Students can also read MCQ Questions for Class 10 Civics Chapter 4 Gender, Religion and Caste Questions with Answers hope will definitely help for your board exams. https://ncertmcq.com/mcq-questions-for-class-10-social-science-with-answers/
Class 10 Social Science Civics Chapter 4 MCQ With Answers
Civics Class 10 Chapter 4 MCQs On Gender, Religion and Caste
Gender Religion And Caste Class 10 MCQ Question 1.
Which of the following countries has a record of high participation of women in the political sphere of the society?
(a) India
(b) Bangladesh
(c) France
(d) Finland
Answer:
Class 10 Civics Chapter 4 MCQ With Answers Question 2.
On an average an Indian woman works…………..more than an average man every day.
(a) One hour
(b) Half an hour
(c) Two hours
(d) One and a half hour
Answer:
(a) One hour
Gender Caste And Religion Class 10 MCQ Question 3.
Fill in the blank by choosing the most appropriate option:
………………… provides that equal wages should be paid to equal work.
(a) Wages act
(b) Equal Remuneration Act
(c) Equal Wages Act
(d) Labour Code
Gender Religion And Caste MCQs Question 4.
Fill in the blank in regards to the information about the Child Sex Ratio (0-6 years) of India in 2011?
Ratio 901-925- Himachal Pradesh; Ratio below 850-……………..
(a) Madhya Pradesh
(b) Punjab
(c) Kerala
(d) Haryana
Answer:
(b) Punjab
Gender Religion And Caste MCQ Question 5.
Sexual Division of labour signifies which of the following statements?
(1) Gender division emphasises not all people can do all kinds of work.
(2) Gender division means division between communities.
(3) Caste is the basis of Gender Division.
(4) Type of the work decides whether a man will do it or a woman will do it.
(5) Religion decides which work should be done by who.
(a) (1). (3) & (4) (b) (1), (2) & (4)
(c) (1) & (3) (d) (4) & (1)
Answer:
(d) (4) & (1)
![]()
MCQ Of Chapter Gender Religion And Caste Class 10 Question 6.
In local self-government institutions, at least one third of all positions are reserved for„
(a) Men
(b) Women
(c) Children
(d) Scheduled tribes
Answer:
(b) Women
Class 10 Civics Chapter 4 MCQ With Answers In Hindi Question 7.
Identify the reason why caste alone cannot determine elections in India.
(I) No party can win the votes of all the voters of a caste or community.
(II) Political parties appease certain castes and ignore others.
(III) No parliamentary constituency in the country has a clear majority of one single caste, people from different castes live in each constituency.
(IV) Mobilising and securing political support has brought new consciousness among the lower castes.
(a) (I) only
(b) (II) only
(c) (I) & (IV) only
(d) (i), (II) & (III) only
Answer:
MCQ On Gender Religion And Caste Class 10 Question 8.
In India, seats are reserved for women in:
(I) Lok Sabha
(II) State legislative assemblies
(III) Cabinet of Chief Minister
(IV) Panchayati Raj bodies
(a) (I), (M) & (IV)
(b) (II), (III) & (IV)
(c) (II) & (III)
(d) (I) & (IV)
Answer:
(d) (I) & (IV)
Explanation: One-Third of seats in local government bodies – in panchayats and municipalities – are now reserved for women. There are more than 10 lakh elected women representatives in rural and urban local bodies.
Question 9.
Which among the following statements about the Constitution of India is wrong?
(a) It prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion.
(b) It gives official status to one religion.
(c) It ensures equality of citizens within religious communities.
(d) It ensures everyone’s freedom to profess any religion.
Answer:
Question 10.
Human rights groups in our country have argued that most of the victims of communal riots in our country are
(a) Women
(b) Children
(c) Religious minorities
(d) People with disabilities
Answer:
(c) Religious minorities
![]()
Question 11.
What is the literacy rate of men in India?
(a) 73%
(b) 76%
(c) 75%
(d) 78%
Answer:
Question 12.
What is the child sex ratio (number of girl children per thousand boys) in India?
(a) 999
(b) 872
(c) 919
(d) 912
Answer:
(c) 919
Question 13.
A ………….. proportion of women attend higher educational institutions than men.
(a) Greater
(b) Smaller
(c) Equal
(d) Almost negligible
Answer:
(b) Smaller
Explanation: Women are not allowed to study in a lot of families, especially when the resources are limited because it is considered that men are supposed to work and provide for the family while women are supposed to do caregiving activities.
Question 14.
The proportion of women among the highly paid and valued jobs is still very
(a) Large
(b) Small
(c) Negligible
(d) Equal to that of men
Answer:
(b) Small
Question 15.
Castes in India have:
(a) Stayed the same throughout the time
(b) Changed completely in the last 5 years
(c) Experienced certain changes but not many.
(d) Increased its influence
Answer:
(c) Experienced certain changes but not many.
![]()
Question 16.
Which of the following instances express the severest form of communal politics?
(a) Violence and Riots
(b) Elections
(c) Inter-caste marriages
(d) Abstinence from religion
Answer:
Question 17.
The total percentage of Backward Classes estimates their population to be around per cent.
(a) 61%
(b) 54%
(c) 42%
(d) 41%
Answer:
(d) 41%
Question 18.
Which of the following principles compelled political leaders to gear up to the task of mobilising and securing political support?
(a) Universal adult franchise
(b) Communalism
(c) One man- One vote- One woman- no vote
(d) Religion is the base of politics
Answer:
(a) Universal adult franchise
Explanation: Universal adult franchise and the principle of one-person-one-vote compelled political leaders to gear up to the task of mobilising and securing political support. It also brought new consciousness among the people of castes that were hitherto treated as inferior and low.
Identify the following on basis of the hints given:
Question 19.
Identify the following on basis of the hints given:
(1) In 2011, this group of Castes were 16.6 percent of total people in India.
(2) The group is also known as Dalits.
(3) They were subjected to exclusion and untouchability.
Answer:
Correct and Rewrite / True-False
State whether the following statements are True or False. If false, correct the statement.
Question 20.
Gender division tends to be understood as natural and unchangeable.
Answer:
True
![]()
Question 21.
Boys and girls are brought up to believe that the main responsibility of women is housework and bringing up children.
Answer:
True
Question 22.
Earlier, only women were allowed to participate in public affairs, vote and contest for public offices.
Answer:
False
Earlier, only men were allowed to participate in public affairs, vote and contest for public offices.
Explanation: Although women constitute half of humanity, their role in public life, especially politics, is minimal in most societies. In fact women, women had to fight for their voting rights to participate in elections.
Question 23.
Political expression of gender division and political mobilisation does not help to improve women’s role in public life.
Answer:
Question 24.
The percentage of elected women members in Lok Sabha has touched 14.36 per cent of its total strength for the first time in 2014.
Answer:
False
The percentage of elected women members in Lok Sabha has touched 14.36 per cent of its total strength for the first time in 2019. Explanation: One Third of seats in the Lok Sabha and State Assemblies have been reserved for women.
Question 25.
In Indian government, cabinets are largely all-female even when aman becomes the Chief Minister or the Prime Minister.
Answer:
False
In Indian government, cabinets are largely all-male even when a woman becomes the Chief Minister or the Prime Minister.
![]()
Question 26.
Although women constitute half of humanity, their role in public life, especially politics, is minimal in most societies.
Answer:
True
Question 27.
Expression of caste differences in politics gives many advantaged communities the space to demand their share of power.
Answer:
Fill in the blanks with suitable information:
Question 28.
Castes and Caste system in modern India have undergone a great change because of [CBSE 2019]
Answer:
Urbanisation, growth of literacy and education
Question 29.
The Indian Constitution provides to all individuals and communities freedom to profess, practice and propagate any religion because
Answer:
India is a secular State.
Explanation: Indian Secularism believes in equal respect and equal distance from all religions to promote equality. Western secularism believes abstinence from religion. Indian Constitution does not have any official religion.
![]()
Question 30.
The representation of women in Indian Parliament is still low as compared to European countries because
Answer:
women are not educated, trained and encouraged enough.
Question 31.
……………. is the literacy rate among men and ………… is the literacy rate for women in India.
Answer:
76% and 54%
Question 32.
The Equal wages Act was passed in……………
Answer:
Question 33.
In 2011, the Scheduled Castes were ………… and the Scheduled Tribes were of the country’s population.
Answer:
16.6 percent and 8.6 percent
![]()
Question 34.
Scandinavian countries like ………. the participation of women in public life is very high.
Answer:
Sweden
Question 35.
The disproportionately large presence of ‘upper caste’ among the urban middle classes in our country is because
Answer:
Assertion Reasoning questions Class 10 Civics Chapter 4
In each of the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding statement of Reason (R). Select the correct answers to codes (a), (b), (c) or (d) as given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
(d) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct.
Answer:
Question 36.
Assertion (A): It is not politics that gets caste-ridden, it is the caste that gets politicized.
Reason (R): Politics brings caste into the political arena.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Question 37.
Assertion (A): Elections are all about caste and nothing else.
Reason (R): Every candidate and party needs to win the confidence of more than one caste and community to win elections.
Answer:
![]()
Question 38.
Assertion (A): Caste is an important source of economic inequality.
Reason (R): It regulates access to resources of various kinds.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Explanation: Caste decided the allocation of resources. A Lot of backward classes have become even worse because of inequality of education and opportunities.
Question 39.
Assertion (A): The ruling party and the sitting MP or MLA frequently lose elections in our country.
Reason (R): Caste is the only factor that affects Politics.
Answer:
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
Explanation: Caste is not the only factor that affects politics. The performance of the leaders, their control and their decisions, their ideologies and methodologies also affect the result of elections.
Question 40.
Assertion (A): Caste groups that had access to education under the old system have done very well.
Reason (R): Education helps in development of people.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
![]()
Question 41.
Assertion (A): Unless women control power, their problems will not get adequate attention.
Reason (R): They are not given attention because the decision making bodies have no representation of women and men are unable to relate to women issues.
Answer:
Question 42.
Assertion (A): Politics based on caste identity alone is not very healthy in a democracy.
Reason (R): It can divide the society into different communities and cause inequalities.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Question 43.
Assertion (A): Caste division leads to tensions, conflict and even violence.
Reason (R): Violence is a positive expression of caste divisions.
Answer:
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
Explanation: Violence is a negative expression of caste divisions. The negative expression of caste division leads to tensions, conflict and even violence.
Question 44.
Assertion (A): Caste matters in electoral politics.
Reason (R): Caste affects the choice of people in elections. People choose according to their castes.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Explanation: Caste affects the choice of people. A lot of other factors affect electoral politics.
(Competency Based Questions (CBQs))
Question 1.
Read the given source and answer the question that follows:
Boys and girls are brought up to believe that the main responsibility of women is housework and bringing up children women do all work inside the home such as cooking, cleaning, washing clothes, tailoring, looking after children, etc., and men do all the work outside the home. It is notthat men cannot do housework; they simply think that it is for women to attend to these things.
Which of the following concepts have been reflected in this source?
(a) Communalism
(b) Sexual division of labour
(c) Family structure of India
(d) Society of India
Answer:
(b) Sexual division of labour
Explanation: Sexual division of labour entails stereotyping of labour-related works according to sexes. For example, works like cooking, cleaning and washing clothes have been categorised into works to be done by women while works Like earning and providing are categorised into works to be done by men.
![]()
Question 2.
Read the given source and answer the question that follows:
Shree was livid. He wanted a wife who would cook for him, wash his clothes and take care of his ailing parents. Instead, Kriti was a woman or a man who believed in equal rights and opportunities for men and women. She wanted Shree to help her at home so she could also go for her job. She also wanted to provide for their family equally.
Which of the following words can replace the underlined sentence?
(a) Feminist
(b) Patriarch
(c) Ideal Housewife
(d) Modern
Answer:
(a) Feminist
Question 3.
Read the table given below and answer the question that follows:
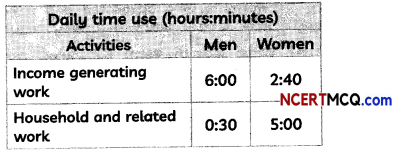
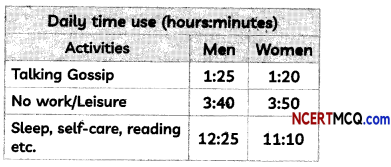
Which of the following is the reason for women’s income generating work figures being drastically less than those of men?
(a) Women work less
(b) Women sleep more
(c) The work of women remains invisible.
(d) The work of women is not worth money.
Answer:
(c) The work of women remains invisible.
Explanation: Work of the women remains invisible. The work done by men is more visible because most of their work leads to generation of income. A bulk of women’s work is household related and thus remains unpaid and invisible.
Question 4.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Most tailors or cooks in hotels are men. Similarly, it is not that women do not work outside their home. In villages, women fetch water, collect fuel and work in the fields. In urban areas, poor women work as domestic helpers in middle class homes, while middle class women work in offices. In fact the majority of women do some sort of paid work in addition to domestic labour. But their work is not valued and does not get recognition. The result of this division of labour is that although women constitute half of humanity, their role in public life, especially politics, is minimal in most societies.
(A) Give a label to the tendency of stereotyping labour/works based on gender.
(a) Female exploitation
(b) Sexual Division of Labour
(c) Casteist Division of Labour
(d) Labour determinism
Answer:
(b) Sexual Division of Labour
Explanation: A system in which all work inside the home is either done by stereotyping or labelling of certain tasks as female-oriented and others as male oriented.
(B) Who does the employers discriminate against while paying wages?
(a) Women
(b) Men
(c) High Caste groups
(d) Middle Class groups
Answer:
(C) What do feminist movements stand for?
Answer:
Feminist women stand for equal political, social, employment related and educational opportunities for women.
(D) Assertion (A): Political movements and mobilisation helped women gain strength.
Reason(R): It helped them raise their voices against the indiscriminate practices.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
(d) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Question 5.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
The Census of India records the religion of each and every Indian after every ten years. The person who fills the Census form visits every household and records the religion of each member of that household exactly the way each person describes it. If someone says she has ‘no religion’ or that he is an ‘atheist’, this is exactly how it is recorded. Thus we have reliable information on the proportion of different religious communities in the country and how it has changed over the years.
Since Independence, the total population of each community has increased substantially but their proportion in the country’s population has not changed much. In percentage terms, the population of the Hindus, Jains and Christians has declined marginally since 1961. Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
(A) Which of the following committees is also called the Sachar Committee?
(a) Prime Minister’s High Level Committee
(b) Home Affairs Committee
(c) NSSO
(d) Ministry of Statistics and High Committee
Answer:
(a) Prime Minister’s High Level Committee
(B) Fill in the blank with an appropriate option:
Scheduled Tribes- Adivasis; Scheduled Castes- …………………
(a) Subcastes
(b) Outcastes
(c) Below Castes
(d) Tricaste
Answer:
(b) Outcastes
(C) Who of the following is the perfect definition of an atheist?
(a) Ram worships Lord Krishna and visits temples everyday.
(b) Srikanth does not wear any religious thread and does not let his brother wear any because he believes there is no supreme power.
(c) Ali does not eat any meat during holy month.
(d) Kriya visits the church every day.
Answer:
(D) Which of the following groups have declined in population since 1961?
(a) Hindus
(b) Scheduled Caste
(c) Muslims
(d) Scheduled Tribes
Answer:
(a) Hindus
Explanation: In percentage terms, the population of the Hindus, Jains and Christians has declined marginally since 1961. The proportion of Muslim, Sikh and Buddhist population has increased slightly.
Question 6.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Partly due to their efforts and partly due to other socio-economic changes, castes and caste system in modern India have undergone great changes. With economic development, large scale URBANISATION, growth of literacy and education, OCCUPATIONAL MOBILITY and the weakening of the position of landlords in the villages, the old notions of CASTE HIERARCHY are breaking down.
Now, most of the times, in urban areas it does not matter much who is walking along next to us on a street or eating at the next table in a restaurant. The Constitution of India prohibited any caste-based discrimination and laid the foundations of policies to reverse the injustices of the caste system. If a person who lived a century ago were to return to India, she would be greatly surprised at the change that has come about in the country. Yet caste has not disappeared from contemporary India. Some of the older aspects of caste have persisted.
Even now most people marry within their own caste or tribe.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
(A) Which of the following leaders have contributed in changing the caste system?
(a) EVRPeriyar
(b) Abdul Kalam
(c) Pt. Nehru
(d) Subhash Chandra Bose
Answer:
(a) EV R Periyar
(B) Which of the following has not been instrumental in changing the Caste system in India?
(a) Urbanisation
(b) Growth of literacy and education
(c) Occupational Mobility
(d) Change in geography of a country
Answer:
(d) Change in geography of a country
(C) Fill in the blank with an appropriate option:
……………. is an old aspect of caste which has persisted even today.
(a) Caste marriages
(b) Widow remarriage
(c) Untouchability
(d) Child marriage
Answer:
(c) Untouchability
Explanation: Other social issues do not relate to Caste groups in general.
(D) Which of the following is the correct definition of Caste Hierarchy?
(a) Caste hierarchy is a ladder-like formation in which all caste groups are placed from the ‘highest’ to the ‘lowest’ caste.
(b) Caste hierarchy is a pool of castes.
(c) Caste hierarchy is a bucket of castes where they are arranged according to alphabets.
(d) Caste hierarchy is a ladder-like formation in which all lingual groups are attached.
Answer:
![]()
Question 7.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Unlike gender differences, the religious differences are often expressed in the field of politics.
Consider the following: Gandhiji used to say that religion can never be separated from politics. What he meant by religion was not any particular religion like Hinduism or Islam but moral values that inform all religions. He believed that politics must be guided by ethics drawn from religion. Human rights groups in our country have argued that most of the victims of communal riots in our country are people from religious minorities. They have demanded that the government take special steps to protect religious Minorities. Women’s movement has argued that FAMILY LAWS of all religions discriminate against women. So they have demanded that governments should change these laws to make them more equitable.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
(A) Which of the following beliefs about religion and Politics were that of Gandhiji?
(a) Religion and politics can never be together.
(b) Religion and politics complete each other.
(c) Religion is important for politics to be ethical
(d) Politics is important for religion to sustain.
Answer:
(B) Which one of the following is not a cause of communalism?
(a) Religion as the basis of the nation.
(b) One religion pitted against the other.
(c) State with an official religion.
(d) Religion-less state.
Answer:
(d) Religion-less state.
Explanation: Religion causes communalism when expressed negatively. A religion-less state will never face the issue of communalism.
(C) Which of the following groups form a religious minority?
(a) Scheduled Castes
(b) Jains
(c) Children below 2 years
(d) Underprivileged people
Answer:
(c) Jains
Explanation: The other three are not religious minorities.
(D) Which of the following laws are discriminatory according to women?
(a) Civic Laws
(b) Criminal Laws
(c) Family Laws
(d) Moral Laws
Answer:
(c) Family Laws
Explanation: The other three are non- discriminatory towards any group.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Mention one special feature of the caste system in India?
Answer:
In most societies, occupations are passed on from one generation to another. Occupational divisions are sanctioned by rituals.
Question 2.
Name a few political leaders and social reformers who advocated and worked to establish a society without any inequalities
Answer:
![]()
Question 3.
What does the term ‘Scheduled’ denote in ‘Scheduled castes’ and ‘Scheduled tribes’?
Answer:
These groups include hundreds of castes or tribes whose names are listed in an official Schedule in the Indian Constitution. Hence, they are called Scheduled.
Question 4.
What was the child sex ratio in India in the 2011 census?
Answer:
The child sex ratio is 919 females to 1000 males.
Question 5.
Read the following information and write a single term for it.
The Constitution of India provides freedom to profess and practice any religion to all its citizens. The Constitution of India prohibits discrimination on religious grounds.
Answer:
The Constitution of India promotes Secularism.
Question 6.
“Caste system is still prevalent in the Indian society.” Suggest anyone measure to abolish it.
Answer:
Casteism can be abolished by providing educational, employment opportunities, and health facilities to all the citizens of the country without any prejudice or discrimination.
Question 7.
“Sometimes elections are all about castes in India.” How can this situation be avoided?
Answer:
Question 8.
Suggest any one way to protect women from domestic oppression.
Answer:
Educating women can help them stay aware. This way, they can also learn about various laws made for their protection and save themselves from domestic oppression.
![]()
Question 9.
Suggest any one way to create communal harmony among various communities of India.
Answer:
One way to create communal harmony among communities is to respect and accept all religions equally.
Question 10.
Suggest any one way to change ‘family laws’ of all religions.
Answer:
Question 11.
How much representation do local governments provide for women in India?
Answer:
One-Third of all the seats present in the institutions are reserved for women.
Question 12.
What do you mean by patriarchal society?
Answer:
Patriarchal society is a male-dominated social system wherein males hold primary and maximum power. In this society, women are not given equal chances.
Question 13.
In which constitutional institution have seats been reserved for women?
Answer:
Local Self Government bodies.
Question 14.
By what term is a p jrson known who believes in equal rights and opportunities for women?
Answer:
Feminist
Question 15.
State any one provision in the Indian constitution which makes India a secular state.
Answer:
Question 16.
Has the caste system really disappeared from India? Justify with reasons.
Answer:
No, the Caste System has not disappeared. Politics is still dominated by religion and caste.
Question 17.
What is urbanisation ?
Answer:
Urbanisation is the shift of population from rural areas to urban areas.
![]()
Question 18.
Mention any one of the factors that are decisive in elections.
Answer:
Question 19.
Stdte any one negative result of paying exclusive attention to caste in a democracy.
Answer:
This can lead to diversion of interest and attention from poverty, development and corruption.
Question 20.
How has the relationship between caste and economic status changed?
Answer:
It is possible to find very rich and very poor people in every caste which was not true decades ago. Thus , there are cases where caste and economic status are different.
Question 21.
Define Below Poverty line?
Answer:
Below the poverty line means those who spent Rs. 327 or less per person per month in rural and Rs. 454 or less per person per month in urban areas
Question 22.
What is sexual division of labour ?
Answer:
It is a system in which work is divided based on one’s gender.
Explanation: All work inside the home is either done by the women of the family, or organised by them through the domestic helpers.
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science with Answers
Class 10 Social Science Civics MCQ:
