (higher yield, improved quality),
- Disease resistance.
Question 60.
Name three cropping patterns which are ecofriendly and explain them. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
Crop rotation, intercropping and mixed cropping.
- Crop Rotation: It is growing of different crops in a pre-planned succession in the same field, e.g., Rice and wheat, Maize, Potato Sugarcane and Pea. The choice is based on different requirements, availability of irrigation, nutrients and depth of the root system.
- Inter-cropping: It is growing of two or more crops simultaneously in the same field but in different row patterns. Crops are selected for intercropping on the basis of different nutrient requirement and different sowing and reaping times. eg. Soyabean.
- Mixed cropping: It is the technique of growing two or more different crops together in the same field, e.g., Groundnut and Sunflower.
Question 61.
(a) How many plant nutrients are supplied by soil ?
How are these nutrients replenished in the soil ?
(b) What do you mean by green manure ? Which nutrients are supplied to the soil by it ? (CCE 2016)
Answer:
(a) 13 out of 16 chemical elements are supplied by soil. The nutrients are replenished in the soil by addition of manure and fertilizers.
Manures and fertilizers are added to fields mainly to replenish minerals which get depleted due to withdrawal by crop plants and leaching down to lower strata of soil.
- Manures add small quantity of all minerals to the soil. They improve soil hydration, soil aeration and activity of soil micro-organisms, some of which are required for solubilisation of heavy minerals.
- Fertilizers are nutrient specific which contain one or more minerals in concentrated form. They meet the immediate and complete mineral requirement of high yielding varieties. However, they harm soil structure and cause pollution of crops, soil, ground water and nearby surface waters. A combination of both manure and fertilizer is highly useful.
(b) Green Manure: It is manure formed inside soil from young green crop plants ploughed hack into soil. The green manure crops are generally quick growing legume crops which are mulched by ploughing them back into field in tender stage (about 6 — 8 weeks) only, generally at the time of flowering. These crops are completely decomposed in about 1—2 months when the next crop can be sown.
Question 62.
Explain the desirable traits obtained after cross-breeding an indigenous and and exotic breed of poultry birds.
(CCE 2016)
Answer:
- Breeding: The natural method involves the cross-breeding of the indigenous cows with the bulls of high ‘milk yielding foreign breeds by the mating process. This traditional method of breeding is carried out during the high fertility period (or heat) of the cow or buffalo.
- Artificial Insemination (Artificial Breeding): The process of storing semen of a desired male animal and then introducing it into the genital tract of a selected female animal by the use of suitable instruments to produce a better breed of the offspring animals is called artificial insemination. (More than 6000 artificial insemination centres have been established in different parts of our country).
Question 63.
(a) Mention the type of shelters which should be provided to cattle in dairy farming
(b) Mention the preventive measures taken to control diseases of dairy animals,
(c) What are the food requirements of daily animals.
(CCE 2016)
Answer:
(a)
- Space. It should provide proper space to each animal and a small enclosure for sick animals.
- Protection. It should protea the animals from rain, storm, heat, cold and predators.
- Hygiene. There should be proper arrangement for hygienic disposal of urine and excreta like cemented floor with slope, drains and water supply.
(b) Preventive Measures,
- Vaccination,
- Protection from external parasites
- Protection from flies
- Hygienic disposal of excreta
- Regular cleaning.
(c) Food requirement of dairy animals is of two types
- Maintenance requirement for supporting metabolic activity and healthy life,
- Milk producing requirement for supporting and enhancing milk production during lactation period, e.g, feed additives like minerals, vitamins, more protein and fat.
Roughage
- Fibre Content. It has high fibre content and is coarse in nature.
- Cellulose. Roughage is largely cellulose in nature.
- Nutrients. Carbohydrate content is good. Other nutrients are poor.
Ex. Hay, pounded straw, green fodder.
Concentrate
- There is less fibre content. Coarseness is also low.
- Cellulose content is low.
- It is rich in carbohydrate, protein, fat, mineral and vitamins.
Ex. Grains, seeds, oil cakes, bran.
Question 64.
Define hybridisation. Mention three basic types of cross¬breeding practices. Describe any one of them. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
Hybridisation: It is crossing two types of individuals having different types of superior traits in order to obtain offspring (called hybrids) having good traits of both the parents. Hybridisation is also called cross breeding. The three types of cross-breeding are intravarietal, intervarietal and interspecific. In plant breeding intervarietal hybridisation is the common method of variety improvement. It involves
- Choice of Parents. Two older varieities of crop having different desirable characteristics, are selected. For example, if we want to obtain a variety having higher yield as well as disease resistance, we should select two existing varieties of crops, one having higher yield and the other having more resistance to diseases.
- Cross-Breeding the Two Parents. Uncontaminated pollen grains of plants of one variety are dusted over the stigmas of the plants of other variety and vice versa. The offspring are hybrids with good characters of both the parents. However, all the desired traits rarely appear in them. Threrefore, back-crossing with one or the other parent and self fertilization are performed to bring out all the desired traits, preferably in homozygous state.
Hope given Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources are helpful to complete your science homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online science tutoring for you.