On this page, you will find Reproduction in Plants Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 12 Pdf free download. CBSE NCERT Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants will seemingly help them to revise the important concepts in less time.
CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Notes Reproduction in Plants
Reproduction in Plants Class 7 Notes Understanding the Lesson
1. The production of new individuals or young ones from their parents is known as
2. Most plants have roots, stems and These are called the vegetative parts of a plant. After a certain period of growth, most plants bear flowers.
3. There are two ways by which plants produce their offsprings; (i) asexual and (ii) sexual
4. There are several methods of asexual reproduction such as fragmentation, budding, spore formation and vegetative propagation.
5. When reproduction is through the vegetative parts of the plant, like stem, leaves or roots, it is known as vegetative propagation.
6. Artificial methods of vegetative propagation include layering, cutting and grafting.
7. Flowers are the reproductive parts of a plant.
8. The stamens are the male reproductive part and the pistil is the female productive part of the flower.
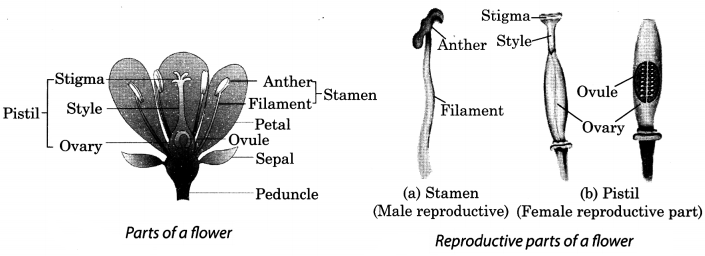
7. A stamen consists of the anther and the filament. Anther contains pollen grains which produce male gametes.
8. A pistil consists of stigma, style and ovary. The ovary contains one or more ovules. The female gamete or the egg is formed in an ovule.
9. The flowers which contain either only the pistil or the only the stamens are unisexual flowers and those that contain both stamens and pistil are called bisexual flowers. For example, corn, papaya, etc., produce unisexual flowers, whereas mustard, rose, etc. have bisexual flowers.
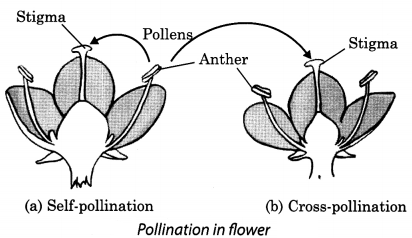
10. The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of the flower is called It takes place with the help of wind, water and insects.
11. If the pollen lands on the stigma of the same flower, it is called self-pollination [Fig. 12.3(a)],
12. When the pollen of a flower lands on the stigma of another flower of the same plant, or that of different plant of the same kind, it is called cross-pollination [Fig. 3(b)].
13. The process of fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote is called fertilisation.
14. The cell which results after fusion of the gametes is called a The zygote develops into an embryo.
15. Fruit is the mature ovary whereas ovules develops into a seed, which contains the developing embryo.
16. Seeds are dispersed to different places. That is why same kind of plants grow at different places in nature. Seed dispersal is aided by wind, water and animals.
17. Seed dispersal helps the plants in
- preventing overcrowding,
- avoiding competition for sunlight, water and minerals and
- invading new habitats.
Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Notes Important Terms
Asexual reproduction: It is the type of reproduction in which new individuals are formed without the fusion of male and female gametes. For example, fragmentation, spore formation, cutting, layering, etc.
Budding: Budding is a form of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site.
Embryo: The zygote formed after fertilisation divides many times to form a multicellular structure called an embryo inside the seed. Embryo germinates to form a plant.
Fertilisation: The process of fusion of male and female gametes (to form a zygote) is called fertilisation.
Fragmentation: A type of asexual reproduction process, in which an organism breaks up into two or more fragments or pieces that can grow into new individuals is called fragmentation.
Gametes: The male and female reproductive cells are called gametes. In plants pollen grains produce male gametes and ovules produce female gametes.
Hypha: Any of the thread-like filamentous structure in fungus is called hypha.
Ovule: It is a structure inside the ovary which contains female gamete inside it.
Pollen grain: Pollen grain is male reproductive cells which produce male gametes.
Pollen tube: The tubular outgrowth from the pollen, grain that penetrates the ovule and releases male gametes there.
Pollination: The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of a flower is called pollination.
Reproduction: It is the process by which new organisms are produced from their parents.
Seed dispersal: The spreading or transport of seed to different places is called seed dispersal.
Sexual reproduction: It is the type of reproduction in which new individuals are formed due to fusion of male and female gametes. For example, when plants reproduce with the help of seeds.
Spore: The spore is an asexual reproductive body which is covered by a hard protective coat to resist unfavourable conditions such as high temperature and low humidity.
Sporangium: It is an enclosure in which spores are formed.
Vegetative propagation: When new plants are formed from vegetative parts (roots, stems, leaves and buds) of the plants, it is known as vegetative propagation.
Zygote: In sexual reproduction, the cell form from the fusion of male and female gamete is called a zygote.