Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Maths with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 1 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Maths Basic Term 2 Set 1 with Solutions
Time allowed: 2 hours
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- The question paper consists of 14 questions divided into 3 sections A, B, C.
- Section A comprises of 6 questions of 2 marks each. Internal choice has been provided in two questions.
- Section B comprises of 4 questions of 3 marks each. Internal choice has been provided in one questions.
- Section C comprises of 4 questions of 4 marks each. An internal choice has been provided in one questions. It contains two case study based questions.
Section – A (12 marks)
Question 1.
Two cubes each of volume 27 cm3 are joined end to end to form a solid. What is the surface area of the resulting cuboid?
OR
A sector of a circle of radius 12 cm has the angle 120°. It is rolled up so that two bounding radii are joined together to form a cone. What is the volume of the cone ? (2)
Answer:
Let, the length of each edge of cube be x cm.
Volume of cube = x3
∴ x3 = 27
∴ x = 3 cm
Length of cuboid formed = 3 + 3 = 6 cm
Breadth of cuboid formed = 3 cm
Height of cuboid formed = 3 cm
Surface area of the cuboid . formed = 2 (lb + bh + hl)
= 2(6 × 3 + 3 × 3 + 3 × 6)
= 2(18 + 9 + 18)
= 2 x 45 = 90 cm2
OR
Length of arc = \(\frac{\theta}{360^{\circ}}\) × 2πr
= \(\frac{\theta}{180^{\circ}}\) × πr
= \(\frac{120}{180} \times \frac{22}{7}\) × 12
= Circumference of base cone
r’ = \(\frac{2}{3} \times \frac{12}{2}\)
= 4 cm
and l = 12cm
h = \(\sqrt{l^{2}-r^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{12^{2}-4^{2}}\)
= \(\sqrt{l^{2}-r^{12}}\)
= \(\sqrt{128}\)
= 8√2 cm
Volume of cone = \(\frac{1}{3}\)πr2h
= \(\frac{1}{3} \times \frac{22}{7}\) × 42 × 8√2
= 189.61 cm3
Related Theory:
Sector of a circle is the portion Ifa disk enclosed by two radii and an arc on joining the 2 radii, the figure obtained Will be a 3-D figure.
Question 2.
For which condition, the quadratic equation (a2 + b2) x2 – 2(ac + bd)x + (c2 + d2) = 0, has equal roots? (2)
Answer:
Hem, quadratic equation le
(a2 + b2) x2 – 2(ac + bd)x + (c2 + d2) = 0
Then for equal mots,
D = 0
or B2 – 4AC = 0
Here A = a2 + b2
B = – 2(ac + bd)
C = c 2 + d2
∵ (-2(ac + bd)2 – 4 × (a2 + b2)(c2 + d2) = 0
⇒ [4a2c2 + b2d2 + 2abcd] — 4(a2c2 + b2d2) + a2d2 + b2c2 = 0
⇒ -4(a2d2 + b2c2 – 2abcd) = 0
⇒ (ad – bc)2 = 0
⇒ ad = bc
![]()
Question 3.
The following table gives the life time in days of 100 bulbs.
| Life time in days | Numbers of bulbs |
| Less than 50 | 8 |
| Less than 100 | 23 |
| Less than 150 | 55 |
| Less than 200 | 81 |
| Less than 250 | 93 |
| Less than 300 | 100 |
Change the above distribution as frequency distribution then find the number of bulbs in class interval 150-200. (2)
Answer:
The given distribution can be changed to frequency distribution:
| Class | Frequency |
| 0-50 | 8 |
| 50-100 | 15 |
| 100-150 | 32 |
| 150-200 | 26 |
| 250-300 | 7 |
| Total | 100 |
And number of bulbs in class interval 150-200 is 26.
Related Theory:
For converting the distribution into C.I, subtract the frequency of previous ci ass from that class.
Question 4.
What is the maximum sum of the following AP series 20 + 19 \(\frac{1}{3}\) + 18 \(\frac{2}{3}\) +18 +…. (2)
Answer:
Given series is 20 + 19 \(\frac{1}{3}\) + 18 \(\frac{2}{3}\) +18 +….
Here, first term,
a = 20
Common difference
d = 19\(\frac{1}{3}\) – 20
= \(\frac{58}{3}\) – 20
= \(\frac{58-60}{3}=\frac{-2}{3}\)
The sum will be maximum when all, terms are positive.
So. Let the n term of AP is 0.
i.e Tn = 0
⇒ a + (n – 1)d = 0
⇒ 20 + (n – 1) × \(\left(\frac{-2}{3}\right)\) = 0
⇒ \(\frac{2(n-1)}{3}\) = 20
⇒ 2(n – 1) = 60
⇒ n – 1 = 30
⇒ n = 31
So, Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\)(a + l)
= \(\frac{31}{2}\)(20 + 0)
= 310
Caution
Convert the mixed fraction terms of AP to improper fraction
Question 5.
The frequency distribution of agricultural holdings in village is given below:
| Area of land (in hectare) | Number of families |
| 1-3 | 20 |
| 3-5 | 45 |
| 5-7 | 80 |
| 7-9 | 55 |
| 9-11 | 40 |
| 11-13 | 12 |
What is the modal agricultural holdings of the village? (2)
Answer:
Modal Class = 5 – 7, with maximum frequency 80
Now, lower limit, l = 5
Frequency of modal class, f1 = 80
Frequency of class preceeding modal class, f0 =45
Frequency of class suceeding modal class f2 = 55
Height of C.F. = 2
Mode = l + \(\frac{f_{1}-f_{0}}{2 f_{1}-f_{0}-f_{2}}\) × h
= 5 + \(\frac{80-45}{160-45-55}\) × 2
= 5 + \(\frac{35 \times 2}{60}\)
= 5 + \(\frac{70}{60}\)
= 5 + 1.17
= 6.17
Question 6.
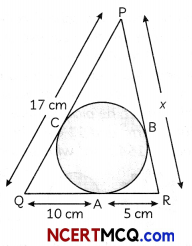
In the figure, all three sides a triangle touch the circle what is the value of x.
OR
In the given figure; two concentric circle are drawn with centre O. Two tangents are drawn from an outer circle to the inner circle.
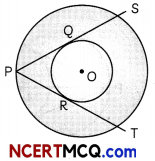
If PR = 5 cm find the length of PS. (2)
Answer:
Since, tangents from on external point to a circle are equal
∴ PC=PB
QC = QA = 10 cm
AR = BR = 5 cm
Now, PC = PQ – QC
= 17 – 10
= 7 cm
∴ PC = PB = 7cm
Then, PR = x = PB + BR
= 7 + 5
= 12cm
Related Theory
The Length of segment between the given point (on the tangent) and the point of contact with the circle is called the length of the tangent
OR
Since, length of tangent from an external point are equal
∴ PQ = PR = 5 cm
Join QQ
Now, PS is a chord in a bigger circle.
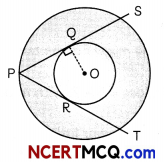
And ∠OQP = 90°, as PQ is tangent to smaLler circle and OQ is the radius:
∴ PQ = QS as perpendicular from centre bisects the chord
∴ PQ = QS = 5 cm
Then, PS = PQ + QS
= 5 + 5
= 10cm
Section – B (12 marks)
Question 7.
Evaluate the common difference of an AP, whose first term is \(\frac{1}{2}\) and 8th term is \(\frac{17}{6}\). What is the ratio of the 4th term and 50th term?
OR
The angles of a triangle are in AP. If the greatest angle equals the sum of the other two, then find the angles. Also, find that these angles are multiple of which angle. (3)
Answer:
Let, a be the first term and d be the common difference of the AP.
Then nth term, T = a + (n – 1)d
Given. nth term, T8 = \(\frac{17}{6}\)
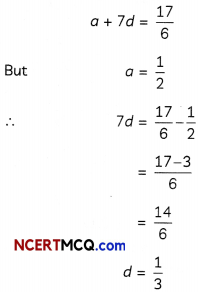
Now, 4th term. T4 = a + 3d
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) + 3 × \(\frac{1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{3}{2}\)
50th term, T50 = a + 49d
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) + 49 × \(\frac{1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{101}{6}\)
Required Ratio = \(\frac{\frac{3}{2}}{\frac{101}{6}}\)
= \(\frac{3}{2} \times \frac{6}{101}\)
= 9: 101
OR
Let the angles of a triangle are a – d, a and a + d.
Since, sum of the 3 angles of a triangle
= 180°
⇒ a – d + a + a + d = 180°
3a = 180°
a = 60°
So. the angles are 60° – d, 60° – d, 60° and 60° + a.
A.T.Q.
Greater angle = Sum of 2 smatter angles
60 + d = 60 – d + 60
2d = 60
d = 30°
Hence, the required angles of a triangles are 60° – 30°, 60° and 60° + 30° i.e. 30°, 60° and 90° respectively. Here, we see that above angles are multiple of 30°.
Related Theory:
if we suppose that an AP has n terms, then we know that th term of an AP is given by an = a + (n – 1)d. So, ourAP becomes a, a + d, a + 2d, …. a(n – 2)d, a + (n – 1)d.
![]()
Question 8.
From the top of a tower of height 50 m, the angles of depressions of the top and bottom of a pole are 30° and 45° respectively. Find
(A) How far the pole is from the bottom of a tower?
(B) Height of the pole (3)
Answer:
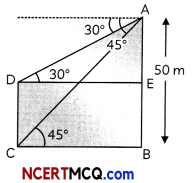
Here, AB is a tower of height 50 m.
(A) Tower of height. AB = 50 m
and ∠ADE = 30°
∠ACS = 45°
In ∆ACB,
tan 45° = \(\frac{AB}{BC}\)
1 = \(\frac{50}{\mathrm{BC}}\)
BC = 50 m
Then, pole is at 50 m distance from the tower.
(B) In ∆ADE,
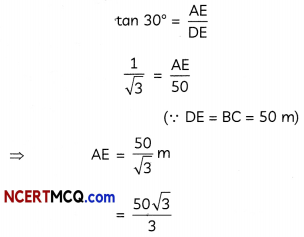
Then, height of pote = CD = BE
= AB – AE
= 50 – 28.87
= 21.13 m
Question 9.
In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. PA and PB are tangent and ∠APB = 75°, find ∠AQB and ∠AMB. (3)
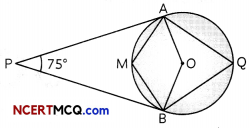
Answer:
Given, a circle with centre O and PA and PB are tangents to the circle.
In quadrilateral ∆PBO, AO ⊥ AP and OB ⊥ BP
∴ ∠PAO = ∠PBO = 90°
In quadrilateral, APBO
∠APB + ∠PBO + ∠PAO + ∠AOB = 360°
∠AOB = 360° – [75 + 90 + 90]
= 360°- 255°
= 105°

In cyclic quadrilateral AQBM
∠AQM + ∠AMB = 180°
∠AMB = 180° – 52\(\frac{1^{\circ}}{2}\)
= 180° – 52\(\frac{105^{\circ}}{2}\)
= \(\frac{255^{\circ}}{2}\) = 127\(\frac{1^{\circ}}{2}\)
Hence, ∠AQB = 52\(\frac{1^{\circ}}{2}\)
And ∠AMB = 127\(\frac{1^{\circ}}{2}\)
Related Theory
In a circle, angle drawn at the centre of the circle is twice the angle drawn by the radius in other segment.
Question 10.
Solve the quadratic equation:
2(x – 3)2 + 3(x – 2) (2x – 3) = 8(x + 4) (x – 4) – 1 to get the value of x. (3)
Answer:
2(x2 + 9 – 6x) + 3[2x2 – 4x – 3x + 6]
= 8(x2 – 16) – 1
⇒ 2x2 + 18 – 12x + 6×2 – 12x – 9x + 18
⇒ 8x2 – 128 – 1
⇒ 8x2 – 33x + 36
⇒ 8x2 – 129
⇒ – 33x = – 129 – 36
⇒ – 33x = – 165
⇒ x = \(\frac{165}{33}\)
= 5
Section – C (16 marks)
Question 11.
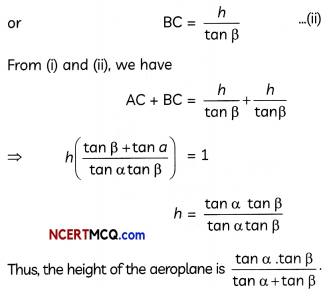
From an aeroplane vertically above a horizontal plane, the angles of depression of two consecutive kilometre stones on the opposite sides of the aeroplane are found to be α and β. Show that the height of the aeroplane is \(\frac{\tan \alpha \tan \beta}{\tan \alpha+\tan \beta}\)
OR
A man is watching from the top of the tower that a boat is speeding away from the tower. The, boat makes the angle of depression of 60° with the man’s eye when at a distance of 75 m from the tower. After 10 seconds, the angle of depression becomes 45°. What is the approximate speed of the boat, assuming that it is running in still water? (4)
Answer:
Let P be the position of the plane, A and B be the positions of two stones one kilometre apart. Angles of depression of stones A and B are α and β respectively.
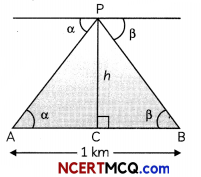
Let PC = h
In right-angled ∆ACP, we have
tan α = \(\frac{\mathrm{PC}}{\mathrm{AC}}\)
⇒ h = AC tan β
or AC= \(\frac{h}{\tan \alpha}\) …………(i)
In right-angled ∆PCB, we have
tan β = \(\frac{PC}{BC}\)
⇒ h = BC tan β
OR
Here, AB is a tower and C and D be the positions of the boat.
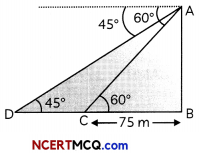
Here BC = 75 m
Then, in ∆ABC
tan 60° = \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{BC}}\)
⇒ √3 = \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{75}\)
⇒ AB = 75√3 m
Now, in ∆ABD
tan 45° = \(\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{BD}}\)
⇒ AB = BD = 75√3 m
Now. CD = BD – BC
= 75√3 – 75
= 75(√3 – 1)m
= 55 m
Distance
Now, Speed = \(\frac{\text { Distance }}{\text { Time }}\)
= \(\frac{55}{10}\) m/sec
= 5.5 m/sec
= 19.8 km/hr
![]()
Question 12.
To find out the concentration of SO2 in the air (in parts per million i.e. ppm), the data was collected for 30 localities in a certain city and it is presented below:
| Concentration of SO2 (in ppm) | Frequency |
| 0.00-0.04 | 4 |
| 0.04-0.08 | 9 |
| 0.08-0.12 | 9 |
| 0.12-0.16 | 2 |
| 0.16-0.20 | 4 |
| 0.20-0.24 | 2 |
What is mean concentration of SO2 in air? (4)
Answer:
For finding the mean, the table is converted as:
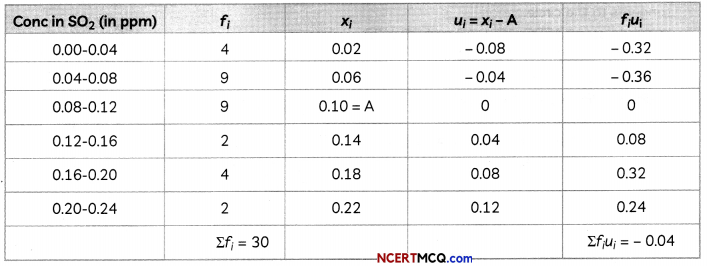
For mean
x̄ = A + \(\frac{\Sigma f_{i} u_{i}}{\Sigma f_{0}}\)
= 0.10 – \(\frac{0.04}{30}\)
= \(\frac{3-0.04}{30}\)
= \(\frac{2.96}{30}\)
= 0.099
Hence, the mean concentration of SO2 in air is 0.099 ppm.
Question 13.
Case Study – 1
As board exams are approaching very shortly, so Priya started her practice for the same. She is very much confused about the concept of tangents and circles. Her mother told her to practice the concepts, in which she which she is confused and finding difficult to solve, she draw a circle of radius 6 cm from a point 10 cm away from its centre and constructed the pair of tangents to the circle. Few questions came to her mind while drawing the tangents : Give answers to her questions by looking at the figure.
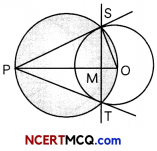
(A) If the angle between the two tangents is 60°, then what is the ∠SOT? (2)
Answer:
Since, quad. PSOT is a cycLic quadriLateral
∴ ∠SPT + ∠SOT=180°
∠SOT = 180° – 60°
= 120°
(B) What is the length of the tangent draw to the circle with centre? (2)
Answer:
As radius of circle,
OS = 6 cm
and OP = 10cm
Nov tangent Is perpendbåar to the radius
∴ OP2 = PS2 + OS2
PS = \(\sqrt{100-36}\)
= \(\sqrt{64}\) = 8 cm
![]()
Question 14.
Case Study – 2
Corona virus (covid-19) sis an infections disease caused by the SARS Cav-2 virus. Due to this pandemic, school, colleges had come to halt. To make the best use of this time teacher decided to give the class-X student a working project. Ajay had to make a project on corona virus for science task of his school. For making this project, he picks sphere which has volume 38808 cm3 and 11 cylindrical shapes, each of volume 1540 cm3 with Length 10 cm.
(A) When cylindrical shapes are pasted on the sphere, then what is the total area remains uncovered by cylindrical shapes on the surface of the sphere ? (2)
Answer:
Surface area of sphere
= 4πr2
= 4 × \(\frac{22}{7}\) × 21 × 21
= 88 × 63
= 5544 cm2
Now, area of a circle of one cylinder
= πr2
= \(\frac{22}{7}\) × 7 × 7
= 154 cm2
Total areo of drde of 11 cylinders = 154 × 11
= 1699 cm2
Total area remained uncovered on the surface of sphere
= 5544 – 1694
= 3850 cm2
(B) What is total volume of the model formed using sphere and cylinders? (2)
Answer:
Total volume of model formed = Volume of sphere + 11 × Volume of cyLinder
= 38808 + 11 × 1540
= 38808 + 16940
= 55,798 cm3.









