Online Education for RS Aggarwal Class 9 Solutions Chapter 11 Circle Ex 11B
These Solutions are part of RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9. Here we have given RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Chapter 11 Circle Ex 11B.
Other Exercises
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Chapter 11 Circle Ex 11A
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Chapter 11 Circle Ex 11B
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Chapter 11 Circle Ex 11C
Question 1.
Solution:
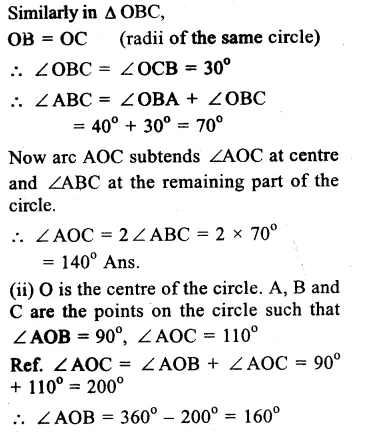
(i) O is the centre of the circle
∠OAB = 40°, ∠OCB = 30°
Join OB.
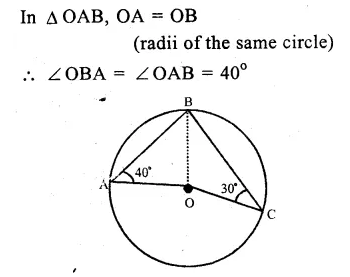
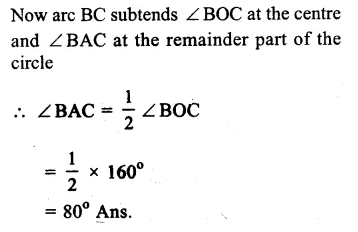
Question 2.
Solution:
O is the centre of the cirlce and ∠AOB = 70°
∵ Arc AB subtends ∠AOB at the centre and ∠ACB at the remaining part of the circle.
∵ ∠ACB = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) ∠AOB = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) x 70°
=> ∠ACB = 35°
or ∠OCA = 35°
In ∆OAC,
OA = OC (radii of the same circle)
∴ ∠OAC = ∠OCA = 35° Ans.
Question 3.
Solution:
In the figure, O is the centre of the circle. ∠PBC = 25°, ∠APB =110°
∠ APB + ∠ BPC = 180° (Linear pair)
=> 110° + ∠ BPC = 180°
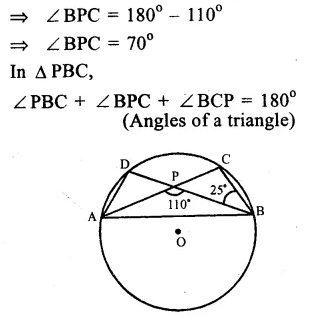
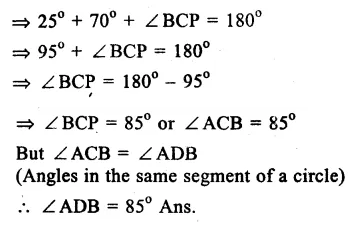
Question 4.
Solution:
O is the centre of the circle
∠ABD = 35° and ∠B AC = 70°
BOD is the diameter of the circle
∠BAD = 90° (Angle in a semi circle)
But ∠ADB + ∠ABD + ∠BAD = 180° (Angles of a triangle)
=> ∠ADB + 35° + 90° = 180°
=> ∠ADB + 125° = 180°
=> ∠ADB = 180° – 125° = 55°
But ∠ACB = ∠ADB (Angles in the same segment of the circle)
∠ACB = 55° Ans.
Question 5.
Solution:
O is the centre of a circle and ∠ACB = 50°
∴ arc AB subtends ∠ AOB at the centre and ∠ ACB at the remaining part of the circle.
∴ ∠ AOB = 2 ∠ ACB
= 2 x 50° = 100
∴ OA = OB (radii of the same circle)
∴ ∠ OAB = ∠ OBA (Angles opposite to equal sides)
Now in ∆ OAB,
∠ OAB + ∠ OBA + ∠ AOB = 180°
=> ∠ OAB + ∠ OAB + ∠ AOB = 180° (∠OAB = ∠OBA)
=> 2 ∠ OAB + 100°= 180°
=> 2 ∠ OAB = 180° – 100° = 80°
=> ∠OAB = \(\frac { { 80 }^{ o } }{ 2 } \) = 40°
Hence, OAB = 40° Ans.
Question 6.
Solution:
(i) In the figure,
∠ABD = 54° and ∠BCD = 43°
∠BAD = ∠BCD (Angles in the same segment of a circle)
∠BAD = 43°
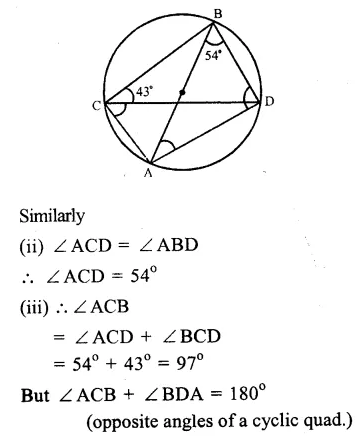
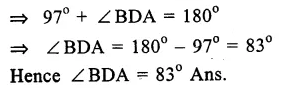
Question 7.
Solution:
Chord DE || diameter AC of the circle with centre O.
∠CBD = 60°
∠CBD = ∠ CAD
(Angles in the same segment of a circle)
∠CAD = 60°
Now in ∆ ADC,
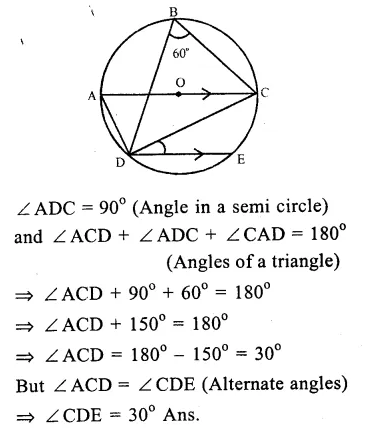
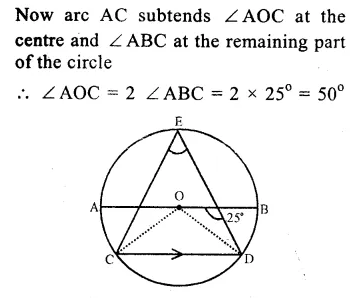
Question 8.
Solution:
In the figure,
chord CD || diameter AB of the circle with centre O.
∠ ABC = 25°
Join CD and DO.
AB || CD
∠ ABC = ∠ BCD (alternate angles)
Question 9.
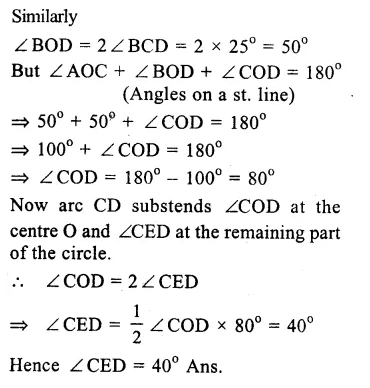
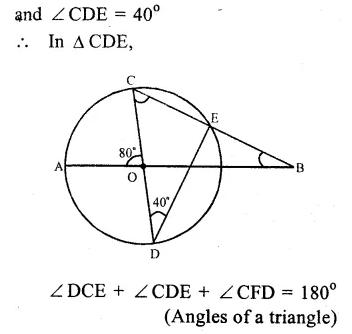
Solution:
AB and CD are two straight lines passing through O, the centre of the circle and ∠AOC = 80°, ∠CDE = 40°
∠ CED = 90° (Angle in a semi circle)
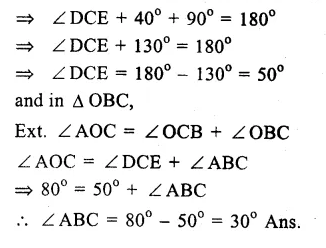
Question 10.
Solution:
O is the centre of the circle and ∠AOB = 40°, ∠BDC = 100°
Arc AB subtends ∠AOB at the centre and ∠ ACB at the remaining part of the circle
∠ AOB = 2 ∠ ACB
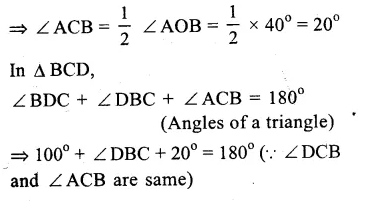
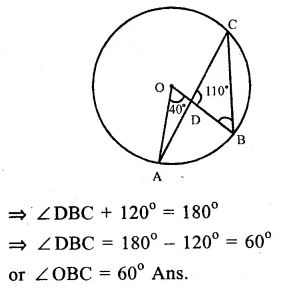
Question 11.
Solution:
Chords AC and BD of a circle with centre O, intersect each other at E at right angles.
∠ OAB = 25°. Join OB.
In ∆ OAB,
OA = OB (radii of the same circle)
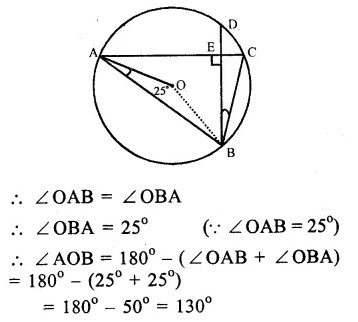

Question 12.
Solution:
In the figure, O is the centre of a circle ∠ OAB = 20° and ∠ OCB = 55° .
In ∆ OAB,
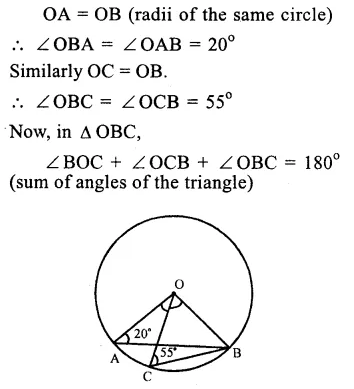
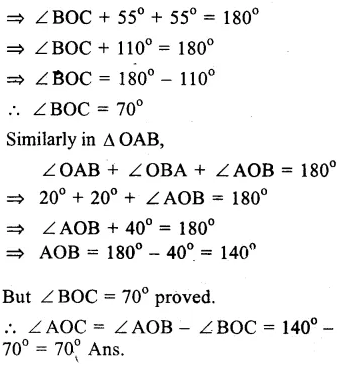
Question 13.
Solution:
Given : A ∆ ABC is inscribed in a circle with centre O and ∠ BAC = 30°
To Prove : BC = radius of the circle
Const. Join OB and OC
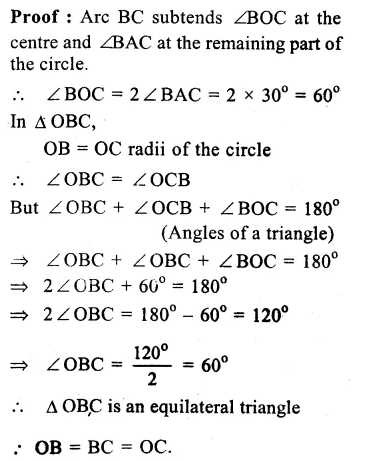

Question 14.
Solution:
In a circle with centre O and PQ is its diameter. ∠PQR = 65°, ∠SPR = 40° and ∠PQM = 50°
(i) ∠PRQ = 90° (Angle in a semicircle) and ∠PQR + ∠RPQ + ∠PQR = 180° (Angles of a triangle)
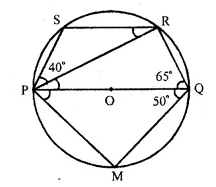
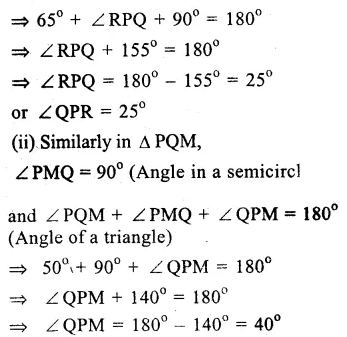

Hope given RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Chapter 11 Circle Ex 11B are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.