RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 16 Probability Ex MCQS
These Solutions are part of RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions. Here we have given RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 16 Probability MCQS
Other Exercises
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 16 Probability Ex 16.1
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 16 Probability Ex 16.2
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 16 Probability Ex VSAQS
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 16 Probability Ex MCQS
Question 1.
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
If a digit is chosen at randon from the digits 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, then the probability that it is odd, is
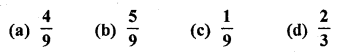
Solution:
Total number of digits from 1 to 9 (n) = 9
Numbers which are odd (m) = 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 = 5
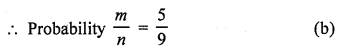
Question 2.
In Q. No. 1, the probability that the digit is even, is
![]()
Solution:
Total numbers of digits from 1 to 9 (n) = 9
Numbers which are even (m) = 2,4, 6, 8 = 4
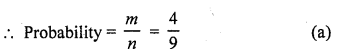
Question 3.
In Q. No. 1, the probability that the digit is a multiple of 3 is
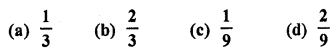
Solution:
Total numbers of digits for 1 to 9 (n) = 9
Number divisible by 3 (m) = 3, 6, 9 = 3
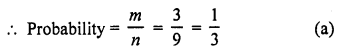
Question 4.
If three coins are tossed simultaneously, then the probability of getting at least two heads, is
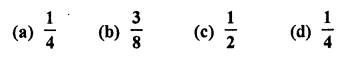
Solution:
Three coins are tossed simultaneously, then possible events will be (n) = 2 x 2 x 2 = 8
The results will be
(HHT), (HTH), (THH), (THT), (TTH), (HTT), (HHH), (TTT)
∴ Probability of getting at least two heads are

Question 5.
In a single throw of a die, the probability of getting a multiple of 3 is
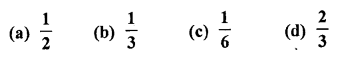
Solution:
A die is thrown, the possible number of events (n) = 6
Now multiple of 3 are 3, 6 which are 2
∴ m = 2
![]()
Question 6.
The probability of guessing the correct answer to a certain test questions is \(\frac { x }{ 12 }\) If the probability of not guessing the correct answer to this question is \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) , then x =
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 6
Solution:

Question 7.
A bag contains three green marbles, four blue marbles and two orange marbles. If a marble is picked at random, then the probability that it is not an orange marble is
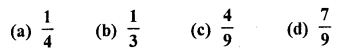
Solution:
In a bag, there are 3 green, 4 blue and 2 orange marbles
∴ Total marbles (n) = 3 + 4 + 2 = 9
No. of marbles which is not orange =3+4=7
∴m = 7
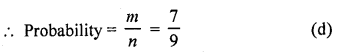
Question 8.
A number is selected at random from the . numbers 3, 5, 5, 7, 7, 7, 9, 9, 9, 9. The probability that the selected number is their average is
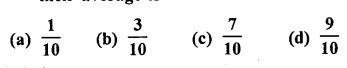
Solution:
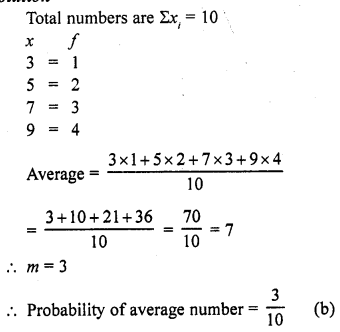
Question 9.
The probability of throwing a number greater than 2 with a fair dice is
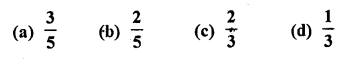
Solution:
∵ A dice has 6 numbers
∴ n = 6
Numbers greater than 2 are 3, 4, 5, 6
∴ m = 4
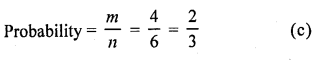
Question 10.
A card is accidently dropped from a pack of 52 playing cards. The probability that it is an ace is
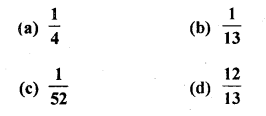
Solution:
No. of card in a pack (n) = 52
A card is drawn at random
∴ No. of ace (m) =4
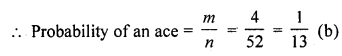
Question 11.
A number is selected from numbers 1 to 25. The probability that it is prime is

Solution:
A number is selected from the numbers 1 to 25
Probability of prime number which are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23 = 9
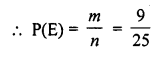
Question 12.
Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event?
(a) \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
(b) -1.5
(c) 15%
(d) 0.7
Solution:
-1.5 cannot be the probability as it is always from 0 to 1 which is always positive (b)
Question 13.
If P (E) = 0.05, then P (not E) =
(a) – 0.5
(b) 0.5
(c) 0.9
(d) 0.95
Solution:
P (E) = 0.05
∵ P (E) + P (not E) = 1
∴ P (not E) = 1 – P (E) = 1 – 0.05 = 0.95 (d)
Question 14.
Which of the following cannot be the probability of occurrence of an event ?
(a) 0.2
(b) 0.4
(c) 0.8
(d) 1.6
Solution:
Probability of occurrence of an event = 1.6 (d)
Question 15.
The probability of a certain event is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(d) No existent
Solution:
Probability of a certain event = 1 (b)
Question 16.
The probability of an impossible event is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(d) Non – existent
Solution:
Probability of an impossible event = 0 (a)
Question 17.
Aarushi sold 100 lottery tickets in which 5 tickets carry prizes. If Priya purchased a ticket, what is the probability of Priya winning a prize ?

Solution:
No. of lottery tickets = 100
No. of tickets carrying prizes = 5
∴ Probability of ticket buying a prized one

Question 18.
A number is selected from first 50 natural numbers. What is the probability that it is a multiple of 3 or 5 ?


Solution:
Total numbers = 1 to 50 = 50
Numbers which are multiples of 3 or 5, are 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 12, 15, 18, 20, 21, 24, 25, 27, 30, 33, 35, 36, 39, 40, 42, 45, 48, 50 = 23
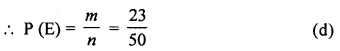
Question 19.
A month is selected at random in a year. The probability that it is March or October, is
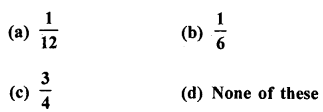
Solution:
No. of months in a year = 12
Probability of being March or October = \(\frac { 2 }{ 12 }\)

Question 20.
From the letters of the word “MOBILE”, a letter is selected. The probability that the letter is a vowel, is

Solution:
No. of total letters in the word MOBILE = 6
No, of vowels = o, i, e = 3

Question 21.
A die is thrown once. The probability of getting a prime number is
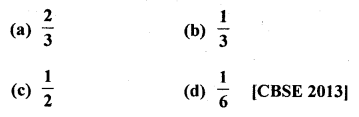
Solution:
Prime number on a die are 2, 3, 5
∴ Probability of getting a prime number on the face of the die

Question 22.
The probability of getting an even, number, when a die is thrown once is
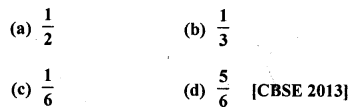
Solution:
Even number on a die are 2, 4, 6 3
∴ Probability (P) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 6 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (a)
Question 23.
A box contains 90 discs, numbered from 1 to 90. If one disc is drawn at random from the box, the probability that it bears a prime number less than 23, is
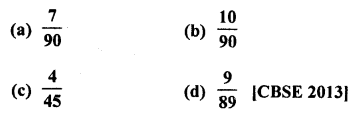
Solution:
Number of discs in a box = 90
Numbered on it are 1 to 90
Prime numbers less than 23 are = 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19 = 8
Probability of a number being a prime less
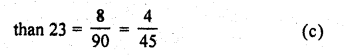
Question 24.
The probablity that a number selected at random from the numbers 1, 2, 3, …..,15 is a multiple of 4, is
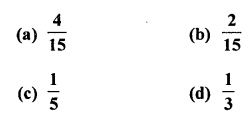
Solution:
Total outcomes = 15
(∵15 numbers are given)
Favourable outcomes for a multiple of 4 = 3 (i.e. 4, 8, 12)
∴ Probability of selecting a number which is
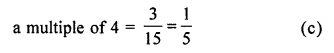
Question 25.
Two different coins are tossed simultaneously. The probability of getting at least one head is

Solution:
When two different coins are tossed simultaneously, then total possibilities = 4,
i.e. (H, H), (H, T), (T, H), (T, T)
Number of favourable outcomes for at least one head = 3, i.e. (H, T), (T, H), (T, H).

Question 26.
If two different dice are rolled together, the probability of getting an even number
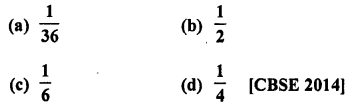
Solution:
Rolling two different dice,
Number of total events = 6 x 6 = 36
Number of even number on both dice are 22, 24, 26, 42, 44, 46, 62, 64, 66 = 9
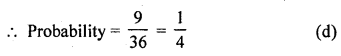
Question 27.
A number is selected at random from the numbers 1 to 30. The probability that it is a prime number is

Solution:
Total outcomes of selecting a number from 30 numbers = 30
Favourable numbers (prime numbers) = 10,
i.e., (2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29)
∴ Probability of selecting a prime number

Question 28.
A card is drawn at random from a pack of 52 cards. The probability that the drawn card is not an ace is
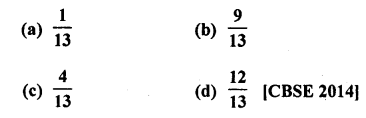
Solution:
Total events = 52 cards
Probability of card which is not in ace Number of card = 52 – 4 = 48
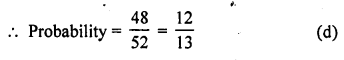
Question 29.
A number x is chosen at random from the numbers -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3 the probability that |x| < 2 is


Solution:
Total possible number of events (n) = 7
Now |x| <2
x < 2 or -x <2 ⇒ x > -2
∴ x
⇒ x = 1, 0 , -1, -2, -3 or x = -1, 0, 1 , 2, 3
∴ x = -1,0,1
∴ m = 3
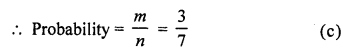
Question 30.
If a number x is chosen from the numbers 1,2,3 and a number is selected from the numbers 1, 4, 9, then P (xy < 9)

Solution:
Numbers x = 1, 2, 3 and y = 1, 4, 9
Now xy= 1,4, 9, 2, 8, 18, 3, 12, 27 = 9
∴ n = 9
and xy < 9 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 8
∴m = 5

Question 31.
The probability that a non-leap year has 53 Sundays, is

Solution:
In a non leap years, number of days = 365 i.e. 52 weeks + 1 day
∴Probability of being 53 Sundays
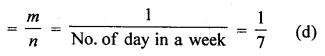
Question 32.
In a single throw of a pair of dice, the probability of getting the sum a perfect square is

Solution:
A pair of dice is thrown simultaneously
∴ No. of total events (n) = 6 x 6 = 36
Which are
(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6)
(2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6)
(3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6)
(4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6)
(5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6)
(6, 1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6)
∴Event whose sum is a perfect square are (1,3), (2, 2), (3, 1), (3, 6), (4, 5), (5, 4), (6, 3)
∴m = 7
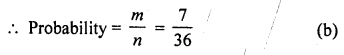
Question 33.
What is the probability that a non-leap year has 53 Sundays ?
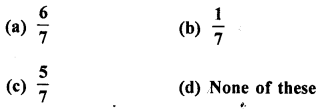
Solution:
No. of days in a non leap year = 365
∴No. of days more than complete weeks = 1 day
∴ Probability of 53 Sundays in a non-leap year

Question 34.
Two numbers ‘a’ and ‘6’ are selected successively without replacement in that order from the integers 1 to 10. The probability that \(\frac { a }{ b }\) is an integer, is

Solution:
a and b are two number to be selected from the integers = 1 to 10 without replacement of a and b
i.e., 1 to 10 = 10
and 2 to 10 = 9
No. of ways = 10 x 9 = 90
Probability of \(\frac { a }{ b }\) where it is an integer
∴ Possible event will be
= (2, 2), (3, 3), (4, 2), (4, 4), (5, 5), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 6), (7, 7), (8, 2), (8, 4), (8, 8), (9, 3), (9, 9), (10, 2), (10, 5), (10, 10), = 17

Question 35.
Two dice are rolled simultaneously. The probability that they show different faces is

Solution:
Two dice are rolled simultaneously
∴ No. of total events = 62 = 36
∴ No. of different face can be
= 36 – (same faces)
Same face are (1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (4, 4), (5, 5) and (6, 6) = 6
∴ 36-6 = 30
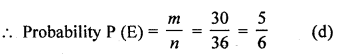
Question 36.
What is the probability that a leap year has 52 Mondays ?

Solution:
No. of days in a leap year = 366
No. of Mondays = 52
Extra days = 366 – 52 x 7
= 366 – 364= 2
∴ Remaining days in the week = 7-2 = 5
∴Probability of being 52 Mondays in the leap

Question 37.
If a two digit number is chosen at random, then the probability that the number chosen is a multiple of 3, is

Solution:
Total number of two digit numbers are 10 to 99
= 99 – 9 = 90
Multiples of 3 will be 12, 15, 18, 21,…. 99
= 33 – 3 = 30
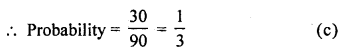
Question 38.
Two dice are thrown together. The probability of getting the same number on both dice is

Solution:
2 dice are thrown together
∴Number of total outcomes = 6 x 6 = 36
Number which should come together are (1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (4, 4), (5, 5), (6, 6)
= 6 pairs
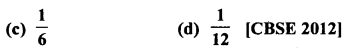
Question 39.
In a family of 3 children, the probability of having at least one boy is
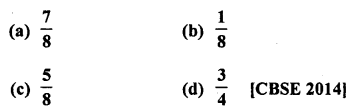
Solution:
Number of children in a family = 3
There can be,
bbb.bbg, bgg and ggg
∴Probability of a family having atleast one boy = \(\frac { 3}{ 4 }\) (d)

Question 40.
A bag contains cards numbered from 1 to 25. A card is drawn at random from the bag. The probability that the number on this card is divisible by both 2 and 3 is
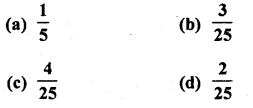
Solution:
Total number of outcomes = 25
The number which is divisible by both 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18, 24.
Number of favourable outcomes = 4 Probability of number which is divisible by both 2 and 3 = \(\frac { 4 }{ 25 }\) (c)
Hope given RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 16 Probability MCQS are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.