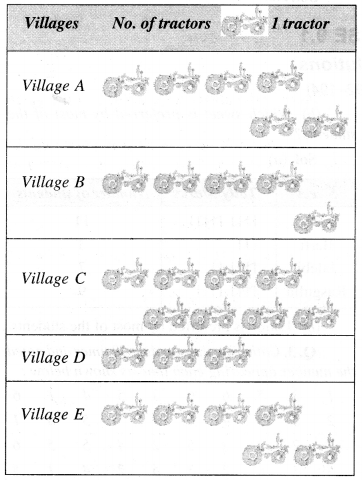
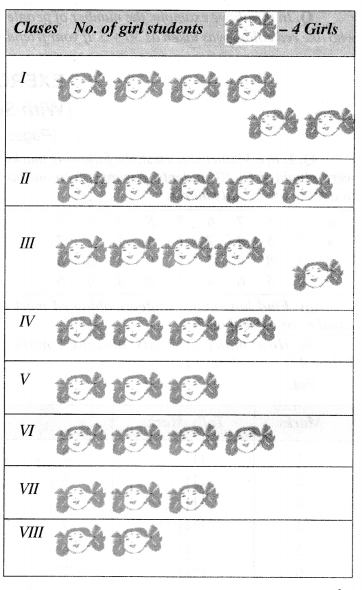
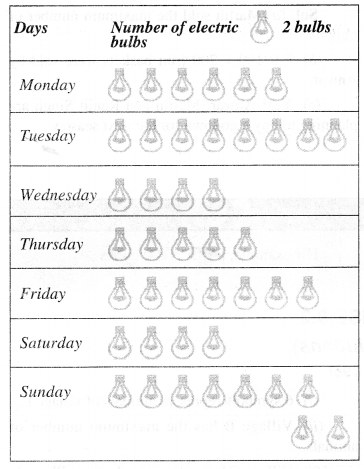
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 13 Symmetry Ex 13.1 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 13 Symmetry Ex 13.1.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 6 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 13 |
| Chapter Name | Symmetry |
| Exercise | Ex 13.1 |
| Number of Questions Solved | 6 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 13 Symmetry Ex 13.1
Question 1.
List any four symmetrical objects from your home or school.
Solution :
The blackboard, the table top, a pair of scissors, the computer disc.
Question 2.
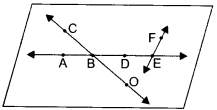
For the given figure, which one is the mirror line, l1 or l2?
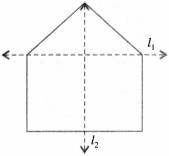
Solution :
I2 is the mirror line.
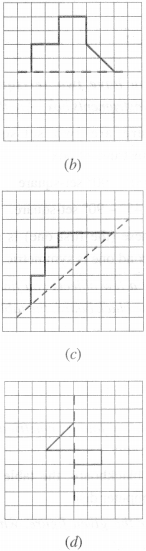
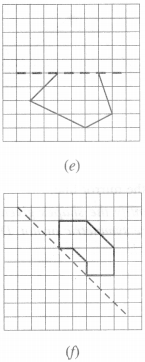
Question 3.
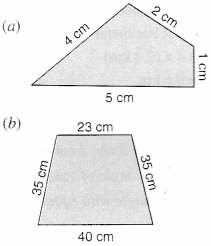
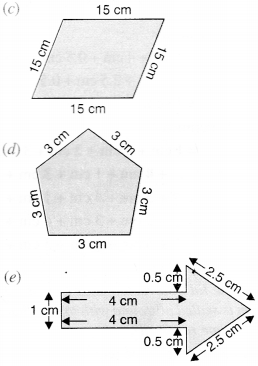
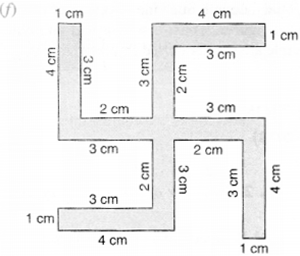
Identify the shapes given below. Check whether they are symmetric or not. Draw the line of symmetry as well.
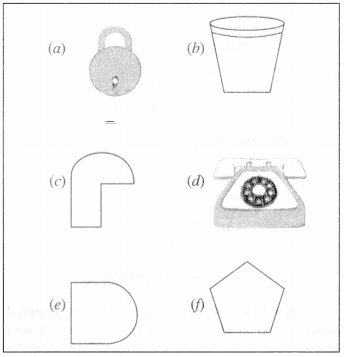
Solution :
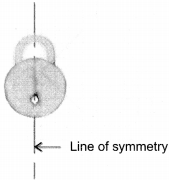
(a) Symmetric
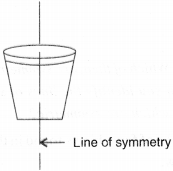
(b) Symmetric
(c) Not symmetric
(d) Symmetric
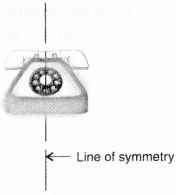
(e) Symmetric
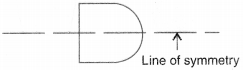
(f) Symmetric
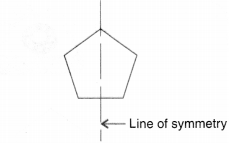
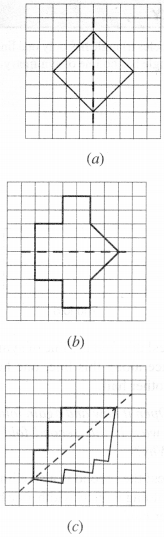
Question 4.
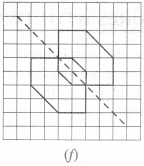
Copy the following on a squared paper. A square paper is what you would have used in your arithmetic notebook in earlier classes. Then complete them such that the dotted line is the line of symmetry.
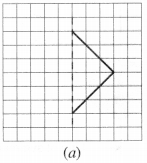
Solution :
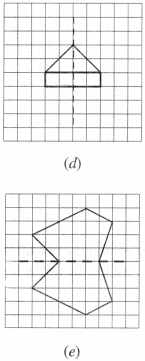
Question 5.
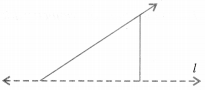
In the figure, l is the line of symmetry. Complete the diagram to make it symmetric.
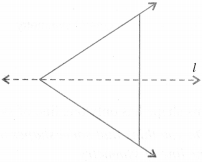
Solution :
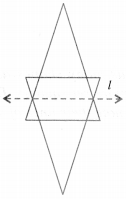
Question 6.
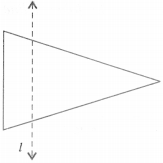
In the figure, l is the line of symmetry. Draw the image of the triangle and complete the diagram so that it becomes symmetric.
Solution :
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 13 Symmetry Ex 13.1 help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 13 Symmetry Ex 13.1, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.