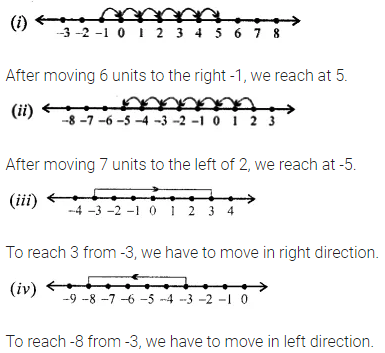
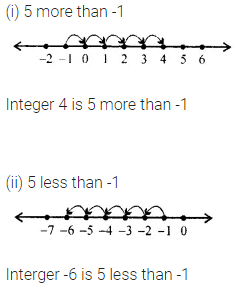
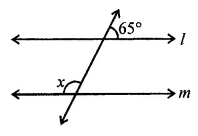
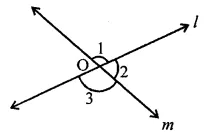
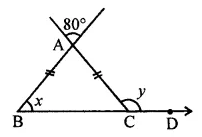
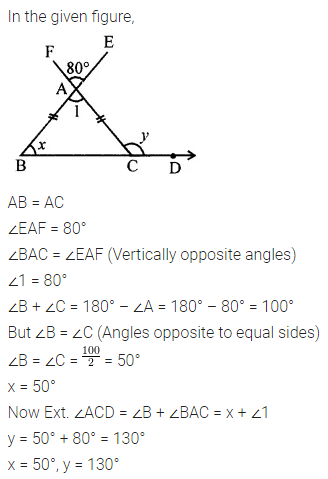
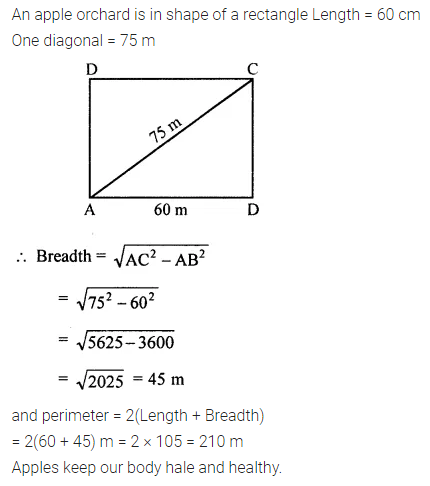
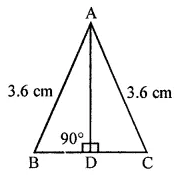
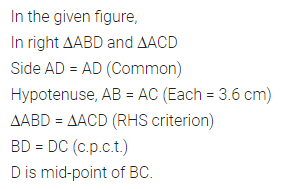
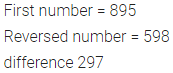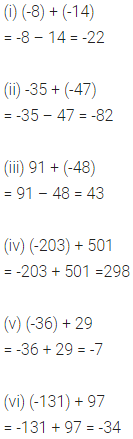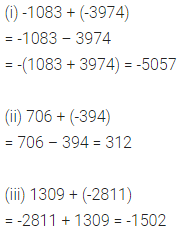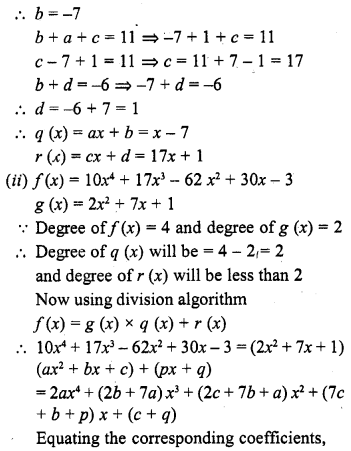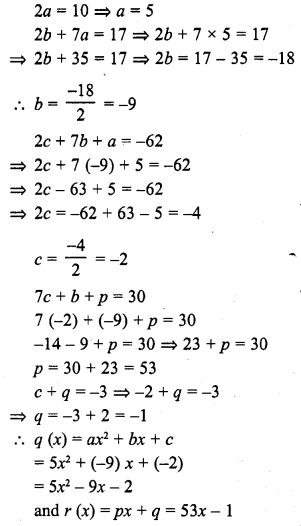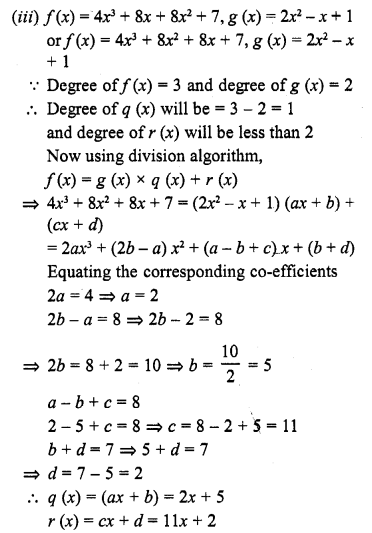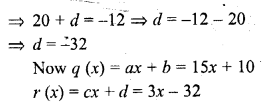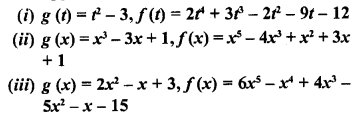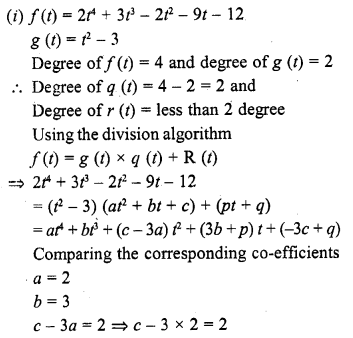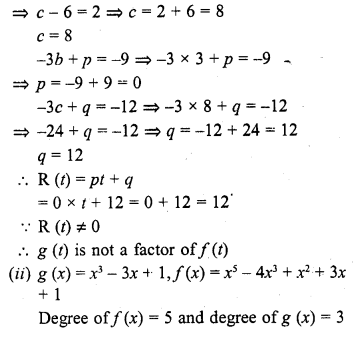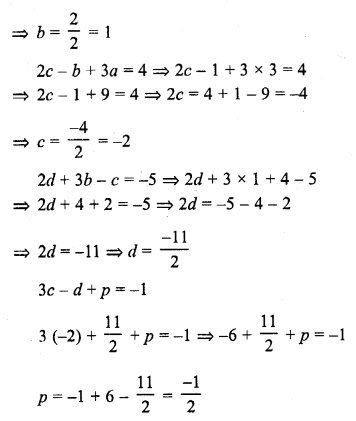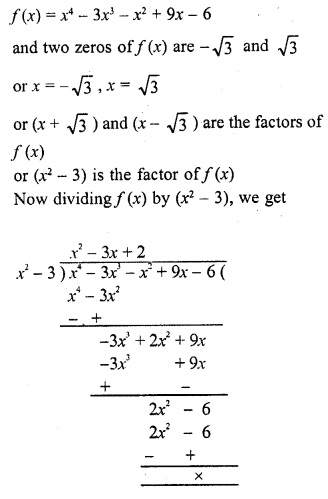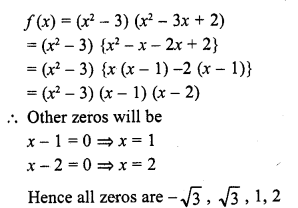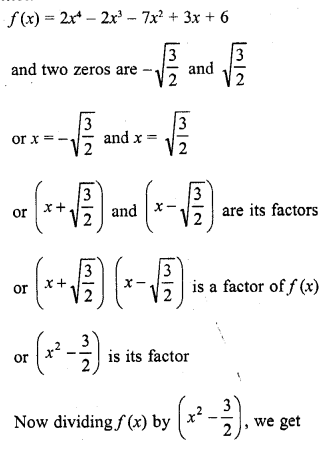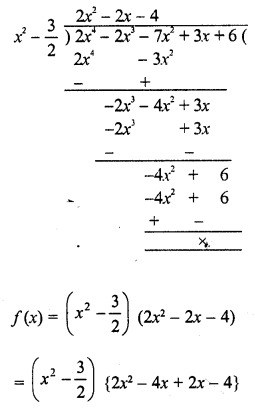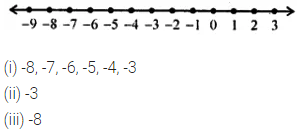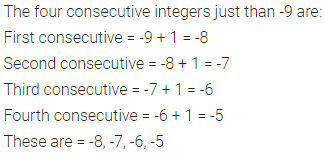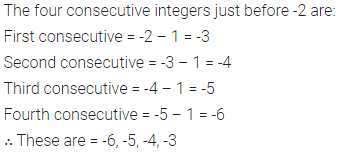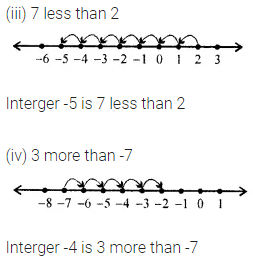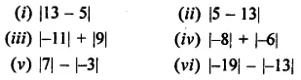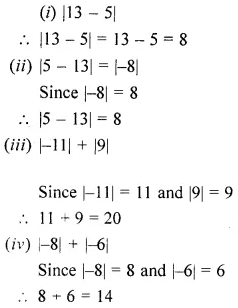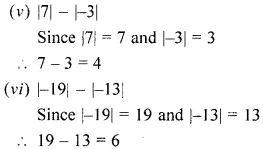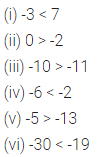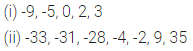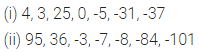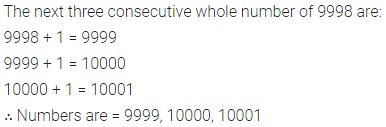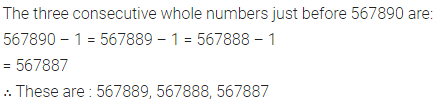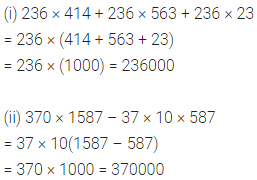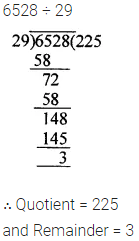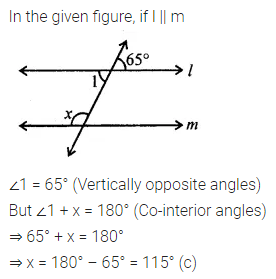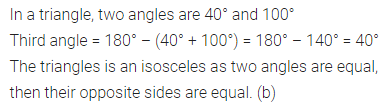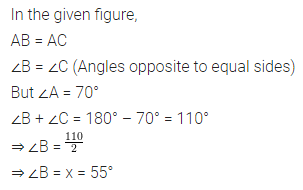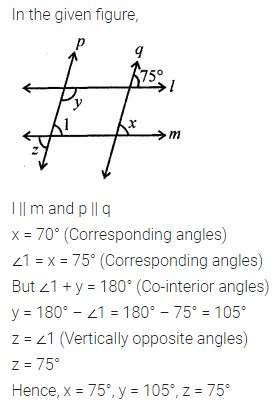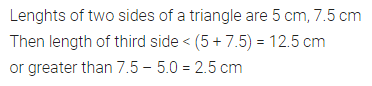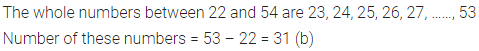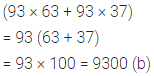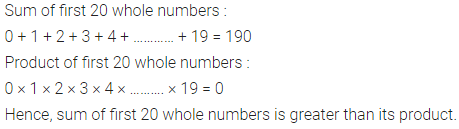ML Aggarwal Class 6 Solutions Chapter 1 Knowing Our Numbers Ex 1.1 for ICSE Understanding Mathematics acts as the best resource during your learning and helps you score well in your exams.
ML Aggarwal Class 6 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 1 Knowing Our Numbers Ex 1.1
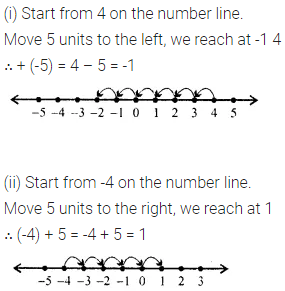
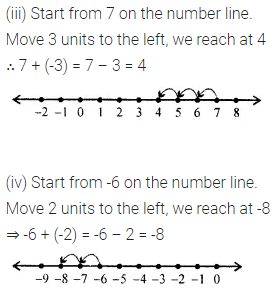
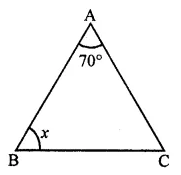
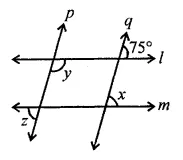
Question 1.
Write the smallest natural number. Can you write the largest natural number?
Solution:
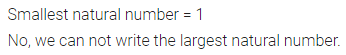
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
(i) 1 lakh = … ten thousand
(ii) 1 million = … hundred thousand
(iii) 1 crore = … ten lakh
(iv) 1 billion =… hundred million.
Solution:
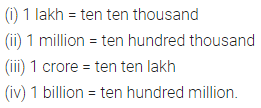
Question 3.
Insert commas suitably and write each of the following numbers in words in the Indian system and the International system of numeration.
(i) 506723
(ii) 180018018
Solution:

Question 4.
Write the following numbers in expanded form:
(i) 750687
(ii) 5032109
Solution:
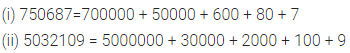
Question 5.
Write the following number in figures:
(i) Seven lakh three thousand four hundred twenty.
(ii) Eighty crore twenty three thousand ninety three.
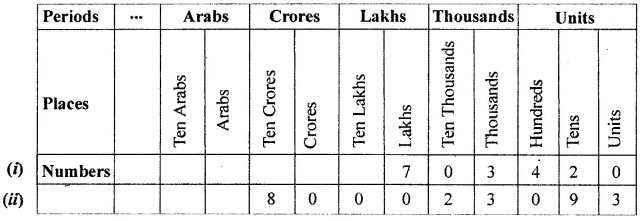
Also write the above numbers in the place value chart.
Solution:
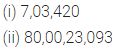
Question 6.
Write each of the following numbers in numeral form and place commas correctly:
(i) Seventy three lakh seventy thousand four hundred seven.
(ii) Nine crore five lakh forty one.
(iii) Fifty eight million four hundred twenty three thousand two hundred two.
Solution:
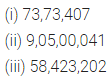
Question 7.
Write the face value and place value of the digit 6 in the number 756032.
Solution:
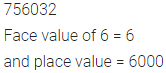
Question 8.
Find the difference between the place value and the face value of the digit 9 in the number 229301.
Solution:

Question 9.
Determine the difference of the place value of two 7’s in 37014472 and write it in words in International system.
Solution:

Question 10.
Determine the product of place value and the face value of the digit 4 in the number 5437.
Solution:
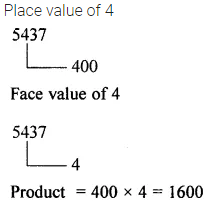
Question 11.
Find the difference between the number 895 and that obtained on reversing its digits.
Solution: