RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables MCQS
These Solutions are part of RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions. Here we have given RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables MCQS
Other Exercises
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.1
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.2
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.3
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.4
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.5
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.6
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.7
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.8
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.9
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.10
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.11
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables VSAQS
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables MCQS
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following.
Question 1.
The value of k for which the system of equations. kx – y = 2, 6x – 2y = 3 has a unique solution is
(a) = 3
(b) ≠ 3
(c) ≠ 0
(d) = 0
Solution:
(b)
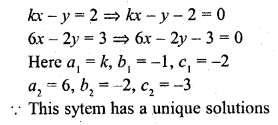
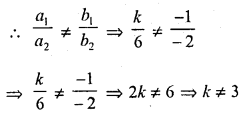
Question 2.
The value of k for which the system of equations 2x + 3y = 5, 4x + ky = 10 has infinitely number of solutions, is
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 6
(d) 0
Solution:
(c)

Question 3.
The value of k for which the system of equations x + 2y – 3 = 0 and 5x + ky + 1 = 0 has no solution, is
(a) 10
(b) 6
(c) 3
(d) 1
Solution:
(a)
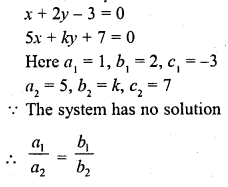
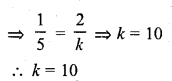
Question 4.
The value of k for which the system of equations 3x + 5y = 0 and kx + 10y = 0, has a non-zero solution, is
(a) 0
(b) 2
(c) 6
(d) 8
Solution:
(c)
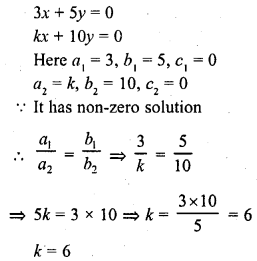
Question 5.
If the system of equations
2x + 3y = 7
(a + b) x + (2a – b) y = 21
has infinitely many solutions, then
(a) a = 1, b = 5
(b) a = 5, b = 1
(c) a = -1, b = 5
(d) a = 5, b = -1
Solution:
(b)
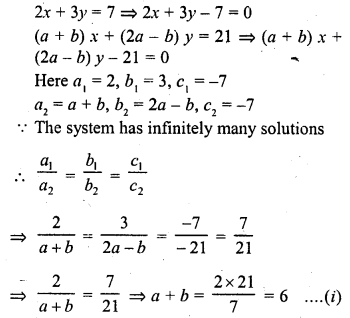
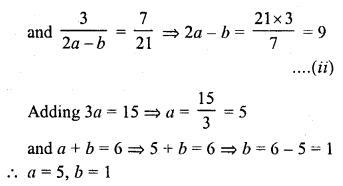
Question 6.
If the system of equations 3x + y = 1 , (2k – 1) x + (k – 1) y = 2k + 1 is inconsistant, then k =
(a) 1
(b) 0
(c) -1
(d) 2
Solution:
(d)

Question 7.
If am ≠ bl, then the system of equations
ax + by = c
lx + my = n
(a) has a unique solution
(b) has no solution
(c) has infinitely many solutions
(d) may or may not have a solution.
Solution:
(a)
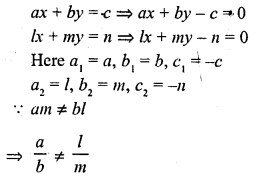
The given system as a unique solution
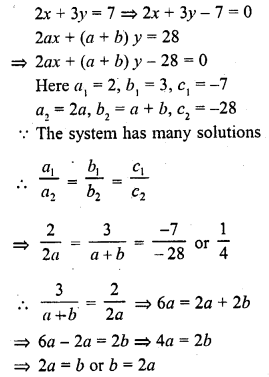
Question 8.
If the system of equations
2x + 3y = 7
2ax + (a + b) y = 28
has infinitely many solutions, then
(a) a = 2b
(b) b = 2a
(c) a + 2b = 0
(d) 2a + b = 0
Solution:
(b)
Question 9.
The value of k for which the system of equations
x + 2y = 5
3x + ky + 15 = 0 has no solution is
(a) 6
(b) – 6
(c) \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\)
(d) None of these
Solution:
(a)
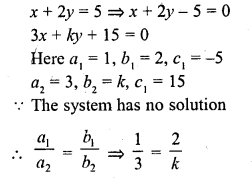
k = 6
Question 10.
If 2x – 3y = 7 and (a + b) x – (a + b – 3) y = 4a + b represent coincident lines, then a and b satisfy the equation
(a) a + 5b = 0
(b) 5a + b = 0
(c) a – 56 = 0
(d) 5a – b – 0
Solution:
(c)

Question 11.
If a pair of linear equations in two variables is consistent, then the lines represented by two equations are
(a) intersecting
(b) parallel
(c) always coincident
(d) intersecting or coincident
Solution:
(d) The system of equation is coincident
The line of there equations are intersecting or coincident
Question 12.
The area of the triangle formed by the line \(\frac { x }{ a } +\frac { y }{ b } =1\) with the coordinate axes a is
(a) ab
(b) 2ab
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) ab
(d) \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) ab
Solution:
(c)
The triangle is formed by the line \(\frac { x }{ a } +\frac { y }{ b } =1\) with co-ordinates
It will intersect x-axis at a and y-axis at y
Area of the triangle so formed = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) x a x b = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) ab
Question 13.
The area of the triangle formed by the lines y = x, x = 6 and y = 0 is
(a) 36 sq. units
(b) 18 sq. units
(c) 9 sq. units
(d) 72 sq. units
Solution:
(b)
The triangle formed by the lines y = x, x = 6 and y = 0 will be an isosceles right triangle whose sides will be 6 units
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) x 6 x 6 = 18 sq. units
Question 14.
If the system of equations 2x + 3y = 5, 4x + ky = 10 has infinitely many solutions, then k =
(a) 1
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(c) 3
(d) 6
Solution:
(d)
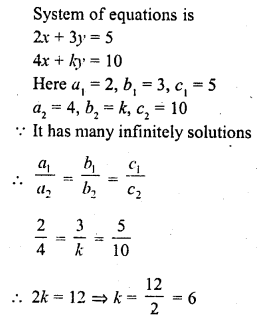
Question 15.
If the system of equations kx – 5y = 2, 6x + 2y = 7 has no solution, then k =
(a) -10
(b) -5
(c) -6
(d) -15
Solution:
(d)
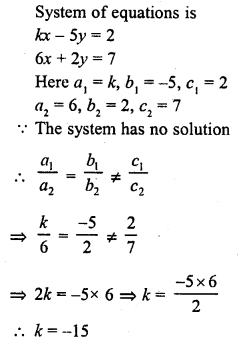
Question 16.
The area of the triangle formed by the lines x = 3, y = 4 and x = y is
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) sq. unit
(b) 1 sq. unit
(c) 2 sq. unit
(d) None of these
Solution:
(a)
The triangle is formed by three lines x = 3, y = 4 and x = y
Its sides containing the right angle will be 1 and 1 units
Area of triangle so formed = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) x 1 x 1 sq. units = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) sq. units
Question 17.
The area of the triangle formed by the lines 2x + 3y = 12, x – y – 1 = 0 and x = 0 is
(a) 7 sq. units
(b) 7.5 sq. units
(c) 6.5 sq. units
(d) 6 sq. units
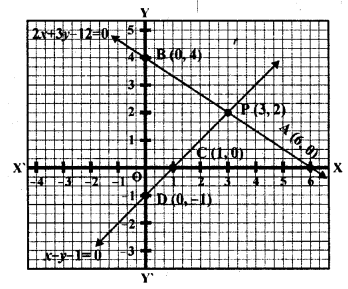
Solution:
(b) In the given graph as shown
The triangle formed by the lines
2x + 3y = 12, x – y – 1 =0 and x = 0
Its base BD = 4 + 1 = 5 units
and perpendicular from P on BD = 6 units
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) x base x height
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) x 5 x 3 = \(\frac { 15 }{ 2 }\) sq. units
= 7.5 square units
Question 18.
The sum of the digits of a two digit number is 9. if 27 is added to it, the digits of the number get reversed. The number is
(a) 25
(b) 72
(c) 63
(d) 36
Solution:
(d) Since the sum of the digits of a two-digit number is 9, therefore
x + y = 9 …(i)
It says if the digits are reversed, the new number is 27 less than the original.
Since we are looking at the number like xy, to separate them, it is actually 10x + y for x is a tens digit.
10y+ x = 10x + y + 27
Simplify it, we get 9y = 9x + 27
y = x + 3 …(ii)
Substitute (ii) into (i), we will have
x + (x + 3) = 9
=> 2x + 3 = 9
=> 2x = 6
=> x = 3
Put back into equation (i),
=> 3 + y = 9 => y = 6
The original number is 36.
Question 19.
If x = a, y = b is the solution of the systems of equations x – y = 2 and x + y = 4, then the values of a and b are, respectively
(a) 3 and 1
(b) 3 and 5
(c) 5 and 3
(d) -1 and -3
Solution:
(a) Since, x = a and y = b is the solution of the equations x – y = 2 and x + y = 4, then these values will satisfy that equations.
a – b = 2 …(i)
and a + b = 4 …(ii)
By adding (i) and (ii), we get
2a = 6
Therefore, a = 3
By putting a = 3 in (i), we get
3 – b = 2 Therefore, b = 1
Thus, a = 3 ; b = 1
Question 20.
For what value k, do the equations 3x – y + 8 = 0 and 6x – ky + 16 = 0 represent coincident lines?
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(b) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(c) 2
(d) -2
Solution:
(c)
Let 3x – y + 8 = 0 …(i)
and 6x – – ky + 16 = 0 …(ii)
Here, a1 = 3, b1 = -1, c1 = 8

Question 21.
Aruna has only ₹ 1 and ₹ 2 coins with her. If the total number of coins that she has is 50 and the amount of money with her is ₹ 75, then the number of ₹ 1 and ₹ 2 coins are, respectively
(a) 35 and 15
(b) 35 and 20
(c) 15 and 35
(d) 25 and 25
Solution:
(d) Let number of ₹ 1 coins = x
and number of ₹ 2 coins = y
Now, by given condition x + y = 50 …(i)
Also, x x 1 + y x 2 = 15
=>x + 2y = 75 …(ii)
On subtracting Eq. (i) from Eq. (ii), we get
(x + 2y) – (x + y) = 75 – 50
=> y = 25
When y = 25, then x = 25
Hope given RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables MCQS are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.