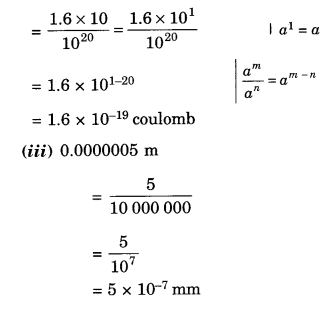
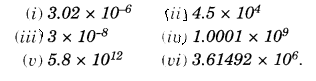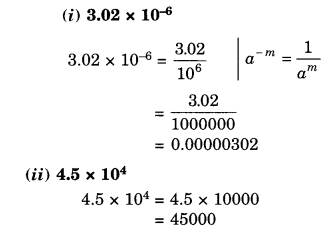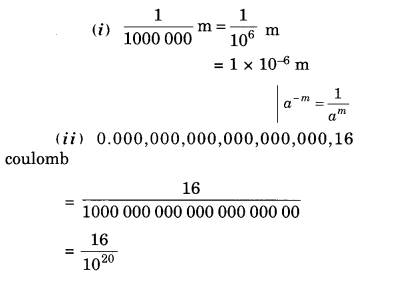NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Direct and Indirect Proportions Ex 13.2 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Direct and Indirect Proportions Ex 13.2.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 8 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 13 |
| Chapter Name | Direct and Indirect Proportions |
| Exercise | Ex 13.2 |
| Number of Questions Solved | 11 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Direct and Indirect Proportions Ex 13.2
Question 1.
Which of the following are in inverse proportion?
(i) The number of workers on a job and the time to complete the job.
(ii) The time is taken for a journey and the distance traveled in a uniform speed.
(iii) Area of cultivated land and the crop harvested.
(iv) The time is taken for a fixed journey and the speed of the vehicle.
(v) The population of a country and the area of land per person.
Solution.
(i) The number of workers on jobs and the time to complete the job are in inverse proportion.
(ii) The time is taken for a journey and the distance traveled in a uniform speed are not in inverse proportion.
(iii) Area of cultivated land and the crop harvested are not in inverse proportion.
(iv) The time taken for a fixed journey and the speed of the vehicle are in inverse proportion.
(v) The population of a country and the area of land per person are in inverse proportion.
Question 2.
In a Television game show, the prize money of 1,00,000 is to be divided equally amongst the winners. Complete the following table and find whether the prize money given to an individual winner is directly or inversely proportional to the number of winners.
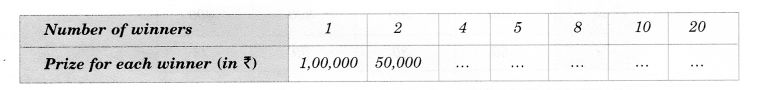
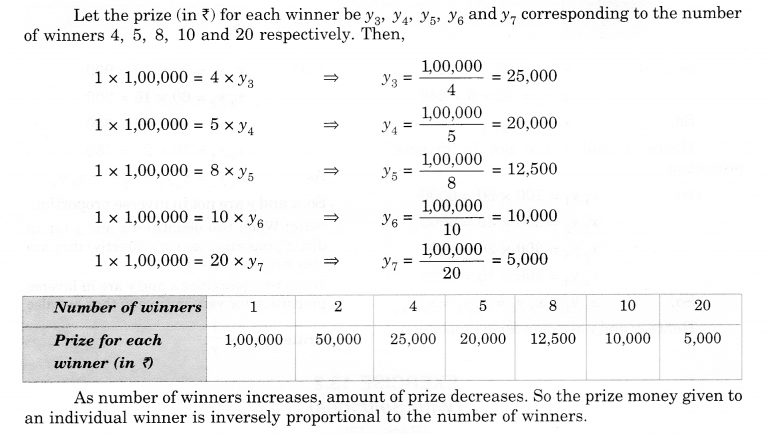
Solution.
Question 3.
Rehman is making a wheel using spokes. He wants to fix equal spokes in such a way that the angles between any pair of consecutive spokes are equal. Help him by completing the following table.
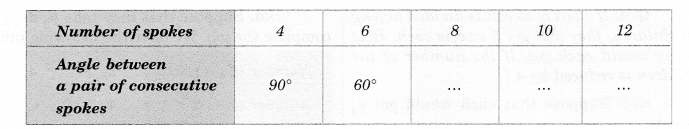
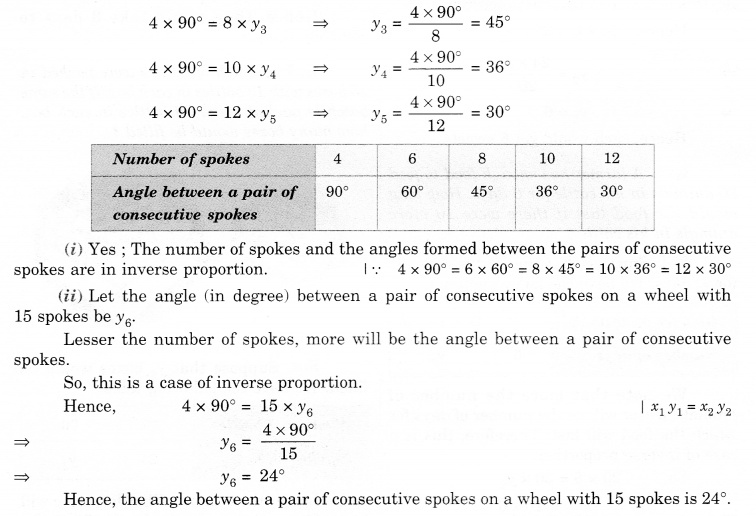
(i) Are the number of spokes and the angles formed between the pairs of consecutive spokes in verse proportion?
(ii) Calculate the angle between a pair of consecutive spokes on a wheel with 15 spokes.
(iii) How many spokes would be needed, if the angle between a pair of consecutive spokes is 40°?
Solution.
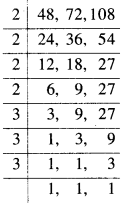
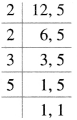
Let the angle (in degree) between a pair of consecutive spokes be \({ y }_{ 3 }\), \({ y }_{ 4 }\) and \({ y }_{ 5 }\) respectively. Then,

Question 4.
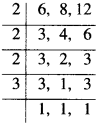
If a box of sweets is divided among 24 children, they will get 5 sweets each. How many would each get, if the number of the children is reduced by 4?
Solution.
Suppose that each would get \({ y }_{ 2 }\) sweets.
Thus, we have the following table.
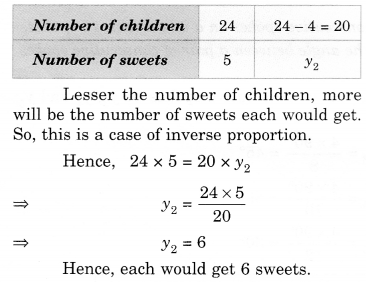
Question 5.
A farmer has enough food to feed 20 animals in his cattle for 6 days. How long would the food last if there were 10 more animals in his cattle?
Solution.
Suppose that the food would last for \({ y }_{ 2 }\) days. We have the following table:

Question 6.
A contractor estimates that 3 persons could rewire Jasminder’s house in 4 days. If, he uses 4 persons instead of three, how long should they take to complete the job?
Solution.
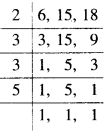
Suppose that they take \({ y }_{ 2 }\) days to complete the job. We have the following table

Question 7.
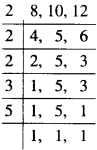
A batch of bottles was packed in 25 boxes with 12 bottles in each box. If the same batch is packed using 20 bottles in each box, how many boxes would be filled?
Solution.
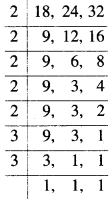
Suppose that \({ y }_{ 2 }\) boxes would be filled. We have the following table:

Question 8.
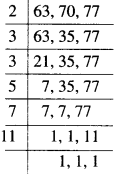
A factory requires 42 machines to produce a given number of articles in 63 days. How many machines would be required to produce the same number of articles in 54 days?
Solution.
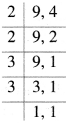
Suppose that \({ x }_{ 2 }\) machines would be required. We have the following table:


Question 9.
A car takes 2 hours to reach a destination by traveling at a speed of 60 km/h. How long will it take when the car travels at the speed of 80 km/h?
Solution.
Let it take \({ y }_{ 2 }\) hours. We have the following table:
sol.

Question 10.
Two persons could fit new windows in a house in 3 days.
(i) One of the persons fell ill before the work started. How long would the job take now?
(ii) How many persons would be needed to fit the windows in one day?
Solution.
(i) Let the job would take \({ y }_{ 2 }\) days. We have the following table:

Clearly, more the number of persons, lesser would be the number of days to do the job. So, the number of persons and number of days vary in inverse proportion.
So, 2 x 3 = 1 x \({ y }_{ 2 }\)
⇒ \({ y }_{ 2 }\) = 6
Thus, the job would now take 6 days.
(ii) Let \({ y }_{ 2 }\) persons be needed. We have the following table:

Clearly, more the number of persons, lesser would be the number of days to do the job. So, the number of persons and number of days vary in inverse proportion.
So, 3 x 2 = 1 x \({ y }_{ 3 }\)
⇒ \({ T }_{ 2 }\) = 6
Thus, 6 persons would be needed.
Question 11.
A school has 8periods a day each of 45 minutes duration. How long would each period be, if the school has 9 periods a day, assuming the number of school hours to be the same?
Solution.
Let each period be \({ y }_{ 2 }\) minutes long.
We have the following table:

We note that more the number of periods, lesser would be the length of each period. Therefore, this is a case of inverse proportion.
So, 8 x 45 = 9 x \({ y }_{ 2 }\)
⇒ \({ y }_{ 2 }=\frac { 8\times 45 }{ 9 } \)
⇒ \({ y }_{ 2 }\) = 40
Hence, each period would be 40 minutes long.
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Direct and Indirect Proportions Ex 13.2 help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Direct and Indirect Proportions Ex 13.2, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.