Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms Class 9 Science Important Questions with Answers PDF will help you in scoring more marks in your exams.
Diversity in Living Organisms Class 9 Important Questions and Answers Science Chapter 7
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Give technical term : A flowering plant whose embryo possesses a single cotyledon. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Monocot.
More Resources
- Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science
- Value Based Questions in Science for Class 9
- HOTS Questions for Class 9 Science
Question 2.
Name the kingdom: A unicellular eukaryotic aquatic organism. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Protista.
Question 3.
Rewrite the scientific name correctly
- panthera tigris
- Periplaneta Americana. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Panthera tigris
- Periplaneta americana.
Question 4.
Name the term used for
- Left and right halves of the body having the same design
- Animals where tissues develop from three germinal layers. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Bilateral Symmetry
- Triploblastic.
Question 5.
State the phylum to which Centipede, Scorpion and Prawn belong. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Arthropoda.
Question 6.
State the phylum to which Liverfluke and Planaria belong.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
Platyhelminthes.
Question 7.
State the phylum to which Antedon (Feather Star) and Asterias (Star Fish) belong. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Echinodermata.
Question 8.
State the system in poriferans that helps in circulating water throughout the body to bring in food and oxygen.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
Canal system.
Question 9.
What is the common feature between bryophytes and frogs ? (CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
Both are amphibians with bryophytes living in moist cool habitats and frogs living both on land and water.
Question 10.
Shyam knew the correct name of Mango but did not follow the conventions while writing it and wrote it as Mangifera Indica. Rewrite the scientific name as per conventions. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Mangifera indica.
Question 11.
Name the group of plants which produces seeds but not fruits. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Gymnosperms ( = Gymnospermae).
Question 12.
Give reason why blue green algae are classified alongwith bacteria and placed in kingdom monera. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Blue-green algae are prokaryotic like bacteria.
Question 13.
Mention the location and function of notochord.(CCE 2012)
Answer:
It lies dorsally, ventral to nerve cord, and provides attachment to muscles.
Question 14.
Write difference between bryophytes and pteridophytes. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Bryophytes are non-vascular cryptogams with dominant gametophyte while pteridophytes are vascular cryptogams with dominant sporophytic plant body.
Question 15.
Name the kingdom having organisms with holes or pores all over the body. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Animalia (phylum porifera).
Question 16.
How would you call the symbiotic relationship between fungi and certain blue-green algae ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Lichen.
Question 17.
Name an organism whose heart is two-chambered. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Fish.
Question 18.
Explain the term symbiosis. (CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
Symbiosis is mutually beneficial obligatory relationship between two organisms, e.g, lichen.
Question 19.
Name the phylum of animal kingdom to which parasitic worms causing diseases such as filarial worm, round worm belong. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Nemathelminthes.
Question 20.
Name one reptile with four chambered heart. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Crocodile.
Question 21.
Write the scientific name of common frog. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Rana tigrina.
Question 22.
Name animal phylum which exclusively has free living marine animals. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Echinodermata.
Question 23.
Name one mammal that lays eggs. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Echidna.
Question 24.
Write the name of phylum to which Hydra and Sea Anemone belong. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Coelenterata (Cnidaria).
Question 25.
Name the phylum to which Sycon and Euplectella belong.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
Porifera.
Question 26.
Name an organism which is called saprophyte. Why is it called so ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Rhizopus. The organism is called saprophyte because it obtains nourishment from organic remains.
Question 27.
What is the habitat of poriferans ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Aquatic, sedentary, attached to solid substratum, mostly in sea but a few fresh water forms as well.
Question 28.
Which is the lowermost category in the hierarchy of classification of groups of organisms ? (CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
Species.
Question 29.
In the hierarchy of classification
- which grouping will have smallest number of organisms with a maximum number of common characteristics and
- which will have the largest number of organisms. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
- Species
- Kingdom.
Question 30.
Name a division of plants which can be classified as cryptogamae. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Thallophyta/Bryophyta/Pteridophyta.
Question 31.
Write one difference between echinodermata and chordata.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
In echinoderms a notochord is absent while the same is present in chordates.
Question 32.
In which Kingdom would you place an organism which is multicellular and without cell wall ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Animalia.
Question 33.
Write the name of a species belonging to coelenterata which lives in colonies. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Obelia, Coral.
Question 34.
Write the two words that constitute binomial nomenclature.(CCE 2012)
Answer:
Genus (generic name) and species (specific epithet).
Question 35.
To which group in the hierarchy of classification saprophytes belong ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Saprophytes mosdy belong to kingdom fungi.
Question 36.
Name the phylum to which turtle and king cobra belong.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
Chordata ( Class Reptilia).
Question 37.
Name the phylum to which Leech and Earthworm belong.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
Annelida.
Question 38.
Name the phylum to which Octopus and Unio/Pila belong.
(CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
Mollusca.
Question 39.
Write one point of difference between radial and bilateral symmetry. (CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
In radial symmetry body can be divided into two equal halves by any vertical plane passing through central axis while in bilateral symmetry body is divisible into two equal halves by only midsagittal plane.
Question 40.
Mention three animal phyla that possess true coelom. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Annelida, Arthropoda, Chordata.
Question 41.
Identify the given specimen and write its characteristic features. (CCE 2012)

Answer:
Moss (Funaria): It has leaf like and stem-like structures. The plant is a gametophyte bearing rhizoids and dependent sporophyte.
Question 42.
In which kingdom will you place an organism which is single-celled, eukaryotic and photosynthetic ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Protista.
Question 43.
Explain the term angiosperm. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Angiosperms are seed plants in which the seeds are produced inside fruits and the sporophylls are aggregated to form flowers.
Question 44.
Poriferans have holes or pores all over the body that lead to a system that helps in circulating water to bring in food and oxygen. Name the system. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Canal system.
Question 45.
Which division amongst plants has the simplest organisms? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Thallophyta.
Question 46.
Write two points of difference between Protozoa and Porifera. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
- Protozoa are unicellular while Porifera are multicellular.
- Protozoa are moslty motile. Porifera are sedentary in the mature state.
Question 47.
Where are seeds of gymnosperms formed ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
On the megasporophylls found in female cones.
Question 48.
Why is it difficult to classify bacteria ? Give two reasons.
(CCE 2014)
Answer:
- Bacteria are microscopic,
- There are limited differences in structure and functions.
Question 49.
Relate the given plant with its division in the scheme of classification (CCE 2014)

Answer:
Spermatophyta-Angiospermae- Dicotyledoneae.
Question 50.
Name the substance which makes the cell wall of fungi.
(CCE 2014)
Answer:
Chitin (=fungus cellulose), a complex carbohydrate.
Question 51.
What do you understand by diploblastic ? Give one example of an organism which is diploblastic. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Diploblastic are animals having two germinal layers, ectoderm and endoderm, e.g. Sycon.
Question 52.
An amoeba and a worm are very different in their body design. State the basic difference between them.
(CCE 2015)
Answer:
Amoeba is a unicellular organism while worm is a multicellular organism.
Question 53.
Arrange the following groups from lower to higher level : Genus, Class, Division, Family, order. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Genus – Family – Order – Class – Division.
Question 54.
Pick the odd one from the following :
(a) Amoeba, Sponge, Euglena, Frog,
(b) Snail, Slug, Squid, Snake. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Sponge
(b) Snake.
Question 55.
How many chambers do most of the reptiles have in their heart ? Name one reptile which has four chambered heart.
(CCE 2015)
Answer:
Incomplete four chambers. Complete four chambers occur in crocodile.
Question 56.
A pore bearing organism like creature ‘A’ belongs to phylum ‘B’ of kingdom animalia. Identify ‘A’ and ‘B’.(CCE2016)
Answer:
A—Sponge.
B—Porifera.
Question 57.
What are lichens ? (CCE 2017)
Answer:
Licherns are dual organisms which have been formed by permanent symbiotic association between an alga and a fungus.
Question 58.
What is symbiotic relationship ? Give an example.
(CCE 2017)
Answer:
Symbiosis is mutually beneficial obligatory relationship between two organisms, e.g, lichen.
Short Answer Questions (2 marks)
Question 1.
- Write one main characteristic feature that differentiates gymnosperms from angiosperms.
- Give one example each of a gymnosperm and an angiosperm. (CCE 2011, 2013)
Answer:
- Gymnosperms possess naked seeds while angiosperms contain seeds enclosed inside the fruit.
- Example of Gymnosperm. Pinus. Example of Angiosperm. Mango.
Question 2.
(i) Identify the class of animals having the following characteristics features :
(a) Warm blooded animals that lay eggs and have four chambered heart and a covering of feathers.
(b) Cold blooded animals having scales and they breathe through lungs.
(ii) Give an example of an animal belonging to each of these classes. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(i)
(a) Aves
(b) Reptilia
(ii) Example of Aves. Pigeon. Example of Reptilia. Snake.
Question 3.
What are the four main characteristics of chordates ? (CCE 2011,2012,2013, 2014)
Answer:
Presence of
- Notochord which in higher forms is transformed into cranium and vertebral column,
- Dorsal Hollow Nerve Cord. In higher chordates, it is transformed into brain and spinal cord.
- Pharyngeal Gill Slits. Present at some stage of life cycle,
- Post-anal tail.
Question 4.
(a) Give one characteristic difference between primitive and advanced organisms.
(b) Name the phylum to which the following are included :
- Spider
- Cockroach
- Prawn
- Housefly. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Primitive organisms have simple basic body design while advanced organisms have more complex body structure with specialisations.
(b) Arthropoda.
Question 5.
What is binomial nomenclature ? Who introduced it ? (CCE 2011, 2012, 2013)
Answer:
Binomial nomenclature is a scientific system of poviding distinct and proper names to organisms where each name consists of two words, generic and specific epithet. It was introduced by Carolus Linnaeus (1751).
Question 6.
(a) What are the two adaptive features of birds ?
(b) What is the scientific name of Ostrich ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Adaptive Features of Birds,
- Body covered by feathers,
- Fore limbs modified into wings.
(b) Ostrich. Struthio camelus.
Question 7.
(a) List two features which differentiate chordates from non-chordates.
(b) In which phylum will you place the organisms which have
- Calcareous spines on their body,
- Presence of holes or pores all over the body. (CCE 2011 )
Answer:
(a) Chordate Features.
- Occurrence of notochord that is transformed into cranium and vertebral column in higher chordates.
- Presence of dorsal hollow nerve cord above the notochord which in higher chordates is transformed into brain and spinal cord.
(b)
- Echinodermata.
- Porifera.
Question 8.
How do saprophytes get their food ? Give two examples of saprophytes. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Saprophytes are organisms that feed on organic remains by the process of external digestion.
Examples. Mushroom, Rhizopus.
Question 9.
Characters of some organisms are given. Identify their group and give an example of each
(a) Single-celled, eukaryotic and photosynthetic.
(b) The body is divided into segments, may be unisexual or hermaphrodite. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
(a) Protista – diatoms.
(b) Annelida – Nereis, Pheretima.
Question 10.
(a) How many chambers do the heart of fish, amphibians and mammals have ?
(b) Name the classes of vertebrates which lay eggs with shells. (CCE (2011)
Answer:
(a)
- Heart of Fish – Two chambered.
- Heart of Amphibians – Three chambered.
- Heart of Mammals – Four chambered.
(b) Reptilia, Aves.
Question 11.
List the major divisions in kingdom plantae. Write the characteristic features of any one of them. (CCE (2011)
Answer:
Divisions of Kingdom Plantae. Thallophyta, Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, Spermatophyta (Gymnosperms, Angiosperms).
Characteristic Features of Bryophyta.
- Absence of vascular tissues.
- Simple vegetative structure.
- Amphibians.
- Plant body gametophyte.
- Sporophyte parasitic over gametophyte.
- Sex organs are multicellular and’jacketed.
- An embryo stage present in the life cycle.
Question 12.
(a) Explain binomial nomenclature. What are its conventions ?
(b) Name the scientist who has given it.
(c) Write its advantage. (CCE 2011, 2012, 2016)
Answer:
(a) Binomial nomenclature is a scientific system of providing distinct and proper two word name to each and every organism.
Conventions.
- It consists of two words, first generic (like noun) and second specific (species).
- Generic name has first letter capital while specific word begins with small letter.
- Both are derived from latin language or are latinised.
- They are printed in italics or are underlined separately in hand-written form.
(b) Binomial nomenclature was given by Carolus Linnaeus (1751).
(c) Advantage:
- It is universal, being the same in all languages and conntries.
- It is distinct and sepcific with no two organisms having the same name.
Question 13.
Why is there a need for classification and systematic naming of living organisms ? (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
Need for Classification. A good system of classification is required for
- Identification of organisms.
- Study of organisms of other regions.
- Study of whole range of organisms, choosing one or a few from each group.
- Find similarities and dissimilarities, relationships and evolutionary trends.
Need for Systematic Naming. It is scientific naming of groups and subgroups and arranging them in a hierarchy with each taxon having some characteristics of its own.
This helps in locating the position of an organism.
Question 14.
Why bryophytes are called the amphibians of the plant j kingdom? (CCE2011, 2013)
Answer:
Bryophytes are called amphibians of plant kingdom as they live in moist, damp and shady places. A layer of water is required on the soil surface for
- Sexual reproduction.
- Protection from transpiration and hence desiccation
- Supply of water to all parts in the absence of vascular tissues.
Question15.
Some reptiles live in water and yet lay eggs with tough covering unlike the amphibians. Why ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Reptiles evolved over land where hard shelled eggs occur for protecting the embryo surrounded by extra-embryonic membranes. Some reptiles went back into aquatic habitats, However, they did not lose their hard shelled eggs which are usually laid over the banks of water bodies.
Question 16.
(a) Define cryptogams.
(b) Name the division of plant kingdom having amphibian plants. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
(a) Cryptogams. They are seedless lower plants where reproductive organs are inconspicuous requiring an external water for fertilization.
(b) Bryophyta.
Question 17.
Bats can fly. Still they are placed in mammals. Why ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Bats are
- Viviparous giving birth to young ones.
- They possess mammae for feeding the young ones.
- The body is covered by hair.
Question 18.
How are fungi
- Similar and
- dissimilar to plants ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Similarity. Presence of cell wall. Dissimilarity. Presence of chitin in cell wall (instead of cellulose) and glycogen (instead of starch) as reserve food.
Question 19.
How do thallophytes and pteridophytes differ from each other ? Write two differences. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
- Thallophytes are the simplest plants with little differentiation while pteridophytes have a well differentiated body design.
- Reproductive organs are single celled with no embryo stage in thallophytes. In pteridophytes the reproductive organs are multicellular and jacketed with an embryo stage being present in the life cycle.
Question 20.
(a) What is biodiversity ? (CCE 2013)
(b) List three/four features of vertebrates.
(CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
(a) Biodiversity. It is the occurrence of different types of organisms and their variants adapted to different environmental conditions and formation of different types of communities.
(b) Features ofVertebrates.
- Notochord replaced by cranium and vertebral column,
- Dorsal nerve cord transformed into brain and spinal cord.
- Presence of paired gill pouches replaced by lungs in land animals.
- A chambered ventral heart is present.
Question 21.
Give reasons for each of the following :
(a) “Blue-green algae are placed in Monera and not in Plantae”.
(b) “Bryophytes and pteridophytes grow in moist and shady places.” (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Blue-green algae are prokaryotes. They are, therefore, placed in Monera. Plantae includes eukaryotes.
(b) Bryophytes and pteridophytes occur in moist and shady places as they require a film of water over the surface of soil for the liberation and passage of sperms to the archegonia.
Question 22.
(a) Write any two important features that are present in all chordates.
(b) Mention one difference between triploblastic and diploblastic animals. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Chordate Features.
- Occurrence of notochord that is transformed into cranium and vertebral column in higher chordates.
- Presence of dorsal hollow nerve cord above the notochord which in higher chordates is transformed into brain and spinal cord.
(b) Difference Between Triploblastic and Diploblastic Animals. Triploblastic animals have three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm), while diplablastic animals have only two germ layers (ectoderm and endoderm).
Question 23.
Write two peculiar characters of sponges. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
- Occurrence of a canal system and two types of pores.
- Presence of flagellated collar cells or choanocytes.
Question 24.
(a) Give one difference between lizards and snakes.
(b) Name the type of nutrition in fungi. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Lizards have limbs and fixed jaw with limited gape while snakes are limbless with movable jaws for wide gape.
(b) Fungi have heterotrophic absorptive nutrition (saprophytic, parastic).
Question 25.
How can we say that Sea Horse is a fish while Jelly Fish is not a fish but a coelenterate ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Jelly Fish (Aurelia) is a diploblastic animal with tissue level organisation, a single opening and tentacles with nematoblasts like coelenterates.
Sea Horse (Hippocampus) possesses fins and gills covered by operculum like other bony fishes.
Question 26.
- Which group of plants is known as flowering plants ?
- On the basis of seed, how a maize plant is different from a pea plant ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
- Angiosperms (angiospermae).
- Seed of Maize has a single cotyledon (monocotyledoneae) while the seed of Pea has two cotyledons (dicotyledoneae).
Question 27.
(a) What are saprophytes ?
(b) Name the kingdom to which they belong.
(c) What is the cell wall of fungi made of ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Saprophytes. They are organisms that feed on dead or decaying organic matter by first secreting digestive enzymes and then absorbing the digested materials.
(b) Kingdom. Fungi.
(c) Cell Wall of Fungi. It is made up of aminosugar polymer called chitin or fungus cellulose.
Question 28.
(a) Identify the class of the following organism having following features,
- Slimy skin and three chambered heart.
- Covering of feathers and four chambered heart.
(b) List two important characteristics of phylum Nematoda.
(CCE 2011, 2013)
Answer:
(a)
- Amphibian (e.g. Frog)
- Bird (e.g. Pigeon).
(b) Nematoda.
- Cylindrical body with bilateral symmetry
- Triploblastic nature with pseudocoelom, digestive system with mouth and anus.
Question 29.
Give any two reasons why mosses are found in moist and humid places. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
- Mosses are prone to get dried up because of the absence of cuticle over their surface. Water can be absorbed by the whole surface.
- Sperms require a thin layer of water on the soil to reach the opened archegonia.
Question 30.
Write the names of parts A, B, C and D. (CCE 2011)
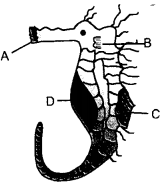
Answer:
A – Mouth.
B – Pectoral fin.
C – Dorsal fin.
D – Brood pouch.
Question 31.
What are gymnosperms ? Give two characteristics. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Gymnosperms are phanerogams which possess exposed (naked) seeds and where the sporophylls are aggregated to form cones.
- Sporophylls are aggregated to form separate male and female cones.
- Seeds do not occur inside fruits but develop exposed over the surface of megasporophylls.
Question 32.
(a) State two characterisics of nematodes.
(b) Identify the phylum with the help of following feactures :
- Spiny-skinned, radial symmetrical and have tube feet,
- Triploblastic, worm-like having segmented body (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a)
- Cylindrical body with bilateral symmetry
- Triploblastic nature with pseudocoelom, digestive system with mouth and anus.
(b)
- Echinodermata
- Annelida.
Question 33.
Who proposed the five kingdom classification ? What is the basis of this classification ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Whittaker (1969). Four criteria have been used for grouping of organisms into five kingdoms—
- Procaryotic and eukaryotic nature
- Unicellular and multicellular nature
- Nutrition
Question 34.
Label X and Y in the given diagram. (CCE 2011)
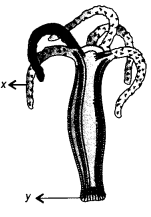
Answer:
X — Stinging cell,
Y — Foot.
Question 35.
Write the major features of fungi (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
- The body called mycelium is made of achlorophyllous threads.
- Cell wall contains chitin.
- Nutrition is heterotrophic and absorptive,
- Reserve food is glycogen and oil.
Question 36.
Enlist four main features of organisms placed in protista.
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
- Unicellular or colonial, mostly aquatic, constituting plankton.
- Eukaryotic organisation with nucleus and membrane bound cell organelles.
- Locomotion present in many with the help of cilia, j flagella and pseudopodia.
- Both asexual and sexual reproduction present. Sexual reproduction without an embryo stage.
Question 37.
Give four main features of phylum coelenterata.
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
- Diploblastic animals with tissue level organisation.
- Body has a single opening for both feeding and elimination.
- Tentacles with cnidoblasts or nematoblasts.
- Nerve cells present but nerve plexus absent.
Question 38.
Give one example of each of
(a) Reptile which has four chambered heart
(b) Egg laying mammal
(c) Parasitic platyhelminthes
(d) Division among plants which has the simplest organisms. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Crocodile
(b) Platypus
(c) Liver-fluke
(d) Uhthrix (thallophyta-algae).
Question 39.
Identify the phylum for the following characteristics given :
(a) Organisms with jointed appendages
(b) Organisms are generally flat worms
(c) Body is segmented
(d) Skin of organisms is full of spines. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Arthropoda
(b) Platyhelminthes
(c) Annelida
(d) Echinodermata.
Question 40.
Write any two characteristics of class mammalia.Name one egg laying mammal. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
- Presence of mammary glands in females
- Presence of body hair.
Egg Laying Mammal. Platypus, Echidna.
Question 41.
An animal is dorsoventrally flattened, has three embryonic germ layers and is acoelomate.
To which phylum does it belong ? What are they commonly called ? Give one example. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Phylum. Platyhelminthes. Common Name Flatworms. Example. Planaria.
Question 42.
Write the name used for the following :
(a) Plants which bear naked seeds
(b) Animals which have pseudocoelom
(c) Animals which maintain a certain body temperature over a wide range of temperature in the environment.
(CCE 2012, 2015)
Answer:
(a) Gymnosperms
(b) Pseudocoelomates-Nemathelminthes
(c) Homoiotherms or warm blooded.
Question 43.
What is parasite ? Give two examples. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Parasite is an organism which obtains its food from a living organism of another species called host. Examples. Fasciola (Liver Fluke), Ascaris (Common Roundworm).
Question 44.
(a) State the number of chambers in the heart of
- Fishes
- Frogs,
(b) Define
- Triploblastic and
- Bilateral Symmetry. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a)
- 2 chambers
- 3 chambers,
(b)
- Triploblastic: Animals having three germinal layers—ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, viz., platyhelminthes to chordates.
- Bilateral Symmetry: It is a symmetry in which organs are paired with each one of the pair lying on right and left sides of the body, e.g., chordates, arthropods.
Question 45.
- Cat, Platypus and Man are all mammals. Yet one of the most unique feature of mammals when considered helps to divide them’ into two groups. What is that feature ?
- Mention two other characteristic features which are common to all the three animals. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Vivipary: Platypus is egg laying mammal while the other two give birth to young ones,
- Presence of hair over the body
- Occurrence of mammary glands in females.
Question 46.
Fungi have cell wall but still they cannot be classified under kingdom plantae. Give two reasons. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Cell wall of fungi contains chitin while in plantae it has cellulose. Further, the reserve carbohydrate food is glycogen in fungi and starch in plantae. Fungi are heterotrophic while most plants are autotrophic.
Question 47.
List two reasons why whales are not grouped with fishes ?
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
Whales are mammals which have
- Four chambered heart, pulmonary respiration and a diaphragm while fishes have two chambered heart, gill respiration and no diaphragm.
- Whales are warm blooded with mammary glands in females. Fishes are cold blooded. Mammary glands do not occur in them.
Question 48.
Jelly fish and Star Fish are not true fishes. To which group do they belong ? Give one characteristic features of each to say they belong to the respective groups. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Jelly Fish: Coelenterata—diploblastic with cnidoblasts. Star Fish. Echinodermata—Spiny skinned with tube feet.
Question 49.
Write four characters of monerans. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Prokaryotic Nature. The genetic material is a single double stranded DNA coiled in the cytoplasm to form nucleoid. A nuclear mambrane is absent.
- Cell Organelles. Membrane covered cell organelles are absent.
- Flagella. If present, they are single stranded.
- Cell Wall. It is made of murein or peptidoglycan.
Question 50.
Give three features of butterfly to justify its classification in phylum arthropoda. Mention one more animal of the same phylum.
Answer:
- Chitinous exoskeleton,
- Jointed appendages
- Open circulatory System.
Other Example. Prawn.
Question 51.
Some fungal species live in permanent mutually dependent relationship with blue-green algae. Name the relationship. Mention where these forms are grown and what they are called ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Symbiosis or mutualism. The dual organisms grow on rocks and tree trunks. They are called lichens.
Question 52.
Write one point of difference between bony fish and cartilaginous fish with one example of each. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
A bony fish has a bony endoskeleton with terminal mouth ‘‘find gill slits covered by operculum, e.g., Labeo. A cartilaginous fish has cartilaginous endoskeleton with ventral mouth and uncovered gill slits, e.g., Scoliodon.
Question 53.
Classify the following fishes as cartilaginous or bony,
- Sting Ray
- Scoliodon (Dog Fish)
- Labeo rohita (Rohu)
- Caulophrynejordani (Angler Fish). (CCE2012)
Answer:
- String Ray. Cartilaginous,
- Scoliodon. Cartilaginous.
- Labeo rohita. Bony,
- Caulophryne jordani. Bony. Cell wall of fungi is made of chitin.
Question 54.
- What is chemical nature of chitin ?
- What is the mode of nutrition in fungi ? (CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
- Chitin is polysaccharide made of N-acetyl glucosamine monomers,
- Absorptive heterotrophic.
Question 55.
Identify the class of animals having following characteristic
(a) Warm blooded having four chambered heart and modified fore limbs for flight,
(b) Organisms having mucous glands in the skin, lack scales, respire either through gills or lungs. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Aves
(b) Amphibia.
Question 56.
Select the odd one with respect to classification. Also give reason for your choice,
(a) Mango, Gram, Rice, Apple.
(b) Prawn, Scorpion, Octopus, Butterfly. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Rice: Rice is monocot while others are dicots,
(b) Octopus: Octopus belongs to mollusca while all others are arthrophods.
Question 57.
How do amphibians respire and reproduce ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Respiration: Amphibians respire through lungs, skin and in many cases gills.
Reproduction: Sexes are separate. Fertilization is external.
Question 58.
Name the phylum to which the following belong.
(a) Silver Fish
(b) Sea Horse,
(c) Star Fish
(d) Jelly Fish. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Silver Fish. Arthropoda.
(b) Sea Horse. Chordata.
(c) Star Fish. Echinodermata.
(d) Jelly Fish. Coelenterata.
Question 59.
Name the four categories used in hierarchical classification of organism. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Kingdom, Division/Phylum, Class, Order.
Question 60.
Write three distinguishing features of phylum echinodermata. Give one example. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Features
- Skin is spiny,
- A water vascular system connected with tube feet is present for helping in locomotion and respiration.
- Symmetry is radial in adults and bilateral in larva. Example. Asterias (Star Fish).
Question 61.
The scientific name for tiger is Pantbera tigris. What does Panthera and tigris represent in binomial nomenclature. Name the scientist who introduced this system of scientific naming of organisms. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Panthera: Genus or generic name, tigris. Species or specific epithet,
- Carolus Linnaeus.
Question 62.
Identify the group :
(a) Animals without tissues, body bearing pores.
(b) Plant body differentiated into roots, stems and leaves but do not produce seeds,
(c) Body dorsoventrally flattened without coelom,
(d) Segmented worms with the body cavity with extensive organ differentiation.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Porifera
(b) Pteridophyta
(c) Platyhelminthes
(d) Annelida.
Question 63.
State the type of body cavity found in platyhelminthes. Write whether they are parasitic or free living. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Parenchymatous body cavity is present but coelom is absent. Both free living (e.g., Planaria) and parasitic (e.g., Fasciola) forms occur in platyhelminthes.
Question 64.
Echinoderms have a system that they use for moving around. Name the system. What is their skeleton made of ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Water vascular or ambulacral system.
- Calcareous plates.
Question 65.
List any two similarities and two differences between Amoeba ‘ and Paramoecium. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Similarities :
- Unicellular nature
- Eukaryotic nature.
- Presence of contractile vacuoles.
Differences :
- Amoeba possesses pseudopodia while Paramoecium has cilia.
- Amoeba has a single nucleus. Paramoecium has two nuclei.
Question 66.
(a) What is scientific name of humans ?
(b) Find the odd one out of Riccia, Funaria, Fern, Marchanda. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Homo sapiens
(b) Fern: It is a pteridophyte while others are bryophytes.
Question 67.
Given below are two groups of organisms belonging to kingdom Animalia.
Write the name of phylum to which they belong.
(a) Octopus, Pita, Unio
(b) Centipede, Prawn, Scorpion.
(CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Mollusca
(b) Arthropoda.
Question 68.
Write two differences between pteridophyte and phanerogam. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
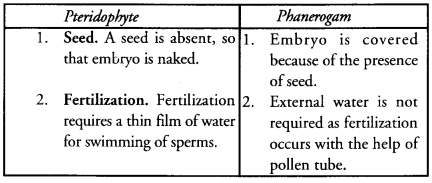
Question 69.
Name the phyla to which the following animals belong :
(a) Star Fish
(b) Leech. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Star Fish-Echinodermata
(b) Leech-Annelida.
Question 70.
Identify the organisms :
(a) A unicellular organism that uses flagella for moving around
(b) An organism that uses pseudopodia for moving around. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Flagella-Euglena
(b) Pisedopodia-Amoeba.
Question 71.
We start classification of plants on the basis of differentiation of plant body,
- Which division lacks a well differentiated body design ?
- Where are such plants predominantly found ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
- Thallophyta – algae,
- Occurrence. Aquatic (both fresh and marine).
Question 72.
Give two features of Cockroach due to which it is classified as arthropod. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
- Chitinous exoskeleton,
- Jointed appendages
- Open circulatory System.
Other Example: Prawn.
Question 73.
Identify ‘X’ and ‘Y’ in the diagram of a part of earthworm. What function is performed by ‘X’. (CCE 2014)
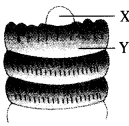
Answer:
X- Prostomium.
Y-Peristomium.
Function of X: Sensory.
Question 74.
After observing an Earthworm, Samir decided to place it in phylum annelida. Which two features did he observe that helped him do so ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
- Long, segmented (metameric segmentation) body
- Presence of rings of microscopic unjointed setae.
Question 75.
Give one function of gills in fishes. To which phylum do the fishes belong ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Gills: They are sites of respiration or exchange of gases between blood and water. Phylum. Chordata.
Question 76.
Mention two features adapted by birds which help them fly. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
- Fore limbs modified into wings,
- Stream-lined body, pneumatic bones.
Question 77.
Name the adaptation of fish which help them in
(a) Floating in water,
(b) Breathing. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(a) Floating: Presence of air sac.
(b) Breathing: Occurrence of gills.
Question 78.
Name the habitat of earthworm and how is it useful to the animal. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Earthworm lives in moist soil from which it can obtain food as decaying organic matter, keep the skin moist for respira¬tion and easily dig narrow burrows
Question 79.
(a) Why is the body of bony fishes stream-lined ?
(b) List two habitats of bony fishes. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(a) Stream-Lined Body. For meeting little resistance during swimming.
(b) Habitats. Fresh and marine waters.
Question 80.
State any two specific features of earthworm. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
- Segmented cylindrical body,
- Occurrence of clitellum.
Question 81.
The body of an organism is stream-lined and has feathers on its body. Identify the organism and write one specific feature of it. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Bird. Presence of wings and a toothless beak.
Question 82.
Why is it difficult to classify bacteria ? Give two reasons.
(CCE 2017)
Answer:
- Bacteria are microscopic,
- There are limited differences in structure and functions.
Question 83.
What is binomial nomenclature ? Explain it with the help of an example. (CCE 2017)
Answer:
Binomial nomenclature is scientific system of providing distinct and proper two word name to each and every organism. For example, the scientific name of Mango is Mangifera indica where Mangifera represents the genus while indica is the specific epithet.
Short Answer Questions (3 marks)
Question 1.
- Draw a neat diagram of Hydra,
- Label mesogloea and gastrovascular cavity,
- Name the group of animals it belongs to.
- Name one species of this group that lives in colonies. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
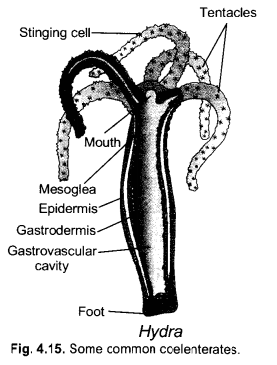
- Label the two parts.
- Phylum coelenterata.
- Corals.
Question 2.
Identify the plant bodies which are named as cryptogamae1. State and explain two characteristics which are exhibited by each category of these plant bodies. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Cryptogamae, the subkingdom of seedless plants, consists of three groups-thallophyta, bryophyta and pteridophyta.
- Thallophyta: Simple, ill-differentiated plant body, e.g., algae like Ulothrix
- Unicellular and nonjacketed reproductive organs
- Embryo stage absent.
- Bryophyta: Simple thallus-like or differentiated into stem and leaf-like structures, e.g., Riccia, Marchantia, Funaria (moss),
- Simplest but amphibious land plants which are fixed by means of rhizoids.
- Plant body is gametophyte. Sporophyte lives on it as a parasite.
- Pteridophyta: Differentiated plant body consisting of true roots, stems and leaves, e.g., ferns,
- Dominant plant body is sporophyte. Gametophyte is small but independent.
- Vascular tissues present but seeds are absent.
Question 3.
List any three groups of plants, which are referred to as vascular plants. Out of these which group is further classified on the basis of number of cotyledons. State its two characteristics. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
Vascular plants are those plants which possess vascular tissues, xylem and phloem, for conduction of water and nutrients respectively. There are three groups of vascular plants or tracheophytes-pteridophytes, gymnosperms and angiosperms.
Angiosperms or flowering plants are classified on the basis of cotyledons present in their seeds, monocotyledoneae (single cotyledon) and dicotyledoneae (two cotyledons). Characteristics
- Sporophylls are organised into flowers.
- Seeds develop inside fruits.
Question 4.
(a) Draw a well labelled diagram of Euglena.
(b) Name the kingdom to which it belongs. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a)
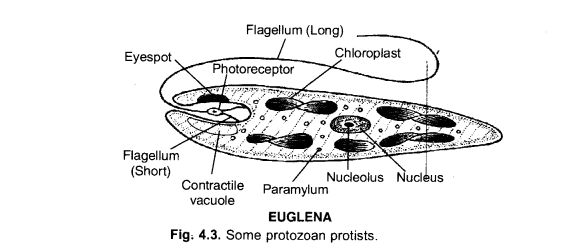
(b) Protista.
Question 5.
Pick up the odd one out and justify your choice by giving reasons :
(a) Moss, Fern, Pinus, Spirogyra.
(b) Sea Cucumber, Octopus, Feather Star, Star Fish. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Pinus: The other three belong to cryptogamae while Pinus is a member of phanerogamae.
(b) Octopus: The other three belong to echinodermata while Octopus is a member of mollusca.
Question 6.
Write any three differences between Amphibia and Mammalia. (CCE 2011)
Answer:

Question 7.
(a) Write down four characteristic features of the members of class Aves.
(b) To which group do the following belong :
(t) Evergreen trees that bear naked seeds.
(it) Plants which have tap root system and two cotyledons in their seeds. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Aves is a class of warm-blooded vertebrates having fore-limbs modified into wings, body covered with feathers and jaws modified into horny toothless beak.
General Characters
- Birds are the flying animals, having exoskeleton of feathers. Skin is dry except for a preen gland for dressing of feathers.
- Body Temperature. Birds are warm blooded
- Body Divisions. Body is divided into head, neck, trunk and tail.
- Fore limbs are modified intowings while hind limbs have four clawed digits which are adapted for walking, running, perching or digging.
- 5. Bones. They are very light because of air spaces (pneumatic bones).
- Jaws are prolonged to form horny beak. Teeth are absent.
- Bird’s Milk. Oesophagus is modified to store and soften the food. It is source of bird’s milk which is used for feeding the young birds.
- Respiratory System. It possesses well-developed lungs which have air sacs attached to them for double respiration.
(b)
- Gymnospermae.
- Dicotyledoneae.
Question 8.
Identify the diagrams. Write the phylum do they belong to. Write down the characteristic features of each phylum.
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Wuchereria (Filarial worm). Phylum. Nematoda (nemathelminthes).
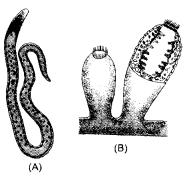
- Cylindrical body with bilateral symmetry.
- Triploblastic with pseudocoelom,
- With both mouth and anus, having primitive system level of organisation.
(b) Sponges. Phylum. Porifera.
- Sedentary adults with hard skeleton of spicules and fibres,
- Diploblasdc with cellular level of organisation,
- Canal system with ostia and osculum, flagellated choanocytes,
Question 9.
Differentiate between annelida and nematoda.
Answer:
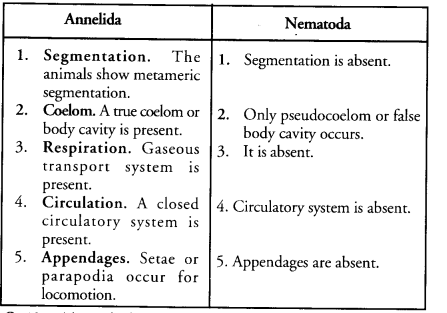
Question 10.
(a) In which two ways amphibians are different from fishes,
(b) Identify the phylum of organisms having the following characteristics :
- Pore bearing animals and radial symmetry,
- Body spiny with radial symmetry,
(c) Why gymnosperms do not require water for fertilization ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a)
- Amphibians have limbs while fishes possess fins,
- Amphibians have lungs while the same are absent in fishes.
(b)
- Porifera
- Echinodermata.
(c) In gymnosperms fertilization occurs through siphonogamy or pollen tube. Therefore, an external source of water is not required for carrying male gametes.
Question 11.
(a) Name the phylum to which each of the following animals belongs to – Silver Fish, Star Fish, Tapeworm, Leech.
(b) List two features of vertebrates. (CCE 2011 )
Answer:
(a)
- Silver Fish – Arthropoda
- Star Fish – Echinodermata.
- Tapeworm- Platyhelminthes.
- Leech – Annelida.
(b) Features of Vertebrates.
- Notochord replaced by cranium and vertebral column,
- Dorsal nerve cord transformed into brain and spinal cord.
- Presence of paired gill pouches replaced by lungs in land animals.
- A chambered ventral heart is present.
Question 12.
How do Aves differ from Mammals ? (three points). (CCE 2011, 2012, 2013)
Answer:
| Aves | Mammalia |
| 1. Wings. Forelimbs are modified into wings. | Wings are absent except in bats. |
| 2. Feathers and Scales. The body is covered with feathers and scales. | Feathers and scales are absent. |
| 3. Skin Glands. Skin is dry. Only a single preen gland is present. | Skin bears a number of sweat and oil glands. |
| 4. Mammary Glands. They are absent. | Female possesses mammary glands for feeding the young |
| 5. Diaphragm. A diaphragm is absent. | A partition called diaphragm is present between abdomen and thorax. |
| 6. Beak. A toothless beak is present. | Jaws do not form a beak. Teeth are present. |
| 7. Bones. They are hollow or pneumatic. | Bones do not possess air cavities. |
| 8. Larynx/Syrinx. Larynx is non-functional. Instead syrinx is present. | Larynx is functional. Syrinx is absent. |
| External air sacs do not occur over lungs. | |
| 9. Air Sacs. Lungs possess external air sacs. | |
| 10. Yolk. Eggs possess a lot of yolk (macrolecithal). | Eggs have little yolk (alecithal). |
| 11. Reproduction. Birds are oviparous. | Mammals are viviparous with the exception of a few species. |
Question 13.
To which group do the following organisms belong and give one reason for each
(a) Cyanobacteria
(b) Euglena
(c) Ulothrix ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Cyanobacteria – Monera. Prokaryotic nature.
(b) Euglena – Protista. Unicellular eukaryote.
(c) Ulothrix – Plantae. Thallophyta-Algae. Little
Question 14.
differentiated autotrophic body with unicellular, non- jacketed sex organs.
- What are vertebrates ?
- Name four subgroups of vertebrates. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
- Vertebrates. They are chordates in which notochord has been replaced by endoskeleton of vertebral column [ and cranium while dorsal nerve cord has been transformed into brain and spinal cord.
- Pisces, Amphibians, Reptiles, Aves, Mammals.
Question 15.
On the basis of the following features, identify the group and give one example of each :
- Presence of notochord at some stage of life,
- Unicellular microscopic and eukaryotic.
- Seeds are enclosed in fruits. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
- Notochord At Some Stage. Protochordata, e.g., Herdmania.
- Unicellular, Microscopic, Eukaryotic. Protista, e.g., Euglena, Amoeba.
- Seeds Enclosed in Fruits. Angiospermae, e.g, Mango, Tomato.
Question 16.
Write one difference for each of the following pairs
- Thallophyta and Bryophyta
- Nematoda and Annelida
- Amphibia and Pisces.
(CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
- Thallophyta and Bryophyta. In thallophyta the reproductive organs are unicellular, non-jacketed with no embryo stage. In bryophyta the sex organs are multicellular, jacketed with an embryo stage.
- Nematoda and Annelida
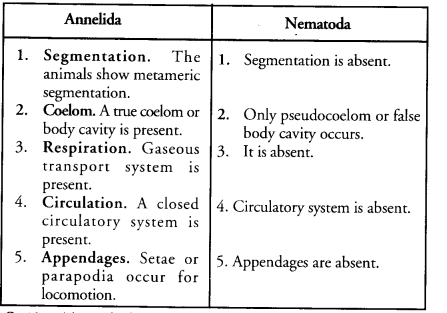
| Pisces | Amphibians |
| 1. Scales. The body is covered by scales. | 1. Scales are absent. |
| 2. Mucous Glands. The skin does not possess mucous glands. | 2. The skin has mucous glands that keep the skin moist and slippery. |
| 3. Fins. Pisces possess fins for locomotion and steering | 3. Fins may occur in larval stage. The adult does not possess fins. Limbs occur instead. |
| 4. Heart. It is two chambered. | 4. Heart is 3-chambered. |
| 3. Lungs. Pisces do not have lungs. | 5. Lungs are present. |
| Examples. Scoliodon, Labeo. | Examples. Frog, Toad. |
Question 17.
(a) List any two main characteristics of chordates.
(b) In which class would you place an organism which has
- Four chambered heart and lays eggs,
- Skeletons made of both bones and cartilage and are cold blooded.
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Chordate Features:
- Occurrence of notochord that is transformed into cranium and vertebral column in higher chordates.
- Presence of dorsal hollow nerve cord above the notochord which in higher chordates is transformed into brain and spinal cord.
(b)
- Aves.
- Pisces.
Question 18.
Name the phylum to which this organism belongs. Write any two characteristic features of the phylum. (CCE 2011, 2012)

Answer:
Mollusca (animal Octopus).
- Soft bodied animals with a shell,
- Unsegmented, triploblastic body with haemocoel. Both shell and haemocoel absent in Octopus.
Question 19.
Classify the following organisms based on the absence/ presence of true coelom, i.e., acoelomate, pseudocoelomate and coelomate :
(a) Scorpion
(b) Sea Anemone
(c) Ascaris
(d) Earthworm
(e) Wuchereria
(f) Nereis. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Scorpion – Coelomate (also haemocoelomate).
(b) Sea Anemone-Acoelomate.
(c) Attïzro-Pseudocoelomate.
(d) Earthworm- Coelomate.
(e) Wuchereria – Pseudocoelomate.
(f) Nereis-Coelomate.
Question20.
What is the most striking features of the following phyla :
- Arthropoda
- Amphibia
- Porifera.
(CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
- Arthropoda: Chidnous exoskeleton and jointed appendages.
- Amphibia: Living in both water and on land with smooth skin having mucous glands and three chambered heart.
- Porifera: Diploblastic, acoelomate, sedentary animals with porous body and canal system.
Question 21.
Name the largest group of animals. Write the salient features of this group. Give two examples. (CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
Largest Group. Arthropoda.
Salient Features
- Presence of jointed appendages.
- Occurrence of chitinous exoskeleton,
- Presence of haemocoel and open circulatory system.
Examples. Cockroach, Housefly, Mosquito.
Question 22.
Classify the following organisms on the presence of coelom— Spongilla, Planaria, Scorpion, Birds, Ascaris, Nerreis.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
Spongilla—acoelomate. Planaria-acoelomate.
Scorpion— coelomate (haemocoelomate).
Birds—coelomate. Ascaris- pseudocoelomate.
Nereis—coelomate.
Question 23.
State the appropriate term for the following :
- Plants which bear seeds with two cotyledons.
- Animals which do not have coelom.
- Edible fungi. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Dicots,
- Acoelomate
- Mushrooms.
Question 24.
State the type of cells monerans have. State their structure and the type of nutrition they have (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Monerans have prokaryotic cells.
Structure: Monerans are basically unicellular. The cells possess peptidoglycan (= murein) cell wall, no membrane bound organelles, genetic material coiled to form nucleoid without any membranous covering.
Nutrition: Varied, both autotrophic and heterotrophic.
Question 25.
Define
- Lichens
- Cryptogams
- Phanerogams. (CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
- Lichens: They are dual organisms which have been formed by a permanent symbiotic association between an alga and a fungus, e.g. Graphis.
- Cryptogams: They are seedless lower plants where reproductive organs are inconspicuous requiring an external water for fertilization.
- Phanerogams: They are seed bearing higher plants which possess conspicuous reproductive organs like cones and flowers, e.g., Pinus, Wheat.
Question 26.
List three distinguishing features between annelid animals and arthropods. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
1. Exoskeleton. Annelids do not have a chitinous exoskeleton which is present in arthropods.
2. Circulatory System. Annelids have a closed circulatory system while arthrpods have open circulatory system.
3. Appendages. Appendages are unjointed in annelids and jointed in arthropods.
Question 27.
(a) On what basis does the embryo of cryptogams differ from that of phanerogams ?
(b) Describe the feature that divides the angiosperms in two groups
(c) State the two subgroups of angiosperms. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Embryo of cryptogams is naked while that of phanerogams is covered being present inside the seed.
(b) Number of cotyledons in the seed.
(c) Dicots and monocots.
Question 28.
(a) What is the function of notochord ?
(b) List out any four features that all chordates possess.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Function of Notochord. It provides attachment to muscles. Phylogenetically it has given rise to jointed axial skeleton of cranium and vertebral column.
(b) Presence of
- Notochord which in higher forms is transformed into cranium and vertebral column,
- Dorsal Hollow Nerve Cord. In higher chordates, it is transformed into brain and spinal cord.
- Pharyngeal Gill Slits. Present at some stage of life cycle,
- Post-anal tail.
Question 29.
Draw a neat diagram of Spirogyra and label the following parts
(a) Outermost layer of cell
(b) Organelle that performs the function of photosynthesis,
(c) Jelly-like substance in the cell where all organelles are suspended.
(d) Darkly coloured and dot-like structrue generally present in the centre of the cell. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
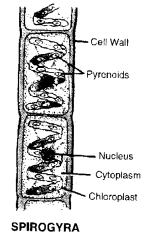
(a) Cell wall (outermost layer of cell)
(b) Chloroplast (organelle that performs the function of photosyntheis)
(c) Cytoplasm (jelly-like substance in the cell).
(d) Nucleus (darkly stained dot-like structrue).
Question 30.
Give reasons for the following :
(a) Echidna and Platypus lay eggs but are considered mammals
(b) Crocodile has four chambered heart but still is a reptile.
(c) Birds have pneumatic bones. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Platypus and Echidna possess body hair and mammary glands like other mammals.
(b) Crocodiles are piokilothermic, lay cleidoic eggs, with body having cornified skin covered with scales and bony plates.
(c) Pneumatic bones are light and strong required for birds in their flight.
Question 31.
Name the phylum to which the following organisms belong :
(a) Organisms which have peculiar water driven tube feet system that they use for moving around.
(b) Organisms which have a foot that is used for moving around and have an open circulatory system.
(c) The organisms have holes or pores all over their body.
They lead to a canal system that helps in circulating water throughout the body. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Echinodermata
(b) Mollusca
(c) Porifera.
Question 32.
Identify and name the following :
(a) Organisms that use dead and decaying organic material as food.
(b) Cell walls of fungi are made of this type of sugar
(c) Kingdom to which Amoeba belongs
(d) An example of moneran
(e) An animal with a pseudocoelom.
(f) A group which has an open circulatory system.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Saprophyte, e.g., Rbizopus.
(b) N-acetyl glucosamine (forms chitin).
(c) Protista (unicellular eukaryotes)
(d) Escherichia coli, a bacterium
(e) Pseudocoelomate, e.g., Ascaris.
(f) Arthropoda.
Question 33.
Classify the following and write one characteristic of each :
(a) Lichen
(b) Sponges
(c) Flatworm. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Lichen: Dual organism made of an alga and a fungus showing mutualism,
(b) Sponges: Porifera. Having inhalent pores or ostia and an exhalent pore or osculum connected by a canal system.
(c) Flatworm: Platyhelminthes. Triploblastic, acoelomate.
Question 34.
“Tapeworm is triploblastic”, what does it mean ? How is Hydra different from Tapeworm in this aspect ? Name the phylum to which Hydra and Tapeworm belong.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
Tapeworm is triploblastic because it has three germinal layers (ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm). Hydra is diploblastic as it has two germinal layers (ectoderm and endoderm). Hydra—coelenterata. Tapeworm-
Platyhelminthes.
Question 35.
(a) Write two distinct features by which vertebrates are differentiated from invertebrates
(b) What are protochordates ? Give two examples.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a)
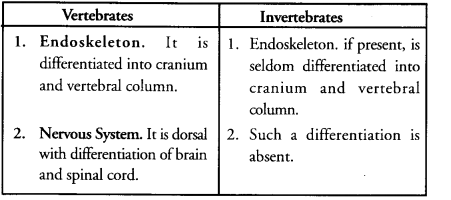
(b) Protochordates are non-vertebrate chordates with a single layered epidermis, hollow dorsal but undifferentiated nerve cord as well as solid notochord in some stage of life cycle, e.g., Amphioxus.
Question 36.
Give other name to the category of plants that are called phanerogams. How are they further classified on the basis of their seeds ? Give example of each category. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Seed plants or spermatophyta. Two categories
- Gymnosperms-naked seeds, e.g., Pinus.
- Angiosperms (Flowering Plants, seeds inside fruits).
Further of two types :
- Monocots—single cotyledon in seeds, e.g., Maize.
- Dicots—two cotyledons in seeds, e.g., Pea.
Question 37.
Write the names of the kingdom for the following organisms
(a) Single celled, eukaryotic and photosynethetic
(b) Multicellular, eukaryotic and photosynthetic
(c) Single-celled, prokaryotic and heterotrophic. (CCE2012)
Answer:
(a) Protista
(b) Plantae
(c) Monera.
Question 38.
(a) Name the kingdom to which Protozoa belong.
(b) Write one important characteristic of that kingdom.
(c) Name the appendages present in
(z) Euglena
{it) Paramoecium. (CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
(a) Protista
(b) Eukaryotic unicellular organisms.
(c) (t) Euglena-Ragellum
{iî} Paramoecium-cilia.
Question 39.
To which class do Salamander and Sparrow belong ?
Write any two differences between these classes.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
Salamanader: Class Amphibia.
Sparrow: Class Aves.
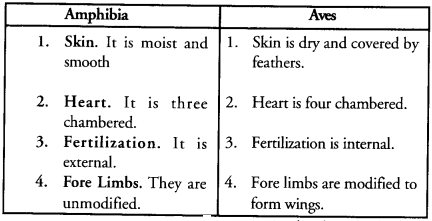
Question 40.
(a) How are food and oxygen circulated in the body of organisms belonging to phylum porifera ?
(b) Why do fish have stream-lined body ?
(c) State the reason for birds having stream-lined body.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) By canal system which has many ostia or inhalent pores and one exhalent pore or ostium. Water circulates due to activity of flagellated collar cells or choanocytes.
(b) Fish have stream-lined body to meet minimum resistance while swimming in water
(c) Stream lined body provides least resistance to birds while flying.
Question 41.
Write one difference between
(a) Monera and Protista
(b) Platyhelminthes and Nematode. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Monera have prokaryotic nature while protista have eukaryotic nature.
(b) Platyhelminthes are acoelomate while nematodes are pseudocoelomate.
Question 42.
‘Snails are soft bodied shelled animal’. Identify the phylum to which they belong. Write any two distinguishing features of the phylum. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Mollusca:
- Unsegmented body with open circulatory system.
- A muscular foot for locomotion.
Question 43.
What are cotyledons ? Name and discuss important features of two classes of angiosperms based on number of cotyledons. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Cotyledons are seed leaves present over embryo axis below the plumule. On the basis of their number, angiosperms have been divided into two classes, monocots and dicots. Monocots. There is a single cotyledon. Monocots have parallel venation, fibrous root system and trimerous flowers.
Dicots: There are two cotyledons. Dicots have reticulate venation, tap root system and pentamerous or tetramerous flowers.
Question 44.
Write two examples of organisms belonging to.
- Nematoda
- Platyhelminthes
- Arthropoda
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Nematoda: Ascaris, Wuchereria.
- Platyhelminthes Planaria (Dugesia), Liver Fluke (Fasciola).
- Arthropoda. Prawn (Palaeomon), centipede (Scolopendra).
Question 45.
Given below is a flow chart for classification of plants, Identify ‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘d, ‘e’ and ‘f’ as an appropriate characteristic or plant group. (CCE 2012)
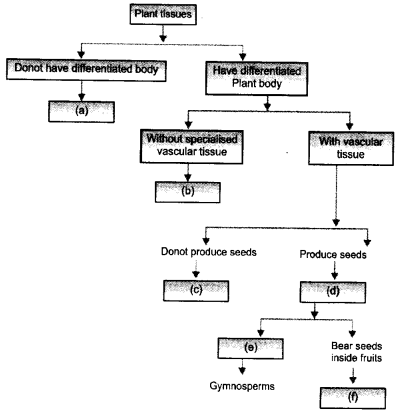
Answer:
(a) Thallophyta
(b) Bryophyta
(c) Pteridophyta
(d) Spermatophyta
(e) Bear naked seeds
(f) Angisperms.
Question 46.
Write four main features of pteridophyta and give any two examples. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Sporophyte: Dominant sporophyte differentiated into stem, leaves and roots.
- Gametophyte: Small but independent.
- Vascular Tissues: Present.
- Seeds: Naked embryo, seeds absent.
Examples. Selaginella, Dryopteris (Fern).
Question 47.
Is the given figure of a dicot or monocot ? Differentiate between dicots and monocots on the basis of venation and number of cotyledons in the seed. (CCE2012)

Answer:
Dicot
- In dicots the leaves have reticulate venation. Venation is parallel in monocots.
- The seeds of dicots have two cotyledons. A single cotyledon is present in the seeds of monocots.
Question 48.
Draw and label any four parts of a bony fish.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
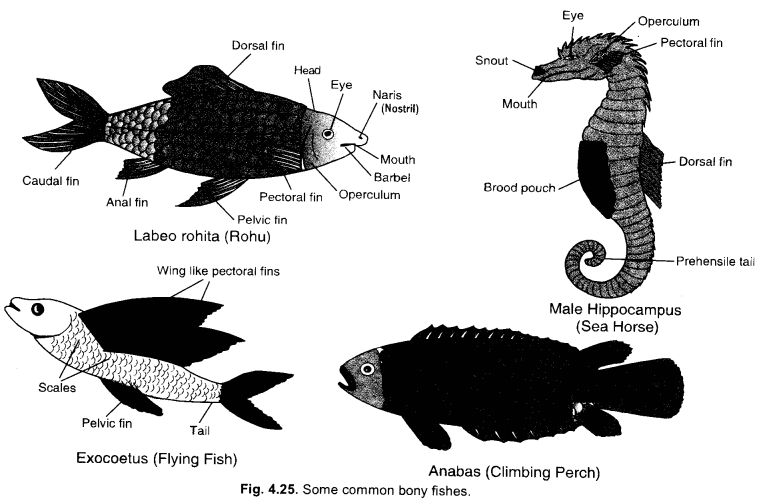
Question 49.
Write one point of difference between the following :
(a) Annelids and arthropods
(b) Thallophytes and ; Pteridophytes
(c) Poriferans and coelenterates. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Annelids have unjointed appendages while arthropods possess jointed appendages.
(b) Thallophytes have simple undifferentiated and nonvascular plant body while it is differentiated and vascular in pteridophytes.
(c) Periferans have a number of inhalent pores and a single exhalent pore while coelenterates have a single opening.
Question 50.
Write one point of difference each between the j following :
(a) Amphibians and reptiles
(b) Aves and mammals
(c) Gymnosperms and angiosperms.(CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Skin is smooth, moist and non-cornified in amphibians while it is dry, scaly and cornified in reptiles.
(b) The body is covered by feathers and scales in aves. Hair occur in mammals.
(c) Gymnosperms possess naked seeds while angiosperms have seeds enclosed in fruits.
Question 51.
Write two examples of each
- Egg laying mammals
- Organisms with open circulatory system.
- Prokaryotic organisms. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
- Egg Laying Mammals. Platypus, Echidna.
- Organisms with Open Circulatory System. Arthropoda, Mollusca.
- Prokaryotic Organisms. Rhizobium, Escherichia.
Question 52.
State reasons for the following :
(a) Bryophytes are called amphibians of the plant kingdom
(b) Gymnosperms are called so.
(c) Birds have wings and feathers. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Bryophytes are called amphibians of plant kingdom as they live in moist, damp and shady places. A layer of water is required on the soil surface for
- Sexual reproduction.
- Protection from transpiration and hence desiccation
- Supply of water to all parts in the absence of vascular tissues.
(b) Gymnosperms are so called as they possess naked seeds (gymnos-naked, sperma—seed).
(c) Birds have wings for flight and feathers for insulation.
Question 53.
Write one characteristic feature of each of the following groups of organisms :
- Cryptogams
- Arthropods
- Mammals. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
- Cryptogams: Absence of seed so that embryo, if present, is always naked.
- Arthropoda: Presence of jointed appendages and legs.
- Mammals: Occurrence of mammary glands in females to nourish new borns.
Question 54.
“Lichens” show symbiotic life form between two organisms.
- Name the two organisms showing this relationship
- Write the kingdom to which each one belongs
- In such relationship, organisms are parasitic or mutually benefitted from each other or mutually dependent on one another. Explain. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
- Lichen: Lichen is formed by an obligate association between a fungus and an alga.
- Fungus-kingdom Fungi. Blue-green alga-kingdom Monera.
- Mutually dependent and mutually benefitted. In lichen, the alga manufactures food for itself as well as fungus. The fungus provides protection to alga, helps in fixation and absorption of water as well as minerals.
Question 55.
State reason for the following :
(a) Fungi are called saprophytes
(b) Platyhelminthes are called so. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Fungi are heterotrophs with absorptive type of nutrition. The free living fungi feed on organic remains. They secrete digestive enzymes into external medium. The organic matter solubilises. It is absorbed by fungi. Hence, fungi are called saprophytes (sapros-tottcn, phyton-phstx).
(b) Platyhelminthes (platy-flat, helminthes-worms) are called flat worms as they are dorsoventrally flattened.
Question 56.
Identify the organisms and write one characteristic feature of the phylum to which they belong. (CCE 2013)
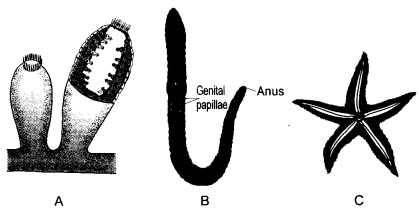
Answer:
A- Sycon: Porifera. Presence of many inhalent pores (ostia) and one exhalent pore (osculum).
B- Earthworm: Annelida. Body is metamerically segmented.
C- Star Fish: Echinodermata. Radial symmetry with spiny exoskeleton.
Question 57.
(a) Give scientific name of human beings.
(b) Write two characteristic features of Aves and Mammals.
(CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Homo sapiens.
(b) Aves: Body covered with feathers, fore limbs modified into wings and jaws modified into horny toothless beak, e.g., Pigeon.
Mammalia: Hair covered body with integumentary glands, mammary glands in females, e.g., Tiger.
Question 58.
(a) Most mammals give birth to young ones. How do they nourish their young ?
(b) Name two egg laying mammals. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(a) Through mammary glands by the females,
(b) Egg Laying Mammals. Platypus, Echidna.
Question 59.
Mr. Sharmas family had gone to visit a garden. Many beau¬tiful roses were there. Mr. Sharmas five year old son Himanshu wanted to pluck few roses. He was told not to do so by his elder sister Kanika who was in class IX.
- Rose belongs to which division of plant kingdom?
- State the number of cotyledons and type of root in rose plant.
- How can you contribute in the preservation of flora and fauna around you ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
- Spermatophyta
- Cotyledons. 2. Root: Tap root.
- Preservation of flora and fauna,
- By not enroaching upon their habitat.
- By not damaging them through over exploitation or de-struction.
Question 60.
Write two examples each of the following :
(a) Animals which do not locomote.
(b) Flightless birds
(c) Molluscs without shell. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(a) Sponges, corals,
(b) Emu, Ostrich, Kiwi
(c) Octopus, Banana Slug.
Question 61.
Write four conventions which are followed while writing the scientific names of organisms. Write the scientific name of tiger. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Conventions.
- It consists of two words, first generic (like noun) and second specific (species).
- Generic name has first letter capital while specific word begins with small letter.
- Both are derived from latin language or are latinised.
- They are printed in italics or are underlined separately in hand-written form.
Tiger: Panthera tigris.
Question 62.
Carolus Linnaeus gave the two kingdom classification. Later ; it was changed by Ernst Haeckel (1894) and in 1969 ; Whittaker gave the five kingdom classification. Do you think that studying about the work done by earlier scientists or j their obsolete theories is useful for students of this genera- i tion ? Give three reasons. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Science is a continuous search of truth. Search is based on the j knowledge previously gained and the appliances available, i As the appliances improve and the knowledge becomes wider and deeper, new truths become known. This changes the | previous concepts or theories.
- It is always rewarding to learn about the past obsolete j theories in the light of then known knowledge. This shall prompt the students to discover loop holes in the present knowledge and theories.
- As the gaps of present day knowledge become apparent, j a student will like to find yet hidden truths.
- Exceptions in the theories bring about their perusral by the students – the truth of yesterday has become fiction of today and truth of today shall become fiction of tomorrow.
Question 63.
Name the phylum to which the following organisms belong :
(a) Earthworm
(b) Planaria
(c) Sycon
(d) Starfish
(e) Housefly
(f) Octopus.
Answer:
(a) Earthworm-Annelida.
(b) Planaria-Platyhelminthes
(c) Sycon-Porifera.
(d) Starfish-Echinodermata.
(e) House- fly-Arthropoda.
(f) Octopus-Mollusca.
Question 64.
- Assign a group to an organism ‘X’ which has notochord in some larval forms,
- What would be the place of occur- rence of‘X’.
- What would be symmetry of‘X’ ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
- ‘X’ — group Protochordata, subphylum Urochordata.
- Sea.
- Bilateral.
Question 65.
To study biodiversity, a group of students are taken to a zoo and another to a safari in the woods. Which is the better way S of learning and why ?
What more can you gain from such experiences ?
(CCE 2014)
Answer:
Safari in the woods is a better way of learning biodiversity j than a visit to Zoo.
- Woods are pieces of natural biodiversity of both plants and animals. Zoo contain only captured or endangered ani¬mals fed and cared by humans.
- Delicate balance of nature can be known only through a visit to the woods.
Question 66.
Learning. Nature should not be disturbed beyond its inbuilt regeneration capacity. Otherwise many organisms will become endangered and disappear for ever.
Will advanced organisms by the same as complex organisms ? If so why ? (CCE 2014, 2015)
Answer:
Yes. Advancement is based on development of specializations. Specialisation occurs where there is more elaboration and hence more complexity. However, there is likelihood of specialisation to lead to overspecialisation which becomes a hindrance to competitive nature of existence in the biosphere. Dinosaurs, giant crocodiles and mammoth have died down due to this reason. Therefore, advancement is possible only if specialisation leads to greater elaboration and efficiency.
Question 67.
Mention the problem which is associated with using local names of organisms. How was this resolved ? Name the scien-tist who had introduced the above solution.
(CCE 2015)
Answer:
Problem: All organisms do not have local names. Some or-ganisms have multiple local names while a local name is also used for two or more organisms. The problem was resolved through the development of binomial nomenclature of organisms. It was introduced by Carolus Linnaeus (1751).
Question 68.
Most mammals give birth to young ones,
(a) How do they nourish their young ones ?
(b) Name two egg laying mamamals. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Young ones are nourished inside the womb through pla-centa and by milk from mammary glands after birth.
(b) Duck-billed Platypus, Echidna.
Question 69.
Classify the following organisms on the basis of absence or presence of true coelom, i.e., coelomate, acoelomate and pseudocoelomate : Ascaris, Herdmania, Earthworm, Planaria, Fishes, Humans. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Acoelomate. Planaria.
Pseudocoelomate. Ascaris.
Coelomate. Herdmania, Earthworm, Fishes, Humans.
Question 70.
Give three differences between monocotyledonous and di-cotyledonous plants. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
| Dicotyledoneae | Monocotyledoneae |
| 1. Cotyledons. In the seeds, the embryo bears two cotyledons.
2. Venation. The leaves show reticulate venation. 3. Vascular Bundles. Vascular bundles of the stem are open and arranged in a ring. 4. Root System. The plants have tap root system. 5. Secondary Growth. Secondary growth occurs. 6. Flowers. Flowers are pentamerous (have five of each floral part) or tetramerous. |
In the seeds, the embryo bears one cotyledon.The leaves show parallel venation.Vascular bundles of the stem are closed and scattered in the ground tissue.The plants have fibrous root system.Secondary growth does not occur.Flowers are trimerous (have three of each floral part). |
Question 71.
Name three plants under the group Thallophyta. Mention three characteristics of this group. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Spirogyra, Ulothrix, Chara, Ulva.
Characteristics :
- Simple body design called thallus.
- Reproductive organs are unicellular and non-jacketed.
- An embryo stage is absent.
Question 72.
Give two examples of organisms belonging to the following phyla :
(a) Arthropoda
(b) Mollusca
(c) Protochordata.
(CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Arthropoda. Cockroach, Mosquito, Prawn.
(b) Mollusca. Pila, Pearl oyster, Octopus.
(c) Protochordata, Balanoglossus, Herdmania, Ampbioxus.
Question 73.
List any three characteristics of the phylum to which Hydra belongs. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Hydra belongs to phylum Coelenterata (= Cnidaria).
Characteristics.
- Diploblastic animals with tissue level organisation.
- Body has a single opening for both feeding and elimination.
- Tentacles with cnidoblasts or nematoblasts.
- Nerve cells present but nerve plexus absent.
Question 74.
(a) What is the scientific name of human ?
(b) To which class of vertebrates does it belong ?
(c) Mention any two character-istics features of this group. ( CCE 2015, 2016)
Answer:
(a) Homo sapiens
(b) Mammalia
(c) Characteristics.
- Seven cervical vertebrae, a diaphragm dividing trunk and hair on the skin,
- Vivipary and nourishing the young one by milk from mammary galnds.
Question 75.
What is classification ? Why do we need to classify organisms ? Mention any two major characteristics used for classifying organisms. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Classification. Classification is the arrangement of organisms into groups and sub-groups on the basis of their similarities and dissimilarities and placing them in a hierarchy that brings out their relationships.
Need for Classification:
- Identification is not possible without any system of classification.
- Classification helps in bringing out similarities and dissimilarities amongst organisms.
- Relationships are built up with the help of classification. They indicate the evolutionary pathways.
- Organisms of other localities and fossils can be studied only with the help of a system of classification.
- It is not possible to study every organism. Study of one or two organisms gives sufficient idea about other members of the group.
- Other branches of biology depend upon proper identification of the organism which is possible only through a system of classification.
Major Characteristics:
- Prokaryotic and eukaryotic nature.
- Unicellularity and multicelliuarity.
- Nutrition.
Question 76.
State reason for the following :
(a) Tapeworm does not have a digestive tract,
(b) Frogs use both skin and lungs for breathing,
(c) Birds have pneumatic / hollow bones.
(CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Tapeworm resides in the area of digestive tract where digested food is available.
(b) Frog lives both over moist land as well as inside water. Lungs are useful over land as well as after coming to the water surface. Moist skin is useful in respiration inside water and soil.
(c) Hollow or pneumatic bones are not only stronger than the solid bones but also make the body light weight for flight.
Question 77.
How do cnidarians (coelenterata) differ from porifera ?
(CCE 2015)
Answer:
| Poriferans | Coelenterates |
| 1. Organisation. It is of cellular level. | It is of tissue level. |
| 2. Pores. A number of inhalent pores or ostia and a single exhalent pore or osculum are present. | There is a single opening. |
| 3. Digestion. It is intracellular. | It is both intracellular and intercellular. |
| 4. Muscle and Nerve Cells. They are absent. | Primitive muscle and nerve cells appear for the first time in coelenterates. |
| 5. Appendages. They are absent. | Appendages are represented by tentacles. |
| 6. Special Cells. The special cells are choanocytes or collar cells. | Special cells are cnidoblasts. |
Question 78.
- Draw the relevance of scientific naming of an organism.
- Who introduced this system of nomenclature ?
- Rana tigrina is the scientific name of common frog.
What do these two terms imply ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
- Advantage,
- It is universal, being the same in all languages and conntries.
- It is distinct and sepcific with no two organisms having the same name.
- Carolus Linnaeus.
- In Rana tigrina, the word Rana signifies genus or ge¬neric name while tigrina is a specific epithet or species.
Question 79.
Differentiate between gymnosperms and angiosperms.
(CCE 2016)
Answer:
| Gymnosperms | Angiosperms |
| 1. Sporophylls. They are aggregated to form cones. | Sporophylls are aggregated to form flowers. |
| 2. Seeds. The seeds are naked. | The seeds are enclosed by fruit wall. |
| 3. Microspores and Megaspores. The micro-spores and megaspores are produced by male and female cones. | They are produced in the same or two different types of flowers. |
| 4. Vascular Tissues. Xylem lacks vessels and phloem lacks companion cells. | Xylem contains vessels and phloem contains companion cells. |
| 5. Ovules. The ovules are not contained in the ovary. | The ovules are enclosed in the ovary. |
| 6. Endosperm. It is haploid. | It is triploid. |
Question 80.
State three bases for classification of organisms into five king-doms. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
Four criteria have been used for grouping of organisms into five kingdoms—
- Procaryotic and eukaryotic nature
- Unicellular and multicellular nature
- Nutrition
Question 81.
Name the scientist who proposed two kingdom classification of living organisms. Name those kingdoms. Write major drawbacks of the proposed classification. ( CCE 2016)
Answer:
- Carolus Linnaeus,
- Plant kingdom and Animal kingdom.
Drawbacks:
- Prokaryotes. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes are placed in the same kingdom.
- Fungi are included amongst plants when they are structurally different from them,
- Organisms like Euglena are included in both the kingdoms,
- Viruses do not belong to either of the kingdom.
Question 82.
(a) Give any two important characteristics of kingdom Fungi.
(b) What is symbiotic relationship between blue-green algae and fungi called ? ( CCE 2016)
Answer:
(a) Protochordates are non-vertebrate chordates with a single layered epidermis, hollow dorsal but undifferentiated nerve cord as well as solid notochord in some stage of life cycle, e.g., Amphioxus.
(b) Lichen.
Question 83.
Classify the following organisms into their respective kingdoms as per Whittaker’s five kingdom classification : Amoeba, Euglena, Birds, Herbs, Cats, Lactobacillus. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
(a) Amoeba—Protista,
(b) Euglena—Protista,
(c) Birds— Chordata (class Aves).
(d) Herbs—Plantae.
(e) Cats — Chordata (class Mammalia),
(f) Lactobacillus—Monera.
Question 84.
State the advanced features present in and seen for the first time (according to evolution) in the following groups :
- Pteridophyta
- Gymnosperms
- Angiosperms.
(CCE 2017)
Answer:
- Pteridophyta: Vascular tissues,
- Gymnosperms: Seeds.
- Angiosperms: Fruits.
Question 85.
Write the names of the following :
- Plants which bear naked seeds
- Animals which have pseudocoelom (any two)
- Animals which maintain a constant body temperature. (CCE 2017)
Answer:
- Gymnosperms
- Nematoda, e.g., Ascaris, Wuchereria.
- Homoeotherms.
Question 86.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of Paramecium and mention the group to which it belongs. (CCE 2017)
Answer:
Group Protista.
Question 87.
Write the difference between amphibians and Pisces.
(CCE 2017)
Answer:
| Pisces | Amphibians |
| 1. Scales. The body is covered by scales. | 1. Scales are absent. |
| 2. Mucous Glands. The skin does not possess mucous glands. | 2. The skin has mucous glands that keep the skin moist and slippery. |
| 3. Fins. Pisces possess fins for locomotion and steering | 3. Fins may occur in larval stage. The adult does not possess fins. Limbs occur instead. |
| 4. Heart. It is two chambered. | 4. Heart is 3-chambered. |
| 3. Lungs. Pisces do not have lungs. | 5. Lungs are present. |
| Examples. Scoliodon, Labeo. | Examples. Frog, Toad. |
Question 88.
State any three differences between cryptogamae and phanerogamae. (CCE 2017)
Answer:
| Cryptogamae | Phanerogamae |
| 1. It contains seedless plants.
2. It has both vascular and non-vascular plants. 3. An external water is required for fertilization. |
It contains seed plants.
It possesses only vascular plants. An external water is not required |
Long Answer Questions (5 Marks)
Question 1.
Draw a flow chart to show different divisions of kingdom plantae and answer the following :
- Which division has the simplest plants ?
- To which division Pinus and Cycas belong ?
- What is the other name given to flowering plants. Classify them on the basis of number of cotyledons present in the seed. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
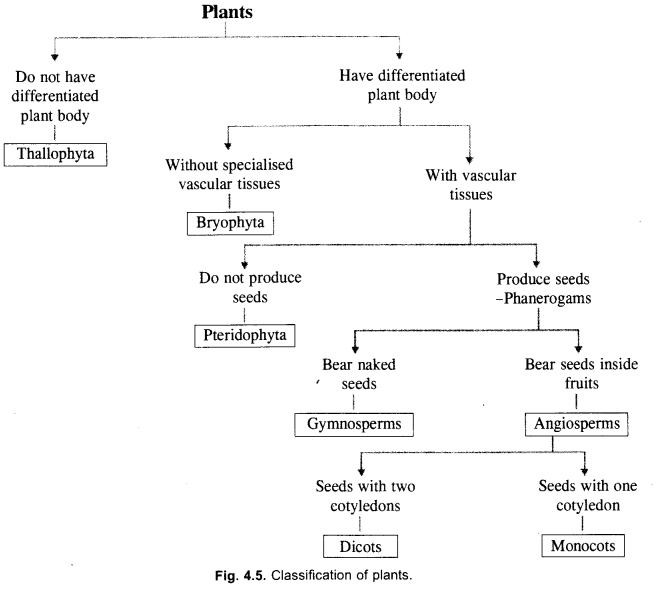
- Simplest Plants: Thallophyta (Algae).
- Pinus and Cycas: Gymnospermae of spermatophyta.
- Angiosperms: Two groups, dicots (with two cotyledons in seeds) and monocots (with one cotyledon in seeds).
Question 2.
- What is the scientific name of human ?
- To which class of vertebrates does it belong ?
- Write five characteristic features of this group. Also mention the exceptions, if any. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Homo sapiens
- Class mammalia.
- Characteristics of Mammalia
- Presence of mammary glands in females.
- Occurrence of hair over the body.
- Cervical vertebrae are seven in number.
- A muscular diaphragm occurs between abdomen and thorax.
- Mammals are viviparous i.e., adult females give birth to young ones.
Exceptions:
Duck-billed Platypus and Echidna are egg laying mammals. Kangaroos and their relatives give birth to young ones in very early stage of development. They are nourished in mother’s marsupium,
Question 3.
(a) Name the group of plants which have unicellular undifferentiated body.
(b) Why are echinoderms named so ?
(c) Name plants not having well differentiated body design.
(d) Name the plants which are perennial, evergreen, woody and bear naked seeds.
Answer:
(a) Diatoms, dinoflagellates.
(b) The animals possess an exoskeleton of spines over the body.
(c) Bryophytes, thallophytes
(d) Gymnosperms.
Question 4.
(a) List two distinguishing features between poriferan and coelenterate animals.
(b) Give reason to justify the following statements
- Platypus and Echidna lay eggs but are considered mammals.
- Crocodiles have four chambered heart but are still reptiles.
- Fore limbs of birds are modified. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Poriferans and Coelenterates
- Pores: Poriferans have a canal system with a number of inhalent pores or ostia and a single exhalent pore or osculum. Coelenterates have a single opening.
- Special Cells: Poriferans possess choanocytes or collar cells. Coelenterates have enidoblasts or stinging cells.
(b)
- Platypus and Echidna possess body hair and mammary glands like other mammals.
- Crocodiles are piokilothermic, lay cleidoic eggs, with body having cornified skin covered with scales and bony plates.
- In birds the fore limbs are modified to form wings for flight.
Question 5.
(a) What is coelom ? State its significance.
(b) Pick out the organisms that have pseudocoelom from the following : Earthworm, Pinworm, Tapeworm and Roundworm
(c) What is peculiar about the coelom of arthropods ? What is such a condition called ? Explain.
(d) To which phylum of animalia do the following belong : Octopus, Pila, Chiton and Unio. Comment on their coelom. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Coelom. It is mesoderm lined fluid-filled space that occurs between alimentary canal and body wall. Significance. Coelom suspends and gives shock proof . environment to various body organs.
(b) Pseudocoelom. Pinworm, Roundworm.
(c) Coelom of Arthropods. True coelom is reduced. Sinuses or spaces in between the organs enlarge and fuse to form blood filled cavity called haemocoel. ‘
(d) Mollusca. They posses haemocoel.
Question 6.
(a) On the basis of characteristics given below, name the phyla :
- Soft bodied animal with muscular foot, mantle and calcareous shell.
- Animals which have double layers of cells, single opening and tentacles.
- Body simple, multicellular, vase-like with pores, opening at one end.
- Largest group of animals, bilaterally symmetrical, segmented, coelomic cavity is blood filled.
(b) “Star Fish cannot be placed under the phylum of pisces.” Explain. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a)
- Mollusca
- Coelenterata
- Porifera
- Arthropoda.
(b) Star Fish is an echinoderm with spiny exoskeleton, water vascular system and tube feet. It does not have any fish-like characters (fins, gills, lateral line organs).
Question 7.
(a) Write four characteristic features of protochordates.
(b) State reasons for the following :
- Tapeworms do not have digestive tract.
- Frogs have both skin and lungs for breathing.
- Whale is a mammal, not a fish. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Characteristic Features of Protochordates.
- Single layered epidermis,
- Occurrence of notochord at least in some stage.
- There is a dorsal hollow nerve cord,
- Gill slits are present,
- A post-anal tail is found.
(b)
- Tapeworm lives in that part of human intestine which contains digested absorbable food.
- Frog has a smooth moist skin richly supplied with blood vessels for cutaneous respiration. Being amphibian it also possesses lungs for breathing over land.
- Whale has pulmonary respiration, four-chambered heart, mammary glands and other traits of mammals. It appears fish like because it lives in water and has a body structure suitable for swimming.
Question 8.
Classify vertebrates in five classes giving two characteristics and an example for each. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
The five classes of vertebrates are pisces, amphibia, reptilia, aves and mammalia.
- Pisces: Stream-lined scale covered body with 2-chambered heart, gills and fins, e.g. Labeo.
- Amphibia: Smooth scale-less body surface with mucous glands, 3-chambered heart and two pairs of limbs, e.g., Frog.
- Reptilia: Dry scale covered skin, incompletely four chambered heart, e.g., Wall Lizard.
- Aves: Body covered with feathers, fore limbs modified into wings and jaws modified into horny toothless beak, e.g., Pigeon.
- Mammalia: Hair covered body with integumentary glands, mammary glands in females, e.g., Tiger.
Question 9.
Classify kingdom Plantae into five groups giving one characteristic feature and two examples of each group.
(CCE 2012, 2015)
Answer:
Plantae is divisible into five groups of thallophyta, bryophyta, pteridophyta, gymnosperms and angiosperms.
- Thallophyta: Simple undifferentiated plant body with unicellular reproductive organs lacking an embryo stage, e.g. Spirogyra, Chara.
- Bryophyta: Simple, amphibious with gametophytic plant body and parasitic sporophyte, e.g., Marchantia, Moss.
- Pteridophyta: Seedless, differentiated, vascular sporophytic plant body with small independent gametophyte, e.g. Lycopodium, Fern.
- Gymnosperms: Vascular plants with exposed or naked seeds, e.g., Pinus, Cycas.
- Angiosperms: Flowering plants with fruits enclosing seeds, e.g. Maize, Rose.
Question 10.
Cockroach, spider and prawn are placed under phylum arthropoda. State the reason for this. Write three other distinct features of this phylum. Give another example of an aquatic arthropod and terrestrial arthropod. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Cockroach, spider and prawn are included in phylum arthropoda because they are segmented triploblastic bilaterally symmetrical animals having jointed appendages.
Other features.
- Chitnous exoskeleton,
- Body divided into head, thorax and abdomen with head and thorax fused in some groups.
- Coelom is reduced. Haemocoel with open circulatory system present.
Question 11.
Aquatic Arthropod. Cancer (Crab). Terrestrial arthropod, Silver Fish.
(a) What is the basis of major division of kingdom plantae ?
(b) What was the modification introduced by Woese in kingdom Monera ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Presence or absence of seeds or distinct reproductive structures dividing plantae into phanerogamae (covered embryo) and cryptogamae (naked embryo or seeds absent),
(b) Woese (1977, 1994) has divided kingdom monera and created two independent kingdom of Eubacteria and Archaea (formerly archaebacteria) on the basis of cell wall, cell membrane and RNA structure.
Question 12.
The following is a list of invertebrates. Classify them into different phyla giving one characteristic morphological feature to justify your classification : (CCE 2012)
(a) Star Fish
(b) Nereis
(c) Housefly
(d) Sycon
(e) Planaria.
Answer:
(a) Star Fish: Echinodermata. Spiny skinned with tube j feet,
(b) Nereis: Annelida. Metameric segmentation, true j coelom with closed vascular system,
(c) Housefly, Arthropoda: Chitinous exoskeleton with jointed appendages,
(d) Sycon: Porifera. Sedentary diploblastic animals with ostia, osculum and canal system,
(e) Planaria: Platyhelminthes. Triploblastic, acoelomate.
Question 13.
What are the five kingdoms of Whittaker ? Give the most important characteristic feature of each kingdom.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Monera: Prokaryotic organisms.
- Protista: Unicellular eukaryotic organisms.
- Fungi: Nonchlorophyllous, spore producing heterotrophs j with cell wall having chitin and glycogen as reserve food,
- Plantae: Photosynthetic organisms having plastids and cellulose cell wall.
- Animalia: Wall-less heterotrophic organisms with holozoic nutrition.
Question 14.
Name the five classes of vertebrates. Compare any two on the basis of their
- Habitat
- Covering of skin
- Respiratory organs
- Chambers of heart
- Reproduction. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Pisces, amphibia, reptilia, aves and mammalia.
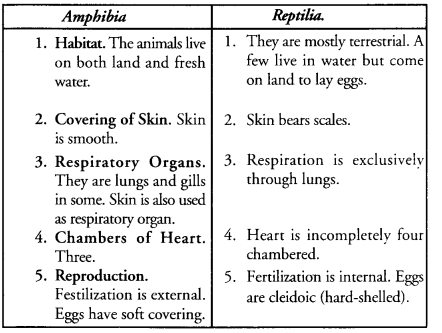
Question 15.
(i) To which division of plantae do algae belong ? Write one characteristic of the division. Give two examples.
(ii) Name the group
(a) Which includes unicellular eukaryotic organisms.
(b) In which mode of nutrition is saprophytic
(c) In which seeds are not enclosed in fruit.
(iii) Write scientific names of
(a) Peacock
(b) Neem
(c) Potato.
(iv) Name the division whose members are called amphibians of plant kingdom,
(v) Write one difference between thallophytes and bryophytes with one example of each. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(i) Algae belong to division thallophyta. Thallophyta is characterised by single celled non-jacketed reproductive structures without an embryo stage, e.g., Ulothrix, Chara.
(ii)
(a) Protista
(b) Fungi
(c) Gymnosperms.
(iii)
(a) Peacock. Pavo cristatus
(b) Neem. Azadirachta indica
(c) Potato. Sotanum tuberosum
(iv) Bryophyta
(v) Reproductive organs are nonjacketed and unicellular in thallophyta (e.g., Ulothrix). They are jacketed and multi-cellular in bryophyta, e.g., Marchantia.
Question 16.
(a) Differentiate between fungi and plantae
(b) Mention the basis of classification among plants to different levels. (CCE 2012, 2015)
Answer:
(a) Differences

(b)
- Presence or absence of conspicuous reproductive organs— phanerogamae and cryptogamae.
- In cryptogamae, undifFerentiated plant body-thallophyta.
- In cryptogamae, plant body differentiated without vascular tissues-bryophyta while with vascular tissues-pteridophyta
- In phanerogamae, gymnosperms if seeds are naked and angiosperms if seeds are enclosed inside fruits.
Question 17.
(a) State two uses of classifying plants and animals into different categories,
(b) List two characteristic features of fungi. Some fungal species live in permanent mutually dependent relationship with cyanobacteria. What is this relationship called ? Where are they found ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a)
- Classifying plants and animals into categories gives us an idea of whole range of diversity found in them
- It help in studying inter-relationships and evolution of various groups.
(b) Characteristics of Fungi.
- The body called mycelium is made of achlorophyllous threads.
- Cell wall contains chitin.
- Nutrition is heterotrophic and absorptive,
- Reserve food is glycogen and oil.
Fungal Relationship With Some Blue-Green Algae or Cyanobacteria.
Symbiosis or mutualism. The dual organisms grow on rocks and tree trunks. They are called lichens.
Occurrence. Rocks, bark of trees, ice.
Question 18.
(a) State four characteristic features of mammals.
(b) Identify the group to which the following belong :
- Plants with body differentiation into stem and leaf-like structures and hidden reproductive organs,
- Plants with tap root system and two cotyledons in the seed,
- Plants that do not have well differentiated body designs.
(CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Mammals are viviparous i.e., adult females give birth to young ones.
(b)
- Bryophytes
- Dicotyledons
- Thallophytes.
Question 19.
(a) State two characteristic features of phylum arthropoda
(b) Identify the organisms on the basis of the following features :
- Egg laying mammal
- A reptile with four chambered heart
- A nematode causing elephantiasis. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a)
- Presence of jointed appendages.
- Occurrence of chitinous exoskeleton,
(b)
- Echidna
- Crocodile
- Wuchereria.
Question 20.
(a) How do poriferan animals differ from coelenterate animals ?
(b) Identify the kingdom on the basis of following features :
- Multicellular eukaryotes without cell wall
- Unicellular eukaryotes
- Multicellular eukaryotic autotrophs. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a)
| Poriferans | Coelenterates |
| 1. Organisation. It is of cellular level. | It is of tissue level. |
| 2. Pores. A number of inhalent pores or ostia and a single exhalent pore or osculum are present. | There is a single opening. |
| 3. Digestion. It is intracellular. | It is both intracellular and intercellular. |
| 4. Muscle and Nerve Cells. They are absent. | Primitive muscle and nerve cells appear for the first time in coelenterates. |
| 5. Appendages. They are absent. | Appendages are represented by tentacles. |
| 6. Special Cells. The special cells are choanocytes or collar cells. | Special cells are cnidoblasts. |
(b)
- Animalia
- Protista
- Plantae.
A person enters a museum and observes animal specimens. He looks at one marked ‘Salamander’ and calls it a lizard.
Question 21.
How will you explain to him that salamanders and lizards belong to different classes by listing out at least four features and give one example each. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Salamander belongs to amphibia and lizard to reptilia.
| Amphibia | Reptilia |
| 1. Skin. It is glandular smooth and moist. | Skin is non-glandular, dry and keratinised. |
| 2. Scales. They are absent. | Scales are present over the body. |
| 3. Claws. Digits do not possess claws. | Digits end in claws. |
| 4. Heart. It is three chambered. | Heart is incompletely four chambered. |
| 5. Fertilization. It is external. | Fertilization is internal. |
| 6. Membranes. Extra-embryonic membranes are absent. | Extra-embryonic membranes are present. |
| 7. Eggs. They have a soft covering. | They have a hard covering or shell. |
| Examples. Frog, Toad. | Examples. Lizards, Snakes, Tortoise. |
Question 22.
Create a flow chart to show the classification of four eukaryotic kingdom ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
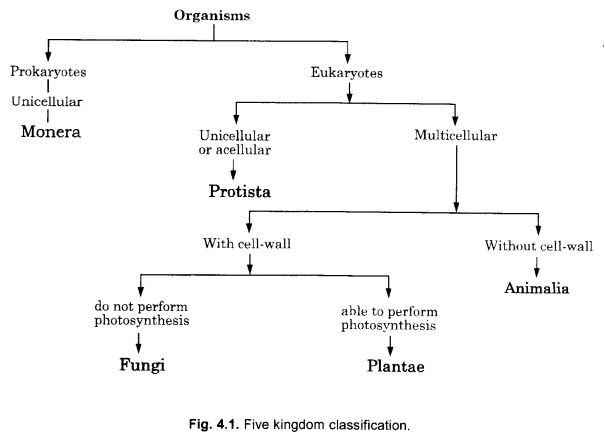
Question 23.
Give the scientific and common name of an organism that possesses the following features :
(a) Are found both on land and water,
(b) Lay eggs on land.
(c) Skeleton made of cartilage,
(d) Hair on their body.
(e) Cold blooded. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(a) Amphibians. Frog – Rana tigrina
(b) Aquatic Reptiles. Crocodile – Crocodylus.
(c) Chondrichthyes – Dog Fish – Scoliodon.
(d) Mammalia. Monkey – Macaca.
(e) Poikieothermous. Garden Lizard – Calntes.
Question 24.
Identify the phylum of animalia in which the animals have
(a) Apseudocoelons
(b) A water driven tube system.
(c) Jointed legs,
(d) Pores in the body leading to a canal system,
(e) Notochord at some stage of their life.
(CCE 2014, 2015)
Answer:
(a) Nemathelminthes
(b) Echinodermata
(c) Arthropoda
(d) Porifera
(e) Chordata (Protochordata).
Question 25.
Prove that Labeo rohita is a chordate. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Labeo rohita is a chordate because it possesses all the chordate characters.
Diagnostic Characteristics:
- Notochord (Gk. noton—back, chorde—cord). It is a long rod-like structure that develops between dorsal nervous system and gut. Notochord functions as a support structure that provides points for attachment to muscles. In higher chordates, notochord is transformed into cranium and vertebral column.
- Dorsal Hollow Nerve Cord. It occurs above the notochord. In higher chordates it gets transformed into brain and spinal cord.
- Pharyngeal Gill Slits (Gill Pouches). They are paired respiratory structures which remain functional throughout life in fishes and some amphibians. In others they occur only in embryo.
- Post-anal Tail. It occurs in most chordates for balancing, protection of genital and anal regions.
Question 26.
Assign appropriate class/phylum/division to the following :
(a) Salamonder
(b) Flying lizard
(c) Ostrich
(d) Bat
(e) Herdmania
(f) Wuchereria
(g) Ulva
(h) Marchantia
(i) Marsilea
(j) Ipomoea. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(a) Salamander. Chordata-Amphibia.
(b) Flying lizard. Chordata-Reptilia.
(c) Ostrich. Chordata-Aves
(d) Bat. Chordata—Mammalia,
(e) Herdmania. Chordata- Protochordata- Urochordata.
(f) Wuchereria. Nemathelm- inthes-Nematoda.
(g) Ulva. Thallop.hyta-Algae.
(h) Marchantia. Bryophyta
(i) Marsilea. Pteridophyta.
(j) Ipomoea. Spermatophyta – Angiospermae – Dicotyledoneae.
Question 27.
State one difference between each of the following :
(a) Thallophyta and Bryophyta
(b) Bryophyta and pteridophyta
(c) Pteridophyta and gymnosperms
(d) Gym¬nosperms and angiosperms
(e) Monocotyledonous and di¬cotyledonous plants. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Thallophyta and Bryophyta. In thallophyta the reproductive organs are unicellular, non-jacketed with no embryo stage. In bryophyta the sex organs are multicellular, jacketed with an embryo stage.
(b) Bryophyta and Pteridophyta. In bryophyta the plant body is non-vascular, gametophytic with parasitic sporophyte. In pteridophyta the plant body is vascular and sporophytic while gametophyte is small and independent.
(c) Pteridophyta and Gymnosperms. Pteridophyta has seedless vascular plants while gymnosperms have naked seeded vascular plants.
(d) Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Thallophyta and Bryophyta In thallophyta the reproductive organs are unicellular, non-jacketed with no embryo stage. In bryophyta the sex organs are multicellular, jacketed with an embryo stage.
(e) Monocotyledonous and Dicotyledonous Plants. Mono- cotyledonous plants have parallel venation, fibrous roots and single cotyledon in seeds. Dicotyledonous plants have reticulate venation, tap roots and two cotyledons in seeds.
Question 28.
Explain the meaning of the terms and give an example in each of the following :
(a) Symbiotic relationship
(b) Cotyle¬dons
(c) Cryptogam
(d) Saprophytic
(e) Prokaryotic.
(CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Symbiotic Relationship. It is a mutually beneficial obligatory relationship between two organisms, e.g. Lichen.
(b) Cotyledons. They are seed leaves present over the embryo axis below the plumule in seeds. A single cotyledon occurs in the seeds of monocots (e.g., Maize) while two cotyledons occur in the seeds of dicots, (e.g., Pea).
(c) Cryptogam. It is a seedless plant with incospicuous reproductive organs and requiring external water for fertilization. e.g. : Ferns, Moss.
(d) Saprophytic. It is an organism that feeds on organic re-mains by the process of external diagestion, e.g., Rhizopus.
(e) Prokaryotic. It is a primitive organism that lacks membrane covered organelles and an organized nucleus, e.g., Escherichia coli.
Question 29.
Associate the following features with appropriate organisms and their kingdom (in ii and iv), division (in i) and phylum (in iii and v) :
- Presence of pyrenoids.
- Presence of heterocysts
- Presence of genital papillae and anus
- Presence of chloroplast and flagella
- Presence of palp and parapodia. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
- Presence of Pyrenoids. Spirogyra—Thallophyta (division).
- Presence of Heterocysts. Nostoc— Monera (kingdom).
- Presence of Genital Papillae and Anus. Earthworm— Annelida (phylum)
- Presence of Chloroplast and Flagella. Euglena—Protista (Kingdom)
- Presence of Palps and Parapodia. Nereis—Annelida (Phylum).
Question 30.
Study the figure and answer the following :
(a) Label A and B.
(b) Identify the organism and its kingdom.
(c) Name two organisms (other the one shown here) belonging to same kingdom.
Answer:
(a) A – Akinete.
B – Heterocyst.
(b) Anabaena – Monera.
(c) Nostoc, Clostridium, Escherichia.
Question 31.
Differentiate between the following :
(a) Amphibia and Mammalia
(b) Arthropoda and Echinodermata
(c) Platyhelminthes and Nematoda.
(CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Amphibia and Mammalia:

(b) Difference between Arthropoda and Echinodermata :
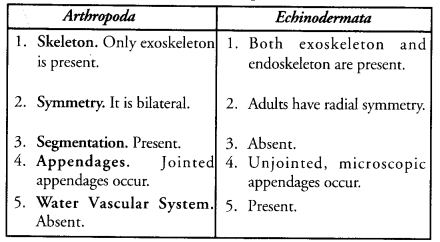
(c) Platyhelminthus and Nematoda :
| Platyhelminthes | Nematheliminthes |
| 1. Form. They are flatworms.
2. Coelom. Platyhelminthes are acoelomate. 3. Digestive Tract. It is incomplete. 4. Sexuality. Animals are hermaphrodite. |
They are cylindrical in form and are called roundworms.
Nemathelminthes are pseudocoelomate. It is complete. Animals are unisexual. |
Question 32.
(a) Identify the picture and mention the phylum and class of kingdom animalia to which it belongs. (CCE 2015)
(b) Label a, b, c, d, e, and f.
Answer:
(a) Torpedo (Electric Ray),
Phylum- Chordata,
Class- Chondrichthyes.
(b) a – Spiracle,
b – Eye,
c – Pelvic fin,
d— Dorsal fin,
e—Tail,
f— Caudal fin.
Question 33.
Give a comparative account of 5 classes of phylum vertebrata based on :
(a) Organ of breathing
(b) Chambers in heart.
(CCE 2015)
Answer:
- Pisces. Gills for breathing.
- Chambered heart.
- Amphibia. Gills, lungs and skin for breathing, 3-chambered heart.
- Reptilia. Lungs for breathing, incompletely 4-chambered heart.
- Aves. Lungs with air sacs for double respiration, four- chambered heart.
- Mammalia. Lungs for breathing, four-chambered heart.
Question 34.
Schematically illustrate the classification of phanerogams. Give two examples of plants with vascular tissues which do not produce seeds. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
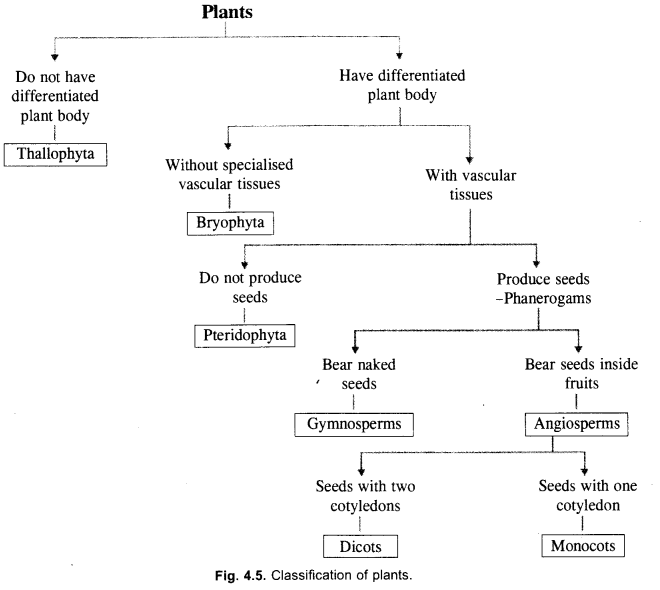
Examples of Seedless Vascular Plants. Selaginella, Fern.
Question 35.
Give a comparative account of the following :
(a) Ulothrix and Funaria
(b) Marchantia and Marsilca
(c) Fern and Pinus,
(d) Cycas and Rose,
(e) Wheat and Gram. ( CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Ulothrix and Funaria. Ulothrix is a filamentous green alga with simple structure of thallophytes. Funaria is a leafy moss plant with differentiated but non-vascular stmcture of bryophytes.
(b) Marchantia is a non-vascular little differentiated bryophyte while Marsilea is a vascular plant of pteridophyta which is differentiated into stem, leaves and roots.
(c) Fern is a seedless vascular plant belonging to pteridophyta while Pinus is a naked seeded vascular plant belonging to gymnosperms.
(d) Cycas is a naked seeded plant belonging to gymnosperms while Rose is covered seeded or fruit bearing plant belonging to angiosperms.
(e) Wheat is a monocot while Gram is a dicot.
Question 36.
Draw a diagram of Euglena and label the following parts : Flagellum, Photoreceptor, Eye Spot, Chloroplast, Nucleus, Contractile Vacuole. ( CCE 2016)
Answer:
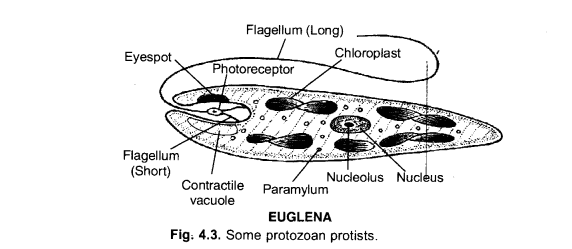
Question 37.
(a) State three distinguishing features between the animals belonging to Aves group and those in the Mammalia group.
(b) List four conventions followed while writing the scientific names ofliving organisms. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
(a) Aves and Mammalia.
| Aves | Mammalia |
| 1. Wings. Forelimbs are modified into wings. | Wings are absent except in bats. |
| 2. Feathers and Scales. The body is covered with feathers and scales. | Feathers and scales are absent. |
| 3. Skin Glands. Skin is dry. Only a single preen gland is present. | Skin bears a number of sweat and oil glands. |
| 4. Mammary Glands. They are absent. | Female possesses mammary glands for feeding the young |
| 5. Diaphragm. A diaphragm is absent. | A partition called diaphragm is present between abdomen and thorax. |
| 6. Beak. A toothless beak is present. | Jaws do not form a beak. Teeth are present. |
| 7. Bones. They are hollow or pneumatic. | Bones do not possess air cavities. |
| 8. Larynx/Syrinx. Larynx is non-functional. Instead syrinx is present. | Larynx is functional. Syrinx is absent. |
| External air sacs do not occur over lungs. | |
| 9. Air Sacs. Lungs possess external air sacs. | |
| 10. Yolk. Eggs possess a lot of yolk (macrolecithal). | Eggs have little yolk (alecithal). |
| 11. Reproduction. Birds are oviparous. | Mammals are viviparous with the exception of a few species. |
(b) Binomial nomenclature is a scientific system of providing distinct and proper two word name to each and every organism.
Conventions:
- It consists of two words, first generic (like noun) and second specific (species).
- Generic name has first letter capital while specific word begins with small letter.
- Both are derived from latin language or are latinised.
- They are printed in italics or are underlined separately in hand-written form.
Question 38.
Identify the phylum/division
- They have kidney like organs for excretion
- They reproduce by spores and have specialised tissue for conduction of water and other substances,
- Their body is dorsiventrally flattened.
(CCE 2016)
Answer:
- Mollusca
- Pteridophyta
- Platyhelminthes.
Question 39.
A plant specimen was found with rhizoids instead of differentiated roots,
(a) Identify the group to which it belongs,
(b) Write any two characteristics of this group
(c) Draw the diagram of a plant belonging to this group.
(CCE 2016)
Answer:
(a) Bryophyta
(b) Aves, Reptilia
(c)
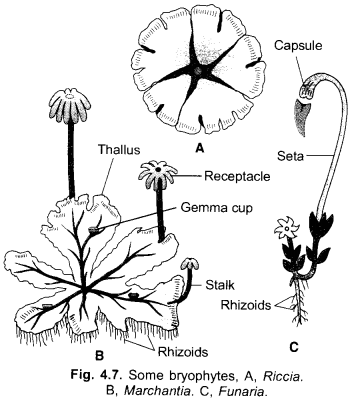
Question 40.
Identify the phylum of kingdom animalia in which the animal has
(a) A pscudocoelom
(b) A water driven tube system
(c) Jointed legs
(d) Pores in the body leading to a canal system
(d) Notochord at some stages of their life. ( CCE 2017)
Answer:
(a) Pseudocoelom—Nematoda
(b) A water driven tube system—Echinodermata
(c) Jointed legs—Arthropoda
(d) Pores in the body leading to a canal system—Porifera
(e) Notochord at some stages of their life—Protochordata.
Question 41.
(a) Which division of plants is called the amphibians of plant kingdom ?
(b) What are characteristics of above division ? (any three)
(c) Give two examples of this division of plant kingdom. (CCE 2017)
Answer:
(a) Bryophyta
(b)
- Very simple nonvascular amphibious land plants
- Gametophytic plant body fixed by means of rhizoids
- Sporophyte parasitic over the gametophyte
(c) Marchantia, Funaria.
Question 42.
(a) What is the largest phylum of animal kingdom.
( b) You are given Leech, Nereis, Scolopendra, Prawn and Scorpion. All of them have segmented body organisation. Will you classify them in are group. ( CCE 2017)
Answer:
(a) Largest Phylum. Arthropoda.
(b) Nereis and Leech belong to annelids while the other three belong to arthropoda. Annelids have unjointed appendages. Arthropods have jointed appendages. They also possess chitinous exoskeleton and open circulatory system. Annelids do not possess chitinous exoskeleton. They have closed circulatory system.
Question 43.
Complete the flow chart using appropriate features of groups : (CCE 2017)
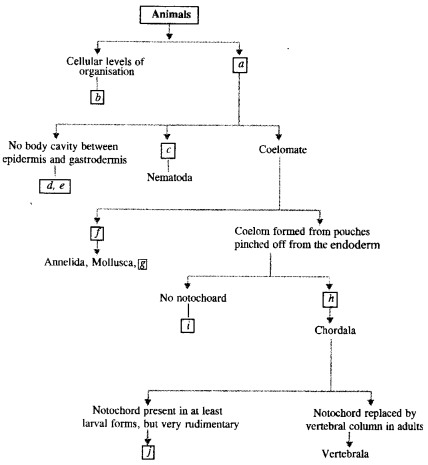
Answer:
a—Tissue level of organisation,
b—Porifera.
c—Pseudocoelom,
d—Coelenterata.
e—Platyhelminthes.
f—Mesodermal cells develop from a single cell during growth of the embryo
g—Arthropoda.
h—Notochord present,
i—Echinodermata.
j—Protochoardata.
Hope given Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms are helpful to complete your science homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online science tutoring for you.