NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Civics Chapter 1 On Equality are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Civics Chapter 1 On Equality.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 7 |
| Subject | Social Science Civics |
| Chapter | Chapter 1 |
| Chapter Name | On Equality |
| Number of Questions Solved | 14 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Civics Chapter 1 On Equality
NCERT TEXTBOOK EXERCISES
Question 1.
In a democracy why is universal adult franchise important?
Answer.
- In a democracy, the universal adult franchise is important because it is based on the principle of equality.
- It authorizes every adult citizen in a country to cast one vote irrespective of her/ his wealth and the communities she/he belongs to.
Question 2.
Re-read the box on Article 15 and state two ways in which this Article addresses inequality?
Answer.
Article 15 of the Indian Constitution Prohibits discrimination and inequalities.
- It allows access to shops, public places, restaurants, etc. to all.
- The general public is allowed to use wells, tanks, bathing ghats maintained wholly or partly by state funds.
Question 3.
In what ways was Omprakash Valmiki’s experience similar to that of the Ansaris?
Answer.
- The dignity of both Omprakash Valmiki and the Ansaris was violated. They were made victims of inequality in treatment.
- Omprakash Valmiki was made to sweep the school, because of his caste, and Ansaris were refused to lease the apartments because of their religion.
Question 4.
What do you understand by the term “all persons are equal before the law”? Why do you think it is important in a democracy?
Answer.
It means that every person, from the President of the country to domestic help like Kanta has to obey the same laws. No person can be discriminated against on the basis of their religion, race, caste, etc. Every person has access to all public places including playgrounds, hotels, shops, and markets. All persons can use publicly available wells, roads, and bathing ghats.
Equality is the soul of democracy. We know that democracy is a form of government which gives equal importance and recognition to all. If inequalities on the basis of race, religion, caste, etc. continue to exist, democracy would never flourish. Instead, it would perish very soon.
Question 5.
The Government of India passed the Disabilities Act in 1995. This law states that persons with disabili¬ties have equal rights and that the government should make possible their full participation in society. The government has to provide free education and integrate children with disabilities into mainstream schools. This law also states that all public places including buildings, schools, etc., should be accessible and provided with ramps.
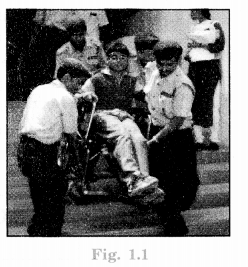
Look at the photograph and think about the boy who is being carried down the stairs. Do you think the above law is being implemented in his case? What needs to be done to make the building more accessible for him? How would his be carried down the stairs affect his dignity as well as his safety?
Answer.
- The above law is not being implemented in the case of the boy who is being carried down the stairs as shown in the photograph.
- There is a need to construct public buildings like schools, hospitals, etc., with the provisions of ramps so that they may be more accessible for persons with disabilities.
- The dignity of the boy is affected by being carried down the stairs because he may feel inferior for his dependency on others for movement in such places. His safety is also at stake as the persons helping him may cause an accident.
INTEXT QUESTIONS
Question 1.
Do you think Kanta has enough reason to doubt whether she really is equal? List three reasons from the story that might make her feel like this. (NCERT Page 6)
Answer.
Yes, Kanta has enough reasons to doubt whether she is really equal.
Reasons:
- She cannot skip work even when her daughter is ill.
- She does not have enough money to take her daughter to the doctor.
- She has to stand in line at a government hospital for her turn to show her daughter to the doctor.
Question 2.
Circle the reference to caste in the matrimonial advertisements given below: (NCERT Page 7)

Answer.
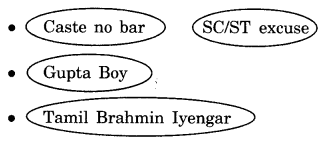
Question 3.
Why do you think Omprakash Valmiki was being treated unequally by his teacher and his classmates? Imagine yourself as Omprakash Valmiki and write four lines about how you would feel if you were in the same situation as him. (NCERT Page 8)
Answer.
Yes, Omprakash Valmiki was being treated unequally by his teacher and his classmates because he was Dalit. We, as Omprakash Valmiki would feel humiliated and many questions would arise in our minds.
Like:
- do we not have soul, heart?
- are we not fit for education?
- why are we treated unequally?
Question 4.
Why do you think the Ansaris were being treated unequally? What would you do if you were in the Ansaris’ position and could not find a place to live because some people did not want to live next to you because of the religion you practice? (NCERT Page 8)
Answer.
- Ansaris were being treated unequally because they belonged to the Muslim religion.
- If we were in Ansaris’ position.
- We would go to the Minority Commission to lodge a complaint against the apartment owners.
- We would try to reason out with people.
Question 5.
If you were one of the Ansaris how would you have responded to the suggestion that you change your name? (NCERT Page 9)
Answer.
I would have responded in these words:
I will not change my name as there is nothing in the name, we all are God’s creation.
Question 6.
Can you think of an incident in your life in which your dignity was violated? How did this make you feel? (NCERT Page 9)
Answer.
- Yes.
- Disgusted.
(Answer will vary from student to student.)
Question 7.
What is the midday meal programme? Can you list three benefits of the programme? How do you think this program might help promote greater equality? (NCERT Page 11)
Answer.
- In the midday meal programme students of primary classes are provided lunch in the schools all over the country.
- Benefits:
- Truancy after recess has decreased.
- More and more children enroll themselves in the schools.
- Would help poor students and improve their concentration.
- Mothers do not have to leave their work in the mid.
- This programme might help promote equality as it would reduce caste prejudices.
- In some places, Dalit women are employed to cook meals for all children.
Question 8.
Find out about one government scheme in your area. What does this scheme do? Who is this scheme set up to benefit? (NCERT Page 11)
Answer.
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (S.S.A.).
- This scheme provides education to those children who do not join schools for one or the other reason.
- This scheme is set to benefit Dalit children mostly.
Question 9.
How does Article 15 of our constitution address inequality?
Answer.
Article 15 of the Indian Constitution Prohibits discrimination and inequalities.
- It allows access to shops, public places, restaurants, etc. to all.
- The general public is allowed to use wells, tanks, bathing ghats maintained wholly or partly by state funds.
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Civics Chapter 1 On Equality help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Civics Chapter 1 On Equality, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.