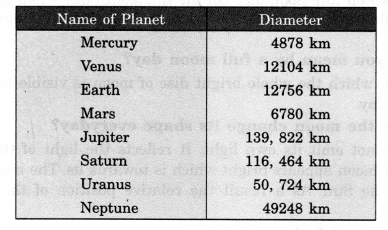
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 7 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 2 |
| Chapter Name | Nutrition in Animals |
| Number of Questions Solved | 13 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
- The main steps of nutrition in humans are ……., ………., ………., ………, and ………….
- The largest gland in the human body is ………..
- The stomach releases hydrochloric acid and ……… juices which act on the food.
- The inner wall of the small intestine has many finger-like outgrowths called ……….
- Amoeba digests its food in the ………..
Answer:
- ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion.
- liver
- digestive
- villi
- food vacuole.
Question 2.
Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
- Digestion of starch starts in the stomach. (T/F)
- The tongue helps in mixing food with saliva. (T/F)
- The gall bladder temporarily stores bile. (T/F)
- The ruminants bring back swallowed grass into their mouth and chew it for some time. (T/F)
Answer:
- F
- T
- T
- T
Question 3.
Tick (√) mark the correct answer in each of the following:
(a) Fat is completely digested in the
(i) stomach
(ii) mouth
(iii) small intestine
(iv) large intestine
(b) Water from the undigested food is absorbed mainly in the
(i) stomach
(ii) food pipe
(iii) small intestine
(iv) large intestine
Answer:
(a) (iii) Small intestine
(b) (iv) Large intestine.
Question 4.
Match the items of Column I with those given in Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| Food components | Product(s) of digestion |
| Carbohydrates | Fatty acids and glycerol |
| Proteins | Sugar |
| Fats | Amino acids |
Answer:
|
Column I |
Column II |
| Food components | Product(s) of digestion |
| Carbohydrates | Sugar |
| Proteins | Amino acids |
| Fats | Fatty acids and glycerol |
Question 5.
What are villi? What are their location and function?
Answer:
The inner walls of the small intestine have thousands of finger-like outgrowths. These are called villi. Villi are located in the small intestine. The villi increase the surface area for absorption of the digested food. Each villus has a network of thin and small blood vessels close to its surface. The surface of the villi absorbs the digested food materials.
Question 6.
Where is the bile produced? Which component of the food does it help to digest?
Answer:
Bile is produced in the liver. The bile juice is stored in a sac called the gall bladder. Bile plays an important role in the digestion of fats.
Question 7.
Name the type of carbohydrate that can be digested by ruminants but not by humans. Give the reason also.
Answer:
Cellulose is a type of carbohydrate that can be digested by ruminants but not by humans. Ruminants have a large sac-like structure called rumen which is present in between the small intestine and large intestine. The cellulose is digested here by the action of certain bacteria which are not present in humans.
Question 8.
Why do we get instant energy from glucose?
Answer:
Because glucose can easily breakdown in the cell with the help of oxygen and gives carbon dioxide, water, and energy.
Question 9.
Which part of the digestive canal is involved in:
- absorption of food ……..
- chewing of food …….
- the killing of bacteria …….
- complete digestion of food ………
- formation of faeces ……..
Answer:
- Small intestine
- Mouth
- Stomach
- Small intestine
- Large intestine.
Question 10.
Write one similarity and one difference between the nutrition in amoeba and human beings.
Answer:
- Similarity: Both amoeba and humans use digestive juices to digest food.
- Difference: Human needs to chew food, whereas, an amoeba, there is no chewing.
Question 11.
Match the items of Column I with suitable items in Column II
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Salivary gland | (i) Bile juice secretion |
| (b) Stomach | (ii) Storage of undigested food |
| (c) Liver | (iii) Saliva secretion |
| (d) Rectum | (iv) Acid release |
| (e) Small intestine | (v) Digestion is completed |
| (f) Large intestine | (vi) Absorption of water |
| (Vii) Release of faeces |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Salivary gland | (iii) Saliva secretion |
| (b) Stomach | (iv) Acid release |
| (c) Liver | (i) Bile juice secretion |
| (d) Rectum | (ii) Storage of undigested food |
| (e) Small intestine | (v) Digestion is completed |
| (f) Large intestine | (vi) Absorption of water |
Question 12.
Label figure of the digestive system.
Answer:
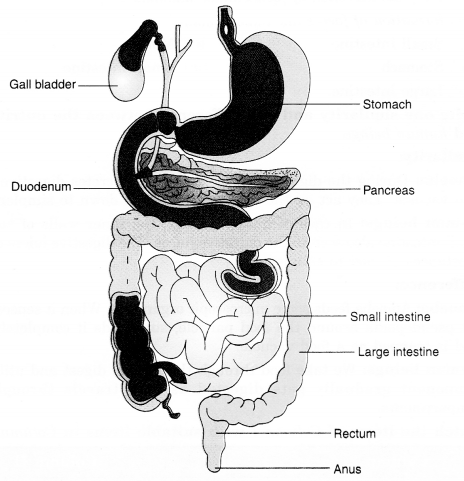
Fig. Human digestive system
Question 13.
Can we survive only on raw, leafy vegetables/grass? Discuss.
Answer:
No. Because to live a healthy life, we need a complete balance of all nutrients. Raw leafy vegetables/grass may have cellulose which can not be digested by us. So, we cannot survive only on raw, leafy vegetables/grass.
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.