Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Biology with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 1 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Biology Term 2 Set 1 with Solutions
Time : 2 Hours
Maximum Marks : 35
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has three sections of 23 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 6 questions of 2 marks each; Sedion-B has 6 questions of 3 marks each, and Section-C has a case-based question of 5 marks.
- There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
- Wherever necessary, neat and properly labeled diagrams should be drawn.
![]()
Section – A
(2 Marks each)
Question 1.
Two potted plants were kept in an oxygen-free environment in transparent containers. Plant A was exposed to green light and Plant B to sunlight. Which one of the two, will show more photosynthesis and is likely to survive longer and why?
Answer:
Plant B will show more photosynthesis Chlorophyll absorbs maximum light In the blue region Of the spectrum, i.e., 400-450 nm and hence photosynthetic rate will also be high. Plant A will show negligible amount of photosynthesis or no photosynthesis, as chlorophyll does not absorb any light in the green region, i.e., 500- 550 nm but reflects light.
Question 2.
Different substrates get oxidized during respiration. How does Respiratory Quotient (R.Q.) indicate which type of substrate, i.e., carbohydrate, fat or protein is getting oxidized?
R.Q. = \(\frac{A}{B}\)
What do A and B stand for? What type of substrates have R.Q. of 1, < 1 or > 1?
OR
Energy is released during the oxidation of compounds in respiration. How is this energy stored and released as and when it is needed.
Answer:
In R.Q., A stands for CO2 released, while B stands for O2 being consumed by unit mass of a substrate. The ratio indicates the type of substrate being consumed in respiration.
Substance like carbohydrates have RQ = 1, during aerobic respiration.
Proteins and fats have R.Q. of < 1 and are found during germination of seeds.
Substrates like organic acids have R.Q. of > 1 under aerobic conditions.
OR
Energy is stored as bond energy of ATP This bond is broken down to release energy when required.
ADP + Pi + Energy → ADP + Pi or ATP
ATP → ADP + Pi + Energy
![]()
Question 3.
Given below is the diagram showing different parts of a stem.
In most of the plants, the terminal bud suppresses the development of lateral buds.
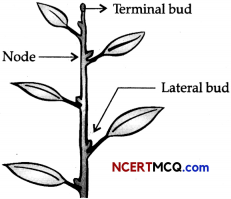
(a) What is this phenomenon called? (1)
(b) Name the phytohormone that can promote the phenomenon. (1)
Answer:
(a) This phenomenon is called Apical dominance.
(b) Auxins are the phytohormones which can promote this phenomenon in plants, e.g., NAA and 2,4-D, etc.
Question 4.
The diagram below shows an ECG of a normal human being. (1)
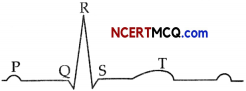
If a patient’s ECG revealed an abnormally long delay between the P wave and the QRS deflection, what would that suggest?
Answer:
If a patient’s ECG revealed an abnormally long delay between P wave and the QRS deflection, it suggests that there is a delay of conduction from the atria to the ventricles, hence the stimulation from SA nodes are conducting stimuli very slowly to the ventricles.
![]()
Question 5.
Sohan was experiencing something abnormal during the urination process. He went to a doctor for a check-up, after which he came to know that his kidneys are damaged. Can you predict what is going to happen to him next?
Answer:
The kidneys are considered as master chemists of the body.
- If they are damaged, it would disturb the normal functioning of his life processes.
- Due to the effect of toxins produced by some bacteria, the filters of tiny uriniferous tubules also get damaged.
- They become perforated with larger holes and allow blood cells, and proteins to pass through them along with the urea and water during filtration of blood in the formation of urine. (Any two)
Question 6.
LH is secreted by Adenohypophysis or anterior pituitary gland. (2)
(a) Mention the other hormone along with which it acts on its target cells/organ. (1)
(b) Give two functions of each hormone. (1)
OR
Study the given diagram.
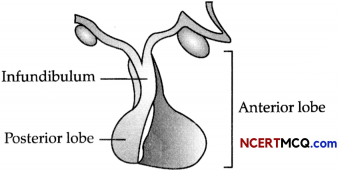
Why is the above gland referred to as the ‘Master gland’?
Answer:
(a) FSH is the other hormone (gonadotropin) along with which it acts on its target cells/organ.
(b) Functions of LH :
- In males, it stimulates spermatogenesis.
- In females, it stimulates ovulation and formation of the corpus luteum.
![]()
Functions of FSH:
- In females, it stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles.
- It regulates the growth and development of secondary sexual characters and other reproductive processes.
OR
- The given diagram is of the pituitary gland. The pituitary is called “Master Endocrine Gland” because of the number of hormones it produces and the control it exercises over the other endocrine glands.
- It itself is under the control of the releasing hormones secreted by the hypothalamus of the brain.
Thus, there is a chain of orders : the hypothalamus directs the pituitary output, which controls the secretion of hormones by other endocrine glands.
Section – B
(3 Marks)
Question 7.
(a) Given below is the diagram showing ATP synthesis during aerobic respiration, replace the symbols A, B, C, D and E by appropriate terms given below:
F1 particle, Pi, 2H+, Inner mitochondrial membrane, ATE F0 particle, ADP (2)
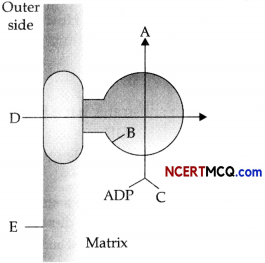
(b) Define the term ETS.
Answer:
(a)
- ATP
- F1 particle
- Pi
- 2H+
- Inner mitochondrial membrane
![]()
(b) The metabolic pathway through which the electron passes from one carrier molecule to another is called Electron Transport System (ETS).
Commonly Made Error
- Students often identify incorrect names of the labels.
Answering Tip
- Practice self-explanatory diagrams with proper labelling, arrows and headings.
Question 8.
Japanese farmers in their rice field observed that certain rice seedlings grow excessively tall and become weak and sterile. One of the Japanese plant pathologists found that, it is due to some disease, which is caused by a fungus. He named this disease as “bakane” or “foolish seedling” disease. Yabuta extracted the active substance i.e., growth-promoting substances and termed them as gibberellin.
(a) Name the fungus, which caused “bakane” or “foolish seedling” disease. (1 + 1/2)
(b) Give three functions of ‘Gibberellin’. (1 + 1/2)
OR
“X” is also called as stress hormone because its synthesis is stimulated by drought, water logging and other adverse environmental conditions. It is produced in many parts of the plants but more abundantly inside the chloroplast of green cells.
(a) Identify “X”. (1)
(b) Mention any two functions of this hormone. (1)
(c) How are they antagonistic to gibberellins? (1)
Answer:
(a) Gibberella fujikuroi is the fungus which causes ‘Bakane’ or foolish-seedling disease. Gibberellin, a plant hormone was discovered from the same fungus.
![]()
(b) The functions of Gibberellins are :
- Bolting and flowering.
- Stem elongation and fruit ripening.
- Parthenocarpy.
- Early seed production. (Any three)
Commonly Made Error
- Some students get confused between the functions of different hormones.
Answering Tip
- Students should learn the functions of phytohormones or plant hormones thoroughly. They should make a flow chart to learn the functions separately.
OR
(a) The hormone “X” is Abscisic add.
(b) Functions of Absdsic acid:
(i) Abscisic acid owes its name to its role in the abscission of plant leaves. In preparation for winter, ABA is produced in terminal buds. This slows plant growth and directs leaf primordia ‘ to develop scales to protect the dormant buds during the cold season.
(ii) It plays an important role in seed development and maturation.
(c) They are antagonistic to gibberellins as gibberellin promotes stem elongation while absdsic add acts as plant growth inhibitor.
![]()
Question 9.
The diagram given below represents a section of human heart.
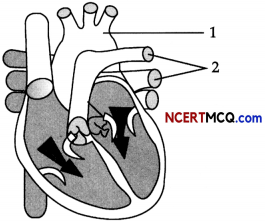
(a) Which parts of the heart are in the diastolic phase? Give a reason to support your answer. (1)
(b) Label the parts numbered 1 and 2 in the diagram. What type of blood flows through them. (1)
(c) What causes the heart sounds ‘LUBB’ and ‘DUBB’. (1)
Answer:
(a) Ventricles
As Tricuspid and bicuspid valves are open/ Semilunar valves are closed.
(b) 1 – Pulmonary artery, deoxygenated blood.
2 – Pulmonary veins, oxygenated blood.
(c) LUBB – Closure of tricuspid and bicuspid valves.
DUBB – Closure of semilunar valves.
Commonly Made Error
- Students often identify the parts of the heart in diastolic phase but many of them fail to give a reason to support the answer.
![]()
Answering Tip
- Carefully learn each and every part of the heart together with their functions.
Question 10.
(a) How is glomerular filtrate hypertonic and hypotonic in descending and ascending limb of loop of Henle respectively? (1 + 1/2)
(b) What is the effect of ADH on collecting tubules? (1 + 1/2)
Answer:
(a) Counter-current system is found in two limbs of loop of Henle. The ascending limb transports Na+ and some urea into surrounding medullary tissue. It is impermeable to water. So, it makes urine dilute or hypotonic. The walls of descending limbs are permeable to water and salt, so Na+ and water from the surrounding fluid are absorbed. Thus, the contents of urine become hypertonic.
(b) ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone): ADH is secreted when the osmotic pressure of blood increases due to excess loss of water from the body. The hormone renders the walls of the distal convoluted tubule (DCT), collecting tubule (CT) and collecting duct of a nephron permeable to water and increases the reabsorption of water into the surrounding tissues and particular capillaries.
The urine becomes hyperosmotic and less in volume and water is conserved in the body.
Commonly Made Error
- Students generally get confused between hypertonic and hypotonic terms and write incorrect answer. Students also write incorrect permeability of descending and ascending limbs of loop of Henle.
![]()
Answering Tip
- Students should understand the terms/concepts clearly, instead of rote learning.
Question 11.
The given diagram represents the structure of a human brain.
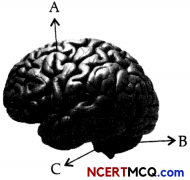
(a) Identify the label A, B and C. (1 + 1/2)
(b) What happens if medulla oblongata is damaged due to some accident? (1)
(c) State any one function of cerebellum. (1/2)
Answer:
(a) In the given structure of brain, the label A represents the cerebrum, Label B is cerebellum, and label C is brain stem.
(b) Medulla oblongata is a part of brain stem, derived from the hindbrain that is continuous with the spinal cord. Its function is a to regulate the reflex responses controlling respiration, heartbeat, blood pressure, and other involuntary processes. So, if medulla oblongata gets damaged, it can lead to respiratory failure, paralysis, or loss of sensation.
(c) Cerebellum maintains equilibrium and posture.
![]()
Question 12.
A patient was complaining of frequent urination, excessive thirst, hunger and tiredness. His fasting blood was found higher than 130 mg/dL on two occasions.
(a) Name the disease. (1)
(b) Give the root cause of this disease. (1)
(c) Explain why the blood glucose level is higher than 130 mg/dL. (1)
Answer:
(a) The disease is Diabetes mellitus.
(b) The failure of the p-cells of the islets of Langerhans of pancreas to produce an adequate amount of insulin, is the root cause of this disease.
(c) It was due to the under secretion of insulin hormone. The under secretion of insulin impairs the following functions:
- Utilisation and uptake of glucose by adipocytes and hepatocytes.
- Conversion of glucose into glycogen by the above target cells.
![]()
Section – C
(5 Marks)
Question 13.
Mitosis is the process of cell division in which one cell gives rise to two genetically identical daughter cells, resulting in cell duplication and reproduction. The major purpose of mitosis is for growth and to replace worn out cells., It is divided into four phases, namely, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
(a) Why is mitosis an equational division? (1)
(b) What would be the consequences if each of the following irregularities occurs during mitosis?
(i) Nuclear membrane fails to disintegrate. (1)
(ii) Duplication of DNA does not occur. (1)
(iii) Centromeres do not divide. (1)
(iv) Cytokinesis does not occur. (1)
OR
In a biology class, teacher explains the students, the different stages of cell cycle. She has drawn a diagram that explains the events taking place during cell cycle of a somatic cell.
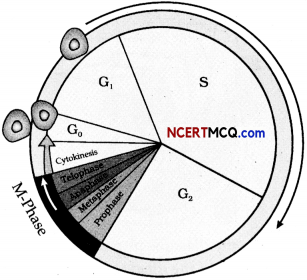
(a) What is G1 phase in the cell cycle? (2)
(b) What amount of DNA is present in the cell during the G2 phase? (1)
(c) How does cytokinesis differ in plant and animal cells? (2)
Answer:
(a) Mitosis is an equational division because the daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes and an equal amount of cytoplasm.
![]()
(b)
- If nuclear membrane fails to disintegrate, the spindle fibers would not be able to reach chromosomes and they would not move towards opposite poles of the cell.
- If duplication of DNA does not occur, then the cell might not be able to surpass S phase of the cell cycle. Thus, the cell will not be able to enter M-phase or if in case it enters mitosis, the cycle will cease.
- If centromeres do not divide, then the daughter cell will receive a complete pair of chromosomes. This may result in trisomy.
- If cytokinesis does not occur, then it would not result in the formation of daughter cells.
OR
(a) Gj phase:
- In this phase, the cell is metabolically active and continuously grows but does not replicate its DNA.
- RNA and proteins are synthesized and the cell grows in size.
![]()
(b) Double the amount of DNA present in the original diploid cell.
(c) Differences between cytokinesis in plant cells and animal cells:
| Cytokinesis in plant cells | Cytokinesis in animals cells |
| In these, cell wall formation starts at the centre of the cell and grows outward to meet the existing lateral walls. | In these cells, cytokinesis is achieved by the appearance of a furrow in the plasma membrane. |
| Formation of new cell wall begins with the formation of a precursor called cell plate. | The furrow gradually deepens and ultimately join in the centre dividing the cytoplasm into two. |