Class 10 Science Biology Chapter 7 MCQ With Answers
Biology Class 10 Chapter 7 MCQs On Control and Coordination
Control And Coordination Class 10 MCQ Question 1.
The electrical impulse travels in a neuron from:
(a) Dendrite Axon → Axonal end → Cell body
(b) Cell body → Dendrite → Axon → Axonal end
(c) Dendrite → Cell body → Axon → Axonal end
(d) Axonal end → Axon → Cell body Dendrite
Answer:
(c) Dendrite → Cell body → Axon → Axonal end
Explanation: The electrical impulse travels from the dendrite to the cell body, and then along the axon to its axonal end. At the end of the axon, the electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals. These chemicals cross the gap, or synapse, and start a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron.
Control And Coordination MCQ Question 2.
In a synapse, a chemical signal is transmitted from:
(a) The dendritic end of one neuron to the axonal end of another neuron.
(b) Axon to cell body of the same neuron.
(c) Cell body to the axonal end of the same neuron.
(d) The axonal end of one neuron to the dendritic end of another neuron.
Answer:
(d) The axonal end of one neuron to the dendritic end of another neuron.
Explanation: The chemical signal is transmitted from axonal end of one neuron to the dendritic end of another nueron. This microscopic gap is called synapse.
MCQ On Control And Coordination Question 3.
In a neuron, the conversion of electrical signal to a chemical signal occurs at/in:
(a) Cell body
(b) Axonal end
(c) Dendritic end
(d) Axon
Answer:
![]()
Class 10 Science Chapter 7 MCQ Question 4.
Which is the correct sequence of the components of a reflex arc?
(a) Receptors Muscles → Sensory neuron → Motor neuron → Spinal cord
(b) Receptors → Motor neuron → Spinal cord Sensory neuron → Muscle
(c) Receptors → Spinal cord → Sensory neuron → Motor neuron → Muscle
(d) Receptors → Sensory neuron → Spinal cord → Motor neuron → Muscle
Answer:
(d) Receptors → Sensory neuron → Spinal cord → Motor neuron → Muscle
Explanation: A stimulus received by the receptors present on skin, is transmitted to the sensory neuron, which carries it to the central nervous system (the spinal cord and brain).
A motor neuron carries the message from the central nervous system to the effector which could be a muscle, a gland or both.
Related Theory
Nerve based pathway performed by an impulse from the receptor of stimulus to the effector organ is called the reflex arc. A reflex action is a nerve mediated automatic and spontaneous response to a certain stimulus without sonsulting the wilt of the individual coughing, sneezing, etc.
MCQ Of Control And Coordination Question 5.
Which of the following statements are true?
(I) Sudden action in response to something in the environment is called a reflex action.
(II) Sensory neurons carry signals from the spinal cord to muscles.
(III) Motor neurons carry signals from receptors to the spinal cord.
(IV) The path through which signals are transmitted from a receptor to muscle or a gland is called reflex arc.
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (I) and (III)
(c) (I) and (IV)
(d) (I) (II) and (III)
Answer:
(c) (I) and (IV)
Explanation: Reflex action is a sudden action in response to some stimuli in the environment. Reflex arc is the path through which signals are transmitted from a receptor to a muscle or a gland.
Class 10 Control And Coordination MCQ Question 6.
Which of the following statements are true about the brain?
(I) The main thinking part of bi in is the hindbrain.
(II) Centres of hearing, smell, memory, sight, etc. are located in the fore-brain.
(III) Involuntary actions like salivation, vomiting and blood pressure are controlled by the medulla in the hind brain.
(IV) Cerebellum does not control posture and balance of the body.
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (I) (II) and (III)
(c) (II) and (III)
(d) (III) and (IV)
Answer:
![]()
Control And Coordination MCQ With Answers Pdf Question 7.
The spinal cord originates from:
(a) Cerebrum
(b) Medulla
(c) Pons
(d) Cerebellum
Answer:
MCQ Of Control And Coordination Class 10 Question 8.
The movement of shoot towards light is:
(a) Geotropism
(b) Hydrotropism
(c) Chemotropism
(d) Phototropism
Control And Coordination Class 10 MCQ With Answers Question 9.
The main function of abscisic acid in plants is to:
(a) Increase the length of cells
(b) Promote cell division
(c) Inhibit growth
(d) Promote growth of stem
Answer:
(c) Inhibit growth
Explanation: Abscisic acid (ABA) is one example of a hormone which inhibits growth. Its effects include wilting of leaves.
Related Theory
Auxin is synthesized at the shoot tip, helps the cells to grow longer. When light is coming from one side of the plant, auxin diffuses towards the shady side of the shoot. This concentration of auxin stimulates the cells to grow longer on the side of the shoot which is away from light.
Gibberellin helps in the growth of the stem.
Cytokinin promotes cell division, and it is natural then that they are present in greater concentration in areas of rapid cell division, as in fruits and seeds.
Abscisic acid inhibits growth. Its effects include wilting of leaves. It is also responsible for falling of senescent leaves.
Class 10 Chapter 7 Science MCQ Question 10.
Iodine is necessary for the synthesis of which hormone?
(a) Adrenaline
(b) Thyroxin
(c) Auxin
(d) Insulin
Answer:
(b) Thyroxin
Explanation: Iodine is necessary for the thyroid gland to make the thyroxin hormone. Thyroxin regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in the body so as to provide the best balance for growth. Iodine is essential for the synthesis of thyroxin. In case iodine is deficient in our diet, there is a possibility that we might suffer from goitre. One of the symptoms in this disease is a swollen neck.
![]()
MCQ Questions For Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Question 11.
Choose the incorrect statement about insulin:
(a) It is produced from pancreas.
(b) It regulates growth and development of the body.
(c) It regulates blood sugar levels.
(d) Insufficient secretion of insulin will cause diabetes.
Answer:
Control And Coordination Class 10 MCQs Question 12.
Select the mismatched pair:
(a) Adrenaline – Pituitary gland
(b) Testosterone – Testes
(c) Oestrogen – Ovary
(d) Thyroxin – Thyroid gland
Answer:
(a) Adrenaline – Pituitary gland
Explanation: Adrenaline is secreted by the adrenal gland, whereas growth hormone is secreted by the pituitary gland.
Control And Coordination MCQ With Answers Question 13.
The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to:
(a) The effect of light.
(b) The effect of gravity.
(c) Rapid cell divisions in tendrillar cells that are away from the support.
(d) Rapid cell divisions in tendrillar cells in contact with the support.
Answer:
Control And Coordination MCQ Class 10 Question 14.
The growth of pollen tubes towards ovules is due to:
(a) Hydrotropism
(b) Chemotropism
(c) Geotropism
(d) Phototropism
Answer:
MCQs On Control And Coordination Question 15.
The movement of sunflower in accordance with the path of the sun is due to:
(a) Phototropism
(b) Geotropism
(c) Chemotropism
(d) Hydrotropism
Answer:
Question 16.
Involuntary actions in the body are controlled by:
(a) Medulla in the forebrain
(b) Medulla in the midbrain
(c) Medulla in the hindbrain
(d) Medulla in the spinal cord
Answer:
(c) Medulla in the hindbrain
Explanation: Medulla is a part of the hindbrain and controls involuntary action.
Question 17.
Which of the following is not an involuntary action?
(a) Vomiting
(b) Salivation
(c) Heartbeat
(d) Chewing
Answer:
(d) Chewing
Explanation: The actions that are not under our direct control are known as involuntary actions. Vomiting, salivation and heartbeat are examples of involuntary action. These involuntary actions are controlled by the medulla in the hindbrain.
![]()
Question 18.
A doctor advised a person to take an injection of insulin because:
(a) His blood pressure was low.
(b) His heart was beating slowly.
(c) He was suffering from goitre.
(d) His sugar level in blood was high.
Answer:
(d) His sugar level in blood was high.
Explanation: A person taking injections of insulin is suffering from diabetes. Insulin is a hormone which is produced by the pancreas. It helps in regulating blood sugar levels. If not secreted in proper amounts, the sugar level in the blood rises, causing many harmful effects.
Question 19.
The hormone which increases fertility in males is called:
(a) Oestrogen
(b) Testosterone
(c) Insulin
(d) Growth hormone
Answer:
(b) Testosterone

Explanation: Testosterone is the male sex hormone necessary for sperm production. In addition to regulating the formation of sperms, testosterone brings changes in appearance seen in boys, at the time of puberty.
Question 20.
Which of the following endocrine glands is unpaired?
(a) Adrenal
(b) Testes
(c) Pituitary
(d) Ovary
Answer:
Question 21.
The junction between two neurons is called:
(a) Cell junction
(b) Neuromuscular junction
(c) Neural joint
(d) Synapse
Answer:
(d) Synapse
Related Theory
- Synapse is the junction between two neurons.
- Cell junction is junction between neighboring cells.
- Neuromuscular junction allows delivery of impulses from neurons to other cells, like muscles cells/gland.
![]()
Question 22.
In humans, life processes are controlled and regulated by:
(a) Reproductive and endocrine systems.
(b) Respiratory and nervous systems.
(c) Endocrine and digestive systems.
(d) Nervous and endocrine systems.
Answer:
Question 23.
Select the row containing incorrect information:
| Endocrine Gland | The function of hormone secreted |
| (a) Thyroid | Regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism |
| (b) Pituitary | Regulates growth and development of the body |
| (c) Pancreas | Increasing blood sugar levels |
| (d) Adrenal | Increasing heart rate |
Answer:
(c) Endocrine Gland: Pancreas; Function of hormone – Increasing blood sugar levels
Question 24.
Look at the figure below and identify the structure labelled incorrectly:
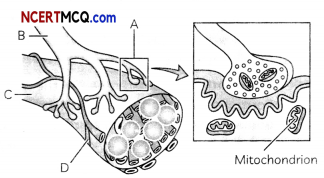

Answer:
(d) D-Dendrite
Explanation: Part labelled D is capillary and not dendrite, as dendrites receive nerve impulses.
Question 25.
Given below are four statements regarding endocrine glands and hoimones. Select the correct statements:
(I) Hormones are secreted by the endocrine glands.
(II) Some endocrine glands secrete hormones in response to other hormones.
(III) Hormones are required in large quantities.
(IV) Many hormones are controlled by some form of a feedback mechanism.
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (I) and (III)
(c) (I), (II), and (III)
(d) (I), (II), and (IV)
Answer:
(d) (I), (II), and (IV)
Explanation: Hormones are very potent substances, which means that very small amounts of a hormone may have profound effects on metabolic processes. Some endocrine glands secrete hormones in response to other hormones. The hormones that cause the secretion of other hormones are called tropic hormones. A hormone from gland A causes gland B to secrete its hormone. Many hormones are controlled by some form of a negative feedback mechanism, in this type of system, a gland is sensitive to the concentration of a substance that it regulates. A negative feedback system causes a reversal of increases and decreases in body conditions in order to maintain a state of stability.
Question 26.
Given below are four statements regarding the movement in plants.
Select the incorrect statements.
(I) Movement in plants happens at a point as the point of touch.
(II) The plants use electrical-chemical means to convey information from cell to cell.
(III) There are specialised tissues in plants for the conduction of information.
(IV) Plant cells change shape by changing the amount of water in them
(a) Both (I) and (III)
(b) Both (I) and (IV)
(c) Both (II) and (III)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 27.
The junction between two nerves is known as:
(a) Synapse
(b) Axon
(c) Dendrite
(d) Capillary
Answer:
(a) Synapse
Explanation: The junction between two neurons is known as synapse. It is the site of transmission of nerve impulses between two nerve cells (neurons) or between a neuron and a gland or muscle cell (effector). A synaptic connection between a neuron and a muscle cell is called a neuromuscular junction.
![]()
Question 28.
The plant hormone that promotes dormancy m seeds and buds is:
(a) Auxin
(b) Gibberellin
(c) Cytokinin
(d) Abscisic acid
Answer:
(d) Abscisic acid
Explanation: Abscisic acid is one example of a hormone which inhibits growth. Its effects include wilting of leaves and promoting dormancy in seeds and buds.
Question 29.
The secretion of which hormone leads to physical changes in the body when you are 10-12 years of age?
(a) Oestrogen from testes and testosterone from ovary.
(b) Oestrogen from adrenal gland and testosterone from pituitary gland.
(c) Testosterone from testes and Oestrogen from ovary.
(d) Testosterone from thyroid gland and Oestrogen from pituitary gland.
Assertion Reasoning questions Class 10 Science Chapter 7
For the following questions, two statements are given: one labeled Assertion (A) and the other labeled Reason (R) Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Question 30.
Assertion (A): A growing plant appears to bend towards the direction of light.
Reason (R): The plant hormone auxin diffuses towards the shady side of the shoot.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the (A).
Question 31.
Assertion (A): Plants convey the acquired information from cell to cell.
Reason (R): Plants have specialized tissues for the conduction of information.
Select the correct answer to the above question from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below:
![]()
Question 32.
Assertion (A): In animals, the brain is the main controlling center for responding to changes in their environment.
Reason (R): The thinking process of the brain is not fast enough in animals.
Answer: (d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Explanation: Reflex arcs have evolved in animals as the thinking process of the brain is not fast enough. Reflex action is any spontaneous, involuntary, and automatic response to a stimulus due to a change in our environment. For e.g. when a person touches a hot plate a sudden action leading to the withdrawal of hand occurs in a certain manner, this path of manner determines the reflex arc.
Reflex arcs have evolved in animals in order to take sudden and involuntary actions which are required in certain circumstances where emergency response is required to save the body from situations that may lead to danger.
(Competency Based Questions (CBQs))
Question 1.
The thyroid gland is a bibbed structure situated in our neck region. It secretes a hormone called thyroxine. Iodine is necessary for the thyroid gland to make thyroxine. Thyroxine regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in the body. It promotes the growth of body tissues also. When there ¡s an excess of thyroxine ¡n the body, a person suffers from hyperthyroidism and if this gland Is underactive it results in hypothyroidism. Hyperthyroidism is diagnosed by blood tests that measure the levels of thyroxine and Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH). Hypothyroidism ¡s caused due to the deficiency of iodine in our diet resulting in a disease called goitre. Iodised salt can be included in our diet ro control it.
(A) Where is the thyroid gland situated in our body?
Answer:
(B) State the function of thyroxine in human body.
Answer:
Thyroxine hormone is secreted by thyroid glands. Thyroxine plays vital roles in: increasing the basal metabolic rate regulating long bone growth. Increasing body’s seasitivity to hormone adrenaline, digestive function.
(C) What is hyperthyroidism?
Answer:
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces excessive amount of hormone thyroxine
Related Theory
Hyperthyroidism means the thyroid gland is overactive and Overactive thyroid can sized up metabolism nervousness, anxiety, loss of mood swings etc.
(D) How can we control hypothyroidism?
Answer:
We can control hypothyroidism by including iodised salt in our diet. Deficiency of iodine in our diet reduces the levels of ISH and a disease called goitre
![]()
Question 2.
While watching the TV show Master Chef Australia, Rima observed that the contestants were blindfolded and then asked to identify cubes of different fruits or food items by smelling and then by tasting them.
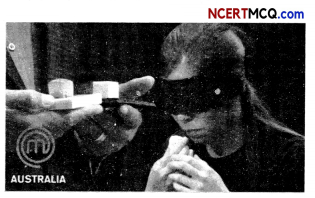
Which of the following statements is correct about receptors?
(a) Gustatory receptors detect taste while olfactory receptors detect smell.
(b) Both gustatory and olfactory receptors detect smell.
(c) Auditory receptors detect smell and olfactory receptors detect taste.
(d) Olfactory receptors detect taste and gustatory receptors detect smell.
Answer:
Question 3.
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) stimulates thyroid gland to produce thyroxine. Study the table given below.
Table: TSH Levels During Pregnancy
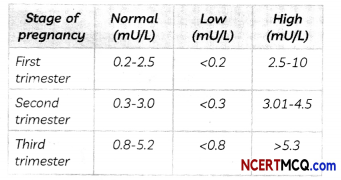
It is important to monitor TSH levels during pregnancy. High TSH levels and hypothyroidism can especially affect chances of miscarriage. Therefore, proper medication in consultation with a doctor is required to regulate/control the proper functioning of the thyroid gland.
(A) Give the full form of TSH.
Answer:
Full form of TSH: Thyroid Stimulating Hormone.
(B) State the main function of TSH.
Answer:
Thyroid stimulating hormone is produced by pituitary gland. Its main function is to regulate the production of hormones by the thyroid gland.)
Related Theory
A TSH test is a blood test that measures TSH i.e. how much of this hormone is present in blood. Thyroid gland is the largest gland endocrine gland, which is H-shaped present in the neck region. Thyroxine produced by thyroid gland regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
(C) Why do TSH levels in pregnant women need to be monitored?
Answer:
(D) A pregnant woman has TSH level of 8.95 mU/L. What care is needed for her?
Answer:
A pregnant woman has TSH levels 8.95 m U/L which is very high in any of the three trimesters. A care is needed for her on regular basis to reduce the levels of TSH.
A regular test of TSH levels every 6-8 weeks should be done.
Proper medication in consultation with a doctor is required to regulate/control the proper functioning of the thyroid gland
Question 4.
Veer accidentally touched a thorn but quickly withdrew his hand. He later realized that he did this without even thinking about it! So, his reflexes were quite quick.

Reflex action is controlled by:
(a) Brain
(b) Spinal cord
(c) Peripheral Nervous System
(d) Autonomic Nervous System
Answer:
(b) Spinal cord
Explanation: Reflex action is an involuntary and nearly instantaneous movement in response to a stimulus. A reflex action involves a very simple nervous pathway called a reflex arc. A reflex arc starts off with receptors being excited on sensing a stimulus. They then send signals along a sensory neuron to the spinal cord, where the signals are passed on to a motor neuron. Invertebrates, most sensory neurons do not pass directly into the brain, but synapse in the spinal cord. The spinal cord acts as the main centre for reflex actions. The spinal cord acts as a link between spinal nerves and the brain.
Question 5.
When Sanket went to a nearby farm with his friend, he found lots of mature fruits and Leaves lying on the ground. He tried to find out the reason behind this.

The substance that triggers the fall of mature leaves and fruits from plants is:
(a) Auxin
(b) Gibberellins
(c) Abscisic acid
(d) Cytokinin
Answer:
(c) Abscisic acid
Explanation: Abscisic acid is one example of a hormone which inhibits growth. Its effects include wilting of leaves and fall of mature leaves and fruits from plants.
![]()
Question 6.
Study are table in which the levels of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) in men are given and answer the questions that follow on the basis of understanding of the following paragraph and the related studied concepts.
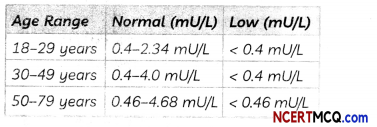
men are at greater risk for developing abnormal TSH levels during instruction, white giving birth and after going through menopause. Found 5% of women in the United States have some kind of thyroid problem compared to 3% of men. Despite claims that high TSH increases risk for heart disease, a 2013 study found no link between high. TSH heart diseases. But a 2017 study showed that older women are specially at risk for developing thyroid cancer if they have high TSH calls along with thyroid nodules.
(A) A 35-year-old woman has TSH level 6.03 mll/L. What change should she bring in her diet to control this level?
Answer:
The normal range of TSH level falls between 0.4 -4.0 m U/L. A 35 year old woman has TSH level 6.03 m U/L. 21 means she has higher level of TSH. Chance are that she may have an underactive thyroid. She should follow iodine rich diet.
Explanation: The deficiency of iodine in the diet of a person produces less thyroxine hormone. When a person will start taking iodine rich diet lies iodised salt, the thyroid gland will work actively to produce more thyroxine hormone.
(B) When do women face a greater risk of abnormal TSH level?
Answer:
Women face a greater risk of abnormal TSH level during menstruation, while giving birth and after going through menopause.
(C) State the consequence of low TSH level.
Answer:
The consequences of low TSH level:
(1) Body metabolism slows down
(2) Weight gain
(3) Forgetfulness
(4) Lack of concentration
(5) Faligne
(6) Depression etc. (Any two)
(D) Name the mineral that is responsible for synthesis of hormone secreted by thyroid gland.
Answer:
Question 7.
Pranay’s father was suffering from diabetes since a long time. Apart from several dietary restrictions, he was given injections of insulin regularly.

Why are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Answer:
Patients of diabetes have insufficient levels of insulin produced by pancreas and are therefore treated by giving injections of insulin. Insulin is a hormone which is produced by the pancreas and helps in regulating blood sugar levels. If it is not secreted in proper amounts, the sugar level in the blood rises causing many harmful effects.
![]()
Question 8.
A student was interested in knowing about various endocrine glands in human body, the hormones secreted by them and their functions. The figure below shows the endrocine glands in human males and females.
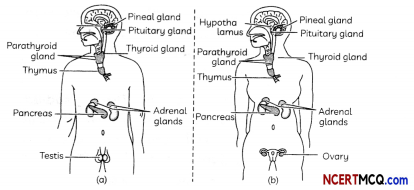
(A) The table below gives the names of some endocrine glands and their functions. Identify the row containing incorrect information:
| Name of Endocrine Gland | Function |
| (a) Thyroid | Regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in the body |
| (b) Pituitary | Regulates growth and development of the body |
| (c) Pancreas | Regulates levels of uric acid in blood |
| (d) Testis | Changes associated with puberty in males |
Answer:
(c) Name of Endocrine Gland : Pancreas;
Function : Regulates levels of uric acid in blood.
Explanation: Insulin is a hormone which is produced by the pancreas and helps in regulating blood sugar levels.
(B) The endocrine gland known as the master gland in human beings is:
(a) Pituitary gland
(b) Hypothalamus gland
(c) Pineal gland
(d) Thymus glands
Answer:
(C) Identify which of the following state¬ments about thyroid gland is incorrect?
(I) Thyroid gland requires iodine to synthesize thyroxin.
(II) Deficiency of iodine in our diet may cause dwarfism.
(III) Thyroxin regulates protein, carbohydrates and fat metabolism in the body.
(IV) Iron is essential for the synthesis of thyroxin.
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (I) and (III)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(D) Name the gland which secretes the growth hormone:
(a) Thyroid
(b) Pituitary gland
(c) Hypothalamus
(d) Adrenal
Answer:
(b) Pituitary gland
Explanation: Growth hormone is one of the hormones secreted by the pituitary and it regulates growth and development of the body. If there is a deficiency of this hormone in childhood, it leads to dwarfism.
(E) The dramatic changes in body features associated with puberty are mainly be¬cause of the secretions of:
(a) Oestrogen from testes and testos¬terone from ovary
(b) Oestrogen from adrenal gland and testosterone from pituitary gland
(c) Testosterone from testes and oes¬trogen from ovary
(d) Testosterone from thyroid gland and ostrogen from pituitary gland
Answer:
(c) Testosterone from testes and ostrogen from ovary
Question 9.
Akriti’s grandfather complained of giddiness since past several days. Her father took her to the physician who checked his blood pressure and immediately prescribed medicines for hypertension.
Which part of the brain is responsible for involuntary actions?
Answer:
The involuntary actions such as blood pressure, vomiting and salivation are controlled by the medulla in the hind-brain.
![]()
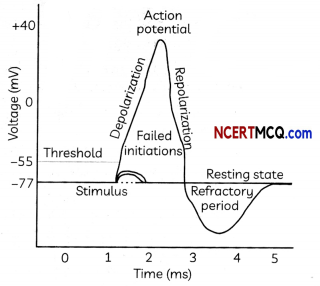
Question 10.
The neurons are cells with some special abilities. These cells get excited, because of the membranes that are in a polarised state. Each neuron has a charged cellular membrane, which means there is a voltage difference between the inside and the outside membrane.
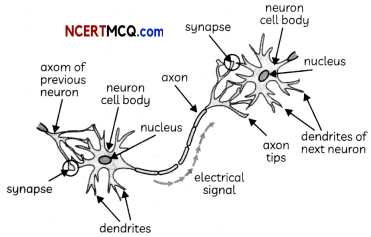
Membrane potential is the difference in the total charge between the inside of the cell and the outside of the cell. Action potential is a short-term change in the electrical potential that travels across the neuron cell.
A nerve impulse is generated when the stimulus is strong. This stimulus triggers the electrical and chemical changes in the neuron. When a nerve impulse is generated, there is a change in the permeability of the cell membrane. The sodium ions flow inside and potassium ions flow outside, causing a reversal of charges. The cell is now depolarised. This depolarization results in an action potential which causes the nerve impulse to move along the length of the axon. This depolarization of the membrane occurs along the nerve. A series of reactions occur where the potassium ions flow back into the cell and sodium ions move out of the cell. This whole process again results in the cell getting polarised, with the charges being restored.
When the nerve impulse reaches the end of the axon, there are some chemicals released from the neurotransmitters. They diffuse across the synaptic gap, which is the small space present between the axon and the receptors. Nerve impulses can be transmitted either by the electrical synapse or the chemical synapse.
(A) From the statements given below regarding polarization and depolarization of neurons, select the row containing the correct information.
| Polarization of Neuron | Depolarization of Neuron |
| (a) The sodium ions flow into the cell and potassium ions move out of the cell. | The sodium ions flow inside and potassium ions flow out-side |
| (b) The potassium ions flow into the cell and sodium ions move out of the cell. | The sodium ions flow inside and potassium ions flow out-side |
| (c) The potassium ions flow into the cell and sodium ions move out of the cell. | The potassium ions flow inside and sodium ions flow out-side |
| (d) The potassium ions flow into the cell and sodium ions move out of the cell. | The potassium ions flow inside and sodium ions flow out-side |
Answer:
(b) Polarization of Neuron: The potassium ions flow into the cell and sodium ions move out of the ceil.
Depolarization of Neuron: The potassium ions flow inside and sodium ions flow outside.
Explanation: When a nerve impulse is generated, there is a change in the permeability of the cell membrane. The cell gets depolarized when the sodium ions flow inside and potassium ions flow outside, causing a reversal of charges. The cell gets polarized when the potassium ion’s flow back into the cell and sodium ions move out of the cell.
(B) Four statements are given below. Select the incorrect statements.
(I) Nerve impulse is generated by the stimulus when a neuron is depolarized.
(II) Nerve impulse is generated by the stimulus when a neuron is polarized.
(III) The polarization of neuron results in an action potential.
(IV) The action potential causes the nerve impulse to move along the axon.
(a) Both (I) and (III)
(b) Both (II) and (IV)
(c) Both (I) and (IV)
(d) Both (II) and (III)
Answer:
(c) Both (II) and (III)
(C) The part of a neuron which receives information from other neurons is/are :
(a) Cell body
(b) Axon
(c) Dendrites
(d) Myelin sheath
Answer:
(D) The part of the neuron through which the impulse travels is:
(a) Axon
(b) Soma
(c) Dendrites
(d) Nucleus
Answer:
(a) Axon
Explanation: Axon is a singLe prominent extension that emerges from the cell body and is responsible for conducting outgoing impulses away from the cell and towards other cells.
(E) Control and coordination in animals is provided by:
(a) Nervous tissues only
(b) Muscular tissues only
(c) Receptors
(d) Both nervous and muscular tissues
Answer:
Question 11.
Sujay was watching a program when he found that several people of a particular region had swollen neck. He tried to gather more information regarding the probable cause of this disease.

Identify the disease they were suffering from and a possible cause.
Answer:
![]()
Question 12.
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurologic disorder that causes the brain to shrink (atrophy) and brain cells to die. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia – a continuous decline in thinking, behavioral and social skills that affects a person’s ability to function independently. The early signs of the disease include forgetting recent events or conversations. As the disease progresses, a person with Alzheimer’s disease will develop severe memory impairment and lose the ability to carry out everyday tasks. Common symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease include memory loss, language problems, and impulsive or unpredictable behavior. This happens because of a loss of connection between the nerve cells, or neurons, in the brain which means that information cannot pass easily between different areas of the brain or between the brain and the muscles or organs.
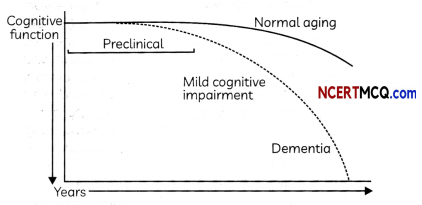
(A) Select the incorrect statement:
(a) Alzheimer’s is a type of dementia that causes memory loss.
(b) It occurs only in elderly people.
(c) The early signs of the disease include forgetting recent events or conversations.
(d) As the disease progresses, a person develops severe memory impairment and loses the ability to carry out everyday tasks.
Answer:
(b) It occurs only in elderly people.
Explanation: Alzheimer’s disease can affect people of any age group and does not occur only in the elderly.
(B) In Alzheimer’s disease there is a loss of connection between the nerve cells, or neurons, in the brain because of which:
(I) Information cannot pass easily be-tween different areas of the brain.
(II) Information cannot pass easily be-tween the brain and the muscles or organs.
(III) Information cannot be acquired by the dendrite.
(IV) Gustatory and olfactory receptors stop working.
Select the correct statements:
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (I) and (IV)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(a) Both (I) and (II)
Explanation: In Alzheimer’s disease there is a loss of connection between the nerve cells, or neurons, in the brain because of which Information cannot pass easily between different areas of the brain and between the brain and the muscles or organs.
(C) Given below are some parts of the brain and their functions.
Select the row containing the correct information:
| Part of Human Brain | Function |
| (a) Hindbrain | The sensation of feeling full during eating a meal |
| (b) Cerebrum | Controls involuntary actions such as salivation and vomitting |
| (c) Medulla | Controls intelligence and memory |
| (d) Cerebellum | Precision of voluntary actions |
Answer:
(d) Part of Human Brain: Cerebellum: Function: Precision of voluntary actions. Explanation: Sensation of feeling full during eating a meal is due to forebrain. Cerebrum controls intelligence and memory whereas the medulla controls involuntary actions such as salivation and vomiting.
(D) The part of human brain that is responsible for maintaining the posture and balance of the body is:
(a) Cerebrum
(b) Medulla
(c) Cerebellum
(d) Pons
Answer:
(E) The main thinking part of the human brain is:
(a) Fore brain
(b) Mid brain
(c) Hind brain
(d) Cerebellum
Answer:
Question 13.
Motor neuron disease (MND) is the name for a group of diseases that affects particular nerves known as motor nerves, or motor neurons. In MND, those neurons generate and die and slowly the muscles become weaker. This eventually leads to paralysis. It is also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or ALS. MND is a progressive disease that usually starts slowly and gets worse over time. Symptoms sometimes starting on one side of the body and then spreading. Usually, the first things people notice are:
(1) weakness in the hands and grip
(2) slurred speech
(3) weakness in the legs, and a tendency to trip
(4) weakness of the shoulder, making lifting diffcult
(5) cramps and muscles twitching
The graph below shows the age wise incidence of MND per 1 lakh of population for men and women.
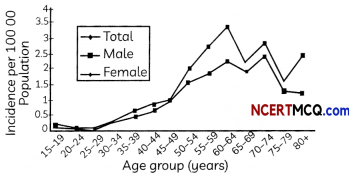
This information, acquired at the end of the dendritic tip of a nerve cell, sets off a chemi¬cal reaction that creates an electrical impulse. This impulse travels from the dendrite to the cell body, and then along the axon to its end. At the end of the axon, the electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals. These chemicals cross the gap, or synapse, and start a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron. This is a general scheme of how nervous impulses travel in the body. A similar synapse finally allows delivery of such impulses from neurons to other cells, such as muscles cells or glands.
(A) Based on the passage above, select the correct statements regarding Motor Neuron Diseases (MND):
(I) MND incidence is higher in men than women.
(II) MND affect sensory neurons.
(III) MND is a progressive disease that usually starts slowly and gets worse over time.
(IV) MND may eventually lead to paral¬ysis as muscles become weaker.
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) (I), (III) and (III)
(d) (I), (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(d) (I), (III) and (IV)
Explanation: Motor Neuron Diseases (MND) affects motor neurons and not sensory neurons.
(B) Select the row containing the incorrect information:
| Type or Part of Neuron | Function |
| (a) Dendrites | These carry signals in the form of electrical impulses away from the cell body |
| (b) Sensory Neuron | These are found in receptors such as the eyes, ears, tongue and skin, and carry nerve im¬pulses to the spinal cord and brain. |
| (c) Motor neuron | These are found in the central nervous system (CNS) and control muscle movements. |
| (d) Relay neuron | Relay neurons are found in the brain and spinal cord and allow sensory and motor neurons to communicate. |
Answer:
(a) Type or Part of Neuron: Dendrites: function: These are found in receptors such as the eyes, ears, tangue and skin and cavry nerve in pulses to the spinal cord and brain.
Explanation: The dendrites receive signals from other neurons or from sensory receptor ceLls. The dendrites are typically connected to the cell body, which is often referred to as the ‘control centre’ of the neuron, as it contains the nucleus. The axon is a long slender fibre that carries nerve impulses, in the form of an electrical signal known as action potential, away from the cell body towards the axon terminals, where the neuron ends. Most axons are surrounded by a myelin sheath (except for relay neurons) which insulates the axon so that the electrical impulses travel faster along the axon.
(C) The motor neurons:
(a) Are found in receptors
(b) Are found in the brain and spinal cord
(c) Are found in the Central nervous system
(d) Carry impulses to the spinal cord and brain
Answer:
(D) In the diagram above, the parts marked A and B are:
(a) Sensory neuron and motor neuron respectively
(b) Sensory neuron and relay neuron respectively
(c) Motor neuron and relay neuron respectively
(d) Motor neuron and sensory neuron respectively
Answer:
(E) In the diagram above, the motor neuron is labelled as:
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Answer:
(c) C
Explanation: The motor neuron carries response from the spinal cord to the effector organs.
![]()
Question 14.
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of the nerves and ganglia outside the brain and spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the limbs and organs, essentially serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body.
In its simplest form, a reflex is viewed as a function of an idealized mechanism called the reflex arc. The primary components of the reflex arc are the sensory-nerve cells (or receptors) that receive stimulation, in turn connecting to other nerve cells that activate muscle cells (or effectors), which perform the reflex action.
A reflex arc is a neural pathway that controls a reflex. In vertebrates, most sensory neurons do not pass directly into the brain, but synapse in the spinal cord. This allows for faster reflex actions to occur by activating spinal motor neurons without the delay of routing signals through the brain. The brain will receive the sensory input while the reflex is being carried out and the analysis of the signal takes place after the reflex action.
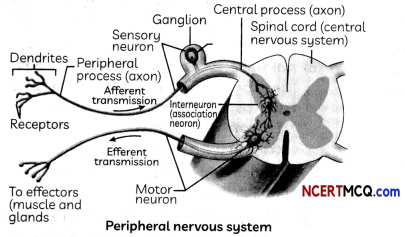
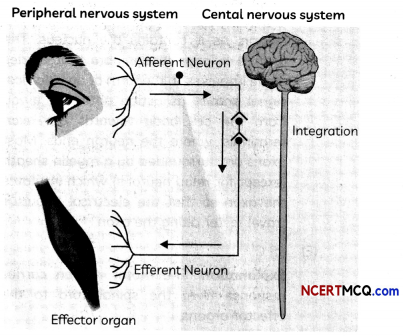
(A) Afferent neurons carry nerve impulses from
(a) CNS to muscles
(b) CNS to receptors
(c) receptors to CNS
(d) effector organs to CNS
Answer:
(c) receptors to CNS
Explanation: The afferent neurons carry nerve impulses from the receptors to the central nervous system, whereas the efferent neurons carry impulses from the CNS to the effector organs.
(B) A neuron that carries information from the peripheral nervous system to the central nervous system is
(a) afferent neuron
(b) efferent neuron
(c) both
(d) none
Answer:
(C) Which of these illustrate a reflex arc?
(a) Brain → Spinal cord → Muscles
(b) Muscles → Receptor → Brain
(c) Muscles → Spinal cord → Brain
(d) Receptor → Spinal cord → Muscles
Answer:
(d) Receptor → Spinal cord → Muscles

Explanation: Reflex arc does not involve the brain. Infact it has evolved in higher animals as the thinking process of brain is not fast enough.
(D) Given below are the parts of the nervous system and their functions. Iden¬tify the row containing incorrect information:
| Part | Function |
| Peripheral Nervous System | Consists of sensory organs |
| Central Nervous System | To organize and analyze information received |
| Afferent Neurons | Carry signals to the brain and spinal cord |
| Efferent Neurons | Carry neural impulses away from the central nervous system and toward muscles |
Answer:
(E) Select the correct statements:
(I) The PNS facilitates communication between the CNS and other parts of the body.
(II) The PNS consists of cranial nerves and spinal nerves
(III) The cranial nerves arise from the spinal cord.
(IV) The CNS carries signals to the brain and spinal cord.
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (I) and (IV)
(d) Both (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(d) Both (III) and (IV)
Explanation: The communication between the central nervous system and the other parts of the body is facilitated by the peripheral nervous system consisting of cranial nerves arising from the brain and spinal nerves arising from the spinal cord.
![]()
Question 15.
Plant hormones are among the most important biochemicals affecting plant growth and yield production under different conditions, including stress. Plant hormones include auxin, abscisic acid, ethylene, gibberellins, cytokinins, salicylic acid, strigolactones, brassinosteroids, and nitrous (nitric) oxide. Plant functioning under stress is affected by plant hormones, which can help the plant to tolerate the environmental stresses. Tropism is the type of plant movement, that is achieved by growth and responsible to directional light The movement is due to the action of auxin inside the plant part. Normally, phototropism, geotropism, hydrotropism and thigmotropism can be identified.
Within the above tropisms, the response of shoot tips are quite different from that of root tips. The basic difference is in the concentration they secreted. The level of auxin secreted from shoot tips is always on the ascending arm of the graph of response. But for the root tips, on the descending arm. Then, their responses become the opposite. The following graph shows the fact.
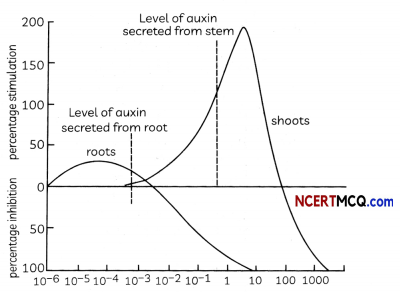
Auxin Concentration (Parts Per Milion)
Nb Logarithmic Scale For Auxin Concentration
(A) Observe the graph above and select the correct statements.
(I) Lower concentration of auxins decrease the growth of roots.
(II) Shoot growth requires greater concentrations of auxins as compared to the growth of roots.
(III) The application of very high concentration of auxin inhibits the growth of shoots directly.
(IV) The response of roots to auxin can thus be represented by an optimum curve with the peak at very low concentration.
(a) Both (I) and (III)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) (I), (III) and (IV)
(d) (II), (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(d) (II), (III) and (IV)
Explanation: Lower concentrations of auxins increases the growth of roots.
(B) The table below lists few plant hormones and their functions. However, one row contains incorrect information. Select the row containing incorrect information.
| Name of the plant hormone | Function |
| (a) Auxin | Promotes cell elongation |
| (b) Gibberellin | Promotes seed germination and stem growth |
| (c) Cytokinin | Inhibits cell division |
| (d) Abscisic acid | Maintains seed dormancy |
Answer:
(c) Name of plant hormone: Cytokinin: Function: Inhibits cell division
Explanation: Cytokinin is a plant hormone that promotes cell division, and they are present in greater concentration in areas of rapid cell division, such as in fruits and seeds.
(C) Plant roots exhibit:
(a) Positive geotropism
(b) Negative geotropism
(c) Positive chemotropism
(d) Negative hydrotropism
Answer:
(D) Which of the following plant hormone is responsible for seed germination?
(a) Auxin
(b) Gibberellin
(c) Ethylene
(d) Abscisic acid
Answer:
(E) The hormone that is a growth inhibitor is:
(a) Auxin
(b) Abscisic acid
(c) Cytokinin
(d) Gibberellin
Answer:
(b) Abscisic acid
Explanation: Abscisic acid is one example of a hormone that inhibits growth. Its effects include wilting of leaves.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which one appears more accurate and why?
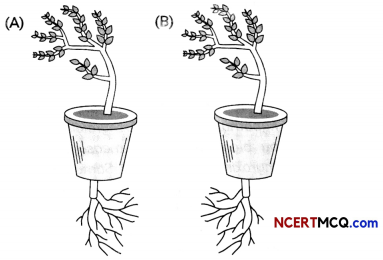

Answer:
(A) is more appropriate as shoots are negatively geotropic and roots are positively geotropic. Hence, shoots grow upwards and roots grow downwards.
Related Theory
The roots of a plant always grow downwards while the shoots usually grow upwards and away from the earth. This upward and downward growth in response to the gravity pull is known as geotropism.
Question 2.
Name the two components of central nervous systems in humans.
Answer:
![]()
Question 3.
How is the spinal cord protected in the human body?
Answer:
Spinal cord is enclosed in a bony cage called the vertebral column.
Question 4.
A potted plant is made to lie horizontally on the ground. Which part of the plant will show (a) positive geotropism?
Answer:
Question 5.
Name any two types of tropism.
Answer:
Phototropism and geotropism.
Question 6.
Name the hormone that helps in regulating level of sugar is our blood. Name the gland that is secreted.
Answer:
Insulin helps in regulating blood sugar level. This hormone is secreted by the pancreas gland.
Question 7.
Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes its growth. Where it is synthesized?
Answer:
Question 8.
Mention the function of adrenaline hormone.
Answer:
The function of adrenaline hormone is to regulate blood pressure, heartbeat breathing rate, carbohydrate metabolism and mineral balance in the body.
Question 9.
State the function of:
(A) gustatory receptors, and
(B) olfactory receptors
Answer:
![]()
Question 10.
Mention the part of the body where gustatory and olfactory receptors are located.
Answer:
Gustatory receptors are located in Cerebrum of fore-brain. Olfactory receptors are located in the Olfactory lobe of fore-brain.