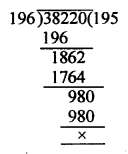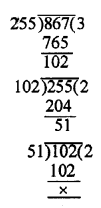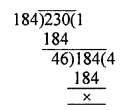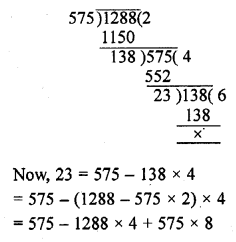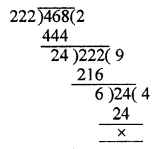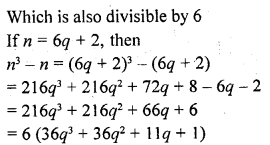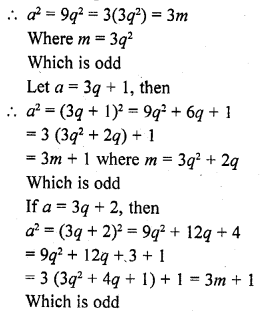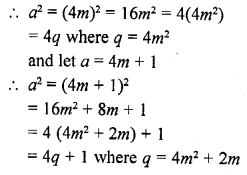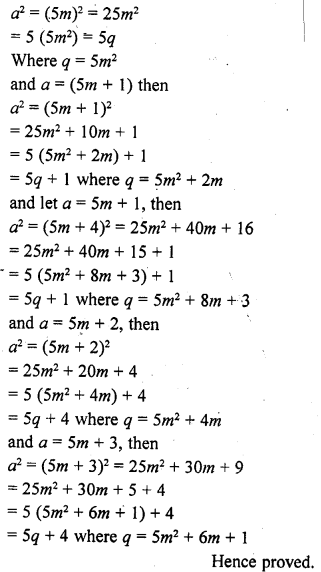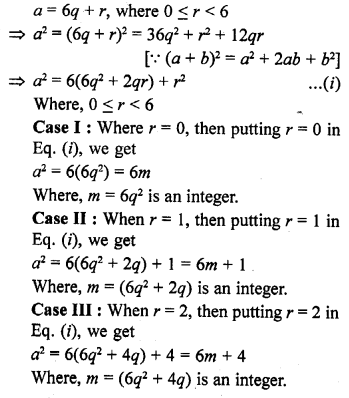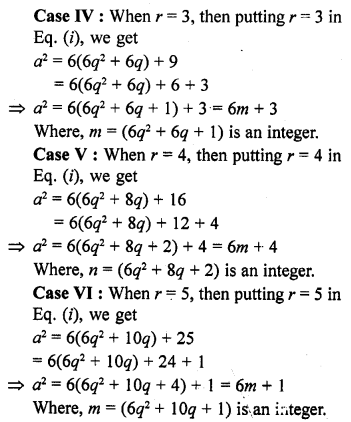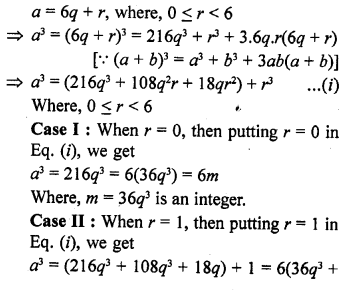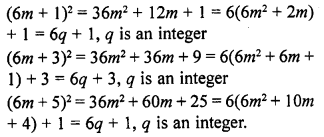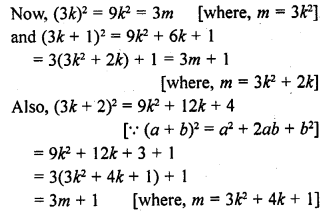RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 1 Real Numbers Ex 1.3
These Solutions are part of RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions. Here we have given RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 1 Real Numbers Ex 1.3
Other Exercises
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 1 Real Numbers Ex 1.1
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 1 Real Numbers Ex 1.2
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 1 Real Numbers Ex 1.3
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 1 Real Numbers Ex 1.4
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 1 Real Numbers Ex 1.5
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 1 Real Numbers Ex 1.6
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 1 Real Numbers VSAQS
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 1 Real Numbers MCQS
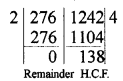
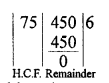
Question 1.
Express each of the following integers as a product of its prime factors :
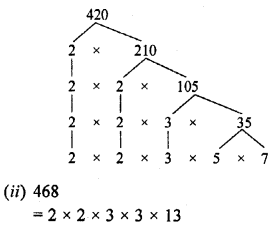
(i) 420
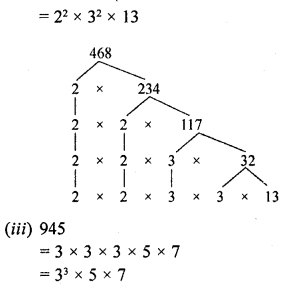
(ii) 468
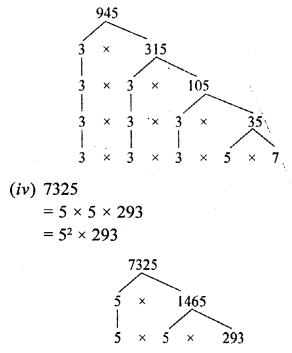
(iii) 945
(iv) 7325
Solution:
(i) 420
=2 x 2 x 3 x 5 x 7
= 22 x 3 x 5 x 7
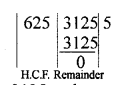
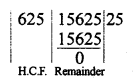
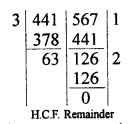
Question 2.
Determine the prime factorization of each of the following positive integer :
(i) 20570
(ii) 58500
(iii) 45470971
Solution:
(i) 20570
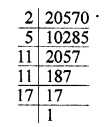
20570 = 2 x 5 x 11 x 11 x 17 = 2 x 5 x 112 x 17

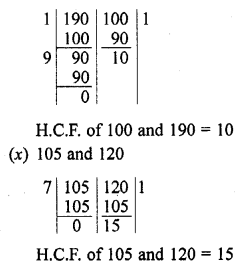
Question 3.
Explain why 7 x 11 x 13 + 13 and 7 x 6 x 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 + 5 are composite numbers ?
Solution:
We know that a composite number is that number which can be factorize. It has more factors other than itself and one
Now, 7 x 11 x 13 + 13 = 13 (7 x 11 + 1) = 13 x 78
Which is composite number
Similarly,
7 x 6 x 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 + 5 = 5(7 x 6 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 + 1)
= 5 x 1009
Which is a composite number
Hence proved
Question 4.
Check whether 6n can end with the digit 0 for any natural number n.
Solution:
No, 6n can’t end with the digit 0 as the number ending 0 can be factorise of the type
2n x 5m only but 6n = (2 x 3)n = 2n x 3n
Which does not has 5m as factors.
Question 5.
Explain why 3 x 5 x 7 + 7 is a composite number. [NCERT Exemplar]
Solution:
We have, 3 x 5 x 7 + 7 = 105 + 7 = 112
Now, 112 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 7 = 24 x 7
So, it is the product of prime factors 2 and 7. i.e., it has more than two factors.
Hence, it is a composite number.
Hope given RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 1 Real Numbers Ex 1.3 are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.