Online Education for Human-Environment Interactions: The Tropical and the Subtropical Region Class 7 Extra Questions Geography Chapter 8
Class 7 Geography Chapter 8 Extra Questions Question 1.
Where does the equatorial region lie?
Answer:
The region which lies between 10°N and 10°S is referred to as the equatorial region.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 8 Worksheet Question 2.
What is river’s mouth?
Answer:
The place where a river flows into another body of water is called the river’s mouth.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 8 Extra Questions And Answers Question 3.
Which parts are drained by the Amazon river basin?
Answer:
- Portions of Brazil,
- Parts of Peru,
- Bolivia,
- Ecuador,
- Columbia and
- Small part of Venezuela.
Human Environment Interactions The Tropical And The Subtropical Regions Extra Question 4.
Which is the largest river basin of the world?
Answer:
Amazon basin.
![]()
Ncert Class 7 Geography Chapter 8 Extra Questions Question 5.
What are tributaries?
Answer:
The small riverS that join the main river are called tributaries.
Chapter 8 Geography Class 7 Extra Questions Question 6.
What is catchment area or river basin?
Answer:
The main river along with all its tributaries that drain an area form a river basin or the catchment area.
Class 7 Geography Ch 8 Extra Questions Question 7.
Which type of vegetation is found in equatorial region? Why?
Answer:
Thick forests grow in the equatorial region because it rains heavily in this region.
Extra Questions For Class 7 Geography Chapter 8 Question 8.
Name two plant parasites found in equatorial region.
Answer:
Orchids and bromeliads.
Geography Class 7 Chapter 8 Extra Questions Question 9.
What are bromeliads?
Answer:
Bromeliads are special plants that store water in their leaves.
Class 7 Chapter 8 Geography Extra Questions Question 10.
What work do men and women perform in the rainforests?
Answer:
Men hunt and fish along the rivers, while women take care of the crops.
![]()
Class 7th Geography Chapter 8 Extra Questions Question 11.
Which crops are grown by the people of rainforests?
Answer:
- Tapioca,
- pineapple and
- sweet potato.
Ch 8 Geography Class 7 Extra Questions Question 12.
Which type of agriculture is practised by the people of rainforests?
Answer:
Slash and burn agriculture.
Geography Chapter 8 Class 7 Extra Questions Question 13.
What is the food of the people residing in rainforests?
Answer:
Manioc (cassava) is the staple food.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 8 Question Answer Question 14.
Which cash crops are grown in the equatorial region?
Answer:
- Coffee,
- maize and
- cocoa.
Human Environment Interaction Class 7 Questions And Answers Question 15.
What is ‘Maloca’ in the Amazon basin?
Answer:
Large apartment-like houses with steeply slanting roofs are called Maloca in the Amazon basin.
![]()
Question 16.
Write the climatic conditions of the Amazon basin.
Answer:
- Amazon basin is characterised by hot and wet climate throughout the year.
- Both days and nights are almost equally hot and humid.
- It rains almost every day.
Question 17.
How have the rainforests of the Amazon basin been made accessible?
Answer:
- The Tranz-Amazon highway have made all parts of the rainforests accessible.
- Aircraft and helicopters are also used to reach various places of the rainforests.
Question 18.
How have developmental activities adversely affected the rainforests?
Answer:
- Development activities have led to gradual destruction of the biologically diverse rainforests.
- A large area of rainforests have disappeared in the Amazon basin.
- The topsoil washes away as the rain falls and the lush forest converts into a barren landscape.
Question 19.
What is slash and burn agriculture?
Answer:
Slash and burn is a way of cultivating land where farmers clear a piece of land by slashing or cutting down trees and bushes. After two or three crops, the soil loses fertility. So farmers abandon that patch and clear another plot of land to cultivate.
![]()
Question 20.
Amazon basin is rich in the variety of wildlife. Explain.
Answer:
- Birds such as toucans, hummingbirds, birds of Paradise are found here, which make loud sounds in the forests.
- Animals like monkeys, sloths and anteating tapirs are found here.
- Various species of reptiles and snakes also thrive in these jungles.
- Various species of reptiles and snakes also thrive in these jungles. Anaconda and Boa constrictor are some of the species.
- Basin is also home to thousands of species of insects.
- Several species of fishes including the flesh-eating Piranha fish is also found in the river.
Question 21.
Between which latitudes does the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin lie?
Answer:
The Ganga-Brahmaputra basin lies in the sub-tropical region that is situated between 10°N to 30°N latitudes.
Question 22.
Name the tributaries of the river Ganga.
Answer:
- The Ghaghra,
- the Son,
- the Chambal,
- the Gandak and
- the Kosi.
Question 23.
What are main features of the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin?
Answer:
- The plains of the Ganga and the Brahmaputra.
- The mountains and the foothills of the Himalayas;
- The Sunderban delta.
Question 24.
Write the climatic conditions of the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin.
Answer:
- The Ganga-Brahmputra basin is dominated by monsoon climate.
- The monsoon brings rains from mid-June to mid-September.
- The summers are hot and the winters cool.
Question 25.
What is population density? Give one example.
Answer:
Population density means the number of persons that live in one square kilometre of area, e.g., the population density of Uttaranchal is 159.
![]()
Question 26.
Name the food crops which are grown in the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin.
Answer:
Rice, wheat, maize, sorghum, gram and millets.
Question 27.
Name the cash crops grown in Ganga-Brahmaputra basin.
Answer:
Sugarcane and jute.
Question 28.
Where is tea grown in the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin?
Answer:
West Bengal arid Assam.
Question 29.
Which type of cultivation is practised in the hilly region?
Answer:
Terrace cultivation.
Question 30.
Where is silk produced in the Ganga- Brahmaputra basin?
Answer:
Bihar and Assam.
![]()
Question 31.
Which regions are covered with mangrove and coniferous trees of Ganga- Brahmaputra basin?
Answer:
- The delta area is covered with the mangrove forests.
- Parts of Uttaranchal, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh are covered with coniferous trees.
Question 32.
Name the cities with population of more than ten lakhs located along the river Ganga.
Answer:
Allahabad, Kanpur, Varanasi, Lucknow, Patna and Kolkata.
Question 33.
Explain how topography plays a dominant role in the distribution of population.
Answer:
- The mountain areas with steep slopes have inhospitable terrain. Therefore, less number of people live in mountain areas.
- The plain areas provide the most suitable land for human habitation. The soil is fertile. Agriculture is the main occupation of the people. Therefore, the density of population of the plains is very high.
Question 34.
Name some places of the Ganga- Brahmaputra basin which are worth visiting.
Or
Why has tourism flourished in the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin?
Answer:
The places which are worth visiting in the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin –
- Taj Mahal on the banks of River Yamuna in Agra.
- Allahabad on the confluence of the River Ganga and Yamuna.
- Buddhist stupas in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.
- Imambara in Lucknow.
- Kaziranga and Manas wildlife sanctuaries in Assam.
Question 35.
Describe the variety of wildlife found in the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin.
Answer:
- Elephants, tigers, deer and monkeys are common.
- The one-horned rhinoceros is found in the Brahmaputra plains.
- In the delta area, Bengal tigers, crocodiles and alligators are found.
- Aquatic life abounds in the fresh river waters, the lakes and the Bay of Bengal. The popular varieties of the fish are the Rohu, Catla and Hilsa.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. Which one of the following terms is used for the Tropical region lying between 10°N and 10°S latitudes?
(a) Temperate region
(b) Equatorial region
(c) Polar region
(d) Sub-Tropical region.
Answer:
(b) Equatorial region.
2. Which one of the following is not a part of the Amazon basin?
(a) Brazil
(b) Ecuador
(c) Columbia
(d) Argentina.
Answer:
(d) Argentina.
3. What kind of climate is found in the Amazon basin?
(a) Cloudy
(b) Hot and wet
(c) Rainy
(d) Cold.
Answer:
(b) Hot and wet.
4. Which one of the following types of forests is found in the Amazon basin?
(a) Tropical Rainforest
(b) Temperate Grasslands
(c) Tropical Deciduous forests
(d) Temperate Deciduous forests.
Answer:
(a) Tropical Rainforest.
5. Which one of the following is different from the other three, with reference to the crops growing in Amazon basin?
(a) Tapioca
(b) Wheat
(c) Pineapple
(d) Sweet potato.
Answer:
(b) Wheat.
![]()
6. Which one of the following is the staple food of Amazon basin?
(a) Manioc (Cassava)
(b) Sugarcane
(c) Coffee
(d) Tea.
Answer:
(a) Manioc (Cassava).
7. What type of agriculture is practised in the Amazon basin?
(a) Intensive agriculture
(b) Subsistence agriculture
(c) Slash and burn agriculture
(d) Plantation agriculture.
Answer:
(c) Slash and burn agriculture.
8. Which one of the following terms is used for the apartment like houses of Amazon basin?
(a) Flat
(b) Circular houses
(c) Composite houses
(d) Maloca.
Answer:
(d) Maloca.
9. By which one of the following mode of transportation the Amazon basin becomes accessible?
(a) Trans-Amazon Highway
(b) Trans-Siberian railway
(c) Leh-Manali Highway
(d) Trans-Canadian Highway.
Answer:
(a) Trans-Amazon Highway.
10. Which one of the following rivers forms the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin?
(a) Yamuna river
(b) Ganga-Brahmaputra rivers
(c) Krishna-Kaveri rivers
(d) Narmada and Tapi rivers.
Answer:
(b) Ganga-Brahmaputra rivers.
![]()
11. What is the latitudinal extent of the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin?
(a) 5°N to 10°N latitudes
(b) 10°N to 20°N latitudes
(c) 10°N to 30°N latitudes
(d) 10°S to 30°N latitudes.
Answer:
(c) 10°N to 30°N latitudes.
12. Which one of the following is the main features of Ganga-Brahmaputra basin?
(a) Malwa plateau
(b) Thar desert
(c) Peninsular plateau
(d) Sunderban delta.
Answer:
(d) Sunderban delta.
13. What type of climate is found in the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin?
(a) Monsoon type of climate
(b) Sub-Tropical type of climate
(c) Savanna type of climate
(d) Sudan type of climate.
Answer:
(a) Monsoon type of climate.
14. Which one of the following wild animals is found in the Brahmaputra plains?
(а) Wild Ass
(b) One horned rhinoceros
(c) Crocodiles
(d) Anaconda.
Answer:
(b) One horned rhinoceros.
15. Which one of the following is the staple food of the people of Ganga- Brahmaputra basin?
(a) Rice and Beans
(b) Wheat and Rice
(c) Rice and Fish
(d) Coffee and Tea.
Answer:
(c) Rice and Fish.
![]()
16. Which one of the following is an important port on the river Hooghly?
(a) Mumbai port
(b) Kandla port
(c) Kolkata port
(d) Marmagoa port
Answer:
(c) Kolkata port.
17. On which one of the following rivers is the Taj Mahal situated?
(a) River Ganga
(b) River Yamuna,
(c) River Narmada
(d) River Tapi.
Answer:
(b) River Yamuna.
18. Kaziranga and Manas Wildlife Sanctuaries are located in;
(a) Assam
(b) Bihar
(c) Allahabad
(d) Uttar Pradesh
Answer:
(a) Assam.
19. Which one of the following cities is located on the confluence of the rivers Ganga and Yamuna?
(a) Patna
(b) Lucknow
(c) Agra
(d) Allahabad.
Answer:
(d) Allahabad.
20. Which one of the following regions is the Bengal tiger found?
(a) Mountains
(b) Delta areas
(c) Deserts
(d) Amazon basin
Answer:
(c) Deserts.












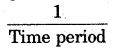 = 5Hz.
= 5Hz.