Class 10 Science Biology Chapter 15 MCQ With Answers
Biology Class 10 Chapter 15 MCQs On Our Environment
Our Environment Class 10 MCQ Question 1.
In the given food chain, suppose the amount of energy at the fourth trophic level is 5 kJ, what will be the energy available at the producer level?
Grass Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk
(a) 5 kJ
(b) 50 kJ
(c) 500 kJ
(d) 5000 kJ
Answer:
Class 10 Science Chapter 15 MCQ Question 2.
The Foodweb is constituted by:
(a) relationship between the organisms and the environment
(b) relationship between plants and animals
(c) various interlinked food chains in an ecosystem
(d) relationship between animals and the environment
Answer:
Our Environment Class 10 MCQ With Answers Question 3.
In an ecosystem, the 10% of energy available for transfer from one trophic level to the next is in the form of:
(a) heat energy
(b) light energy
(c) chemical energy
(d) mechanical energy
Answer:
![]()
Our Environment MCQ Class 10 Question 4.
Choose the incorrect statement from the following:
(a) Ozone is a molecule formed by three atoms of oxygen.
(b) Ozone shields the surface of the Earth from ultraviolet radiations.
(c) Ozone is deadly poisonous
(d) Ozone gets decomposed by UV radiations
Answer:
Ch 15 Science Class 10 MCQ Question 5.
Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several types of organisms belonging to a lower trophic level constitute the:
(a) food web
(b) ecological pyramid
(c) ecosystem
(d) food chain
Answer:
(a) food web
Explanation: Organisms of a higher trophic level feeding on several types of organisms belonging to a lower trophic level constitute the food web.
MCQ On Our Environment Class 10 Question 6.
Expand the abbreviation GAP:
(a) Governmental Agency for Pollution Control
(b) Gross Assimilation by Photosynthesis
(c) Ganga Action Plan
(d) Governmental Agency for Animal Protection
Answer:
(c) Ganga Action Plan
Explanation: GAP, 1985 came in existence to check water pollution in river Ganga.
Class 10 Our Environment MCQ Question 7.
Which of the following are biodegradable substances?
(a) Glass bottle, Grass
(b) Jutebag, polythene bag
(c) Cotton cloth, vegetable peels
(d) DDT, Pen refill
Answer:
MCQ Of Our Environment Class 10 Question 8.
Which of the statement is incorrect?
(a) Producers form the first prophic level.
(b) Produces trap solor energy and transform it into chemical energy in food.
(c) All plants are producers.
(d) Nutrients and energy enter the living world through producers.
Answer:
![]()
Class 10 Science Ch 15 MCQ Question 9.
Which of the following limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain?
(a) Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels
(b) Deficient food supply
(c) Polluted air
(d) Water
Answer:
Chapter 15 Class 10 Science MCQ Question 10.
In the given figure, the various trophic levels are shown in a pyramid. At which trophic level is maximum energy available?
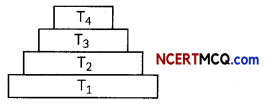
(a) T4
(b) T2
(c) Ti
(d) T3
Answer:
Chapter 15 Science Class 10 MCQ Question 11.
Disposable plastic plates should not be used because:
(a) they are made of materials with light weight
(b) they are made of toxic materials
(c) they are made of biodegradable materials
(d) they are made of non-biodegradable materials
Answer:
Environment Class 10 MCQ Question 12.
Which one of the following stakeholders of forests causes the maximum damage to forest?
(a) People who live in or around the forest
(b) The forest department of the government
(c) The wildlife and native enthusiasts
(d) The industrialists
Answer:
(d) The industralists
Class 10 Chapter 15 MCQ Science Question 13.
Food web is constituted by:
(a) Relationship between the biotic and abiotic components of ecosystem.
(b) Relationship between abiotic compo-nents and recycling of nutrients.
(c) Relationship between biotic compo-nents and biogeochemical cycles.
(d) Various interlinked food chains in an ecosystem.
Answer:
![]()
Class 10 Science Chapter 15 MCQ Online Test Question 14.
Consider a terrestrial food chain: Grass Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Eagle
The energy transfer in the above food chain will be from:
(I) Producer to decomposer
(II) Producer to primary consumer
(III) Primary consumer to secondary consumer
(IV) Tertiary consumer to Secondary consumer
(a) Both (I) and (III)
(b) Both (I) and (IV)
(c) Both (II) and (III)
(d) Both (III) and (IV)
Answer:
MCQ Of Chapter 15 Science Class 10 Question 15.
Which of the statements regarding food chain are correct?
(I) All food chains are of equal length and complexity.
(II) Food chains generally consist of only three or four steps.
(III) The greatest number of organisms in a food chain is of the producers.
(IV) Relationships between organisms can be shown only by straight lines.
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (III) and (IV)
(d) (II), (III) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 16.
Ozone-depleting substances are chiefly utilized in
(I) chimneys
(II) cooling and refrigeration applications and in the manufacturer of foam products
(III) all of the human activities
(IV) burning fossil fuels
(a) Only (I)
(b) Only (II)
(c) (I), (II) and (IV)
(d) (II), (III) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 17.
Consider the chemical reactions taking place at upper atmosphere:
![]()
Select the row containing the correct naming of A, B and C.
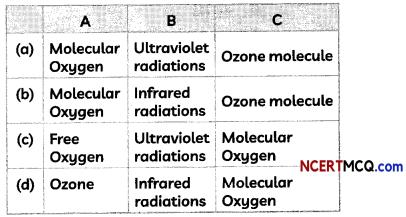
Answer:
(a) A: Molecular oxygen; B: Ultraviolet radiations; C: Ozone molecule
Explanation: Ozone at the higher levels of the atmosphere is a product of Ultraviolet radiation acting on oxygen (02) molecule. The higher energy UV radiations split apart some molecular oxygen (O2) into free oxygen (O) atoms and these atoms then combine with the molecular oxygen to form ozone as shown below:
![]()
![]()
Question 18.
The food habits of the organisms at the second and fourth trophic levels of a typical terrestrial are given in the table below.
Select the row containing the correct food habits:

Answer:
Question 19.
The protocol agreed upon in 1987 organized by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is related to:
(a) Food security
(b) Ozone layer depletion
(c) Global warming
(d) Sustainable deveLopment
Answer:
(b) Ozone Layer depletion

Explanation: In 1987. the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) succeeded in forging an agreement to freeze CFC production at 1986 Levels in order to stop the depletion of ozone layer.
Question 20.
The formation of ozone in the stratosphere is powered by:
(a) UltravioLet radiation
(b) Infrared radiations
(c) Atmospheric oxygen
(d) CFC
Answer:
![]()
Question 21.
Which organism shown in the food chain above wouLd Contain the greatest concentration of chemical pollutants?
Phytoplankton → Krill → Small fish → Tuna → Shark
(a) Phytoplankton
(b) KriLl
(c) Tuna
(d) Shark
Assertion Reasoning questions Class 10 Science Chapter 15
For the following questions, two statements are given one labeled Assertion (A) and the other Labeled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given beLow:
(a) Both (A) and (R) true and (R) is correct explanation of the assertion
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is correct Explanation of the assertion.
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Question 22.
Assertion (A): Green plants of the ecosystem are the transducers.
Reason (R): Producers trap the radiant
energy of the sun and change it into chemical energy.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of assertion. Explanation: Green plants can make their own food. Hence, they are called producers. Since they capture the heat of the Sun to prepare their food, they are also called transducers. The plants prepare their food by trapping the energy of the Sun. They convert this light energy to chemical energy to form ATP molecules.
Question 23.
Assertion (A): Food chains generally consist of only three to four steps.
Reason (R): Autotrophs capture solar energy and convert it into chemical energy.
Answer:
Question 24.
Assertion (A): The maximum concentration of chemicals and pesticides occurs at the first trophic leveL
Reason (R): The chemicals and pesticides are not biodegradable.
Answer:
![]()
Question 25.
Assertion (A): Ozone shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
Reason (R): Ozone at the higher levels of the atmosphere is a product of UV radiations acting on oxygen molecules.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of assertion. Explanation: Ozone is formed when the high-energy UV radiations act on oxygen molecules (O2) and split it into free oxygen atoms (O) which combine with the molecular oxygen to form ozone (O3). Ozone thus shields the earth’s surface from the harmful effects of UV radiation.
Question 26.
Assertion (A): Improvements in our lifestyle have resulted in lesser amounts of waste material generation.
Reason (R): Changes in packaging have resulted in much of the waste generated being non-biodegradable.
Answer:
(d) (A) is false, but R is true.
Explanation: Improvements in our lifestyle have resulted in greater amounts of waste material generation due to changes in attitude and more and more things we use becoming disposable, which are also non-biodegradable.
Question 27.
Assertion (A): Frogs mostly occupy the second trophic level in food chains.
Reason: Frogs mostly feed on insects that depend on plants.
Answer:
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Explanation: Frogs mostly occupy the third trophic level in the food chain since they feed on insects which depend on plants and plants are the primary producers thus they occupy the first trophic level in the food chain. Thus A is false, but R is true.
![]()
Question 28.
Assertion(A): In the food chain third trophic level is occupied by Carnivores.
Reason(R): Some of the carnivores are secondary consumers.
Answer:
Question 29.
Assertion (A): Each step of the level of the food chain forms a trophic level.
Reason (R): The organisms occupying the first trophic levels are called autotrophs.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 30.
Assertion (A): Each step or level of the food chain forms a trophic leveL
Reason (R): The various components of the ecosystem are interdependent.
Answer:
Question 31.
Assertion (A): Polythene bags are non-biodegradable substances.
Reason (B): These bags cannot be broken down by microorganisms to simpler substances.
Answer:
![]()
Question 32.
Assertion (A): The food chains generally consist of only three or four steps.
Reason (B): Our food grains such as wheat and rice, vegetables and fruits and even meat contain varying amounts of pesticides.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Explanation: The food chains generally consist of only three or four steps because after that the energy added to the biomass of each level is reduced and at the fourth trophic level it will be least. Thus Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion
Question 33.
Assertion (A): The amount of ozone in the atmosphere began to increase sharply in the 1980c.
Reason (R): The United Nations environment program (UNEP) succeeded in forging an agreement to freeze CFC production in 1987.
Answer:
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Explanation: The amount of ozone in the atmosphere began to decrease sharply in the 1980s because of the United Nations environment program (UNEP) succeeded in forging an agreement to freeze CFC production in 1987. Thus A is false, but R is true.
(Competency Based Questions (CBQs))
Question 1.
India today is facing the problem of overuse of resources, contamination of water and soil and lack of methods of processing the waste. The time has come for the world to say goodbye to “single-use plastics.” Steps must be undertaken to develop environment-friendly substitutes, effective plastic waste collection and methods of its disposal.
Indore treated 15 lakh metric tonnes of waste in just 3 years, through biomining and bioremediation techniques. Bioremediation involves introducing microbes into a landfill to naturally ‘break’ it down and biomining involves using trommel machines to sift through the waste to separate the ‘soil’ and the waste component.
The city managed to chip away 15 lakh metric tonnes of waste at a cost of around? 10 crore. A similar experiment was successfully carried out in Ahmedabad also.
(A) State two methods of effective plastic waste collection in your school.
Answer:
(B) Name any two uses of “single-use plastic” in daily Life.
Answer:
Uses of “Single-use plastic” in daily life.
- In medical field: Plastic syringes, plastic gloves are made of single-use plastic and are used so that infection can be controlled.
- Single-use plastic is also used in food industry for packing, straws, wrappers, spoons etc.
- In emergency/ disaster situations where food and water has to be transported. Plastic will be light in weight and this packaging will be helpful to transport.
(C) If we discontinue the use of plastic, how can an environment-friendly substitute be provided?
Answer:
(D) Do you think microbes will work similarly in landfill sites as they work in the laboratory? Justify your answer.
Answer:
No, the microbes will not work similarly in landfill sites as they work in laboratory. Microbes need suitable conditions like temperature, moisture etc. and nutrients to grow. In laboratory we provide this atmosphere artificially to microbes for their growth but landfill sites do not have suitable atmosphere to grow.
![]()
Question 2.
Prerna visited a farm along with her family. Her younger brother was interested in knowing what kind of food is eaten by animals such as cows, buffaloes and deers. She told her brother that all these animals are herbivores as these eat only grass and plants.

How much of the net primary productivity of a terrestrial ecosystem is eaten and digested by herbivores?
(a) 100%
(b) 10%
(c) 1%
(d) 0.1%
Answer:
(b) 10%
Explanation: 10% of the net primary productivity of terrestrial ecosystem is eaten and digested by herbivores. According to 10% law, only 10% of the energy entering a particular trophic level of organisms is available for transfer to the next higher trophic level.
Question 3.
Human body is made up of five important components, of which water is the main component. Food, as well as potable water, are essential for every human being. The food is obtained from plants through agriculture. Pesticides are being used extensively for a high yield in the fields.
These pesticides are absorbed by the plants from the soil along with water and minerals and from the water bodies these pesticides are taken up by the aquatic animals and plants. As these chemicals are not biodegradable, they get accumulated progressively at each trophic level.
The maximum concentration of these chemicals gets accumulated in our bodies and greatly affects the health of our mind and body.
(A) Why is the maximum concentration of pesticides found in human beings?
Answer:
As human beings occupy the top level in any food chain, the maximum concentration of these chemicals get accumulated in our bodies due to biological magnification.
Explanation: Pesticides are being used extensively for a high yield in the fields. These pesticides mix up with soil and water. From soil and water, these pesticides are absorbed by the plants along with water and minerals. When herbivores eat this plant food, these chemicals pesticides go into their bodies through the food chain. When the next trophic level, carnivores eat herbivores, these pesticides get transferred to their bodies. As these chemicals are not biodegradable, they get accumulated progressively at each trophic level.
(B) Give on method which could be applied to reduce our intake of pesticides through food to some extent.
Answer:
- We can reduce our intake of pesticides through food to some extent:
- Wash fruits and vegetables before eating. Buy organic and locally grown fruits and vegetables.
- Use non-toxic methods for controlling insects in the kitchen garden. (Anyone).
(C) Various steps in a food chain represent:
(a) Food web
(b) Trophic level
(c) Ecosystem
(d) Biomagnification
Answer:
(D) With regard to various food chains operating in an ecosystem, man is a:
(a) Consumer
(b) Producer
(c) Producer and consumer
(d) Producer and decomposer
Answer:
![]()
Question 4.
Driving the Swach Bharat Abhiyaan forward, several NCOs are working towards the instaLLation of Blue and Green Dustbins for Municipal Corporations and schools in New Delhi. They are also carrying out a drive to educate children about the segregation of two different kinds of waste. The green is meant for wet waste and the blue one is for dry waste. This way they are separating biodegradable waste from non-biodegradable, thus providing various recycling and composting benefits and keeping the neighborhood clean and healthy.

In the following groups of materials, which group(s) contain(s) only non-biodegradable items?
(I) Wood, paper, leather
(II) Polythene, detergent, PVC
(III) Plastic, detergent, grass
(IV) Plastic, Bakelite, DDT
(a) (I)
(b) (II)
(c) (I) and (II)
(d) (II) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 5.
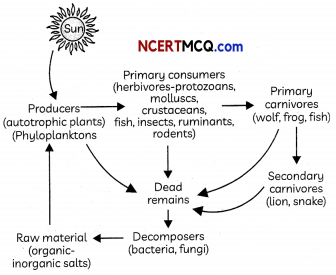
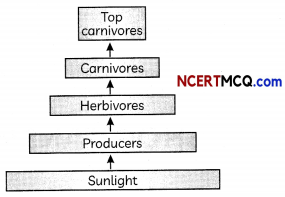
Series of organisms taking part at various biotic levels form a food chain. Each step or level of the food chain forms a trophic level. The autotrophs or the producers are at the first trophic level. They fix up the solar energy and make it available for heterotrophs or the consumers.
The herbivores or the primary consumers come at the second, small carnivores or the secondary consumers at the third and larger carnivores or the tertiary consumers form the fourth trophic level.
The interactions among various components of the environment involve flow of energy from one component of the system to another.
(A) What are trophic levels?
Answer:
Decomposers are microorganisms which breakdown complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances and help in recycling of nutrients. They feed on the dead and decaying bodies of plants and animals. They return the nutrients back to the soil and thus help in making this ecosystem stable e.g. fungi, bacteria.
(B) Give an example of a food chain.
Answer:
(C) What is the role of decomposers in the ecosystem?
Answer:
(D) Explain why the number of trophic levels in a food chain is limited?
Answer:
Only 10% of the energy gets transferred from one trophic level to the next. So after 3 or 4 trophic levels, the energy available for passing on is too less to support another trophic level. Very little usable energy remains after 4 trophic levels. Hence the number of trophic levels in a food chain is limited.
![]()
Question 6.
Nitya observed her grandmother making compost which she used to give to her plants. Composting is the natural process of recycling organic matter, such as leaves and food scraps, into a valuable fertilizer that can enrich soil and plants. Anything that grows decomposes eventually; composting simply speeds up the process by providing an ideal environment for bacteria, fungi, and other decomposing organisms (such as worms, sowbugs, and nematodes) to do their work. The resulting decomposed matter, which often ends up looking like fertile garden soil, is called compost. Fondly referred to by farmers as “black gold,” compost is rich in nutrients and can be used for gardening, horticulture, and agriculture.

The decomposers in an ecosystem:
(a) convert inorganic material to simpler forms
(b) convert organic material to inorganic forms
(c) convert inorganic material to organic compounds
(d) do not breakdown organic compounds
Answer:
(b) convert organic material to inorganic forms Explanation: The microorganisms, comprising bacteria and fungi, break down the dead remains and waste products of organisms. These microorganisms are the decomposers as they break down complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances that go into the soil and are once more used up by the plants.
Question 7.
You might have seen an aquarium, in the first activity, let us try to design an aquarium. What are the things that we need to keep in mind when we create an aquarium? The fish would need a free space for swimming (it could be a large jar), water, oxygen and food. We can provide oxygen through an oxygen pump (aerator) and fish food which is available in the market. If we add a few aquatic plants and animals it can become a self sustaining system.
In the second activity, while creating an aquarium did you take care not to put an aquatic animal which would eat others? Write the aquatic organisms in order of who eats whom and form a chain of at least three steps. A → B → C
(A) Identify the human-made ecosystems from the following:
(I) Ponds
(II) Crop fields
(III) Aquarium
(IV) Lakes
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) (I), (III) and (IV)
(d) (II), (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(b) Both (II) and (III)
Explanation: Ponds and lakes are natural ecosystems, although there are some artificial or human made Lakes too. Aquariums and crop fields are human made ecosystems as these have been made by humans.
(B) The biotic and abiotic components in an aquarium are listed in the table below. Select the row containing the correct answer:
| Biotic Components |
Abiotic Components |
| (a) Aquatic plants and animals, water | Glass tank, aerator |
| (b) Glass tank, aquatic plants and animals | Water, aerator |
| (c) Aquatic plants and animals | Glass tank, water, aerator |
| (d) Glass tank, water, aerator | Aquatic plants and animals |
(a) Ponds are natural ecosystems whereas aquariums are artificial ecosystems.
(b) There are less fishes in an aquarium as compared to a pond or lake
(c) The size of fishes is small in an aquarium as compared to a pond or lake
(d) Decomposers are absent in an aquarium whereas they are present in ponds or lakes.
Answer:
(D) What would have happened if we had put predator fishes in the aquarium?
(a) They would eat all the smaller fishes thereby generating lot of waste.
(b) They would eat away all the food available in the aquarium.
(c) They would compete with smaller fish for food and nutrition.
(d) They would not pose any problem in the aquarium.
Answer:
(E) Consider the following aquatic food chain consisting of three steps:
![]()
Identify the organisms at A, B and C:
(a) A: Zooplankton; B: Phytoplankton; C: Large fish
(b) A: Phytoplankton; B: Zooplankton; C: Small fish
(c) A: Zooplankton; B: Phytoplankton; C: Small fish
(d) A: Phytoplankton; B: Zooplankton; C: Large fish
Answer:
![]()
Question 8.
Ritu went to the shopping mall to buy some gifts for her parents on their wedding anniversary. She was pleasantly surprised to see that all shop owners were giving the items purchased in beautiful and coloured paper bags instead of plastic bags.

Why is it better to use paper bags than plastic bags?
Answer:
Paper is a biodegradable material, as it is obtained from wood whereas plastic is a non- biodegradable material. Therefore, paper is environment friendly whereas plastic causes environmental pollution.
Question 9.
In the first activity, find out what happens to the waste generated at home. Find out how the local body (panchayat, municipal corporation, resident welfare association) deals with the waste. Are there mechanisms in place to treat the biodegradable and nonbiodegradable wastes separately?
Calculate how much waste is generated at home in a day. How much of this waste is biodegradable? Suggest ways of dealing with this waste.
Next, find out how the sewage in your locality is treated. Are there mechanisms in place to ensure that local water bodies are not polluted by untreated sewage. Find out how the local industries in your locality treat their wastes.
(A) In the following groups of waste generated at home, which group contains only biodegradable items?
(a) Glass bottles, news paper, used tea leaves
(b) Polythene, detergent, Plastic packets
(c) Vegetable peels, paper, flowers
(d) Plastic packets, PVC, Glass bottles
Answer:
(c) Vegetable peels, paper, flowers
Explanation: Biodegradable substances are those substances which are easily degraded by natural processes by the action of microorganisms. All materials of plant and animal origin are biodegradable whereas man made substances such as plastic, detergents, PVC, glass, etc are non- biodegradable.
(B) Based on the study of how most local municipal authorities deal with the wastes generated at home, following statements are written. Select the incorrect statement.
(a) The waste generated at home are differentiated into biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials.
(b) All types of wastes are placed in a single bin.
(c) Most of the “dry-waste” is processed at waste-to-energy plants.
(d) Most of the “wet-waste” is sent for composting
Answer:
(C) Which of the following is not the correct practice of dealing with biodegradable wastes?
(a) Composting
(b) Anaerobic digestion of waste
(c) Landfills
(d) Burning
Answer:
(D) Select the correct statements regarding treatment of sewage in any locality:
(I) Sewage is treated at sewage treatment plants.
(II) Sewage treatment is the process of removing contaminants from industrial wastewater only.
(III) Physical, chemical, and biological processes are used to remove contaminants and produce treated wastewater.
(IV) Sewage is treatment is the process of removing contaminants from domestic and municipal wastewater.
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (III) and (IV)
(d) Both (I) and (IV)
Answer:
(E) The best practice followed by local industries in treating their wastes is:
(a) Source reduction and reuse
(b) Incineration
(c) Dumping solid wastes in open drain
(d) Dumping chemical wastes directly into water bodies
Answer:
![]()
Question 10.
Vijay’s science teacher was once sharing experiences about his village life. He explained how as a child, he would often hear the sound of frogs during nights and especially during the rainy days. But the situation has changed now with lesser population of frogs even in villages.

The number of malaria patients in a village increased tremendously when large number of frogs were exported from the village? What could be its cause?.
Answer:
Question 11.
The sun is the ultimate source of light and heat for planet Earth and sets in motion very large and complex systems that develop and sustain life. One such land-based ecosystem is the forest, supporting a biodiverse set of plants, which in turn provide food for other living things. Several distinct types of woodland habitats exist on Earth, such as conifer, deciduous and mixed. A study of the deciduous forest shows how a food chain functions within an ecosystem that experiences distinct seasonal changes.
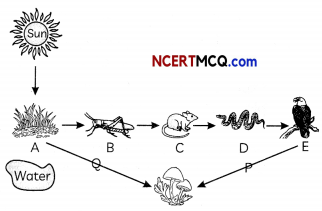
(A) In an ecosystem, the main source of energy is
(a) heat released during transpiration
(b) solar energy
(c) heat released during respiration
(d) water
Answer:
(b) Solar energy
Explanation: Sun is the main source of energy for an ecosystem since green plants or producers are able to synthesize food only with the help of solar energy .
(B) Refer to the figure of food chain given above, identify A, B, C and D and select the correct combination of plots provided in the table below.
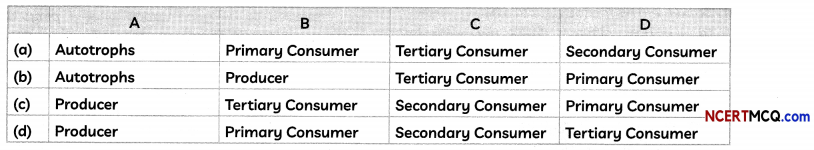
Answer:
(d) A: Producer; B: Primary Consumer; C: Secondary Consumer; D: Tertiary Consumer
Explanation: In all food chains, the green plants are the producers as they synthesize food by utilizing solar energy. The small insects marked !B’ or herbivores are the primary consumers as they feed on plants. Small animals marked ‘C’ are secondary consumers as they feed on small insects and similarly larger carnivores are tertiary consumers and marked ‘D‘ and ‘E’.
(C) Which of the following are functional components of an ecosystem?
(I) Decomposers
(II) Solar energy
(III) Energy flow
(IV)Air
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (III) and (IV)
(C) (I), (II) and (IV)
(d) (I), (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(D) The correct identification of P and Q from the figure of food chain given is:
(a) P: Decomposers, Q: Nutrients
(b) P: Decomposers, Q: SoiL
(c) P: Producers, Q: Nutrients
(d) P Tertiary Consumers, Q: SoiL
Answer:
(E) The effect of completely removing ‘P’ from the food chain would be:
(a) Energy flow would be blocked
(b) Movement of minerals back to soil will be blocked
(c) Rate of decomposition would increase
(d) No carbon dioxide will be available for herbivores for respiration
Answer:
(b) Movement of minerals back to soil will be blocked

Explanation: The organisms marked ‘P’ are the decomposers which help in cleansing our environment by feeding on dead and decaying organisms. They help in movement of minerals or nutrients back to the soil for the producers.
Question 12.
Sanket and his friends went to a nearby orchard to see how different fruits are cultivated. However, they observed that pesticides were being sprayed on the fruits without adhering to any guidelines.

How can excessive use of pesticides to protect the crops from diseases cause long-term damage to mankind?
Answer:
Pesticides are non-biodegradabLe chemicals which enter our food chain through the fruits we eat or are absorbed by the aquatic plants and animals. These concentration of these chemicals increases progressively at each trophic level and maximum concentration is found in human beings. This is known as biological magnification.
![]()
Question 13.
Ozone (O3) is a gas which is present naturally within Earth’s atmosphere and is formed of three oxygen atoms. In the figure we see a standard profile of ozone gas concentration through the Earth’s atmosphere, extending from ground level up to 40 kilometres in altitude. Ozone plays a different role in atmospheric chemistry at different heights in the Earth’s atmosphere. We can differentiate this profile into two key zones:
Tropospheric ozone is that which is present in the lower atmosphere. Throughout most of the troposphere, ozone concentrations are relatively low (as shown in the diagram). Ground-level ozone can have negative impacts on human health and is therefore commonly referred to as ‘bad’ ozone.
Stratospheric ozone is that which is present in the upper atmosphere. As shown in the diagram, concentrations of ozone are higher in the stratosphere than in the troposphere.
The stratosphere includes the zone termed the ‘ozone layer’. In the ozone layer, it is often referred to as ‘good’ ozone since it plays a crucial role in absorbing potentially dangerous ultraviolet (UV-B) radiation from the sun.
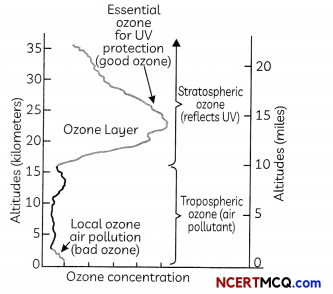
(A) Study the above graph and select the row containing the correct information:
| Good Ozone | Bad Ozone |
| Ionosphere | Mesosphere |
| Stratosphere | Ionosphere |
| Stratosphere | Troposphere |
| Mesosphere | Troposphere |
Answer:
(c) Good ozone: Stratosphere; Bad ozone: Troposphere
(B) Ozone at higher atmosphere is a product of:
(a) Ultraviolet radiation acting on free oxygen.
(b) Infrared radiation acting on oxygen molecule.
(c) Infrared radiation acting on free oxygen.
(d) Ultraviolet radiation acting on oxygen molecule.
Answer:
(C) Select the incorrect statements regarding ozone gas:
(I) It is present only in troposphere.
(II) It is present in very small quantities in stratosphere.
(III) It can be beneficial or harmful, depending upon its location and concentration.
(IV) It shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun.
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) (I), (II) and (111)
(d) (II), (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(a) Both (I) and (II)
Explanation: Ozone is present in very low concentration in the lower atmosphere or troposphere, it is present in higher concentrations in the upper atmosphere or stratosphere. It is quite harmful when present in the lower atmosphere as it causes several diseases in humans. It is beneficial when present in upper atmosphere as it shields the surface of the earth from the harmful ultraviolet radiations of the sun.
(D) Which of the following products contain ozone-depleting substances?
(a) Motorbike, car with AC, Pesticides, Fire extinguisher
(b) Car with AC, refrigerator, fire extinguisher, aerosol sprays
(c) Motorbike, aerosol sprays, Pesticides, Fire extinguisher
(d) Heater, car with AC, Pesticides, Fire extinguisher
Answer:
(E) Which of the following is not the consequence of ozone layer depletion?
(a) Increased ultraviolet rays
(b) Malignant melanoma-Another form of skin cancer
(c) Cataracts and other eye damage
(d) Tides
Answer:
![]()
Question 14.
Monty was travelling to Delhi by road from Chandigarh. He observed a huge mountain like structure on GT Karnal road upon entering Delhi. He came to know that it was actually a landfill site and that Delhi has three landfill sites, viz. at Okhla, Bhalswa and Ghazipur. One can find waste burning at any give time in these landfills. They have also run out of space nearly a decade ago. Although the permissible limit for a garbage dumping is set to 20 meters, these sites have turned into huge mountains well beyond the permissible limit.

Suggest two measures to manage the garbage we produce.
Answer:
Two measures to manage the garbage we produce are listed below:
(1) Segregate the wastes and try to reuse as many items as possible.
(2) Put wet and dry wastes in separate garbage bins so that they can be easily recycled.
Question 15.
Toxic substances move up the food chain and become more concentrated at each level. These substances are often pollutants from industries or pesticides from farming. Consider any small fish that eats plankton that has been tainted with mercury. Hundreds of small fish might then contain just few parts of the mercury, not enough to cause major harm. A bird then might eat hundreds of the small fish. so that now instead of 200 ppm ¡n a single fish, that bird has much higher Levels of mercury. The toxin amplifies as it moves up the food chain. The amount of mercury is measured in ppm, which means parts per million.
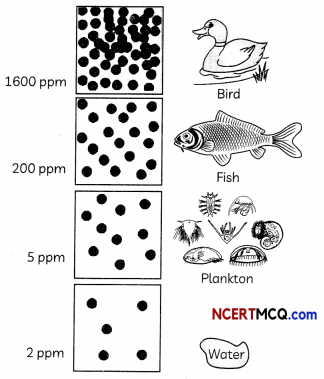
(A) The phenomenon when concentrations of a harmful substance increases in organisms at higher trophic LeveLs in a food chain or food web is:
(a) Artificial eutrofication
(b) Biological accumulation
(c) Biological magnification
(d) Biological pollution
Answer:
(B) The table below gives the organism in a food web containing the Lowest and highest concentration of harmful chemical pollutants.
Select the row containing the correct answer.
|
Lowest Concentration |
Highest Concentration |
| (a) Primary consumers | Secondary consumers |
| (b) Tertiary consumers | Producers |
| (c) Producers consumers | Secondary |
| (d) Producers consumers | Tertiary |
Answer:
(d) Lowest Concentration: Producers Highest Concentration: Tertiary consumers
Explanation: The concentration of harmful chemical pollutants such as DDT and other pesticides increases progressively at each trophic level Therefore, tertiary consumers which occupy the highest trophic level will have the highest concentration and producers which occupy the Lowest trophic level will have the lowest concentration of harmful chemical pollutants.
(C) Which of the following statements are incorrect?
(I) Non-biodegradable wastes are biological in origin.
(II) Biodegradable wastes are degraded by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi.
(III) Biodegradabte wastes enter the food chain and get biologically magnified.
(IV)Non-biodegradable wastes are absorbed by plants from the soil.
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (I) and (III)
(c) Both (II) and (III)
(d) Both (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(b) Both (I) and (III)
Explanation: The biodegradable wastes are biological in origin whereas non-biodegradable wastes are plastic, metals etc. The non-biodegradable wastes enter the food chain and get biologically magnified as we higher up the food chain.
(D) It was observed that at places where DDT was used to control mosquitoes and other pests, the eggs of eagles would become fragiLe and break and the eagle almost became extinct. After DDT was banned by Lawmakers, eagle population has recovered.
The possible reason for this is:
(a) DDT is non-biodegradable and hence found in Largest concentration in tertiary consumers.
(b) DDT is non-biodegradable and found in Largest concentration in producers.
(c) Largest concentration of DDT is found in secondary consumers on which eagle feeds.
(d) DDT is a strong chemical which makes the eggs fragile.
Answer:
(E) Biological magnification is a result of
(a) climate change
(b) food shortages
(c) pollution
(d) extinction
Answer:
![]()
Question 16.
The chemical energy of food is the main source of energy required by all living organisms. This energy is transmitted to different trophic levels along the food chain. The energy flow in the ecosystem is one of the major factors that support the survival of such a great number of organisms. For almost all organisms on earth, the primary source of energy is solar energy.
(A) The flow of energy in an ecosystem is:
(a) Omnidirectional
(b) Unidirectional
(c) Bidirectional
(d) May be unidirectional or bidirectional
Answer:
(B) Non-biodegradable wastes enter the food chain through:
(I) Soil
(II) Water
(III) Air
(IV) Decomposers
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (IV)
(c) Both (I) and (III)
(d) Both (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(a) Both (I) and (II)
Explanation: The non-biodegradable pesticides are either washed down into the soil or into the water bodies. From the soil, these are absorbed by the plants along with water and minerals, and from the water bodies these are taken up by aquatic plants and animals and hence enter the food chain.
(C) What happens to the solar energy incident on the autotrophs in a terrestrial ecosystem?
(a) It is completely captured and converted into food energy by the autotrophs.
(b) A part of it is reverted to the solar input
(c) A part of it is captured and passes to the herbivores.
(d) It moves progressively through the various trophic levels in both directions.
Answer:
(D) In the given food chain, suppose the amount of energy at fourth trophic level is 8 kJ.
Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk
Select the row containing the correct values of the energy available at the producer level and secondary consumer level?
| Energy Available Producer Level | Energy Available at Secondary Consumer Level |
| (a) 800kJ | 8kJ |
| (b) 800kJ | 80kJ |
| (c) 8000kJ | 72kJ |
| (d) 8000kJ | 80kJ |
Answer:
(E) If only 10% of the energy from one trophic level passes up to the next level, what happens to the 90% energy that is not passed on?
(a) It is lost as heat to the environment
(b) It is used in digestion of food and in doing work.
(c) It is used for growth and reproduction.
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) Energy Available at Producer Level: 8000 Id; Energy Available at secondary consumer level: 80 kJ
Explanation: According to 10 percent law, 90% of the energy captured from the previous trophic level is lost to the environment and only 10 percent is made available to the next trophic level.
in this food chain, at the 4th trophic level, 8 kJ energy is available to the snake. Therefore, we can calculate backwards to find energy available at the third, second and first trophic levels.
- Energy available to Snake (Tertiary consumer) = 8 kJ = 10% of 80 kJ
- Energy available to Frog (Secondary consumer) = 80 kJ = 10% of 800 kJ
- Energy available to Grasshopper (Primary consumer) = 800 kJ = 10% of 8000 kJ.
- The energy available to Grass (Producer) = 8000 kJ
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
List two main components of an ecosystem.
Answer:
Two main components of an ecosystem are
- Biotic component
- Abiotic component
Question 2.
What is meant by ‘biological magnification’?
Answer:
Biological magnification is the process by which the harmful and toxic substances enter the food chain and get concentrated in the body of living organisms at each successive level in food chain.
Question 3.
Name any two man-made ecosystems.
Answer:
Examples of man-made ecosystems are aquarium, crop-fields, zoo, botanical garden, Greenhouse
Related Theory
An ecosystem is a self-sustained unit that comprises of all the interacting living things together with their non-living environment Manmade or artificial ecosystems that are carefully maintained in controlled environment.
Biodiversity in the man-made ecosystem will be very low as compared to natural ecosystem.
![]()
Question 4.
Why should biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes be discarded in two different dustbins?
Answer:
Question 5.
What is meant by tropic level in a food chain? Construct a terrestrial food chain with four trophic levels. The energy flow in a food chain is always unidirectional. Why?
Answer:
Trophic level = Each step or level of the food chain forms a trophic level.
- The ultimate source of energy used by living organisms is the sun.
- Only 1% of solar radiations are captured by green plants in a terrestrial ecosystem and converted into food energy by photosynthesis. This energy is stored as chemical energy of food.
- When green plants (producers) are eaten by primary consumers (Herbivores) a lot of heat is lost as heat to the environment and other activities. Only 10% of the food eaten is turned into its new body and is available for the next level of consumers (Primary carnivores).
- Only 10% amount of organic matter reaches the next level of consumers (secondary carnivores).
- Since, amount of available energy goes on decreasing at each trophic level, food chains usually consist of only 3 to 4 trophic levels. For example, grass receives 6000 J of energy from the sun. It will pass 10% of energy as per 10% law to grasshopper i.e. 600 J and so on.

Question 6.
What will be the amount of energy available to the organisms of the 2nd trophic level of a food chain, if the energy available at the first trophic level is 10,000 joules?
Answer:
Question 7.
Why do producers always occupy the first trophic level on every food chain?
Answer:
![]()
Question 8.
Give 2 examples of each:
(A) Organisms occupying the first trophic level
Answer:
Organisms occupying the first trophic level: trees, shrubs, grass.
Related Theory
Green plants make their own food by the process of photosynthesse. The food or energy is transferred from one organism to the other through food chain. So the srarting point of a food chain in produces i.e., plant occupy the first prophic level.
(B) Abiotic factors of an ecosystem
Answer:
Abiotic factors of an ecosystem: soil, water, Light.
Related Theory
All the ecolytems are made of the main components biotic and abiotic components. The biotic component (living organisms) interact continuously with abiotic component (non-living component).
Question 9.
What are the advantages of doth bags over plastic bags during shopping?
Answer: